biology
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology
biology
year9
grade8
dna
nutrition
variables
biology year 9
biology grade 8
easy biology
biology exam revision
enzymes
prokaryotic
eukaryotic
foods
alleles
punnett squares
DNA
genotype
cells
animal cells
plant cells
levels of organization
levels of organisation
active transport
bacteria
viruses
fungi
animals
pathogens
diffusion
osmosis
rate of movement
protein
dominant
recessive
homozygous
heterozygous
phenotype
genotype
monohybrid
mutation
inheritance
inheritence
amino acids
science skills
independant variable
dependant variable
control variable
8th
Last updated 1:29 PM on 5/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
independent variable
the one that changes
2
New cards
dependant variable
the one that is measured
3
New cards
control variable
the one that stays the same
4
New cards
sensitivity
respond to the surroundings
5
New cards
respiration
release of energy cells
6
New cards
excretion
removal of metabolic waste
7
New cards
reproduction
production of new organisms
8
New cards
growth
increase in number of cells
9
New cards
nutrition
taking in food
10
New cards
prokaryotic
Type of cell lacking a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Examples include bacteria and archaea.
11
New cards
eukaryotic
A type of cell that has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
12
New cards
similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are basic units of life, contain genetic material in the form of DNA, and are capable of carrying out essential cellular processes such as metabolism and reproduction.
13
New cards
difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
Prokaryotic organisms lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are generally smaller and simpler in structure compared to eukaryotic organisms, which have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
14
New cards
nucleus
The center of a cell that contains genetic material and controls cell functions.
15
New cards
mitochondria
Organelle that produces energy in eukaryotic cells through cellular respiration.
16
New cards
ribososmes
Photosynthesis:
Process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, using carbon dioxide and water.
Process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, using carbon dioxide and water.
17
New cards
cell membrane
This structure surrounds and protects the cell, controlling the movement of substances in and out.
18
New cards
lysosomes
Organelles that contain digestive enzymes to break down waste materials and cellular debris. They are involved in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and the recycling of cellular components.
19
New cards
cytoplasm
The jelly-like substance that fills a cell and surrounds its organelles, where many cellular processes take place.
20
New cards
vacuole
Organelle found in plant and animal cells that stores water, nutrients, and waste products. It helps maintain turgor pressure and regulates pH levels.
21
New cards
cell wall
Structure that surrounds the cell membrane in plant, fungi, and bacterial cells. Its main function is to provide support and protection to the cell.
22
New cards
chloroplasts
Organelles found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll, which is used in photosynthesis to convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
23
New cards
the importance of cell differentiation in the development of specialised cells
…………. is crucial in the development of specialised cells as it allows cells with identical genetic information to acquire distinct structures and functions. This process enables cells to specialise for specific tasks, contributing to the formation of tissues, organs, and ultimately the complex functioning of multicellular organisms.
24
New cards
pathogens
……… are microorganisms or agents that can cause disease in living organisms, including humans, animals, and plants. They include various types of bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and parasites. Pathogens are capable of invading the host's tissues and disrupting normal bodily functions, leading to infections and illnesses.
25
New cards
examples of pathogens
\~Bacteria (ex: e.coli) eukaryotic
\~Viruses (ex: AIDS) neither
\~ Fungi (ex: mucor) eukaryotic
\~ Protozoa (ex: malaria) unicellular eukaryotes
\~Parasites (ex. tapeworms) eukaryotic
\~Protoctists (ex. algae) eukaryotic
\~Viruses (ex: AIDS) neither
\~ Fungi (ex: mucor) eukaryotic
\~ Protozoa (ex: malaria) unicellular eukaryotes
\~Parasites (ex. tapeworms) eukaryotic
\~Protoctists (ex. algae) eukaryotic
26
New cards
are bacteria eukaryotic or prokaryotic
they are prokaryotic
27
New cards
are fungi eukaryotic or prokaryotic
are eukaryotic
28
New cards
are parasites eukaryotic or prokaryotic
they are eukaryotic
29
New cards
are viruses eukaryotic or prokaryotic
they are neither prokaryotic or eukaryotic
30
New cards
are protozoa eukaryotic or prokaryotic
they are unicellular eukaryotic
31
New cards
are protoctists eukaryotic or prokaryotic
eukaryotic
32
New cards
how does a virus differ from a bacterium
…….. need a host to survive
viruses are generally smaller than ……..
……. bacteria is a living organism, while …… can replicate only within the host cell
viruses are generally smaller than ……..
