L18 Hearing and abalnce
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the main function of the auditory system?
To convert acoustic (mechanical) energy into nerve impulses that encode sound.
What features of sound are encoded by the auditory system? (4)
M
P/F
S
L/I
Modality (sound), pitch (frequency), spatial location, and loudness (intensity).
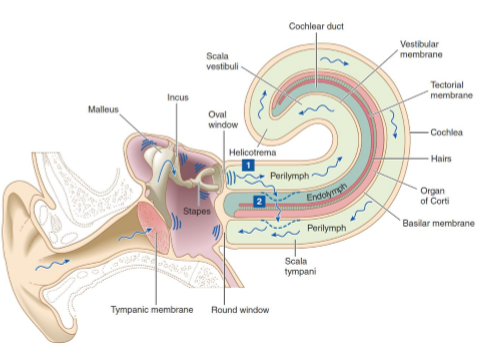
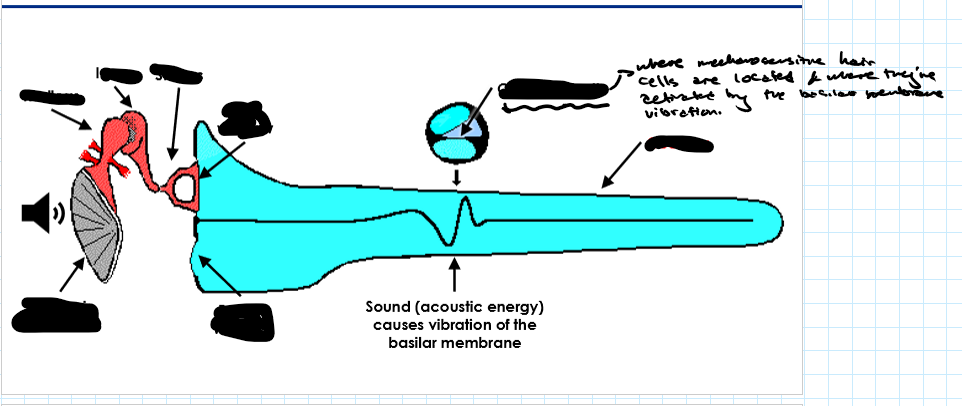
Outline the process of sound transduction from ear to nerve impulse. (5)
Sound waves hit the tympanic membrane → vibrations.
Vibrations move the ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) which amplifies the sound
Stapes vibrates the oval window → creates fluid wave in an up down motion to the round window in cochlea.
Wave moves the basilar membrane.
Hair cells in the Organ of Corti are deflected → nerve impulses generated
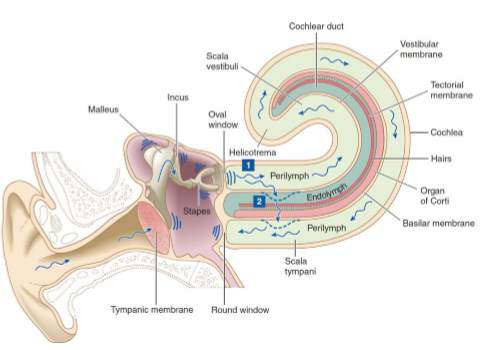
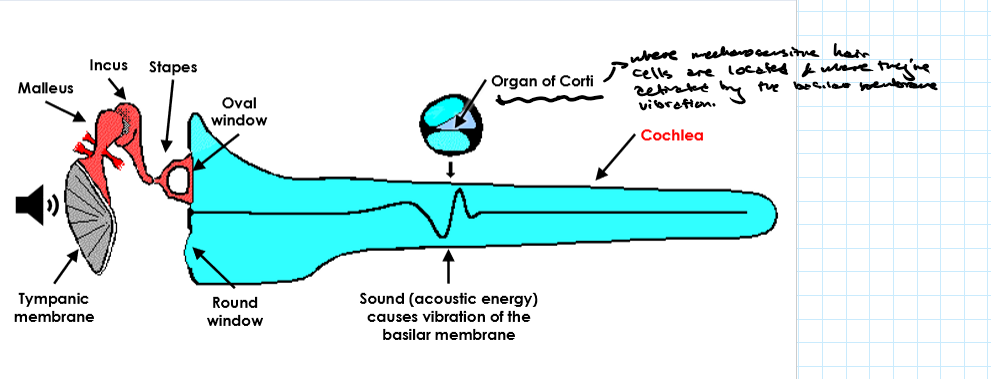
What is the function of the cochlea?
Acts as a peripheral mechano-transducer, converting sound vibrations into electrical signals.
Where are hair cells located?
How many rows of inner vs. outer hair cells are there?
Which hair cells send most auditory information to the brain?
What do outer hair cells primarily do?
In the Organ of Corti, which sits atop the basilar membrane.
1 row of inner hair cells and 3 rows of outer hair cells.
Inner hair cells (~95% of afferent neurons).
Amplify and fine-tune sound vibrations via an electromechanical motor process.
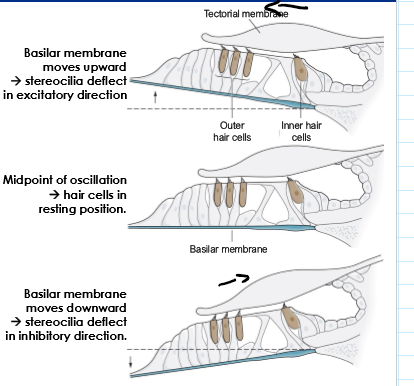
What causes movement at the stereocilia
Movement of the basilar membrane upward hair cells against the tectorial membrane, shearing the stereocilia
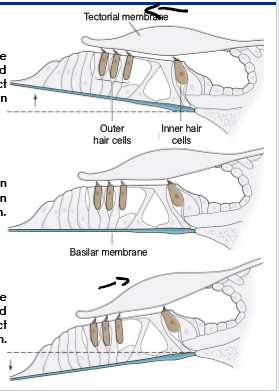
What happens to the stereocilia when the Basilar membrane move up and when it moves down
Deflect in excitatory direction
Deflect in inhibitory direction
What happens when stereocilia bend toward the tallest stereocilium? step by step
What happens when stereocilia bend away from the tallest stereocilium? step by step
Ion channels open → more potassium enters, depolarisation occurs, VGCC open causing calcium in causing more release of neurotransmitters → increased AP rate.
