ARCH & UD 10A Midterm Monuments
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
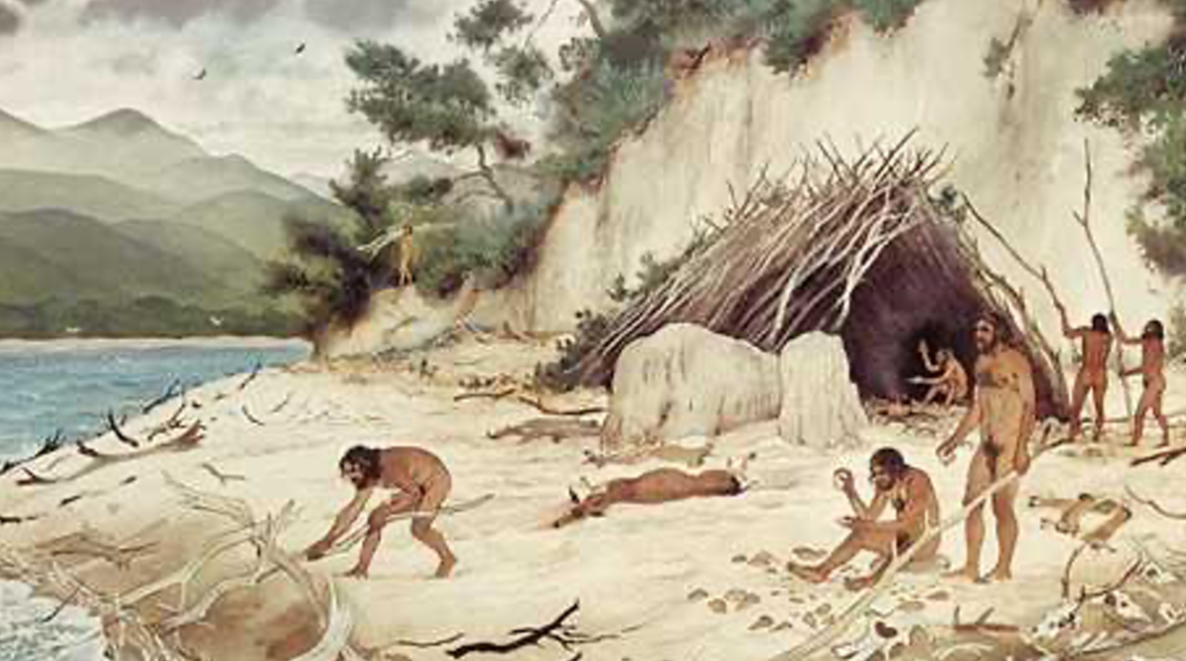

Terra Amara; -; Nice, France; hunter-gatherers, ~400,000 BCE, tensile hut
Held up from the tension created by sticks and posts
Built out in the open, in contrast with previous cave dwellings
Made with whatever the hunter-gatherers could find around them (e.g., sticks, stones)
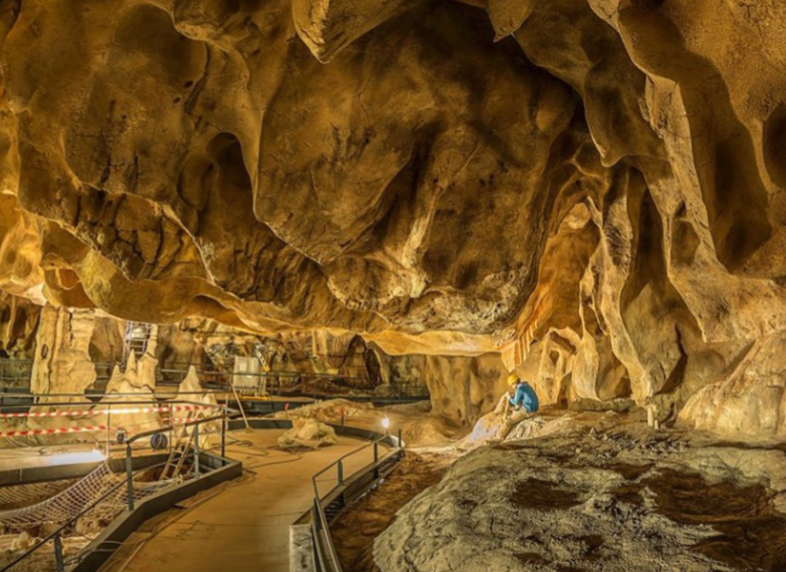

Chauvet Cave; -; France; -; ~30,000 BCE; cave-dwelling
The entrance is high up. As it’s a space you can’t easily enter, it’s symbolic of the sanctity of the dwelling
Cave paintings from generations of different people demonstrate the cave’s religious significance
End-chamber of the cave has a painting of a gigantic woman associated with assumed great goddess. Implies forms of religion early in human history.
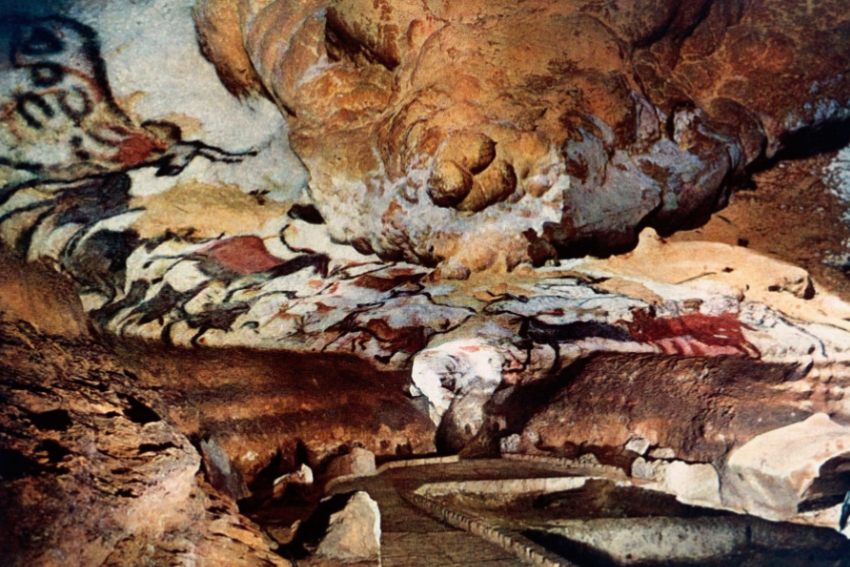

Lascaux; -; Montignac, France; ~15,000 BCE; cave-dwelling
The entrance is high up. As it’s a space you can’t easily enter, it’s symbolic of the sanctity of the dwelling
The inside of the dwelling is dark compared the the bright outside: a symbolic reference to birth
6,000 individual drawings of animals, humans, and abstract signs
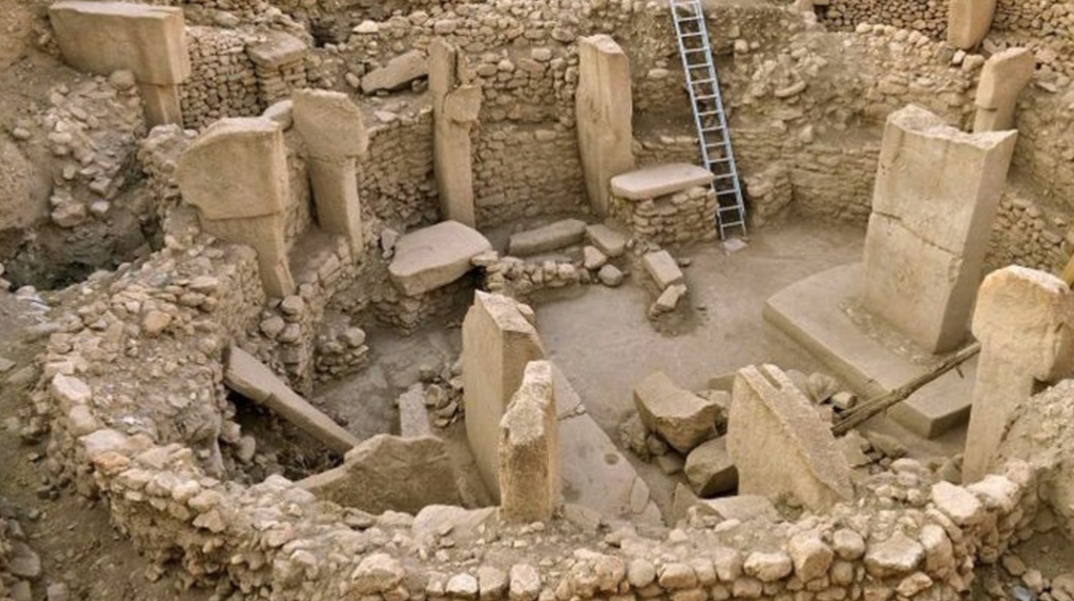

Gobekli Tepe; -; Anatolia, Turkey; ~9,500 BCE; stone age settlement
Walls are filled in with rubble in the middle
Carved with relatively simple stone tools
T-shaped tiers embedded in the walls
Ritualistic space, as exemplified by its relative durability (more important spaces ⇒ more durable)
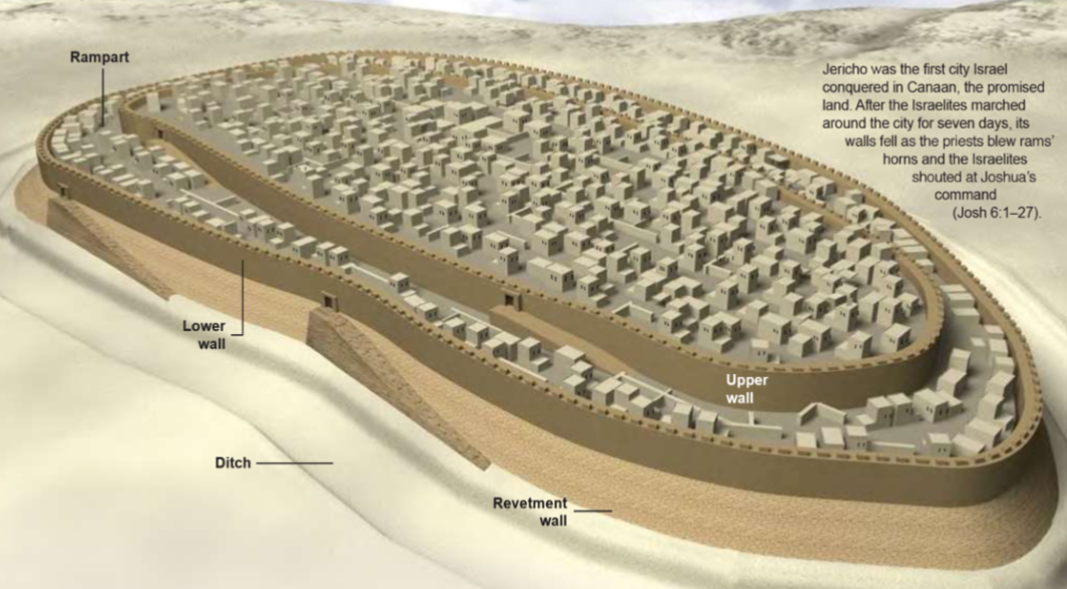
Jericho; -; West Bank, Palestine; 7,500 BCE; early city
one of the oldest civilizations in the world, and first walled city in this region (wall = protection)
presence of obsidian is evidence of early trading relations (obsidian in not available in the area)
has a large, conical tower possible for defense or tombs or to inspire awe in the ppl
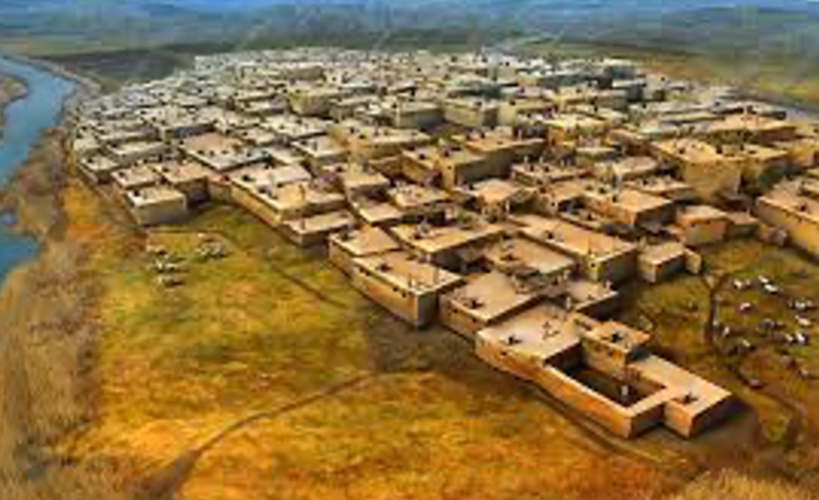

