Module 1 Foundations Review
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Scientific Method
Observation
Question
Hypothesis
Experiment
Data Collection
Does the data support the hypothesis?
What are the 6 characteristics of life?
Reproduction
Metabolism
Growth + Development
Homeostasis
React to Environment
Cell(s)
Remember My Green Hat + Red Cap
Metabolism
Uses and stores energy
What is the identity of an atom?
An atom’s identity is based on the number of protons (+) in an atom
Isotope
An isotope is the same element only differing in the number of neutrons
ex: Carbon 12 and Carbon 14
How many electrons can the shell closest to the nucleus hold?
A maximum of 2
How many electrons can an outer shell hold?
A maximum of 8
What is a valence electron?
Electrons that are found in the outermost shell (valence shell) of an atom
Covalent bond
Occurs when two atoms share valence electrons to fill their valence shell.
Ionic bond
Occurs when atoms accept/giveaway electrons in order to be stable
ex: An atom has 1 valence electron and another has 7. The first needs to lose an electron and the other needs to gain one. So the first transfers a sole electron to the other.
Cation
Ion with a positive electrical charge
-meaning it lost an electron
Anion
Ion with a negative electrical charge
-meaning it gained an electron
Van der Waals Reaction
An especially weak attractive force (bond) between atoms
ex: gecko walking on wall (doesn’t take much force to knock it off)
Hydrogen Bond
Weak attraction (bond) between molecules involving hydrogen
ex: water molecules H20
Cohesion
like molecules are attracted to each other
Special property of water
Adhesion
Special property of water where a molecule is attracted to a molecule of a different type.
-the negative charges in one molecule are attracted to the positive charges in another
Mole
amount of a substance (in grams) that is numerically equivalent to the molecular weight of a substance
What is the constant number of molecules in 1 mole?
6.02×10²³ molecules (Avogadro’s Number)
What is a pH scale?
A measure of how acidic an object is
Acids? pH?
Substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water
(pH less than 7)
Bases? pH?
Substances that release hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water, and accept H+
(pH greater than 7)
Solute
What is being dissolved
Solvent
Does the dissolving
Solution
Liquid mixture where the solute is equally distributed in the solvent
What is the pH level of a solution with 10-² moles/liter?
Has a pH level of 2 making it very acidic.
What is a neutral pH level?
7 or 10^(-7) moles/liter
What are the 4 types of macromolecules?
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Nucleic Acids
How many calories does one gram of protein produce?
4 calories per gram
Amino acids
molecules that combine to form proteins
What is the backbone of all amino acids?
Nitrogen, Carbon alpha, and Carbon beta
What creates the shape of proteins?
Negative and positive charges of amino acids repel and attract each other forming bonds that fold the string of amino acids into a 3d shape
What are the major bonds between amino acids?
Ionic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Van der waals Attractions
(weak)
Disulfide bridge (strong)
Denaturing
Breaking the bonds between proteins (changing the shape of a protein)
Roles of Proteins
Structural (hair and nails)
Transport
Chemical reactions (enzymes)
Carbohydrates (ratio)
Organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
How many calories does one gram of carbohydrate produce?
4 calories
4 kinds of carbohydrate
Monosaccharide
Disaccharide
Oligosaccharide
Polysaccharide
Monosaccharide
Simple sugar made of 1 single chain of amino acid
ex: glucose
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharide linked together
ex: glucose + fructose = sucrose
Oligosaccharide
Several monosaccharides (3 or more)
Polysaccharide
Hundreds/thousands of monosaccharides
ex: starch, chitin, cellulose
Lipids
nonpolar hydrocarbon compounds that are insoluble in water
How many calories does one gram of lipids produce?
