Transport Across Cell Membranes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
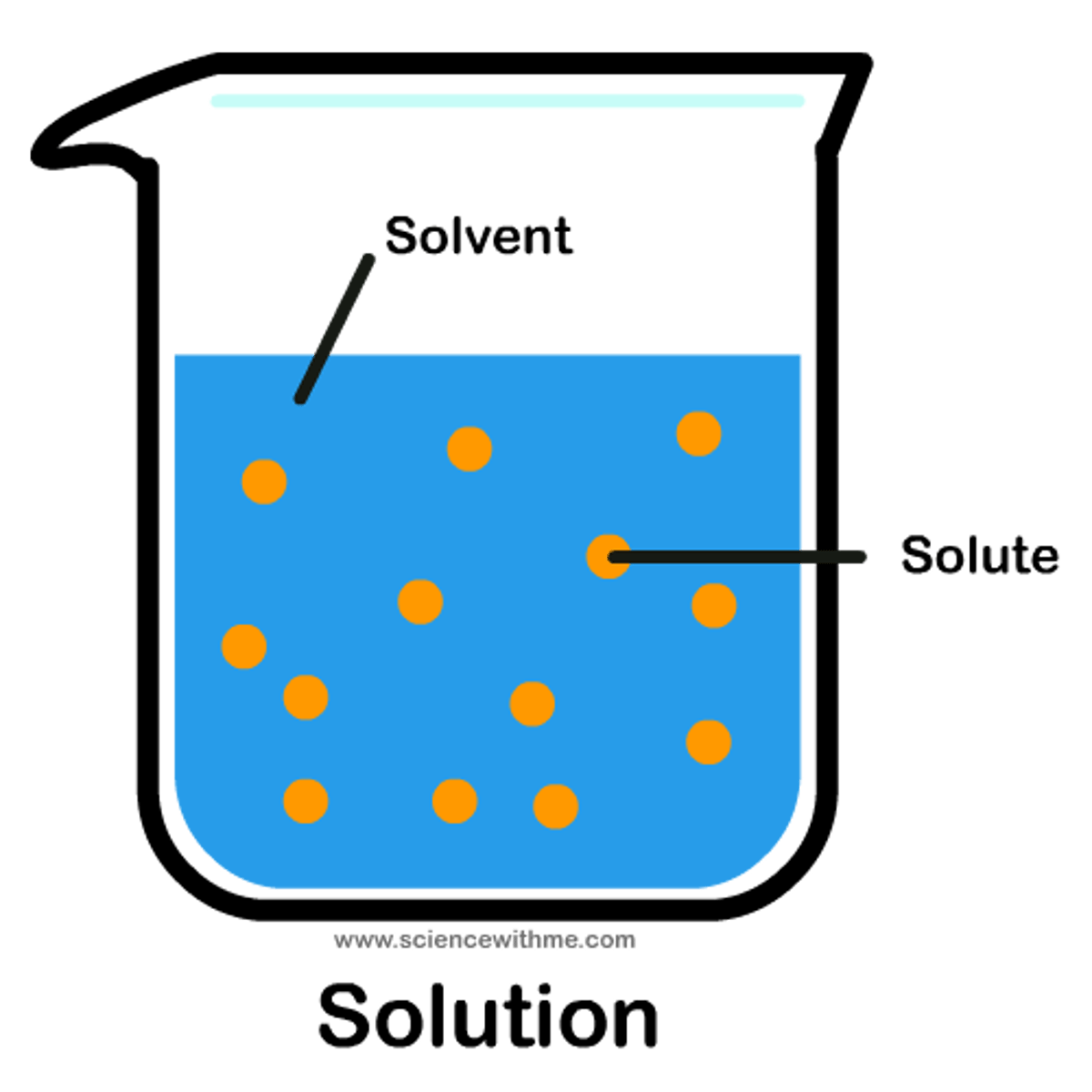
solvent
The liquid that the solute is dissolved in.
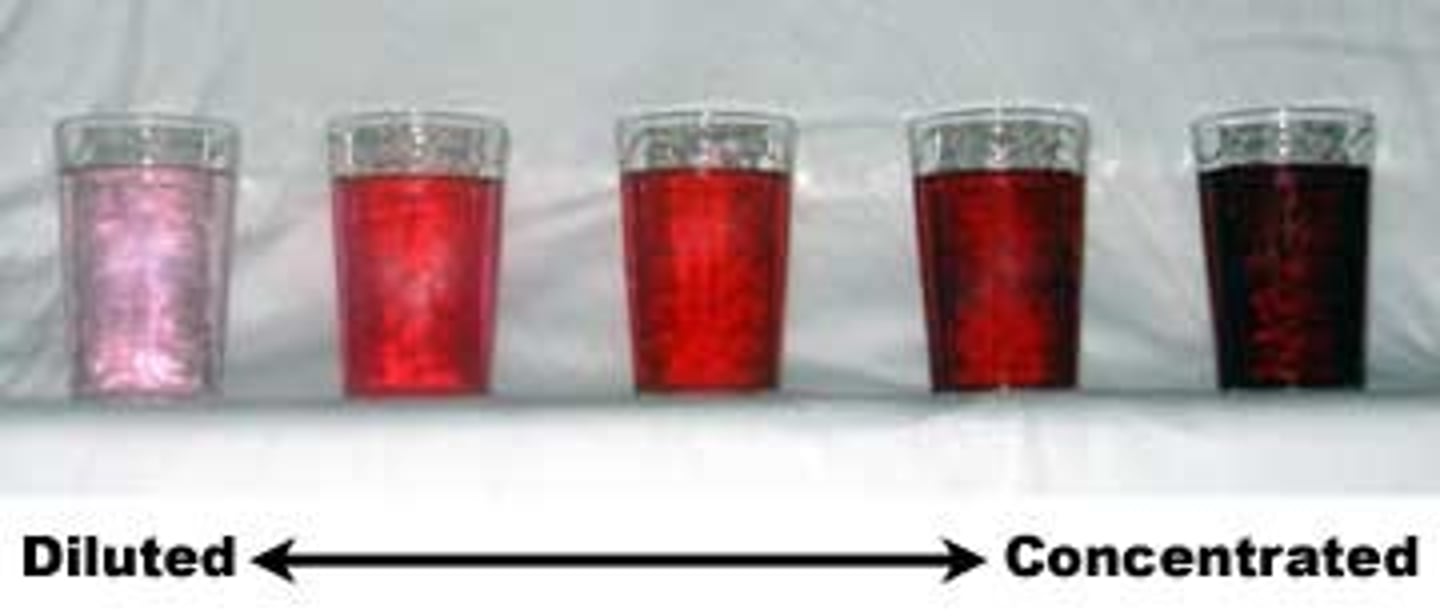
concentration
A measure of the amount of solute dissolved in a solvent.