Catalhoyuk; -; Anatolia, Turkey; 7100 BCE; early city
Since its homes were primarily made of mudbrick and wood, we see rectangular buildings in contrast to circular
Typically enter homes through a hole in a roof down a ladder (can remove ladder for defense)
Excavated statue of the great goddess provides evidence of religion
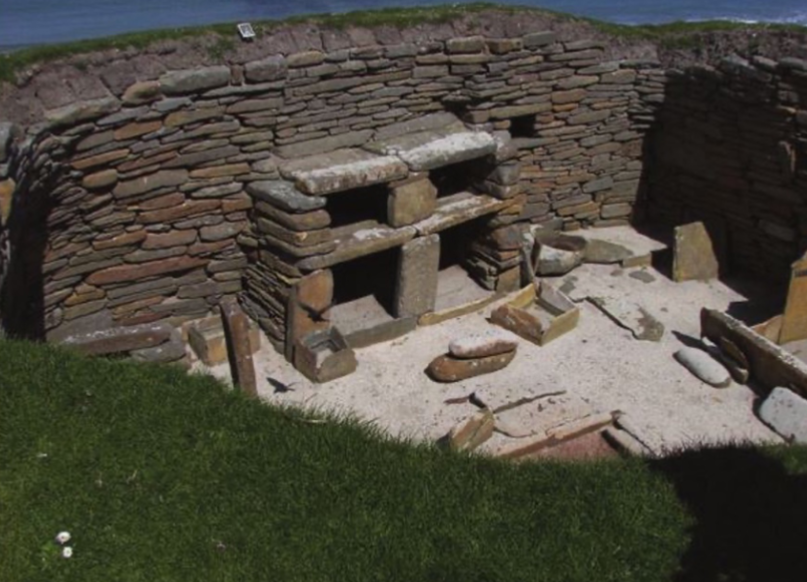

Skara Brae; -; Orkney Islands, Scotland; 3200 BCE; neolithic settlement
Settlements are made out of stone- likely because stone was more abundant than wood. Plus, stone is fireproof and more stable
Intricate walls built with stacks of flat, rectangular stones
Most structures built by a stonemason, who cuts and shapes the stones
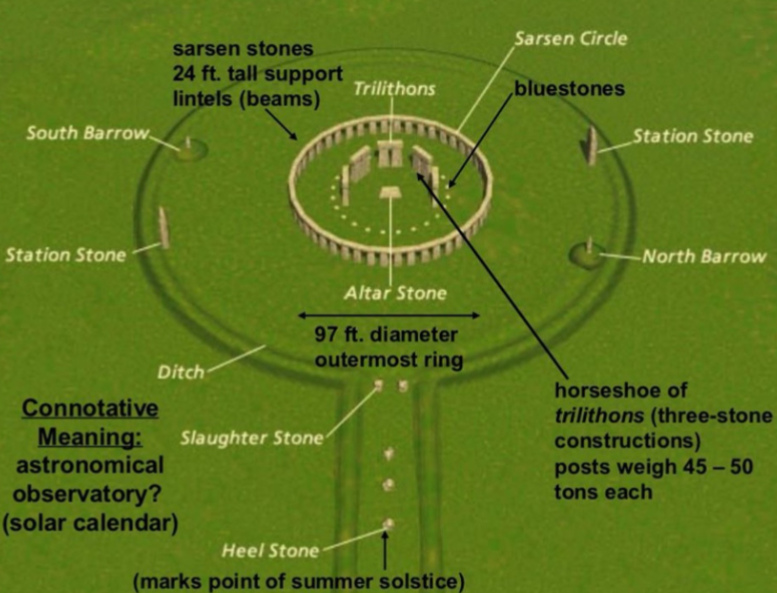
Stonehenge; -; Wiltshire, English; 3100BCE; Megalithic stone circle
Made with mortise (like key) and tenon (joint of 2 connecting piecing of wood) which creates stability
Lintel forms a continuous circle around the top. Mortise and tenon locked lintel.
Reveals refinery in craft, geometry, and astronomical knowledge
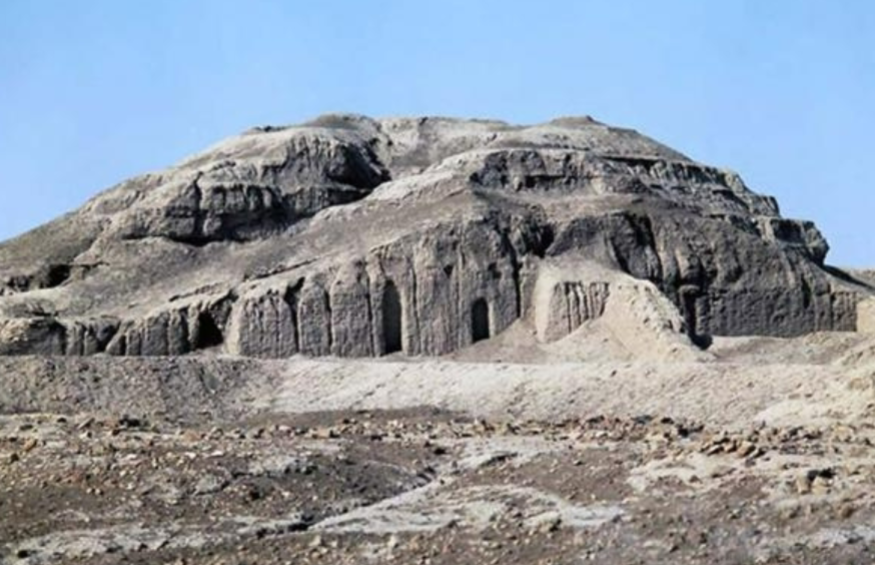

Ziggurat of Uruk/White Temple; -; Warka, Iraq, Sumerians (city of Uruk), ~3200-3000 BCE, Ziggurat
High elevation protects the site from annual flooding and is symbolic of how the gods are “above” the commonfolk
Meandering pathway towards the temple makes the act of entry/exit like an act of pilgrimage
The inside would be lit with incense and the structure had little windows; hence, almost like a separate world from the outside.
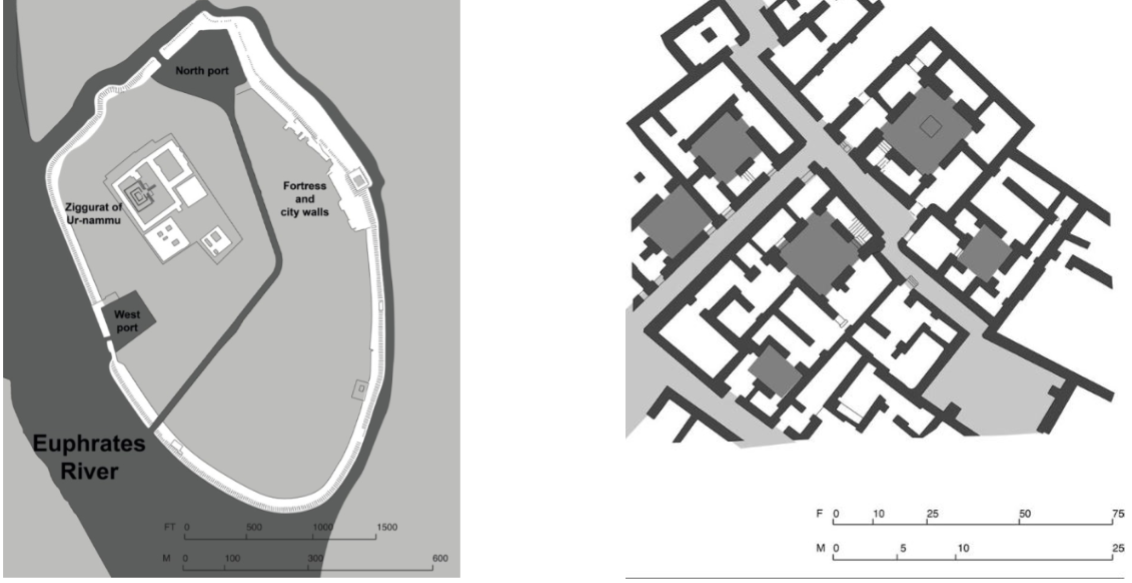
Settlement of Ur; -; Iraq; Sumerians; ~3,800 BCE, early city
Surviving ziggurat at the center of the city indication that religion is most important
People of higher ranks would live at higher elevations
Houses were in tightly packed blocks
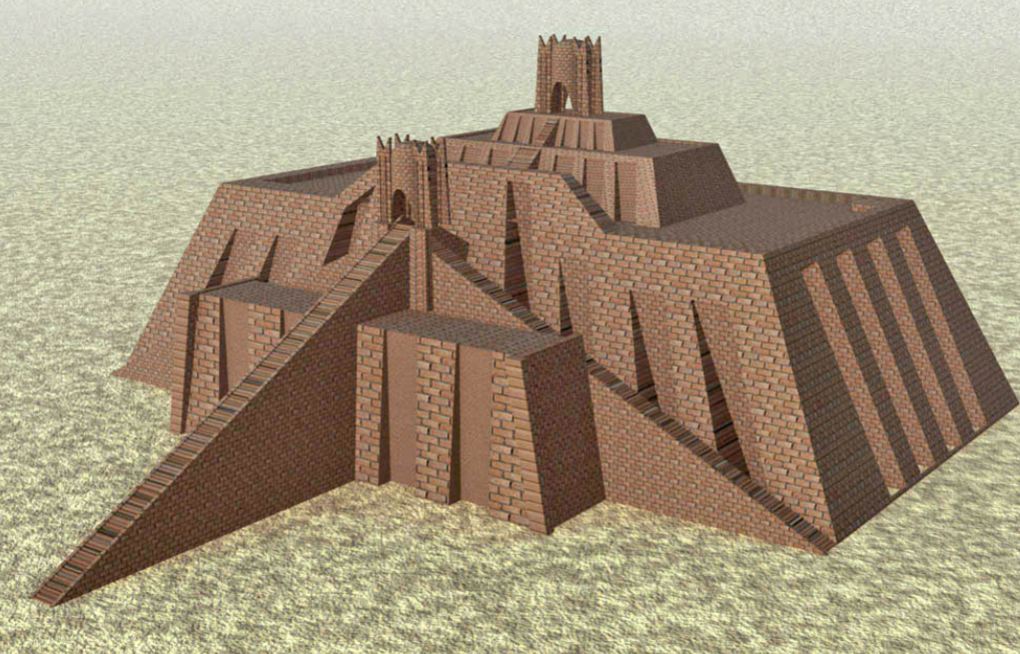