……. bacteria is a living organism, while …… can replicate only within the host cell
33
New cards
fungi are/have
some are multicellular
all have a nucleus
none contain chloroplasts
all have cell walls
all have a nucleus
none contain chloroplasts
all have cell walls
34
New cards
bacteria are/have
none are multicellular
none have a nucleus
some have chloroplasts
all have cell walls
none have a nucleus
some have chloroplasts
all have cell walls
35
New cards
protoctists are/have
none are multicellular
all have a nucleus
some contain chloroplasts
some have cell walls
all have a nucleus
some contain chloroplasts
some have cell walls
36
New cards
levels of organisation
…………… in organisms include organelles cells, tissues , organs, and systems. These levels build upon each other, with each level performing specific functions that contribute to the overall functioning of the organism.
37
New cards
example of an organelle
ex: mitochondria
38
New cards
example of a cell
muscle cells
39
New cards
example of an organ
heart
40
New cards
example of a system
cardiovascular system
41
New cards
diffusion
…. is the passive process by which molecules or particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It occurs due to random molecular motion and seeks to equalise the concentration gradient, leading to a net movement of substances down their concentration gradient.
42
New cards
osmosis
the net movement of water from an area of high water potential to an area of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane until dynamic equilibrium is reached
43
New cards
active transport
a process that involves the movement of molecules from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration against a gradient or an obstacle with the use of external energy
44
New cards
rate of movement
The ….…….. refers to the speed or velocity at which a substance or particle moves within a given time frame. It can be influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration gradient, molecular size, and the presence of barriers or transport mechanisms.
45
New cards
surface area affects rate of movement
…….….. affects the rate of movement by increasing the available space for molecules to interact or diffuse. A larger ………. allows for more efficient exchange of substances, as there is a greater ……….. for molecules to pass through or come into contact with, resulting in faster rates of movement.
46
New cards
distance affects the rate of movement
…….. affects the …….. as an increase in distance generally leads to a slower rate. The larger the ……., the longer it takes for molecules or particles to travel, resulting in a slower rate of movement. Shorter distances allow for faster and more efficient movement between locations.
47
New cards
temperature affects the rate of movement
……….. affects the rate of movement by increasing the kinetic energy of molecules. Higher temperatures result in faster molecular motion, leading to increased collisions and more rapid diffusion or movement of substances. Lower temperatures decrease molecular motion and thus slow down the rate of movement.
48
New cards
the concentration gradient affects the rate of movement
The ………….……. affects the rate of movement by driving the flow of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. A steeper concentration gradient results in a faster rate of movement, while a smaller gradient leads to a slower rate of movement.
49
New cards
DNA
Each molecule of ….….. is a double helix formed from two complementary strands of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds between G-C and A-T base pairs
50
New cards
adenine goes with
thymine goes with
51
New cards
guanine goes with
cytosine goes with
52
New cards
what does the nucleus of a cell contain
chromosomes, in which genes are located
53
New cards
allele
An …… is an alternative form of a gene, occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome, that contributes to variations in traits among individuals of a population.
54
New cards
dominant
In DNA, the term "…….." refers to an allele that expresses its trait even when present in only one copy, overshadowing the expression of a recessive allele.
55
New cards
recessive
In DNA, …….. refers to an allele that is masked or not expressed when a dominant allele is present. ……… alleles typically require two copies to be expressed phenotypically.
56
New cards
homozygous
a condition in which an individual possesses two identical alleles for a specific gene, one inherited from each parent, resulting in a uniform genetic trait expression.
57
New cards
heterozygous
an individual having two different alleles for a particular gene. In DNA, it means that the two copies of the gene possess different genetic information at that specific locus.