concentration gradient
The difference in concentration of a substance on two sides of a membrane
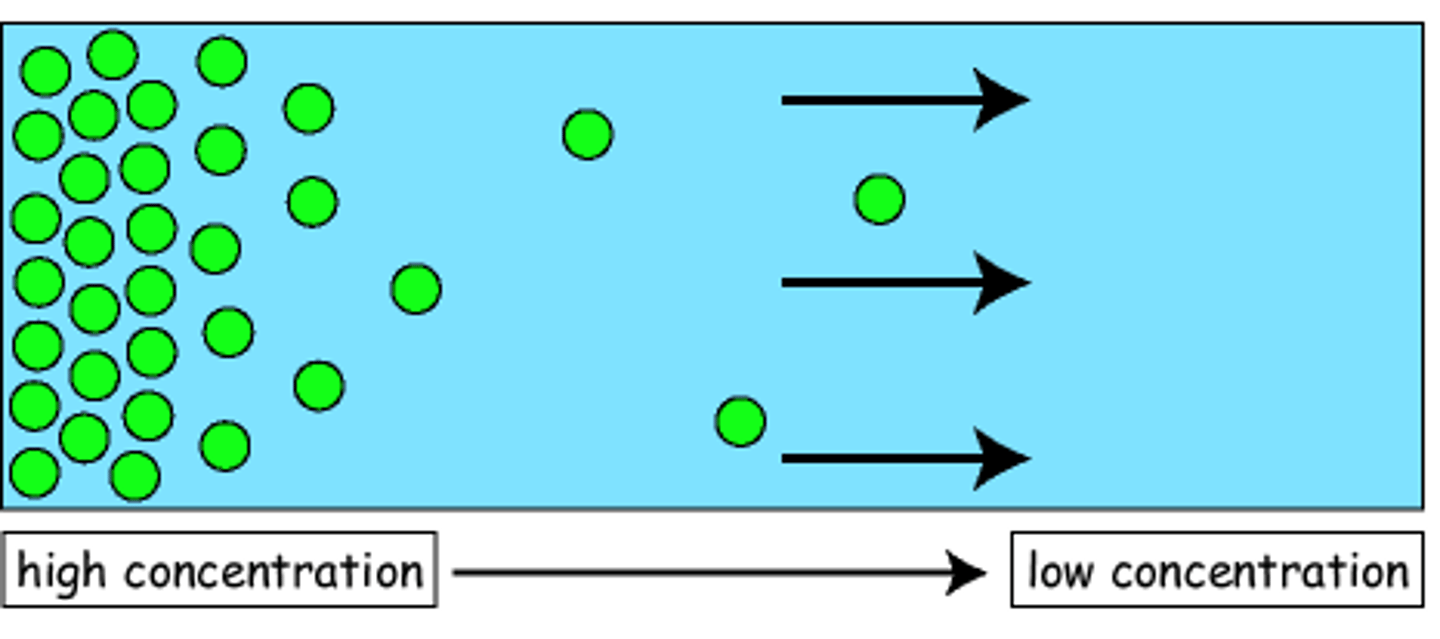
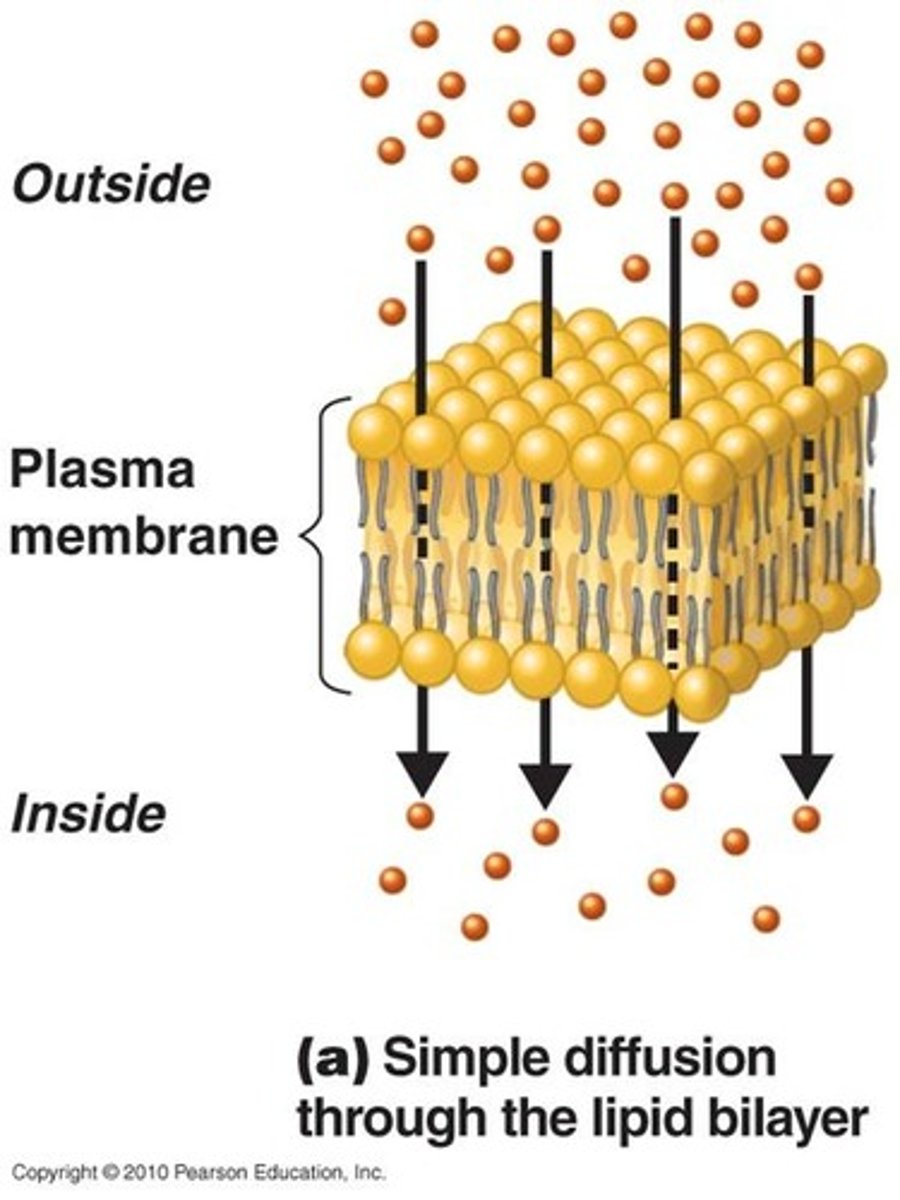
diffusion
Movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
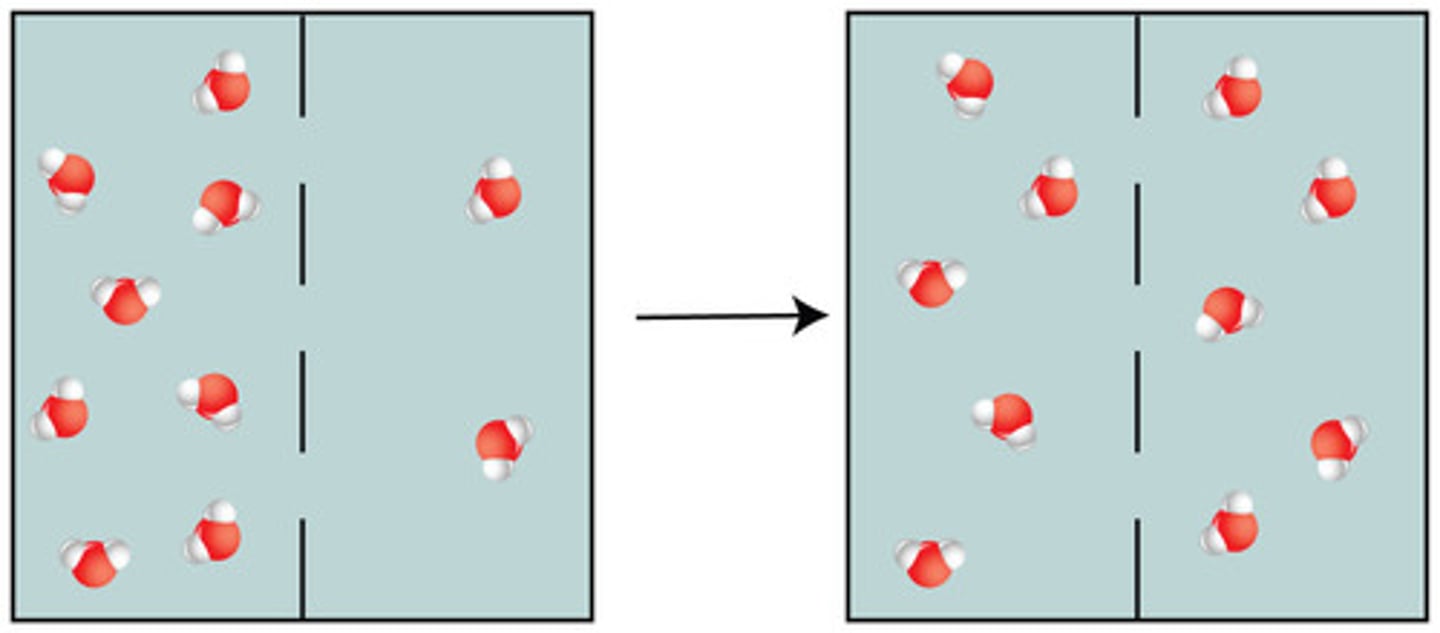
equilibrium
The point at which there is no net movement of particles across a membrane. The particles are equally distant from each other.
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane from hypotonic to hypertonic concentrations.
