Primate Classification 1
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pract 2 Pract 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
A closed orbit indicates a primate or a non-primate?
Primate
Do primates have a long snout or a short snout relative to non-primates?
Primates typically have a shorter snout compared to non-primates
What features distinguish lemurs/lorises (strepsirrhines) from other primates?
Longer snouts, tooth comb, and grooming claw on second toe
True or false? Only lemurs and lorises are strepsirrhines
True strepsirrhines includes lemurs, lorises, and galagos
What features distinguish tarsiers from all other primates?
Enormous eyes relative to body size, no tooth comb, partial post-orbital closure, long hind limbs for leaping, a mix of strepsirrhine and haplorrhine traits
True or false? Humans are apes
True
What features are different between Old World Monkeys and New World Monkeys?
Old World Monkeys (Catarrhines): Narrow, facing down nostrils, 2.1.2.3 dental formula, bilophodont molars, ischial callosities (sitting pads) Africa-Asia
New World Monkeys (Platyrrhines): broad, outward-facing nostrils, 2.1.3.3 dental formula, prehensile tail, central-south America
What features are unique to apes?
Lack of tail, larger brains relative to body size, more complex social behaviors, y-5 molar pattern, greater range of shoulder mobility
Old World Monkeys have bilophodont molars. What are bilophodont molars and what sort of diet are they best suited for?
Two ridges best suited for a folivorous diet - grinding and hearing fibrous plants
Which class of primates have a post-orbital bar?
Strepsirrhines (lemurs and lorises) but lack post-orbital closure
You find an animal skull with forward-facing eyes and a post-orbital plate. Are you likely looking at a primate or a non-primate?
Primate because of post-orbital plate
Which primate class has a 2.1.2.3 dental formula?
Old world monkeys and apes
Which primate class has different dental formula for the maxillary and mandibular dentition?
Sterpsirrhines due to tooth comb in lower jaws
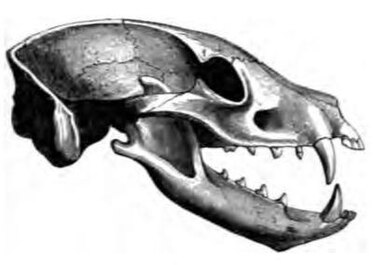
Sharp pointed teeth are good for puncturing the exoskeleton of insects—what kind of diet is this?
Insectivorus diet
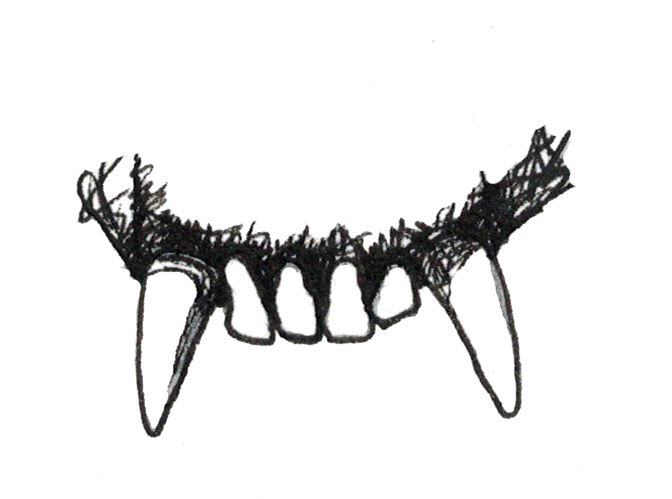
A primate that eats primarily leaves would have what type of teeth? What kind of diet is this?
Sharp shearing crests on molars for cutting leaves and small incisors
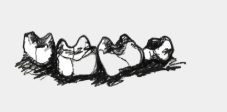
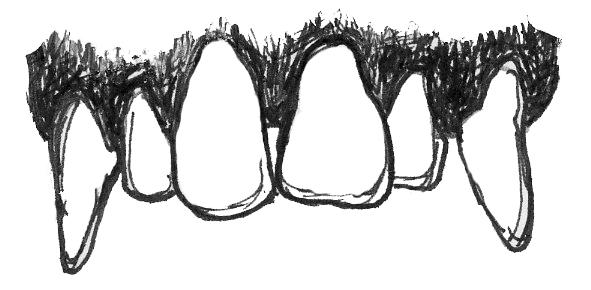
Low-rounded molars and large flat incisors are good for what type of diet?
Frugivorous diets

What kind of dentition would gummivores have?
Strong, sharp incisors for gouging bark tree to obtain sap/gum
Which is harder to digest, leaves or fruit?
Leaves due to cellulose content
Why do folivores have a long, complex gut?
To break down cellulose from plant material
What type of molars do apes have
Y-5 Molars by 5 cusp arranged in Y pattern