Ziggurat of Ur; Ur-Nammu; Iraq; Sumerians (city of Ur); ~3800 BCE; ziggurat
3 staircases with 4 successively smaller platforms - display of hierarchical order in society
Administrative buildings and housing for priests nearby = physical manifestation of church and state
The palace is almost touching the ziggurat - further emphasis on the importance of religion
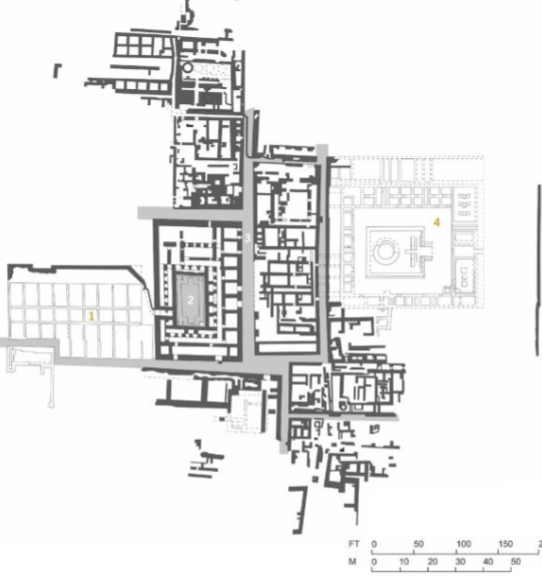
Mohenjo-Doro; -; Pakistan; Harappans; ~2500 BCE, city
More open layout of streets representative of a more open culture
Large-scale infrastructural projects like bathing, sewer systems, and massive granaries
The city had large platforms thought to be as a defense against flooding
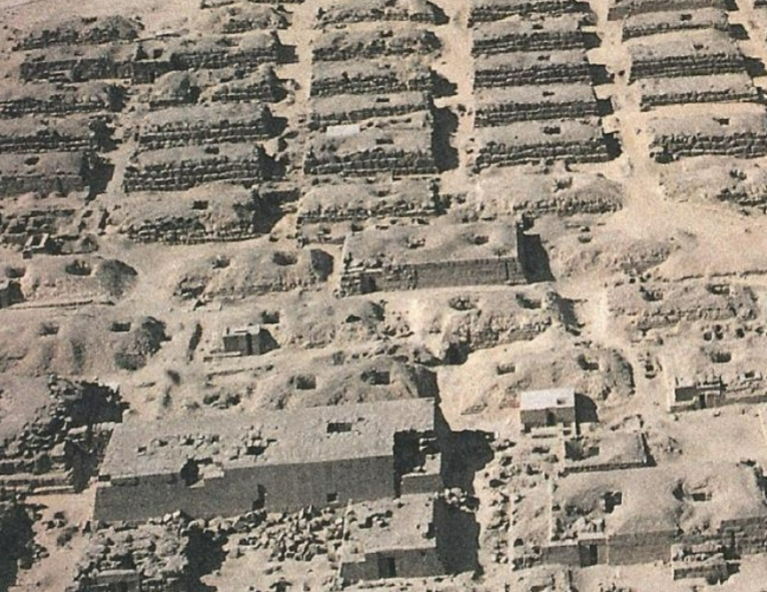

Saqqara; -; Egypt; Old Kingdom; 3000 BCE; necropolis
ancient burial ground meant for Egyptian royalty
contained a number of mastaba tombs- flat-roofed, rectangular tombs
contains the stepped pyramid of Djoser
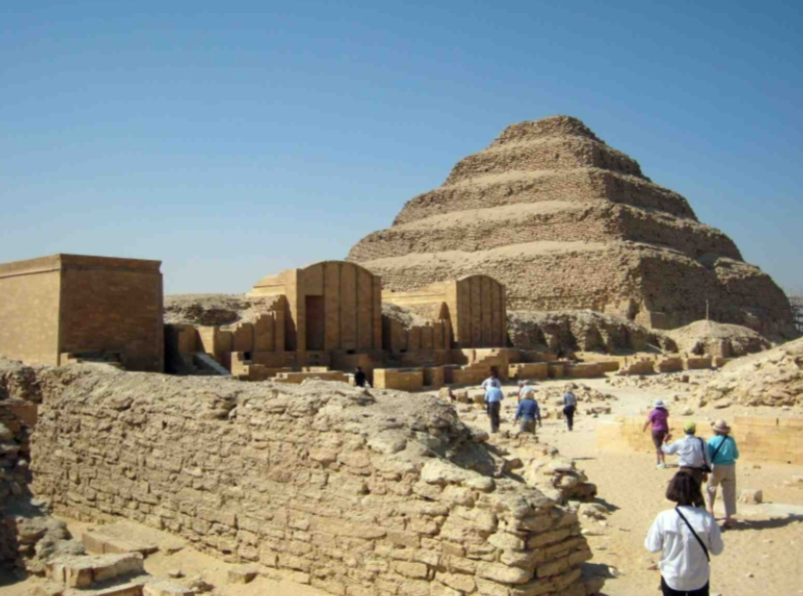

Stepped pyramid of Djoser; Imhotep; Egypt; Old Kingdom; 2600 BCE; Pyramid
Sheer height of the pyramid serves as a physical manifestation between the heavens the earth
Holes in the sides allows citizens to see Djoser’s funerary statues and for Djoser’s ka to see the outside world as well
The addition of multiple chambers would make the pyramid harder to rob
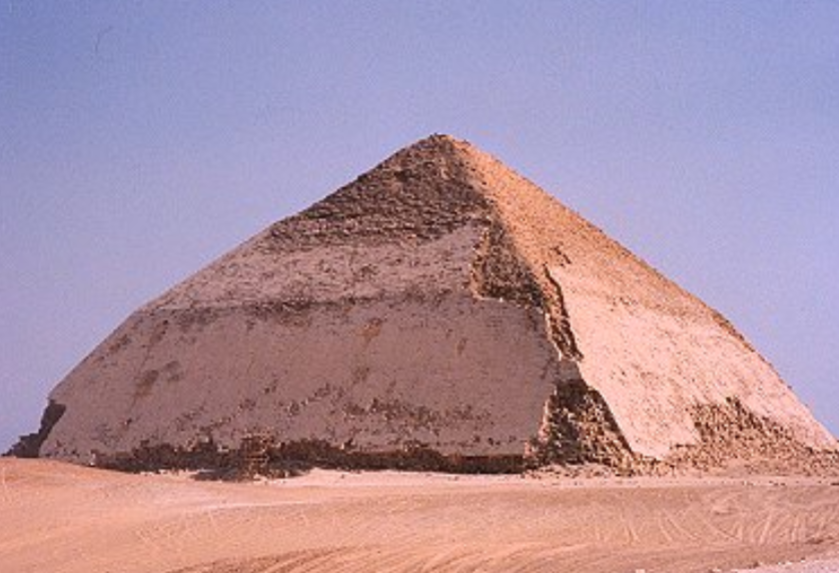

Bent Pyramid; -; Egypt; Old Kingdom; 2600 BCE; Pyramid
Contained a burial chamber and processional complex
Used to be encased in white limestone
Originally was built to steep and was eventually correct, hence the “bent” nature of the pyramid
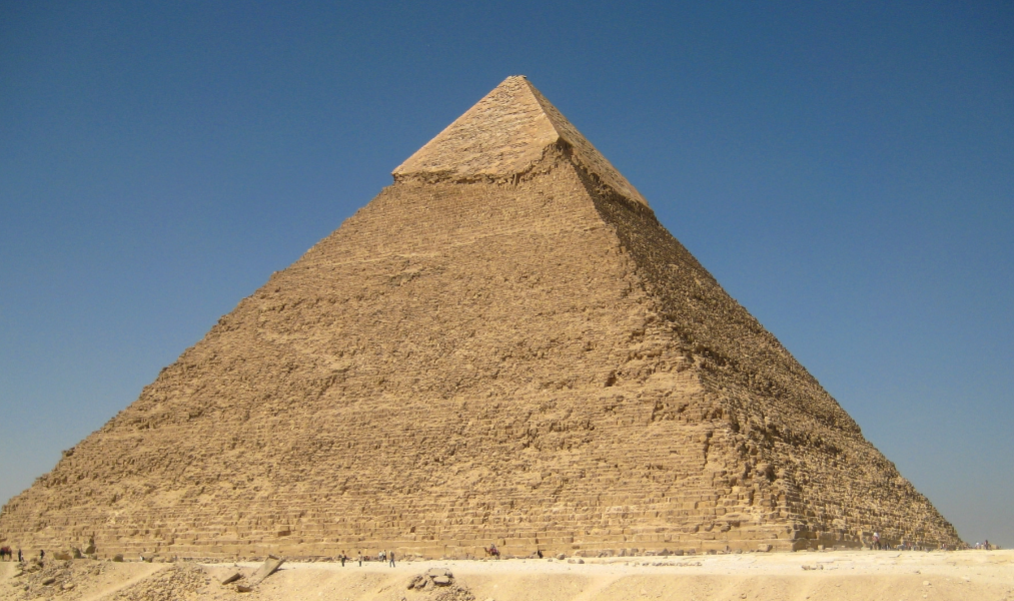

Great Pyramid of Giza; Hemiunu; Egypt; Old Kingdom; 2600 BCE; Pyramid
Intended not to have visible access points. Secret entrance located on North face.
Astonishing feat of bulk and precision, even by modern standards
Sleds and manpower were used to rock rocks over, and a ramp was thought to be used to build the top sections
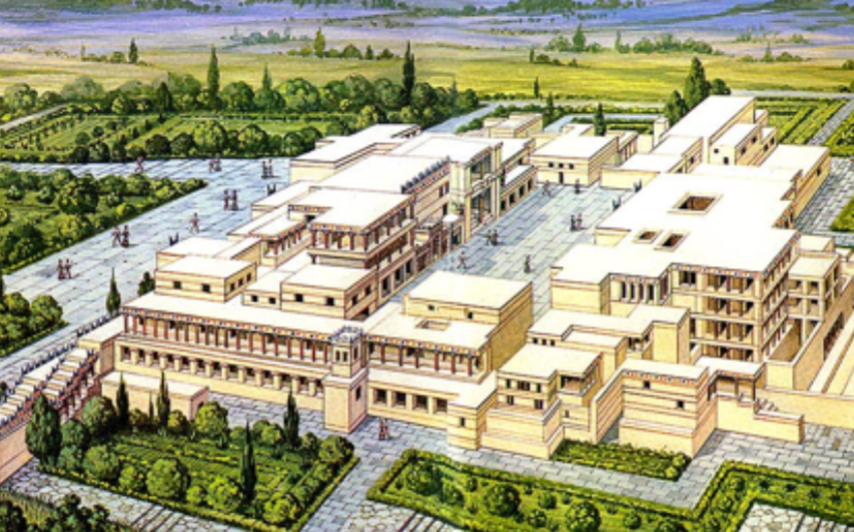