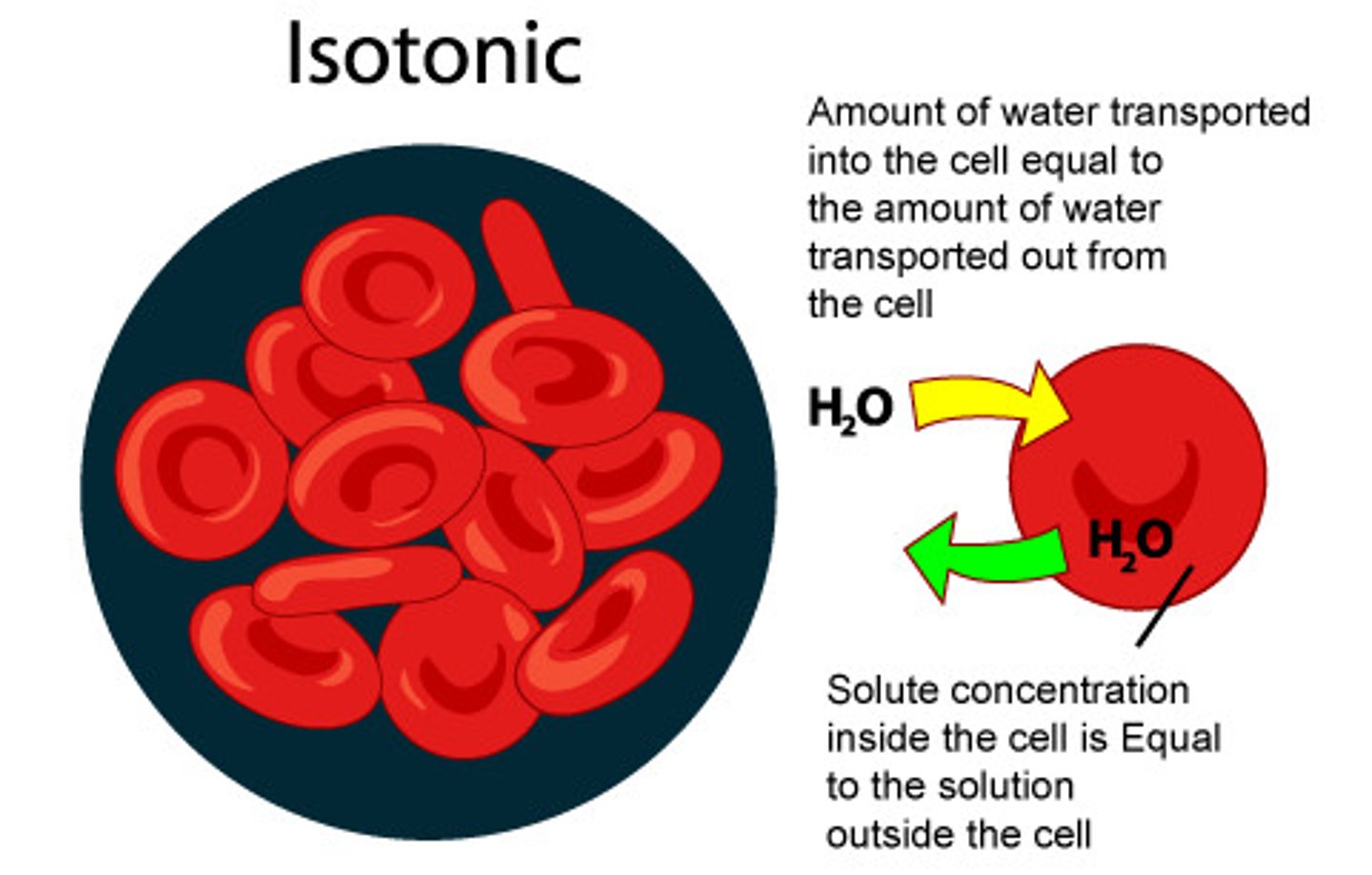
isotonic
When the concentration of two solutions is the same.
hypotonic
In comparing two solutions, referring to the one with a lower solute concentration. (higher water concentration).
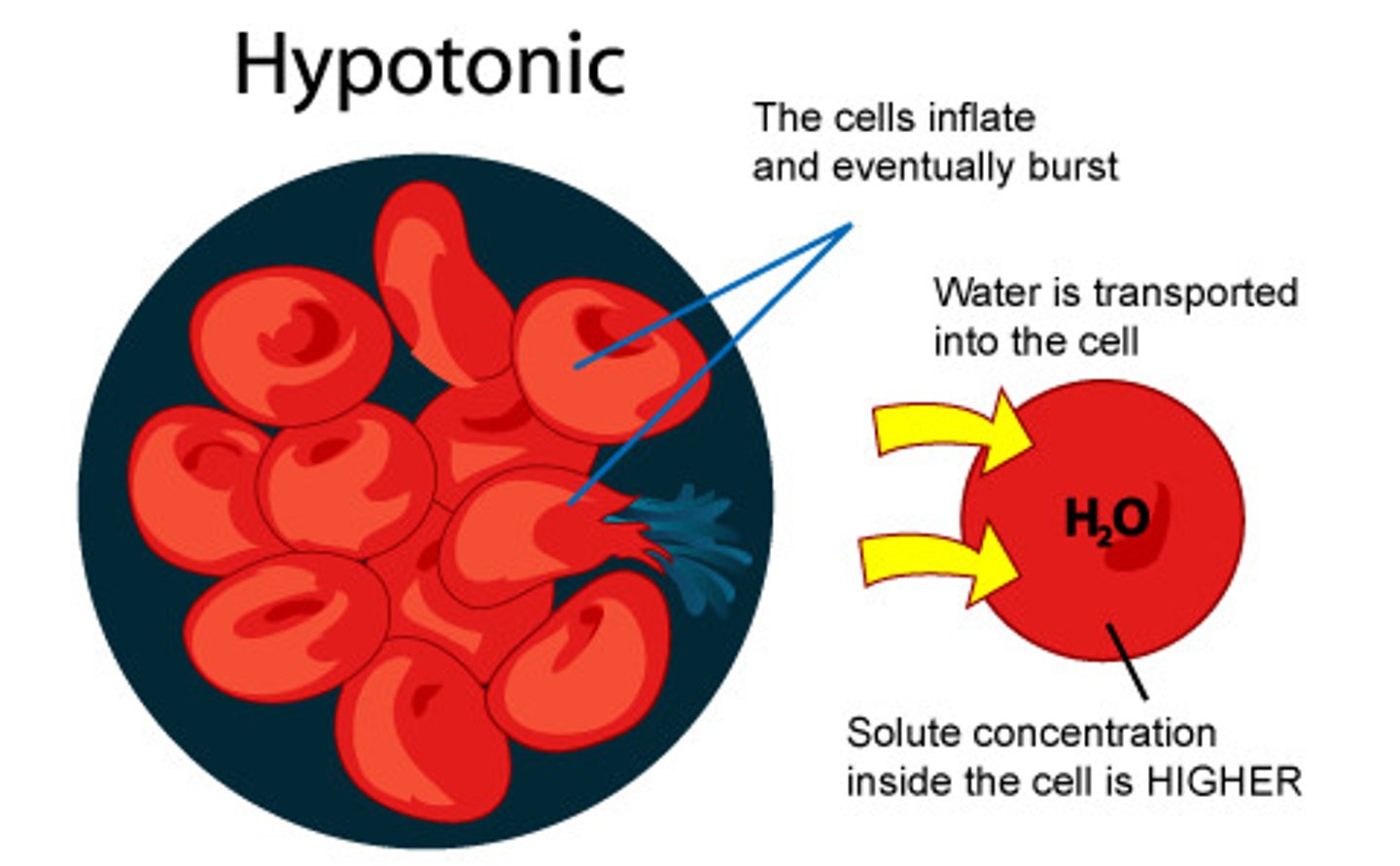
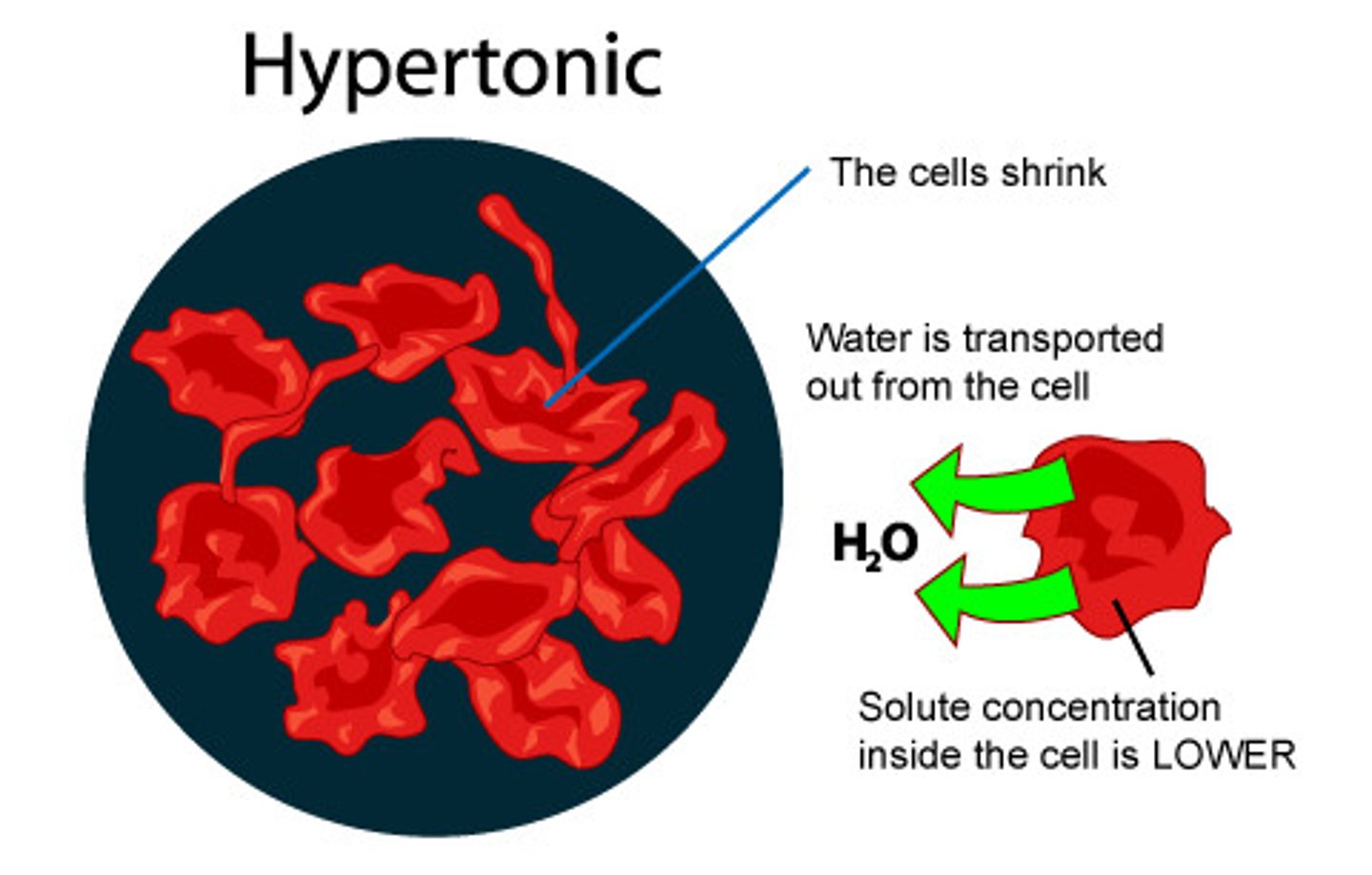
hypertonic