Tip links close, no potassium entery causing hyperpolarisation, calcium channels close, no neurotransmitter released → No AP
Where are low and high frequencies detected in the cochlea
At the base of the cochlea — narrow and stiff region near the oval window.
At the apex (helicotrema) — wide and flexible region.
Why is outer hair cell function critical?
They increase sound sensitivity and frequency discrimination.
How do outer hair cells amplify sound?
Deflection toward tallest stereocilium, depolarisation causes them to shorten
Deflection toward smallest stereocilium, hyperpolarisation causes them to lengthen, enhancing basilar membrane vibration which stimulates inner hair cells and nerve fibres
What causes hearing loss due to loud sound?
What decibel range typically causes outer hair cell damage?
What is the result of outer hair cell loss?
Damage to outer hair cells (most common) or sometimes inner hair cells.
Around 60–70 dB after long-term exposure.
Reduced sound sensitivity especially to high frequencies and clarity (sensorineural hearing loss)
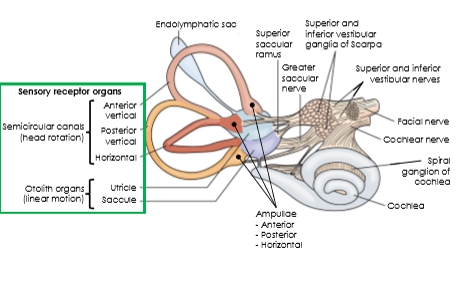
What does the vestibular system detect? (3)
Body position, linear acceleration, and rotational (angular) acceleration.
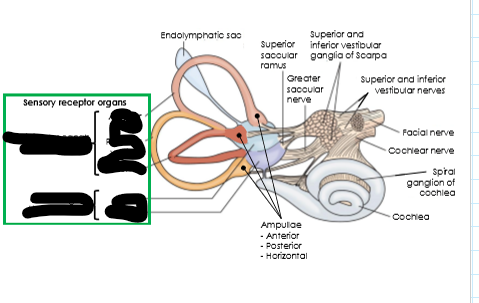
What are the two main components of the vestibular system and what do they detect?
Otolith organs (utricle and saccule) Linear acceleration and head position (relative to gravity).
Semicircular canals. Angular acceleration (rotational movements of the head).
What happens when stereocilia deflect toward the kinocilium?
What happens when they deflect away from the kinocilium?
Why are opposite responses produced in left and right vestibular organs?
Depolarisation → increased firing rate.
Hyperpolarisation → decreased firing rate.
Hair cells are oriented in opposite directions, allowing comparison for balance detection.
What are otoliths and their function?
Calcium carbonate crystals that provide inertia to the gelatinous layer, helping detect head tilt and linear acceleration.
Which way are the utricle and saccule oriented?
Utricle = horizontal; Saccule = vertical.
How are the hair cells in the utricle oriented?
How are the hair cells in the saccule oriented?
How do utricle and saccule orientations together ensure detection of all linear movements?
Their kinocilia face toward the midline; deflection toward the midline = depolarisation.
Their kinocilia face toward the surface; deflection toward the surface = depolarisation.
Their different orientations (horizontal vs vertical) allow detection of acceleration and tilt in all directions.
How do otoliths activate hair cells?
Movement or tilt shifts the gelatinous layer and bends stereocilia toward or away from kinocilium.
How do semicircular canals detect rotation?
What causes depolarisation or hyperpolarisation in semicircular canal hair cells?
Head rotation moves the canal, but endolymph lags behind, deflecting the cupula and hair cells in the opposite direction of movement.
Toward kinocilium: depolarisation → increased firing
Away from kinocilium: hyperpolarisation → decreased firing
What is the cupula?
A gelatinous structure in the ampulla that bends with fluid motion, activating vestibular hair cells
Why are the hair cells in left and right semicircular canals oriented oppositely?
What happens when the head turns left?
To allow mirror-opposite responses — depolarisation on one side and hyperpolarisation on the other — helping detect the direction of head rotation.
Hair cells on the left depolarise (↑ firing); hair cells on the right hyperpolarise (↓ firing).
What is the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)?
What pathway mediates the VOR?
A reflex that stabilises visual images on the retina by moving the eyes in the opposite direction of head movement.
Hair cells → vestibular nerve → vestibular nuclei → oculomotor nuclei → eye muscles.
What happens to eye movement when the head turns left?
Eyes move right, via activation of the appropriate rectus muscles on each side.
What is nystagmus?
What causes post-rotational nystagmus?
A rhythmic eye movement with a slow phase (eye drift) and a fast phase (quick reset).
When spinning stops, endolymph continues moving due to inertia, stimulating hair cells and causing eye flicking even after motion ends.
What is the function of the vestibulospinal reflex?
Outline the vestibulospinal reflex pathway.
Maintains balance and posture by adjusting muscle tone in response to head movement.
Vestibular hair cells → vestibular nerve → vestibular nuclei → cerebellum and vestibulospinal tracts → activate neck, trunk, and limb extensor muscles.