Temple at Knossos; -; Crete, Greece; Minoan Culture; 1500 BCE; temple/palace
Not just one big building with the majority filled, actually made up of many different rooms
Very multi-functional, as seen by things like granaries, storage rooms, administrative rooms, throne rooms, etc.
All centered around a huge courtyard in which its believed things like religious precessions would occur
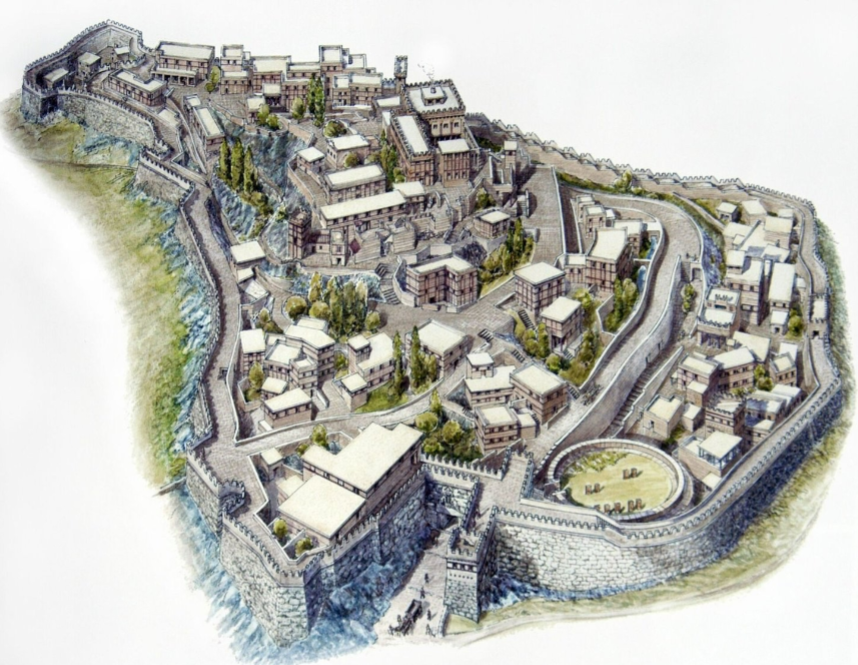
(city of) Mycenae, Argolis, Greece, Myceneans, 1300 BCE, Mycenaean city
The city had a acropolis, an elevated portion of the city, in which the most important buildings would be placed (e.g., administrative buildings)
Most of the city is on a hill - likely a defensive decision.
Surrounded by a thick wall - a further testament for the emphasis on defense.
Single main entrance to the city - another defensive component.
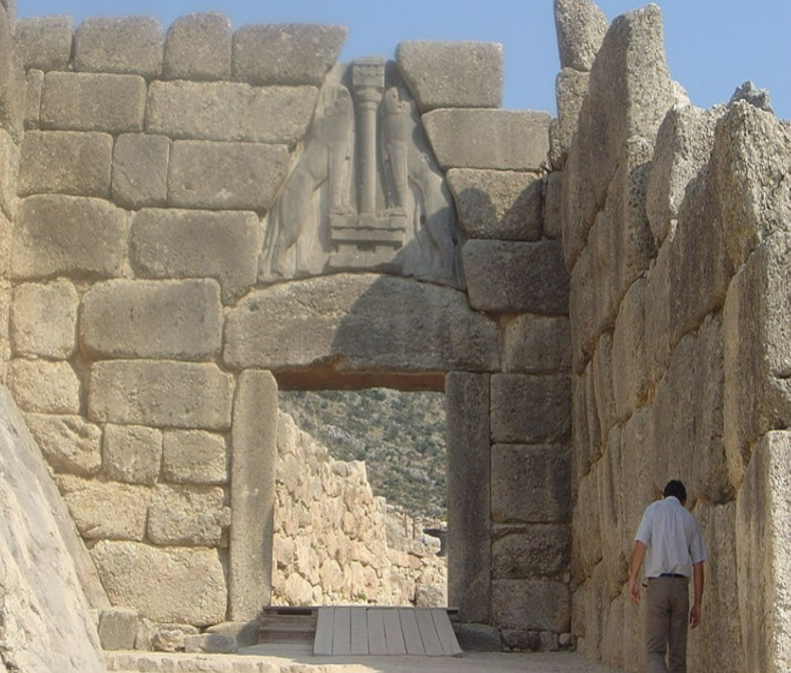

Lion gate; - ; Mycenae; Greece; Mycenaeans; 1300 BCE; city gate
Main entrance to the city of Mycenae
Capped by the carvings of two lions
Made of up huge, roughly cut limestone.
Minoan column indicated a decent amount of trade and respect between Mycenaeans and Minoans
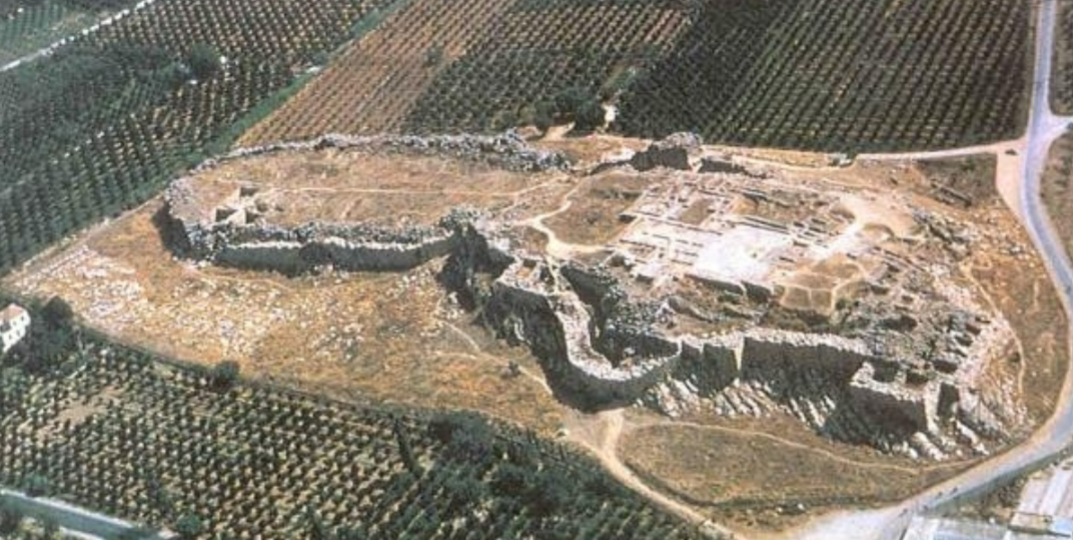

Tiryns; -; Greece; Mycenaeans; 1300 BCE; Mycenaean city
Massive walls surrounded the palace complex (& they’re the best preserved - very important defense), majority of the citizens lived outside the walls
Palace complex, in which king resided, on higher elevation and inside the walls
lower fortress = location of barracks and garrison, ensured that there were soldiers inside walls
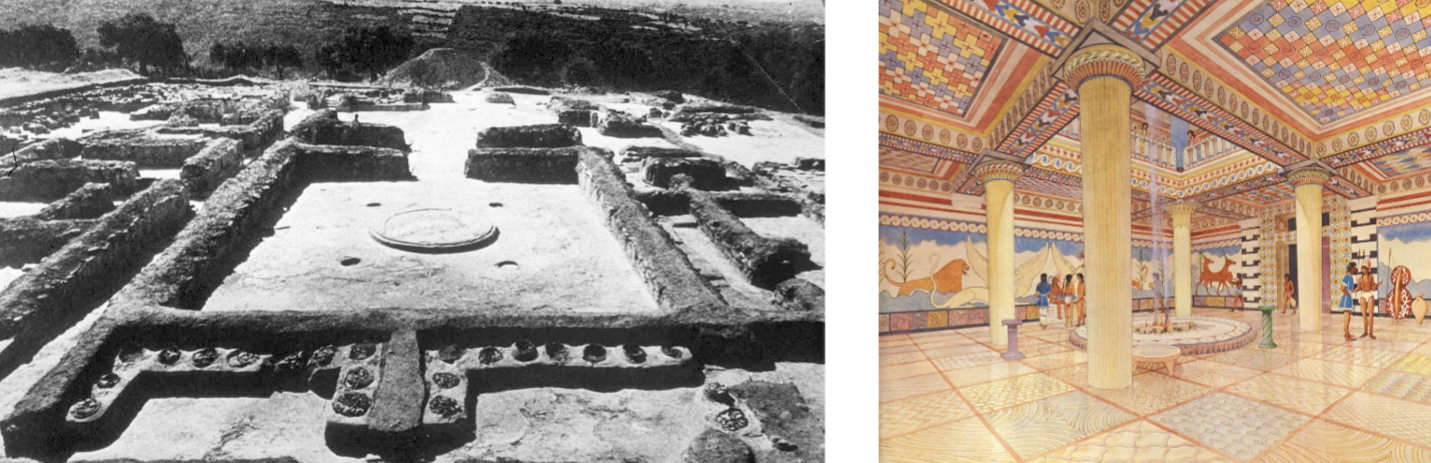
Pylos Megaron; Pylos, Greece; Mycenaean, 1500 BCE, megaron
Would have been colorfully decorated with painted walls
Hearth at center of the room, will hole at the hole for smoke to go out
Central location for administration affairs and where the king met with people
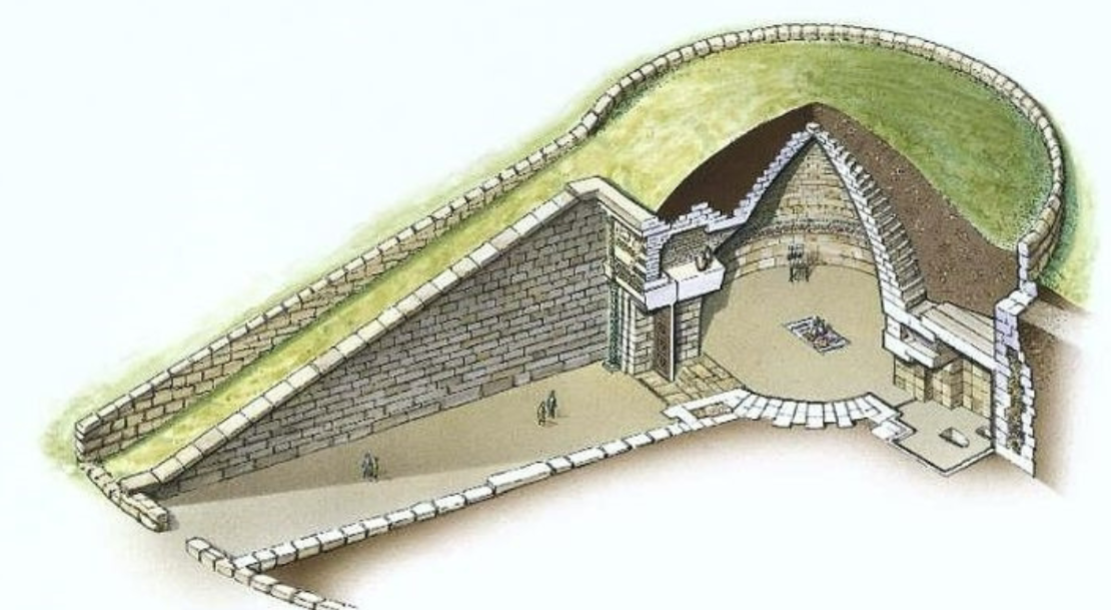
Treasury of Atreus; -; Mycenae, Greece; Mycenaeans; 1300 BCE; beehive tomb
Artificial mound on top makes in better blend into natural landscape
buried with lavish decorations (e.g., decorative dagger, funerary mask)
relief arch supports the structure
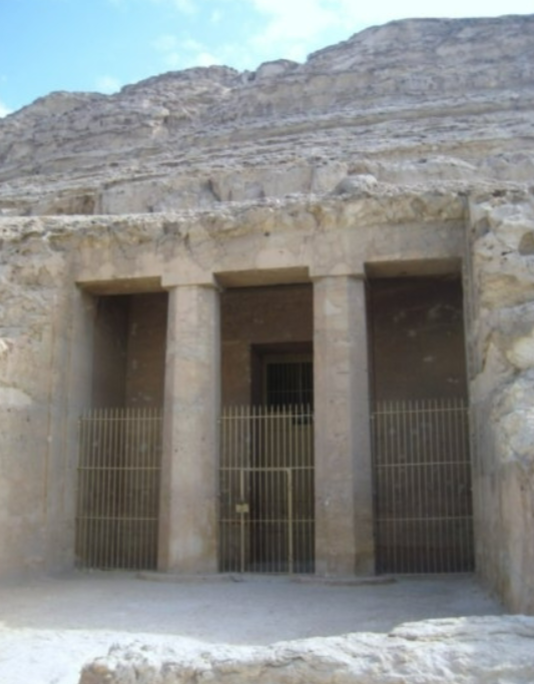