In comparing two solutions, referring to the one with a greater solute concentration. (lower water concentration).
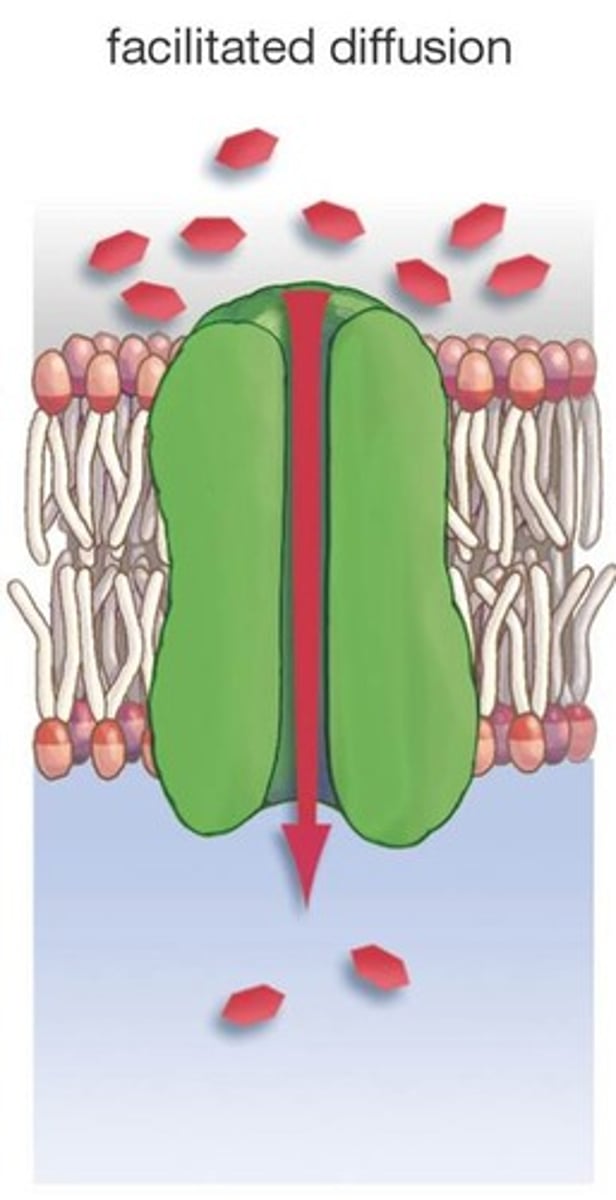
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels.
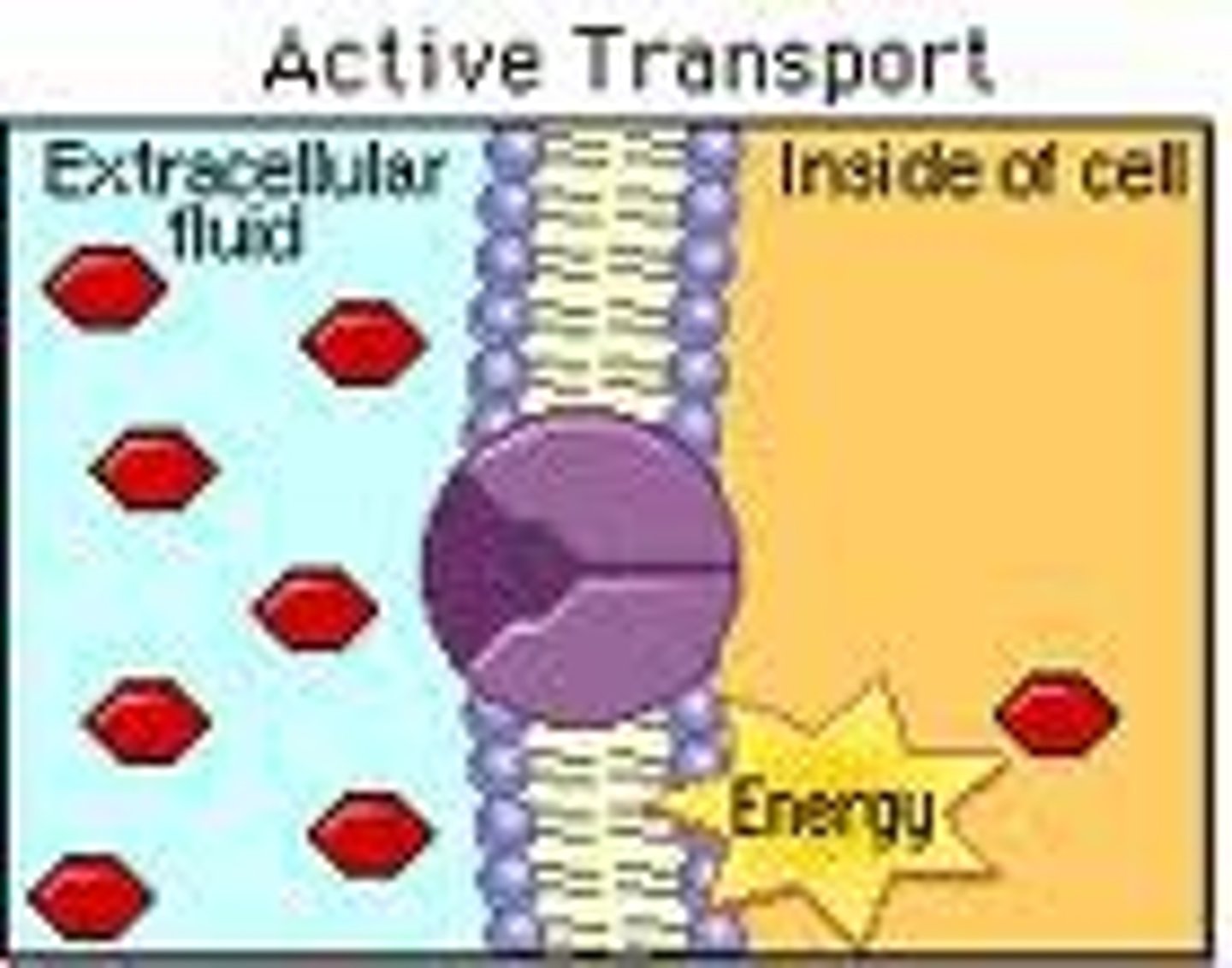
active transport
The movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy.