58
New cards
Phenotype
The observable characteristics in an individual resulting from the expression of genes. visible
59
New cards
Genotype
the collection of alleles that determine an organism's characteristics. non visible
60
New cards
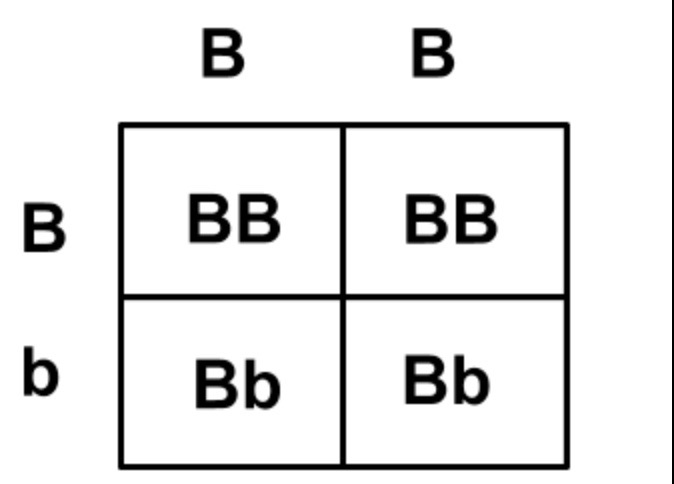
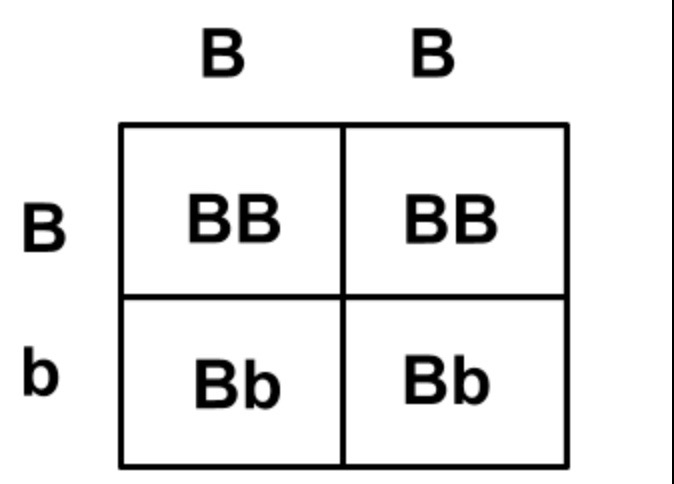
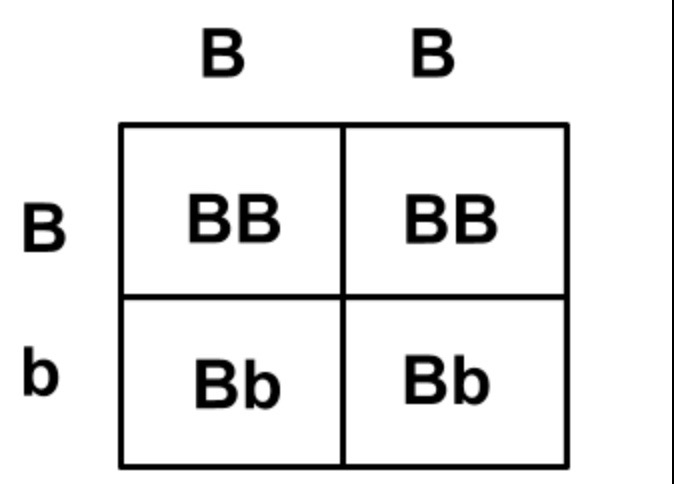
patterns of monohybrid inheritance using a genetic diagram (punnett squares)
Monohybrid inheritance involves the inheritance of a single gene. A Punnett square, a genetic diagram, is used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of the parents.
61
New cards
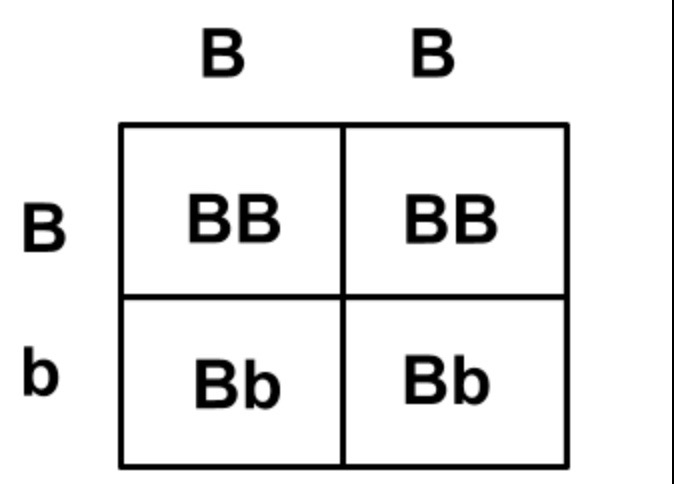
the dominant allele (BB) “dominates” over the recessive allele. the recessive allele (bb) is “submissive” to the dominant allele
b + b = bb
B + b = Bb
b + B = Bb
B + B = BB
B + b = Bb
b + B = Bb
B + B = BB
62
New cards
mutation
A change in the DNA base sequence, known as …….. , can lead to altered amino acids in a protein. This can affect the protein's structure and function, potentially changing the organism's characteristics. These changes can range from subtle modifications to significant disruptions in biological processes, leading to various phenotypic outcomes. If inherited, can lead to variations in traits and genetic disorders.