The tomb of Amenemhet; -; Beni-Hasan, Egypt; Middle Kingdom Egypt; 1800 BCE; tomb
Quite small compared to the previous pyramids, not glorifying the pharaoh in the same way
Columns of the tomb are purely decorative
Since it is a rock-cut tomb, the workers didn’t have to move any materials around since the materials they were using were already there
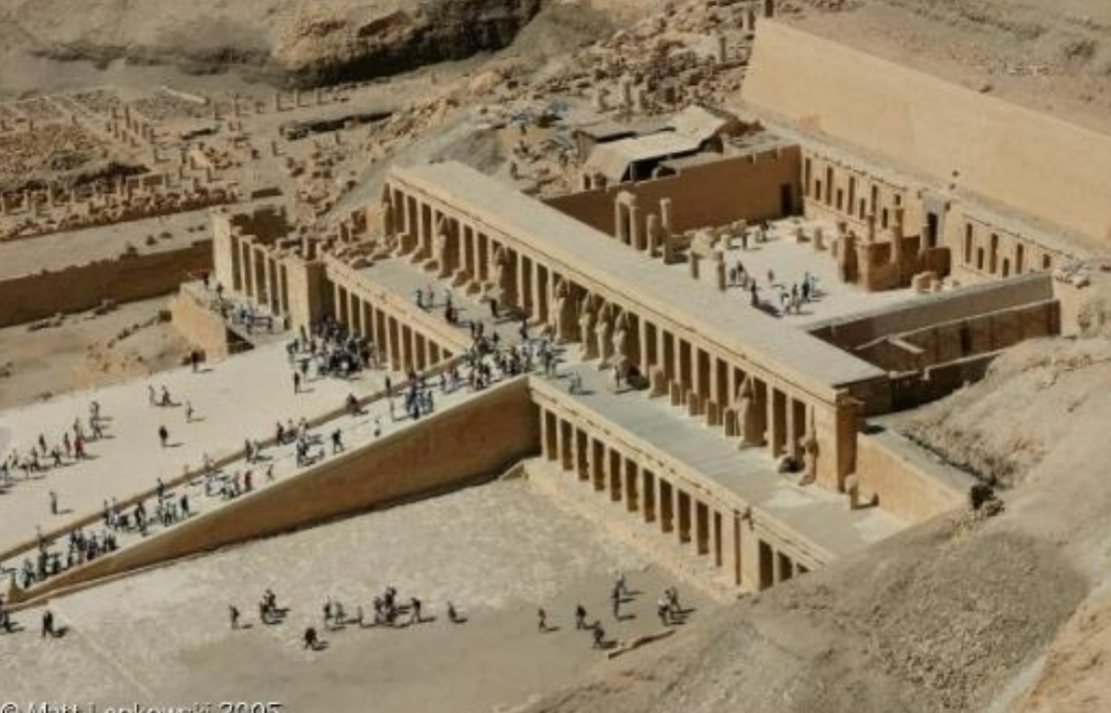

Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut; Deir el-Bahri, Egypt; Middle Kingdom Egypt; 1500 BCE; Tomb/temple
Columns in the temple are proto-doric columns
The tombs are near the back of the temple, designed allowed for people to worship the gods along with Hatshepsut herself
Many of Hatshepsut’s statues and references have been destroyed (patriarchy)
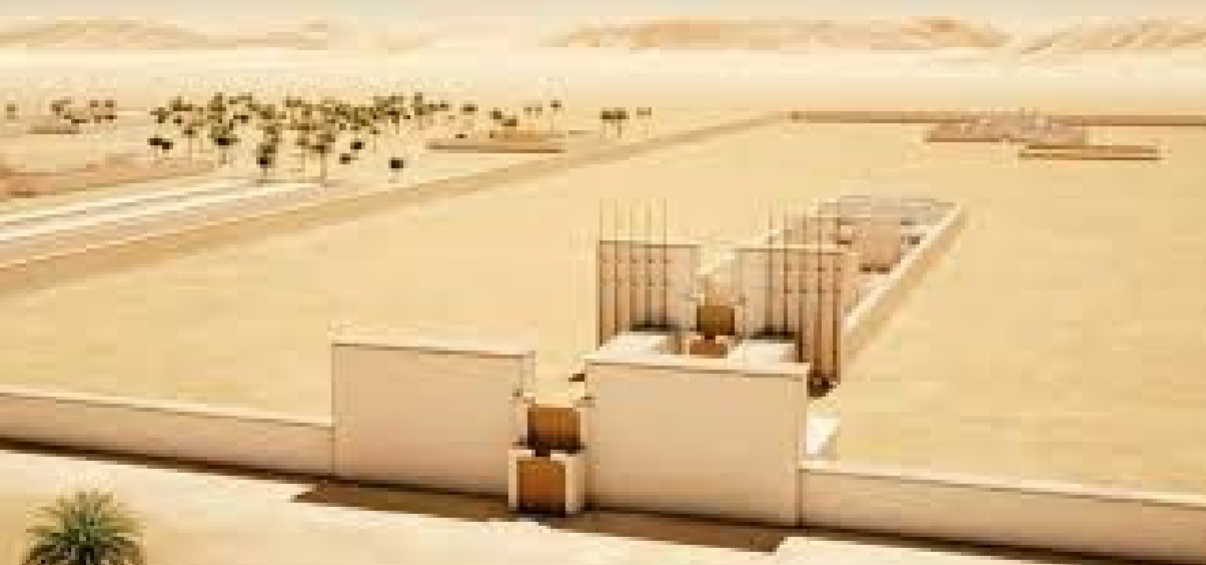

Amarna; Akhenaten; Egypt; New Kingdom; 1300 BCE; city
Uncompleted capital city during the Amarna period
The great temple and royal palace was physically linked by a bridge
Artwork unique in that Queen Nefertiti is shown by herself in some of the excavated art.
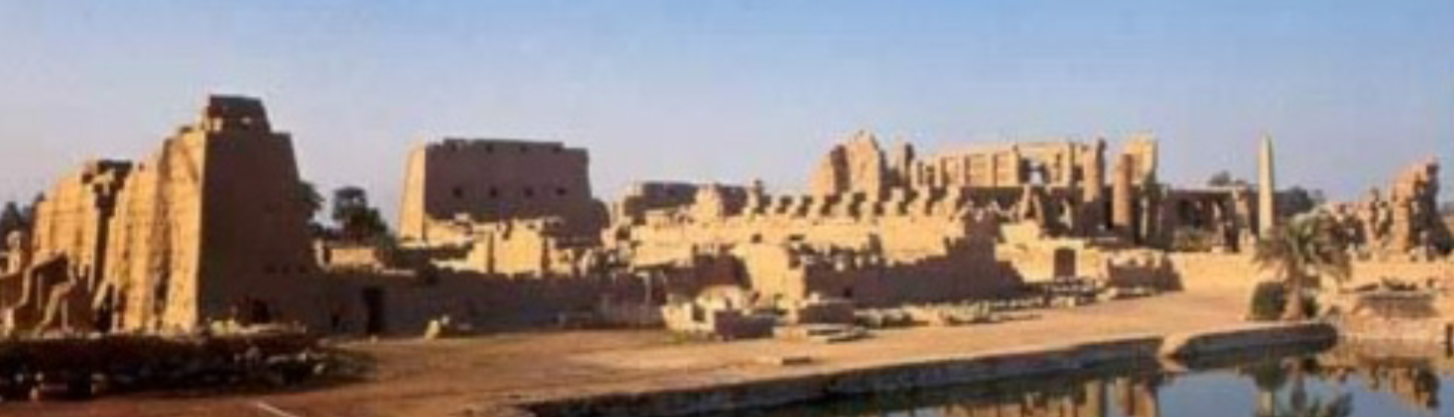

Karnak temple complex; -; Luxor, Egypt; New Kingdom; 1400 BCE; Temple
Contained The Great Hypostyle hall
Main of worship dedicated to the Theban triad of gods
Built over many generations
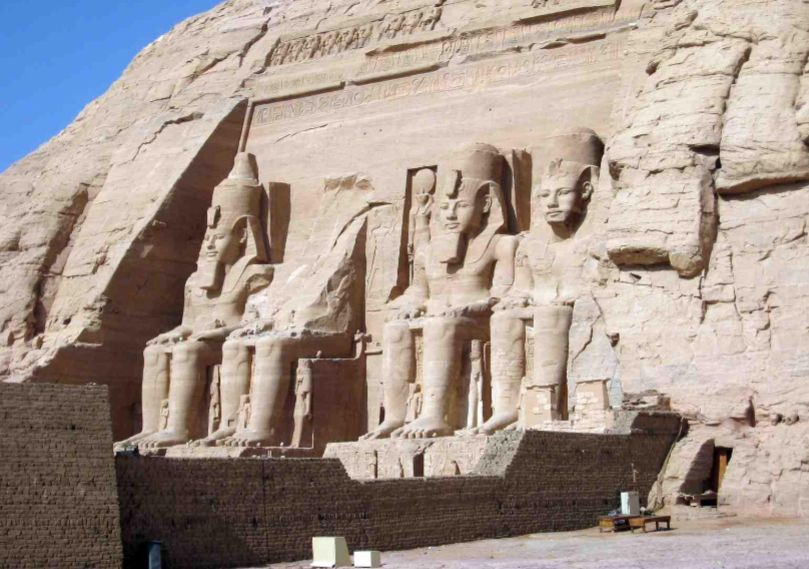