endocytosis
A process in which a cell engulfs extracellular material through an inward folding of its plasma membrane.
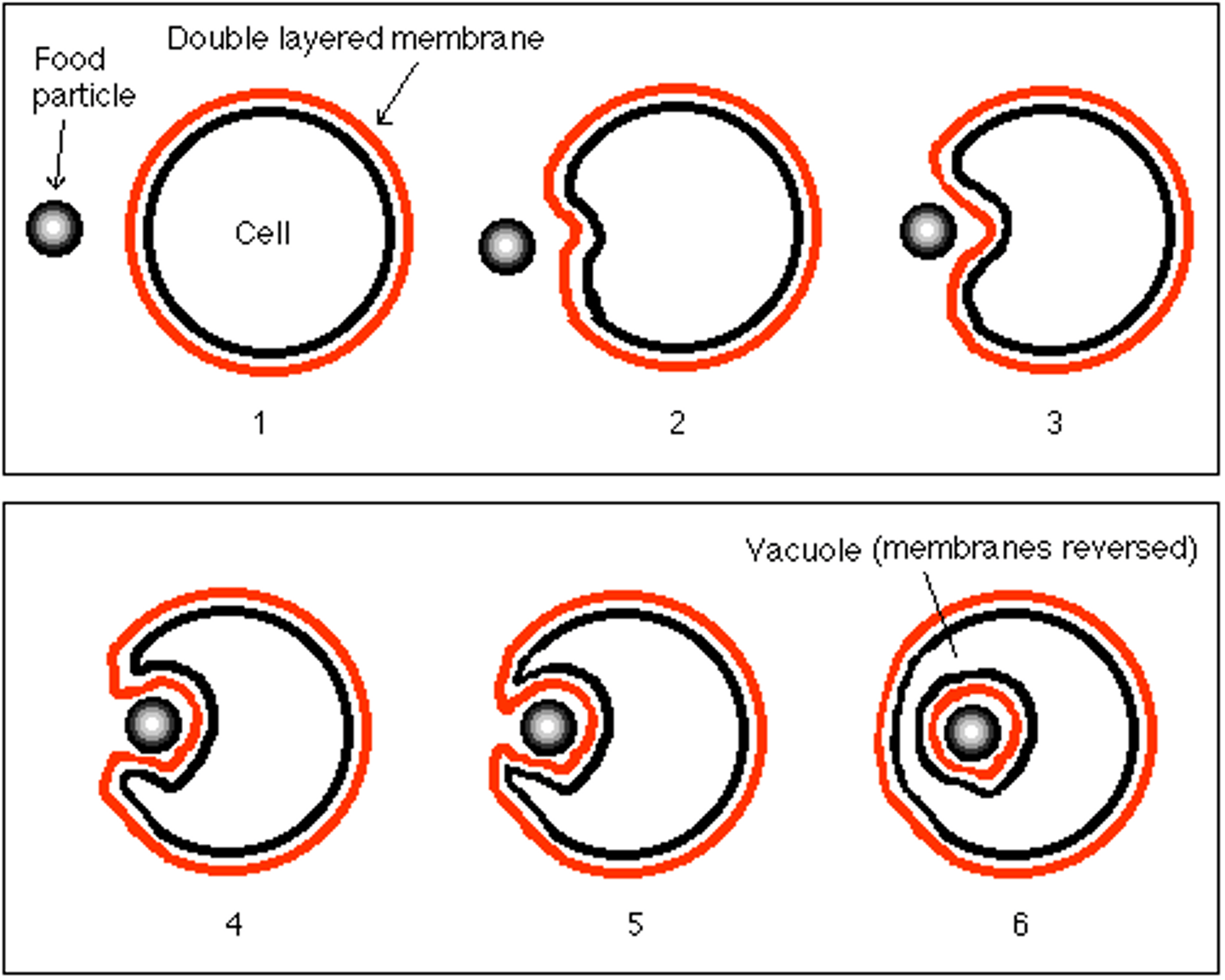
phagocytosis
The process by which a cell engulfs solid substances (food, bacteria, etc.)
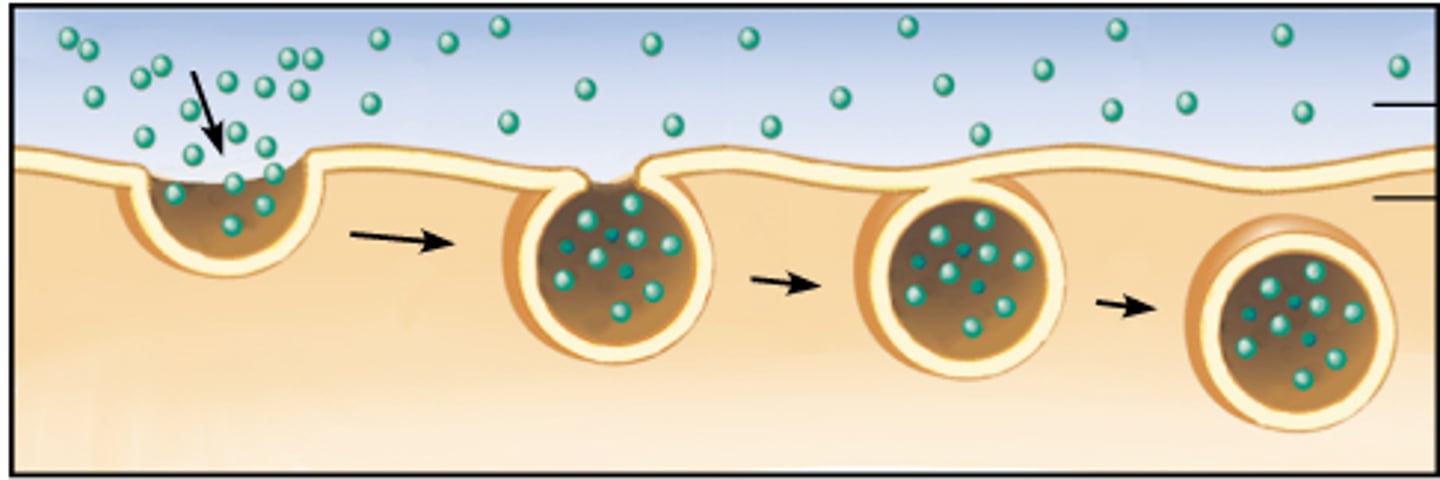
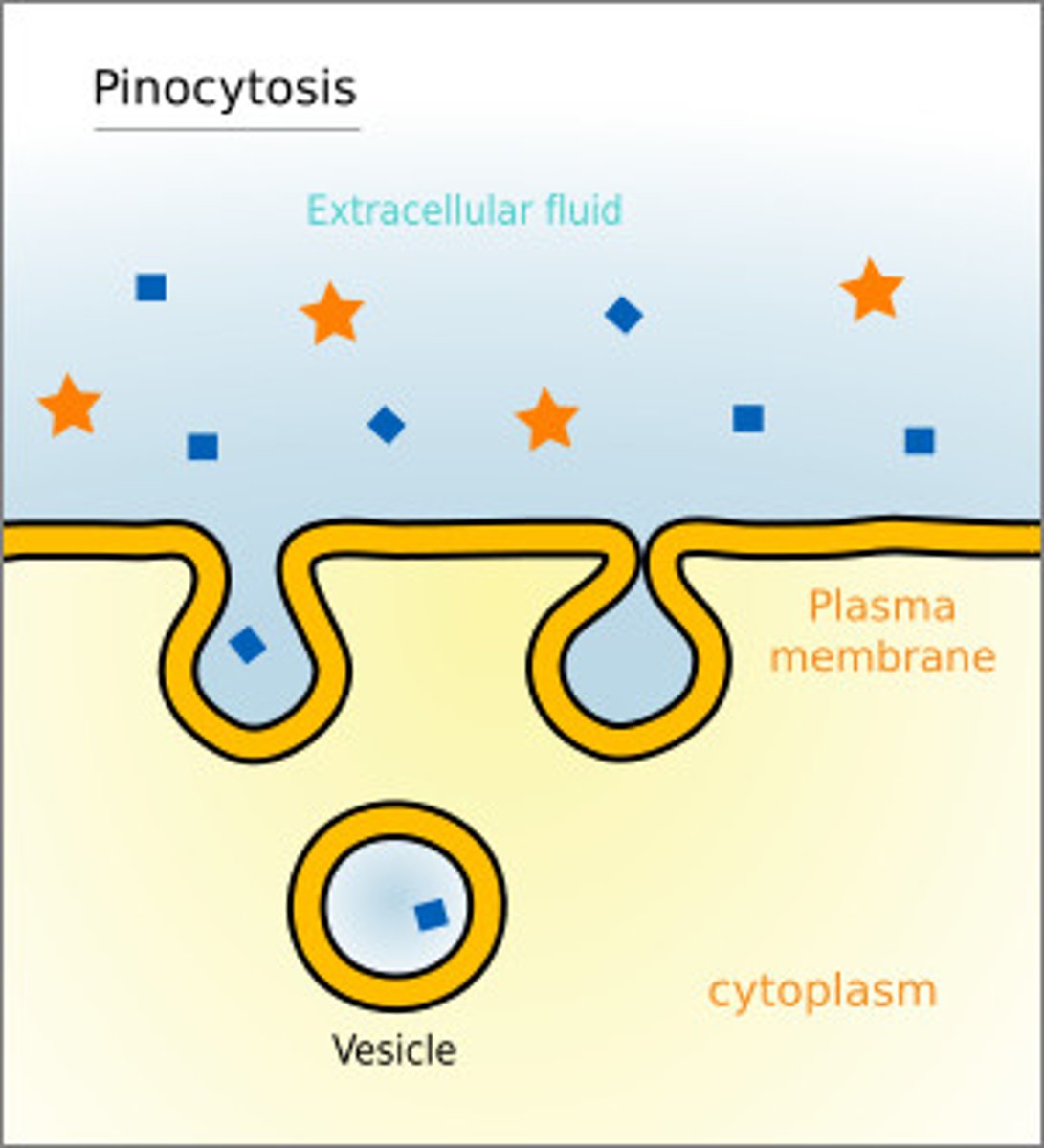