63
New cards
carbohydrates
……… contain the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. plant cell walls are made of the ………., cellulose. plants store ……… as starch. the starch in plant cells is insoluble, it has no osmotic effect on the cell.
64
New cards
the storage carbohydrate animal is
glycogen, which is found mainly in the muscles and the liver.
65
New cards
proteins
…….... contain the elements of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen . ………. are formed from amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds to create complex, three-dimensional structures.
66
New cards
lipids
……. contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Some ……. may also contain phosphorus (P) and other elements. ……. are diverse molecules that include fats and oils, composed of fatty acids and glycerol.
67
New cards
enzyme
they are proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reaction in our bodies. They build up some substances, and break others down.
68
New cards
Enzymes and biological catalysts in metabolic reactions
Enzymes act as biological catalysts in metabolic reactions, facilitating chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for them to occur. They speed up the rate of reactions, enabling efficient metabolism by selectively binding to substrates and converting them into products without being consumed in the process.
69
New cards
Digestive enzymes
……………. play a vital role in breaking down complex food molecules for absorption. Amylase and maltase act on starch, breaking it down into glucose for energy. Proteases break down proteins into amino acids, which are essential for building new proteins and other cellular processes in the body.
70
New cards
denatured enzyme
………………. occurs when the protein structure of the enzyme is disrupted, usually by factors such as high temperatures or extreme pH levels. This disrupts the enzyme's active site, rendering it unable to bind to its substrate and catalyse the intended chemical reaction.
71
New cards
how changes in temperature affect the activity of an enzyme
As the temperature increases so does the rate of enzyme activity. If the temperature decreases there is less kinetic energy, so fewer collisions mean a decrease in enzyme activity. if the temperature is too high or too low
72
New cards
pH
the value at which an enzyme works best
73
New cards
high and low pH…
… denatures enzymes
74
New cards
amylase, salivary gland
break down starch
75
New cards
protease, stomach
break down proteins
76
New cards
restriction, bacteria
cutting DNA at certain points
77
New cards
ligase , cell nucleus
joining DNA / genes
78
New cards
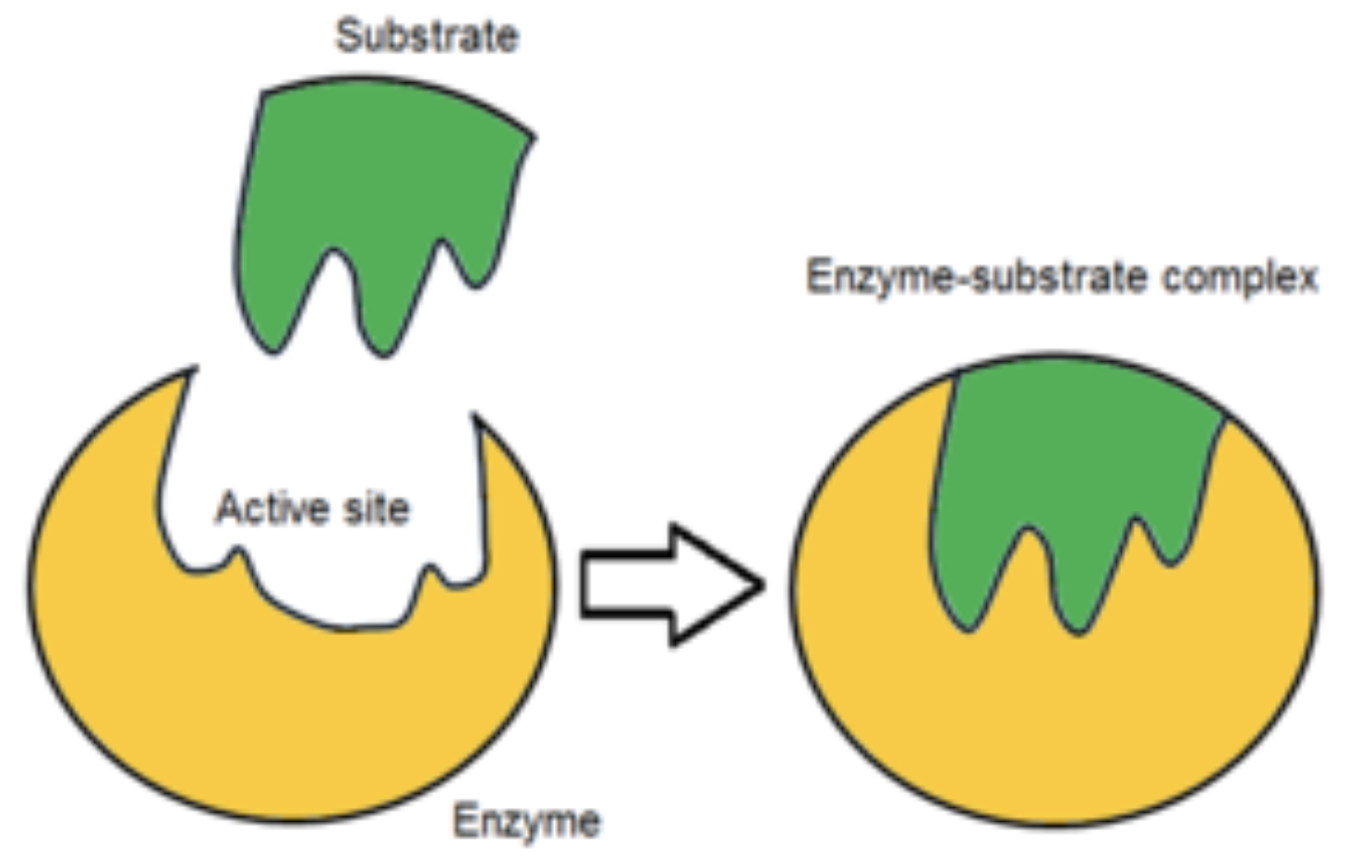
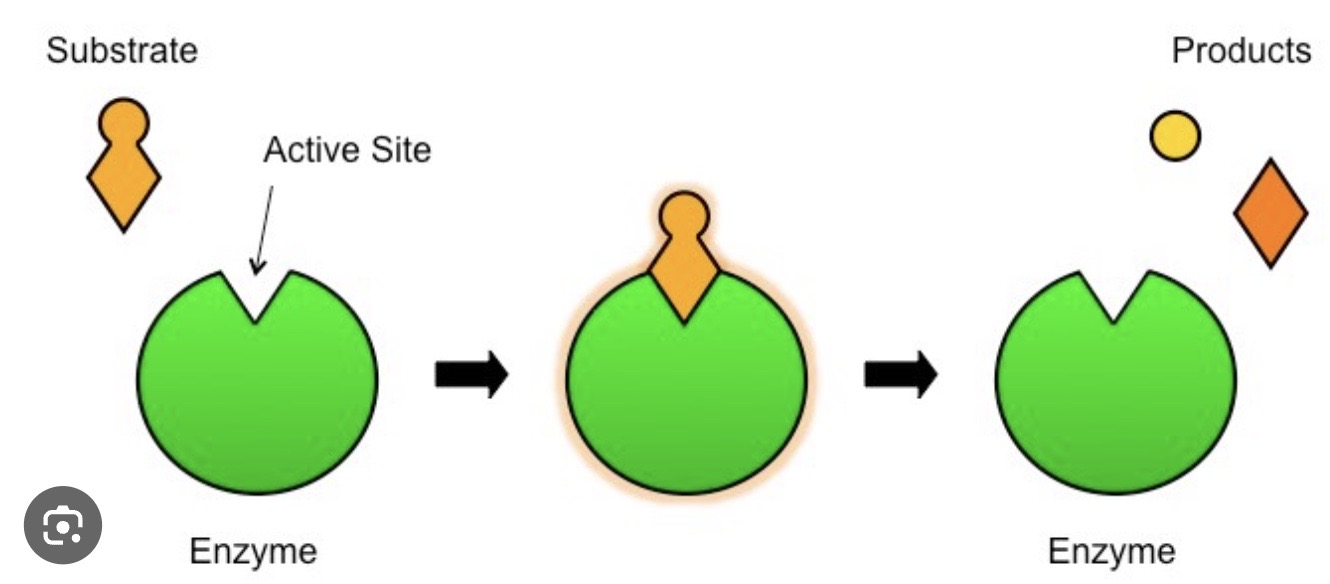
79
New cards
the independent variable goes on the
x axis
80
New cards
the dependent variable goes on the
y axis
81
New cards
concentration gradient
occurs when the concentration of particles is higher in one area than another. In passive transport, particles will diffuse down a concentration gradient, from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration, until they are evenly spaced.
82
New cards
starch
**is a carbohydate**