Temple of Ramesses II; -; Abu Simbel, Nubia, Egypt; New Kingdom Egypt; 1300 BCE; temple
4 identical, massive temples of Ramesses
hieroglyphic engraving on top glorifying Ramesses II
temple was moved in the 1960s as it was in a area of flooding during construction of Aswan High Dam
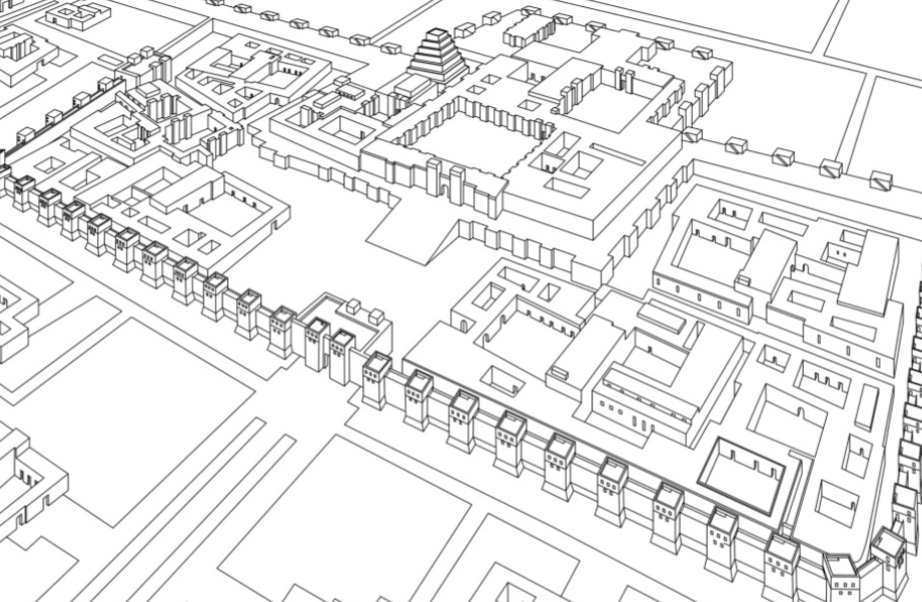
Citadel of Sargon II at Dur-Sharrukin; -; Khorsabad, Iraq; Assyrian (or Neo-Assyrian); 700 BCE; citadel
Thick walls surrounding the structure
Designed so one would need to go through the palace to get through the Ziggurat. Hence, one would symbolically go through the ruler to get to the gods. Architectural legitimacy of the ruler.
Ziggurat had 7 levels with strong, menacing walls.
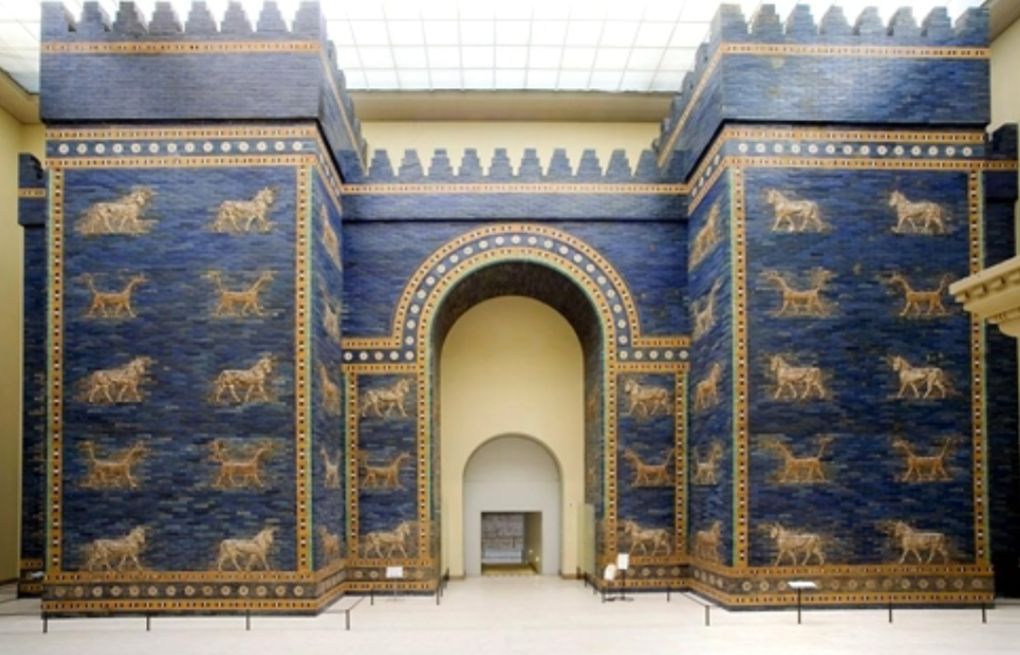

Ishtar Gate; -; Hillah, Iraq; Babylon; 600 BCE; Gate
Depictions of lions, dragons, and bulls representative of deities and intimidating.
Innovated use of glazed brick technology rather than standard mudbricks.
Functioned as the entrance to the processional way
Intense blue color may have been symbolic
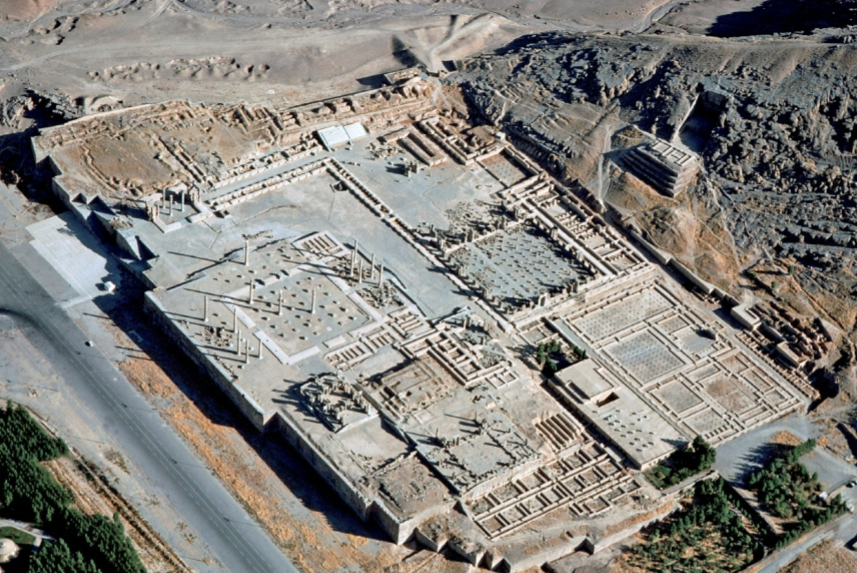

Persepolis; -; Iran; Persians; 500 BCE; city
Abundant roads throughout the city
Many columns feature protomes, adornments that take the form of head and upper torso as animal or human
Appears to have been a large ceremonial complex that was occupied seasonally
presence of apadanas: large hypostyle hall in Persian architecture
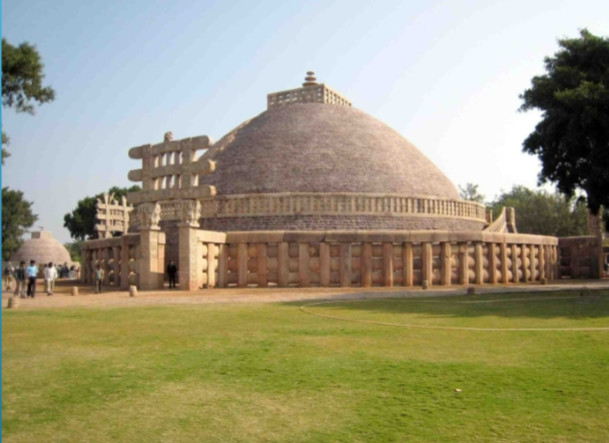

Great Stupa at Sanchi; Madhya Pradesh; India; Mauryans; 300 BCE; Stupa
The gateway is hinged slightly to the left, forcing your body in the correct angle for entry.
Circumambulatory path pathway towards the entrance- makes entering more intentional and like a pilgrimage site.
Four elaborate toranas (ornamental gateways) encircle the stupa.
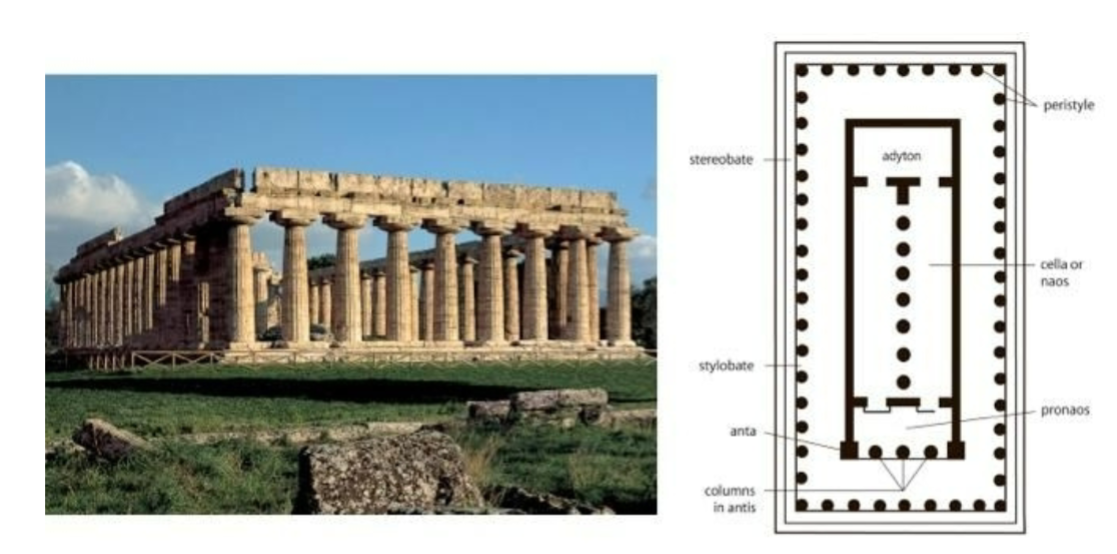
Temple of Hera I; -; Paestum, Italy; Greek colony of Paestum; 600 BCE; Greek temple
Early form of a Doric style temple
Contained 2 cult statues, and two doorways for the 2 different deities
Utilized entasis in which columns were thin and the tops and bottoms and thick in the middle. Helped with support but not as elegant.
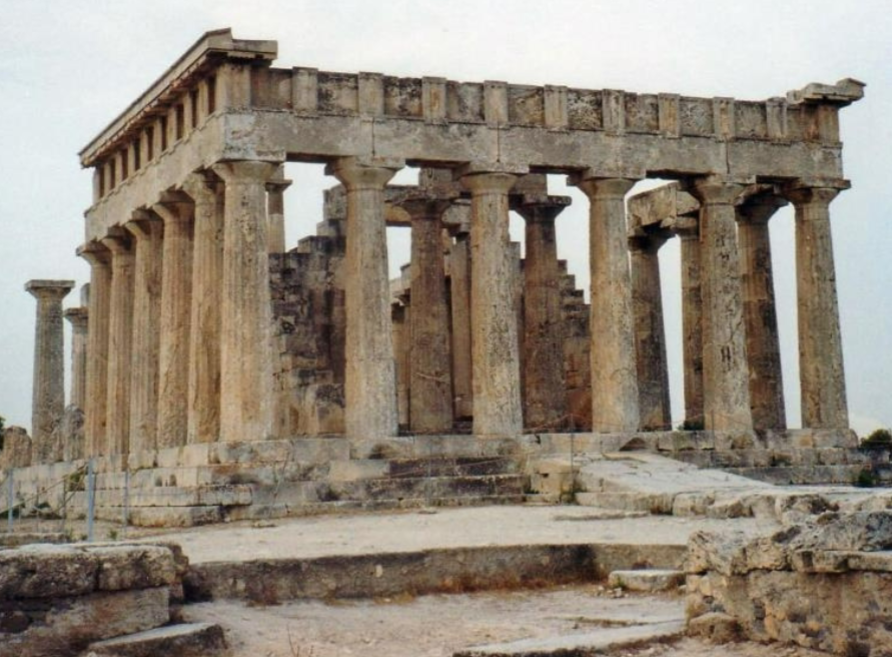