pinocytosis
process by which a cell takes in liquid from the surrounding environment.
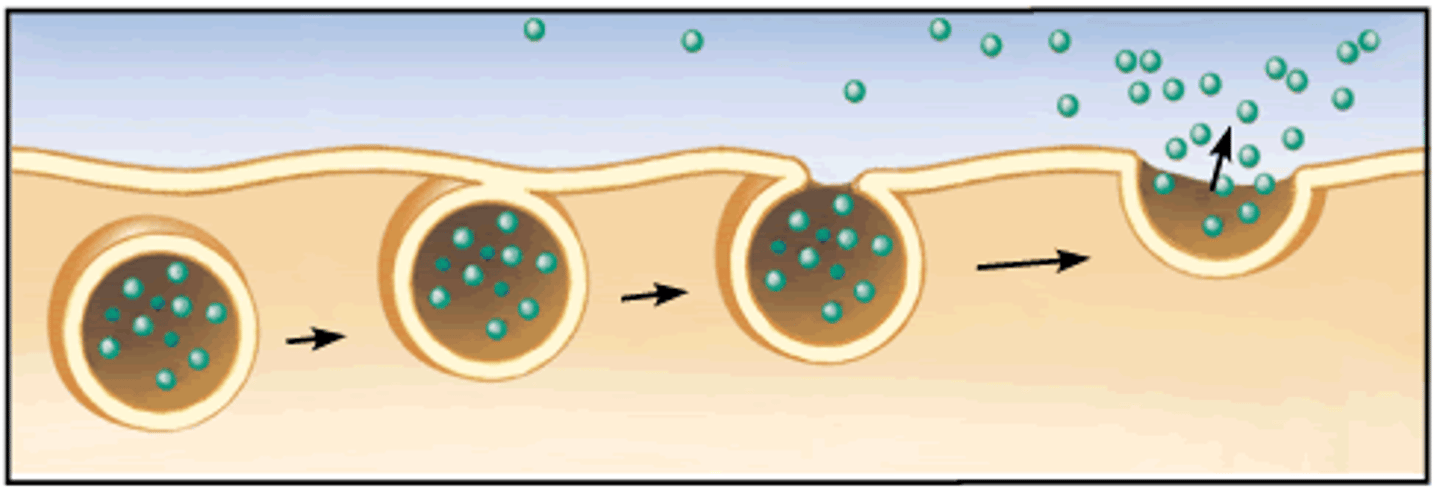
exocytosis
Moving of molecules out of the cell using active transport.
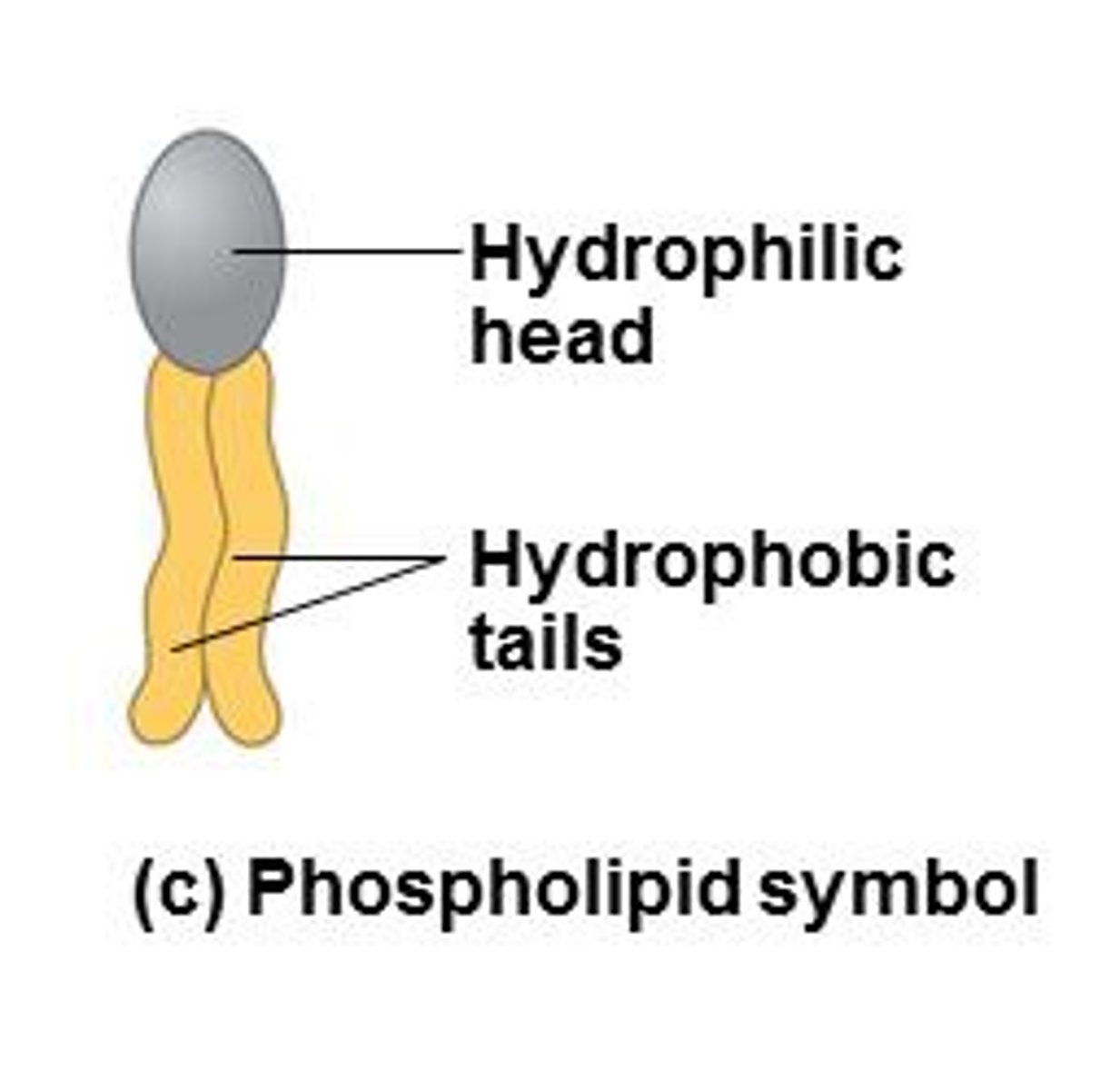
phospholipid
A lipid that contains a phosphate group and that makes up the structure of cell membranes.