9 calories per gram
Types of lipids
Triglycerides
Phospholipid
Steroids
Triglyceride
Simple lipid that can be solid at room temperature (fat) or liquid at room temp. (oil)
Phospholipid
lipid containing a phosphate group
Saturated Fat
fatty acid chain is completely saturated in hydrogen
-solid at room temp
Unsaturated fat
fatty acid chain with single double bond
-liquid at room temp
Phospholipid bilayer
formed when the hydrophilic phosphate containing heads of two phospholipids pack together with heads facing out
-basic structure of cell membrane
Steroids
Natural/synthetic hormone containing a hydrogenated ring system
ex: estrogen, testosterone, cholesterol
Catabolism
breaking down of a molecule
Anabolism
Building up
ex: anabolic steroids build up body mass
Nucleic Acid
macromolecule that carries genetic information
How many calories does one gram of nucleic acid produce?
Not used for metabolism
-if metabolized they would only provide around 2 calories
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
-fundamental hereditary material of all organisms
RNA
ribonucleic acid
-single strand
Nucleotide? structure?
basic chemical unit in nucleic acids
-built up of nitrogenous base, sugar, and phosphate
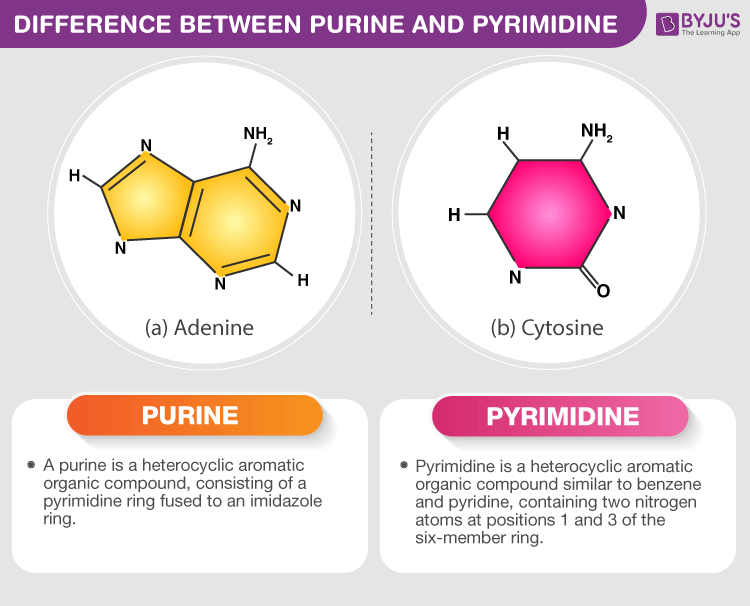
Pyrimidine base
6 membered single-ring structure
ie: cytosine, thymine, uracil
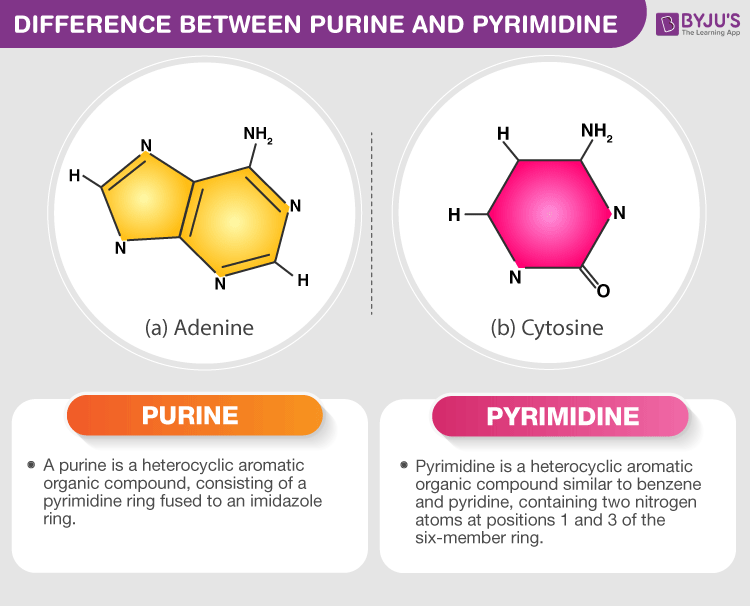
Purine
fused double ring structure
ie: adenine, guanine
Bonds between nitrogenous bases
Adenine bonds with thymine (uracil)
Guanine bonds with cytosine