Temple of Aphaia; -; Aegina, Greece; Greek city states; 500 BCE; Greek temple
Doric-style temple
Pediments display Greek “dominance” over barbarians in the Trojan wars
Utilized entasis in which columns were thin and the tops and bottoms and thick in the middle. Helped with support but not as elegant.
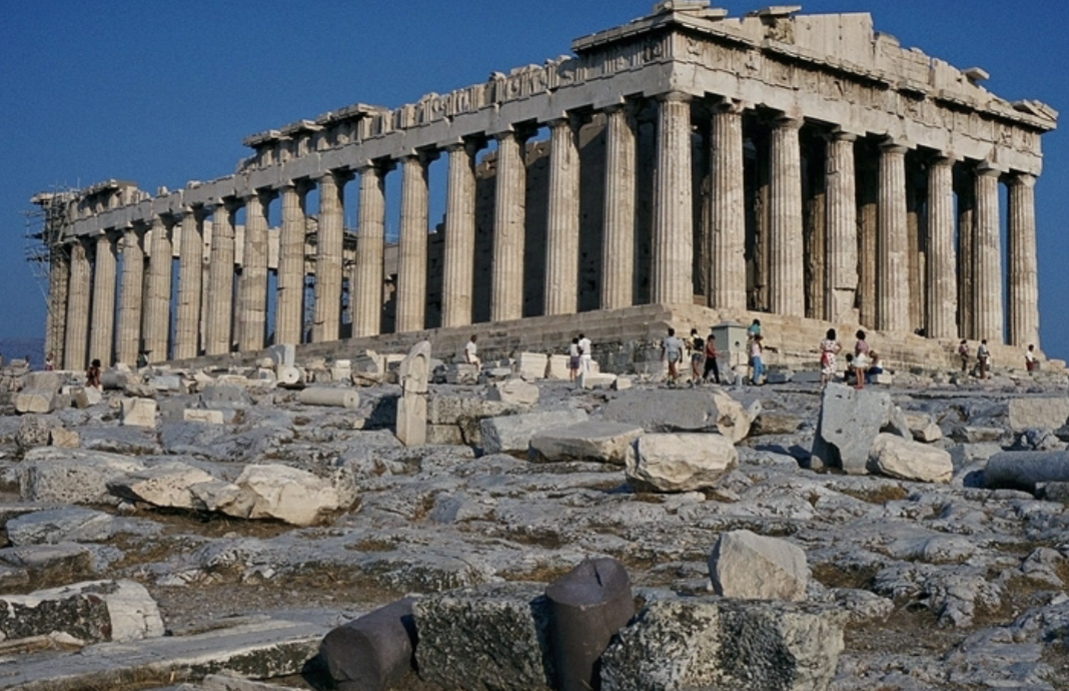

Parthenon; Iktinos and Callicrates (architects), Phidias (sculptor); Athens, Greece; Greek city states (Athens); 400 BCE; Greek Temple
Several visual corrections implemented (making it less perfect to make it look more perfect)
Doric order exterior, ionic order interior
Frieze shows precession. unprecedented in that it puts regular ppl on a sacred temple.
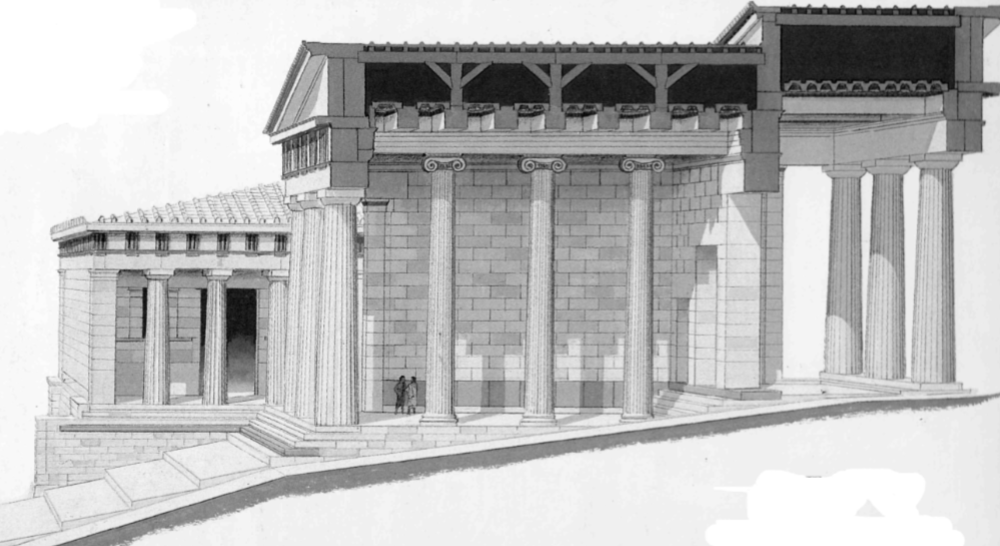

Propylaia; Mnesikles; Athens, Greece; Greek city states (Athens); 400 BCE; Gate
Doric order exterior, ionic order interior
the north wing contained what was essentially one of the earliest known art galleries
Monumental ceremonial gateway to the Acropolis of Athens
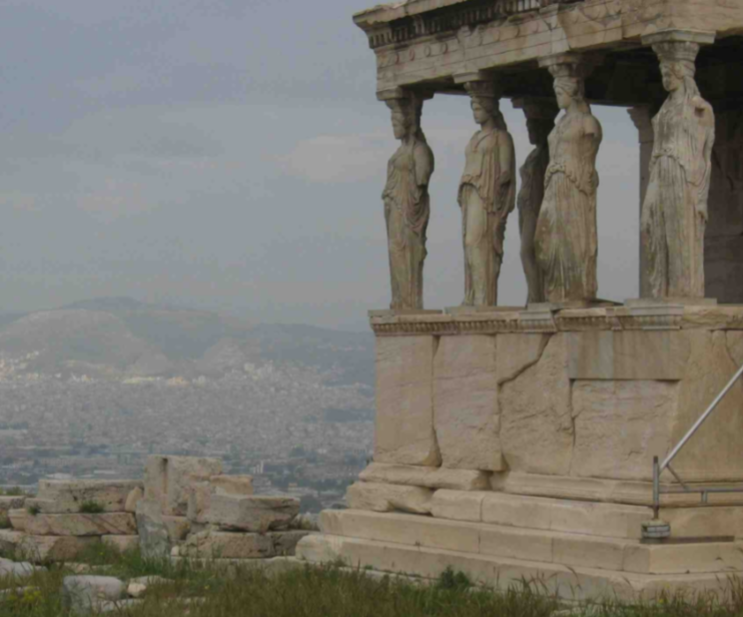

Erechtheion; Mnesikles; Athens, Greece; Greek city states (Athens); 400 BCE; Greek Temple
Less emphasis on “perfect” proportions but more on the natural landscape
Had a karyatid porch with sculpted female figures serving as the column- could be symbolic of how women are supporting society
Had an ionic porch with more fluting than seen previously
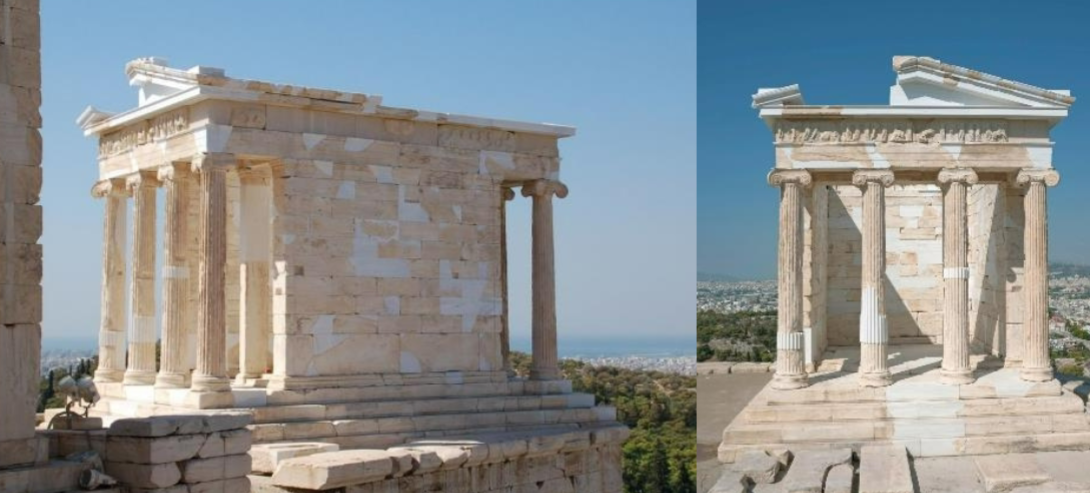

Temple of Athena Nike; Kallicrates; Athens, Greece; Greek city states (Athens); 400 BCE; Greek Temple
Early fully ionic temple on the Acropolis
The slender and fluted Ionic-style columns made the temple seem more slender that previous bulkier columns
Amphiprostyle design, portico with Ionic columns at front and back but not the sides.
Had a richly decorated, continuous frieze, characteristic of ionic style that depict mythology battles and possible historic events
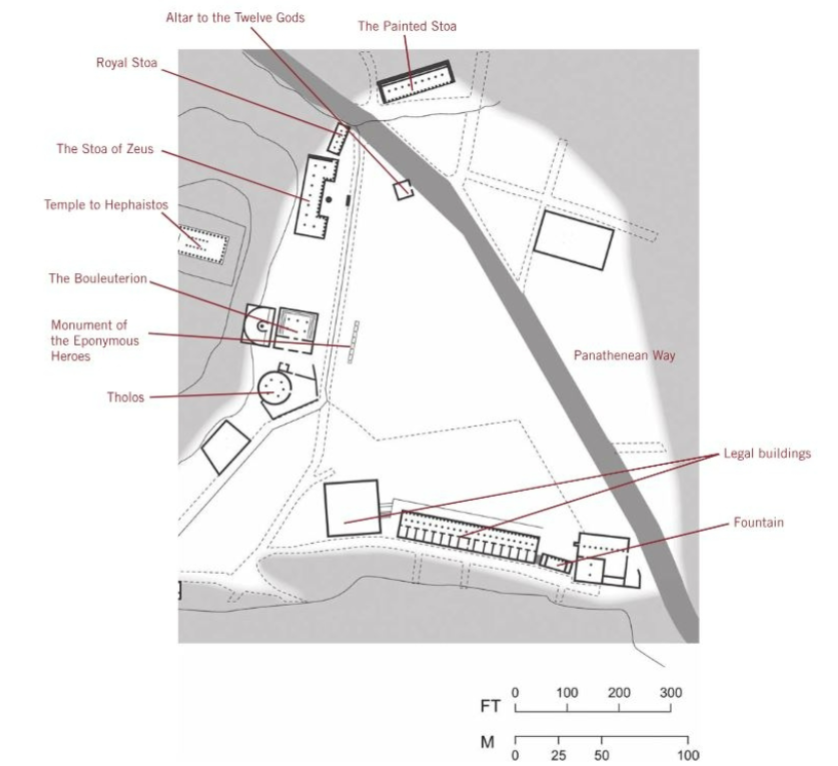
Athenian Agora; -; Athens, Greece; Greek city states (Athens); 600 BCE; Agora (covered walkway)
Contained the Stoa of Attalos II (below), gathering place and economic center.
Very open space. Allowed for it to serve as a central venue for citizens to congregate.
Near the Pynx Hill, where the Assembly met. Emphasizes integral function in politics.