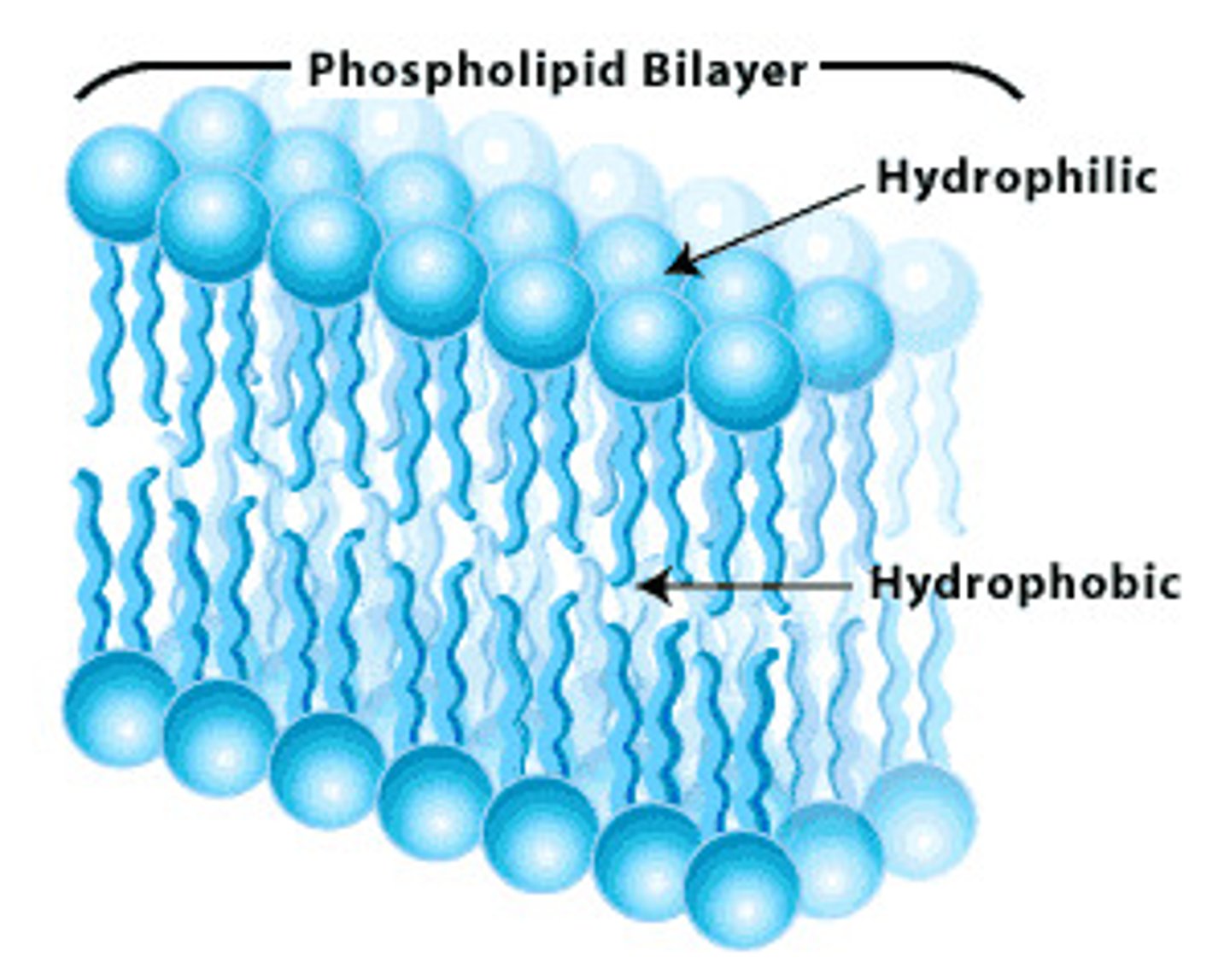
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up cell and organelle membranes.
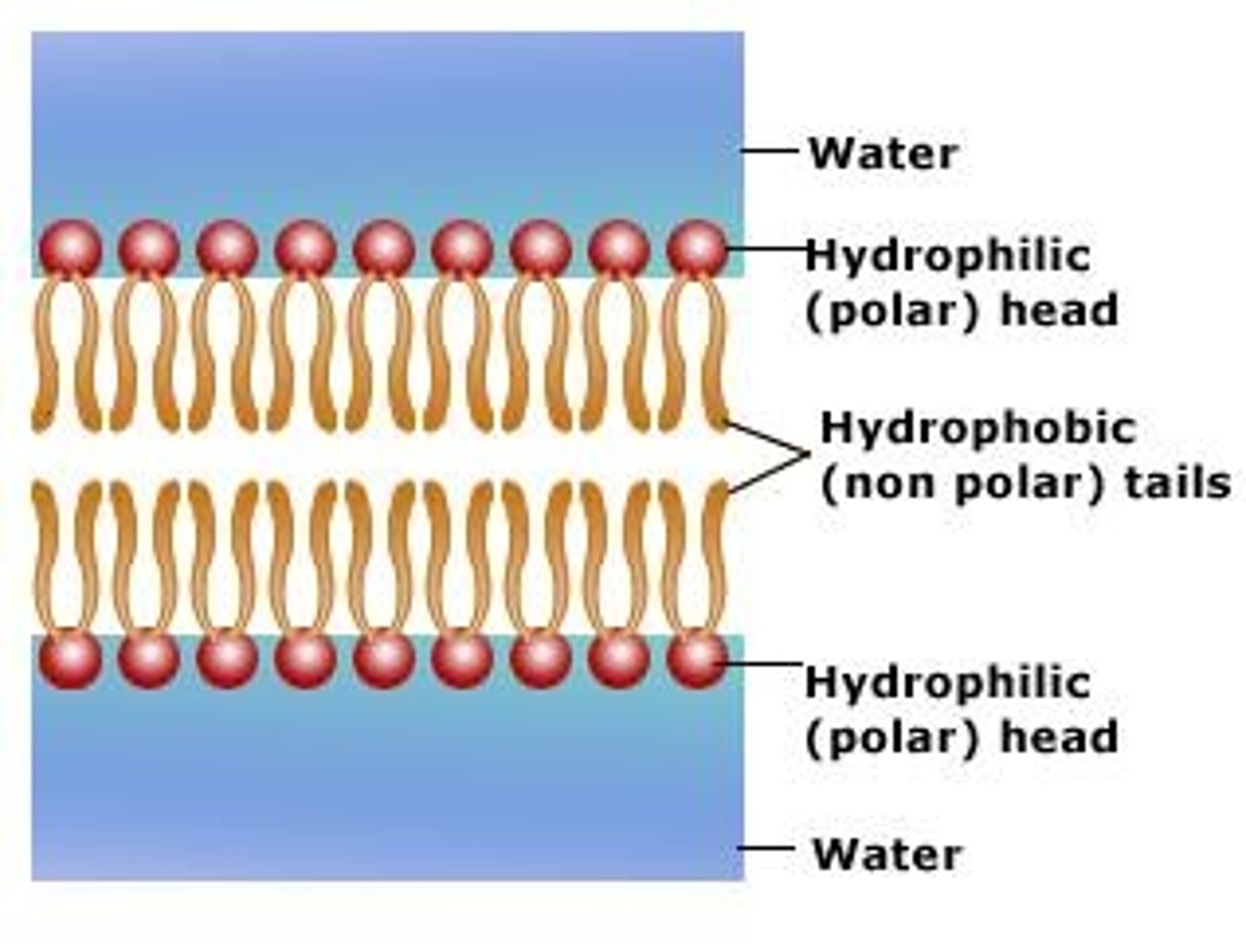
hydrophobic
"Water-fearing"; molecules (or parts of molecules) that do not dissolve in water. (Example - lipid tails of phospholipids)
