ecology slide deck 2 (climate and other abiotic factors affecting species distribution)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
the physical environment influences organisms over what two timescales?
many generations and shorter periods
is weather a long-term average or specific time/place?
specific time/place
is climate a long-term average or specific time/place?
long-term average
weather/climate: which influences reproduction in plant populations?
weather
weather/climate: which influences succession from prairie to a forest?
climate
weather patterns are influenced by two factors, which are...
solar radiation and earth's rotation/movement
what kind of energy is solar radiation?
electromagnetic energy
the hotter an object, the _________ (longer/shorter) the wavelength of energy it emits.
shorter
shorter wavelength =
higher energy
average net radiation =
zero
what is earth's energy budget? hint: where does each half of solar radiation go towards?
1/2 absorbed by atmosphere, 1/2 reflected/scattered by atmosphere and clouds
amount of solar radiation reaching surface varies with what?
latitude
solar radiation strikes earth's surface at a _______ angle with _________ latitudes.
steeper; higher
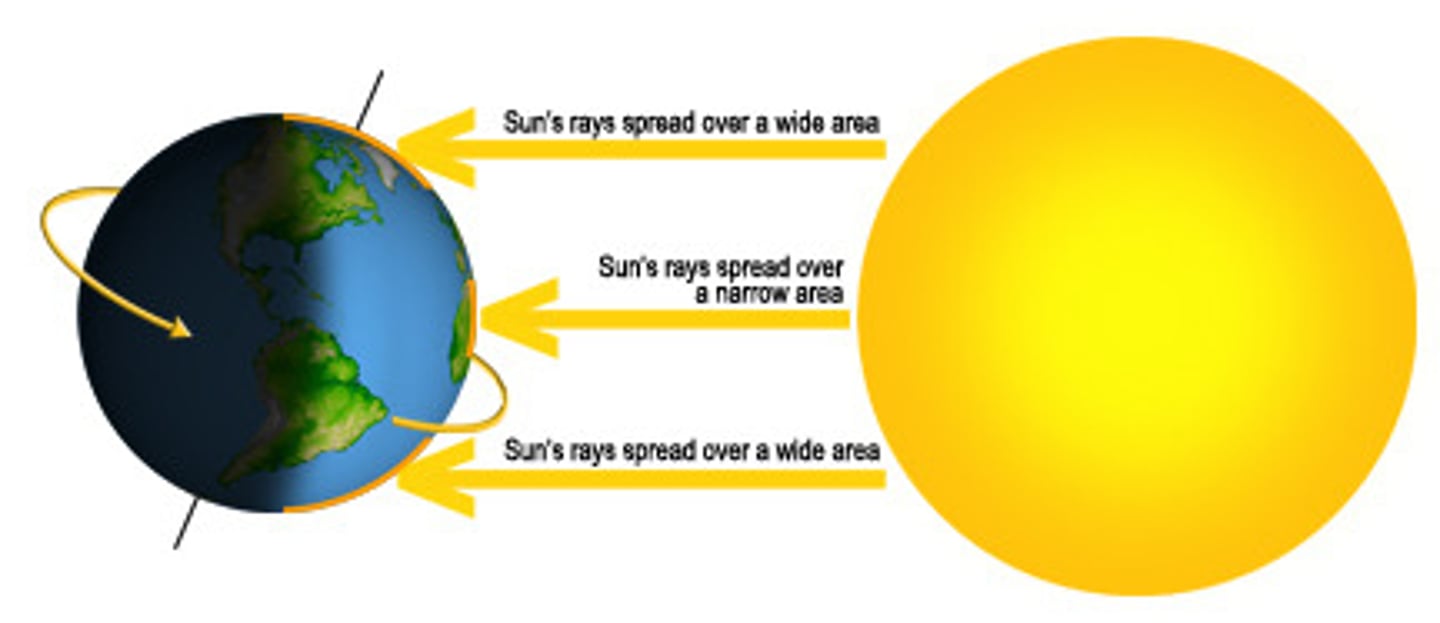
solar radiation strikes earth's surface at a _______ angle over a ________ distance.
direct; shorter
it takes _____ day(s) for earth to rate on its axis.
one
it takes _________ year(s) for the earth to orbit once around the sun.
one
the earth's axis has a tilt of how many degrees?
23
the higher the latitude the more/less seasonal variation?
more
what is a diurnal cycle?
hours of daylight and dark
the diurnal cycle varies with seasons everywhere except at the equator with _______ hrs day/night throughout the whole year
12
day length changes with ____________.
seasonality
day length greatly affects what?
activities of organisms and seasonal productivity
day length can influence ____________ time in winter
foraging
in winter, what is the average difference in minutes in day length along latitudinal ranges?
10.5 minutes
temperate birds reproduce in which season?
spring
does day length increase or decrease in spring?
increase
what can cause seasonal differences in appearance?
seasonal variations
in warm-blooded vertebrates, individuals from cold climates are often ________ than those from warm climates.
larger
what is bergmann's rule?
small size/volume ratios conserve body heat in cooler climates. large size/volume ratios allow heat to be dissipated in warm climates.
small size/volume ratio favors _______ animals
larger
large size/volume ratio favors _______ animals
smaller
________ size/volume ratios conserve body heat in cooler climates
small
_______ size/volume ratios allow heat to be dissipated in warm climates
high
what does bermann's rule mainly apply to?
birds and mammals
body size changes with __________.
latitude
what can affect latitudinal and color distribution of insects?
climate
climate can affect latitudinal and color distribution of _______.
insects
climate can affect __________ and __________ distribution of insects.
latitudinal and color
__________ use wing color to regulate body temperature.
butterflies
butterflies use wing color to regulate _________ _________________.
body temperature
butterflies: warmer climate =
lighter wings
butterflies: cooler climate =
darker wings
_______ and _______ levels can affect any stage in organism life cycles.
temperature and moisture
what are the organism life cycle stages?
survival, reproduction, development of young, interactions with other organisms
which organism life cycle stage has most important effect on distribution?
no answer, difficult to determine
what are examples of other abiotic factors, besides climate, that can affect species' distribution?
pH, nutrient availability, salinity
what is a microclimate?
important determinant of distribution on a local scale
examples of microclimates?
soil temperature, moisture, wind movement
which kind of experiment? no manipulation of variables involved, choose site to study. collect data on various variables
natural experiment
which kind of experiment? natural communities. manipulation of one or a few factors (e.g. introductions/removals)
field experiment
which kind of experiment? synthetic habitat or communities. control abiotic environment and biotic environment
lab experiment
which experimental approach is best?
combination of all three often needed to determine patterns and processes