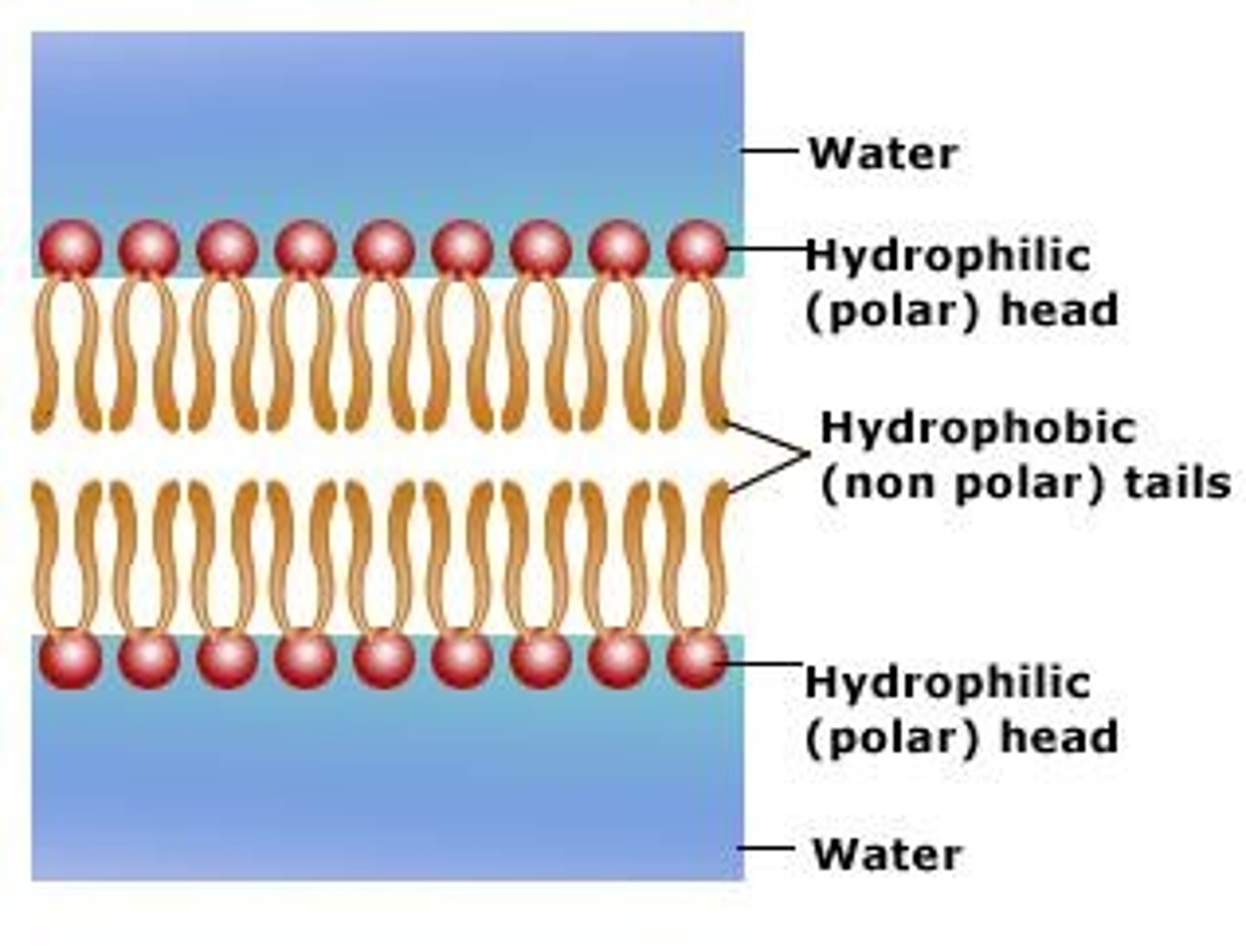
hydrophilic
"Water-loving;" molecules that can dissolve in water. Example: phosphate heads of phospholipids.
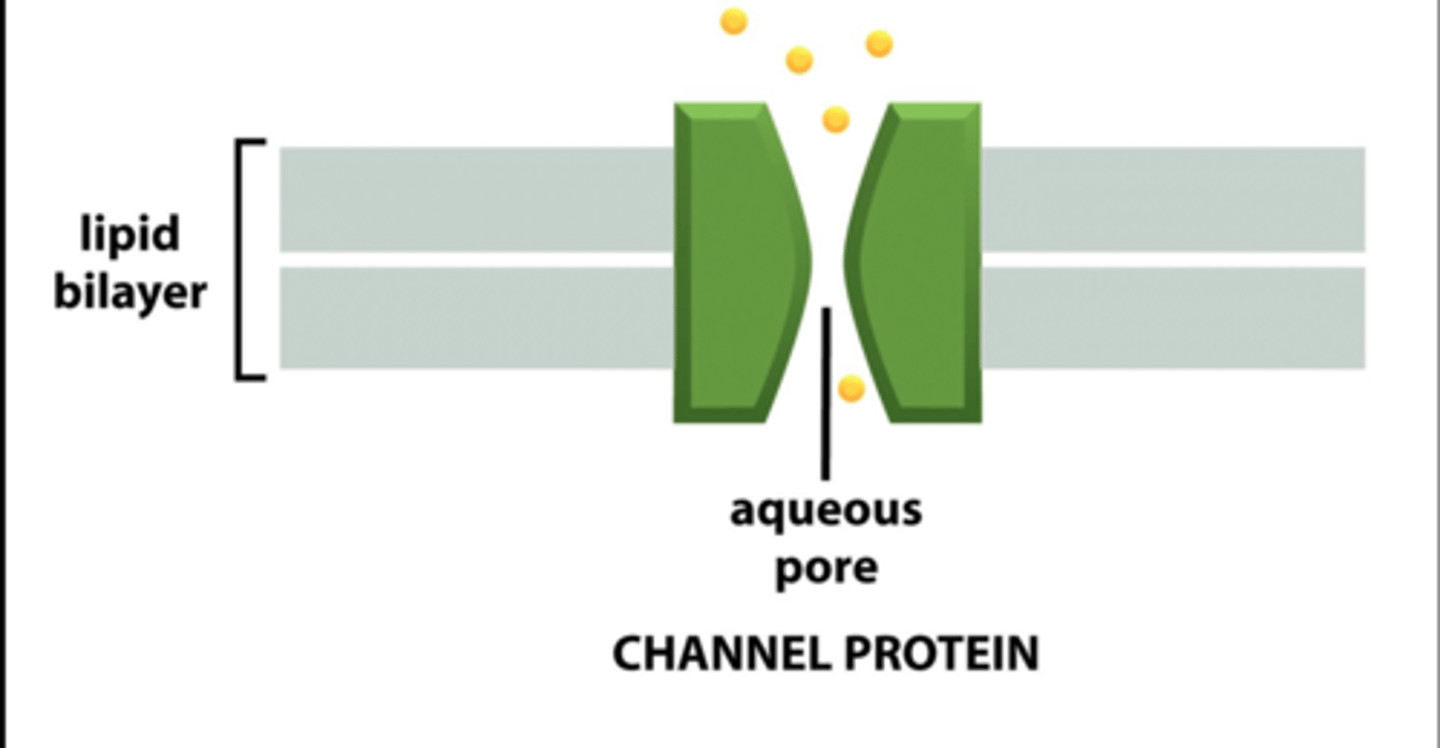
transport/channel protein
Cell membrane protein that helps particles pass from one side of the membrane to the other.