Stoa of Attalos II; -; Athens, Greece; Greek city states (Athens); 600 BCE; Stoa
Wide walkway allowed numerous men to walk comfortably
Fluting only present near the top, evidence of heavy use (eliminates chance for fluting to be chipped)
Two-story colonnade design, advanced for its time
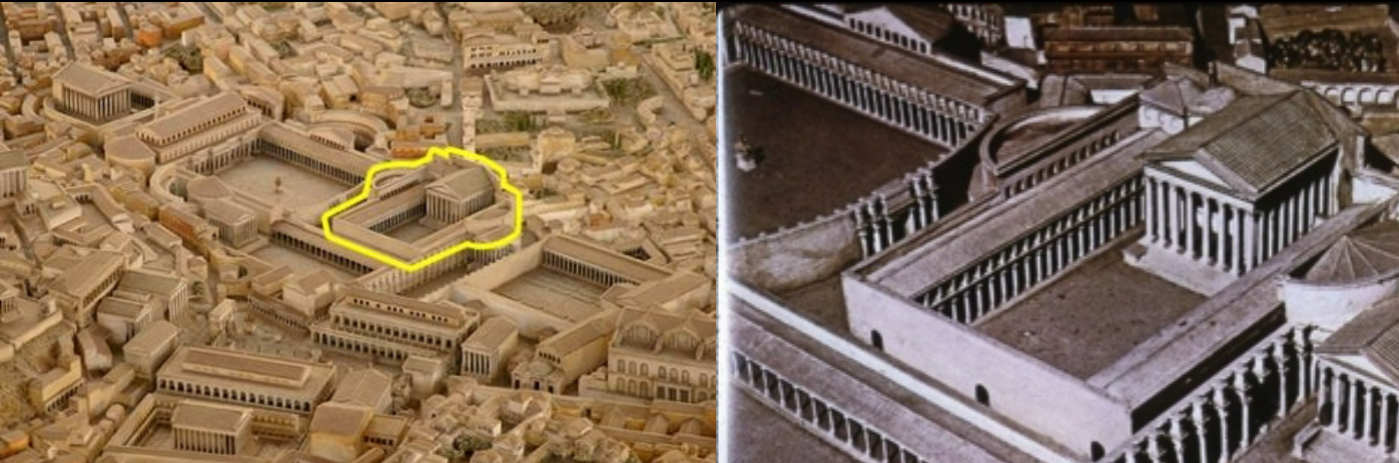

Forum of Augustus; -; Rome, Italy; Roman Empire; 100 BCE; Forum
On the sides of the forum were statues to Great men of Rome (e.g., Julius Caesar (Augustus uncle), Romulus). Essentially Augustus deified his family
Built with lots of finely selected imported materials (shows extent of Roman empire)
The Frieze contains words further glorifying Augustus
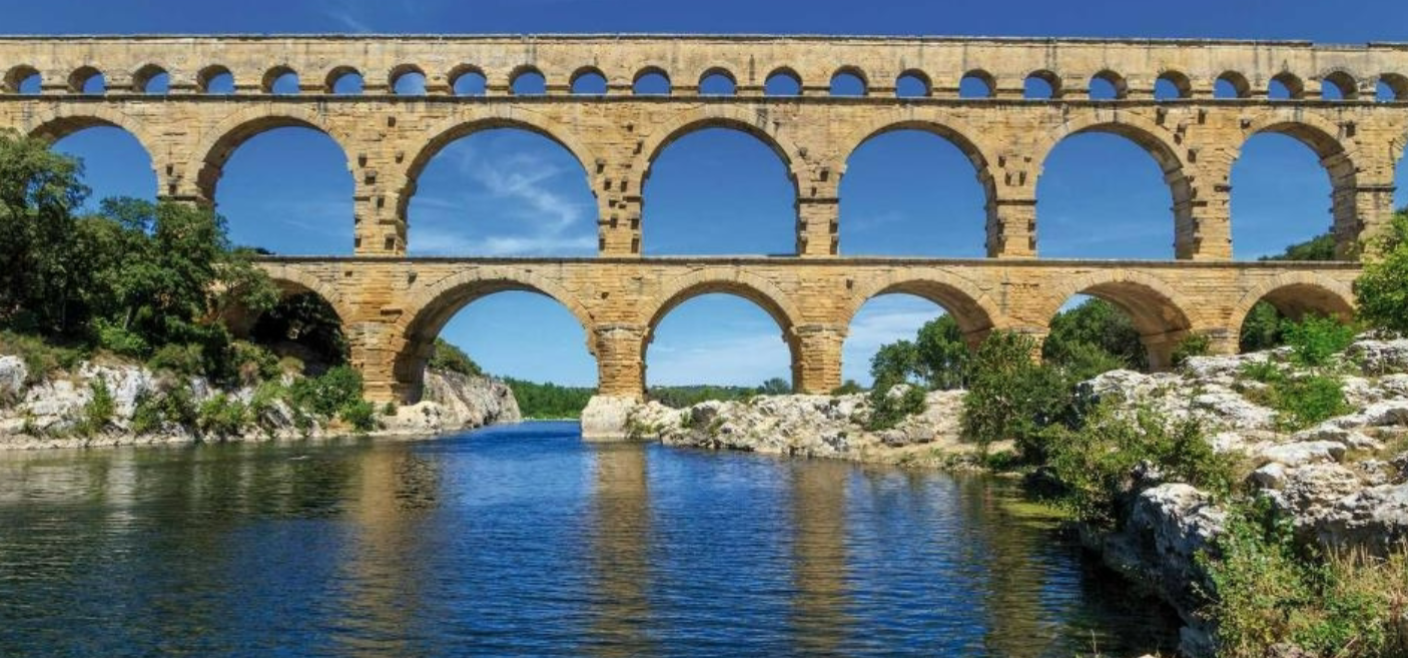

Pont du Gard; -; Nimes, France; Roman Empire; 100 CE; Aqueduct
Functioned as both of bridge (bottom component) and an aqueduct
Gravity was used for the water to flow down the aqueduct, angle for gravity was IMPORTANT
built without the use of mortar, which would require exceptional stone masonry

Nero’s Golden Palace; -; Rome, Italy; Roman Empire; 100CE; Palace
Built on the land burned by a large fire
artificial pool in the middle to act out Naval battles in the middle of his palace
used imported middle from all over the world, demonstrates expansiveness of Roman empire
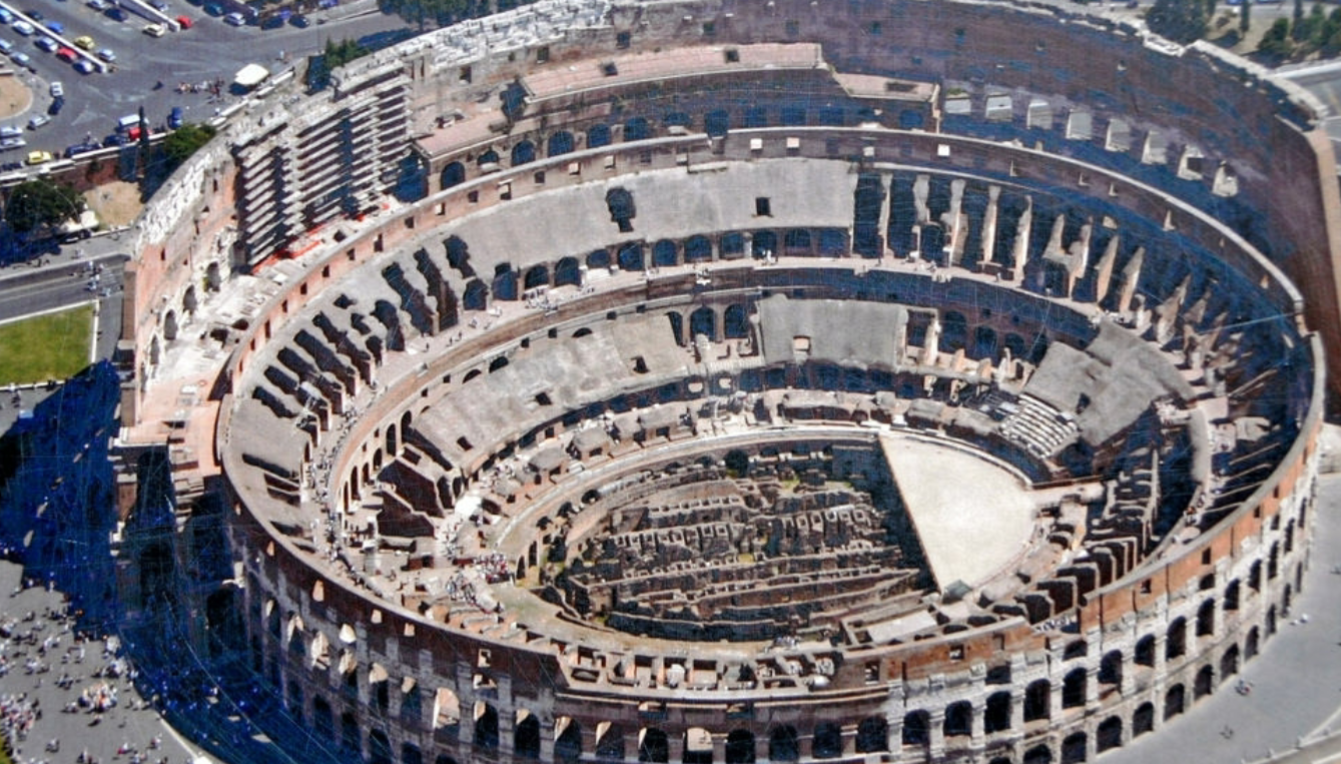

Colosseum; -; Rome, Italy; Roman Empire; 100 CE; amphitheater/stadium
Column type from bottom to top: tuskin → doric → ionic → cartyctean. most simple → most fancy. top = most expensive.
concrete barrel vaulted skeleton forms the structural element
columns are engaged and are purely decorative
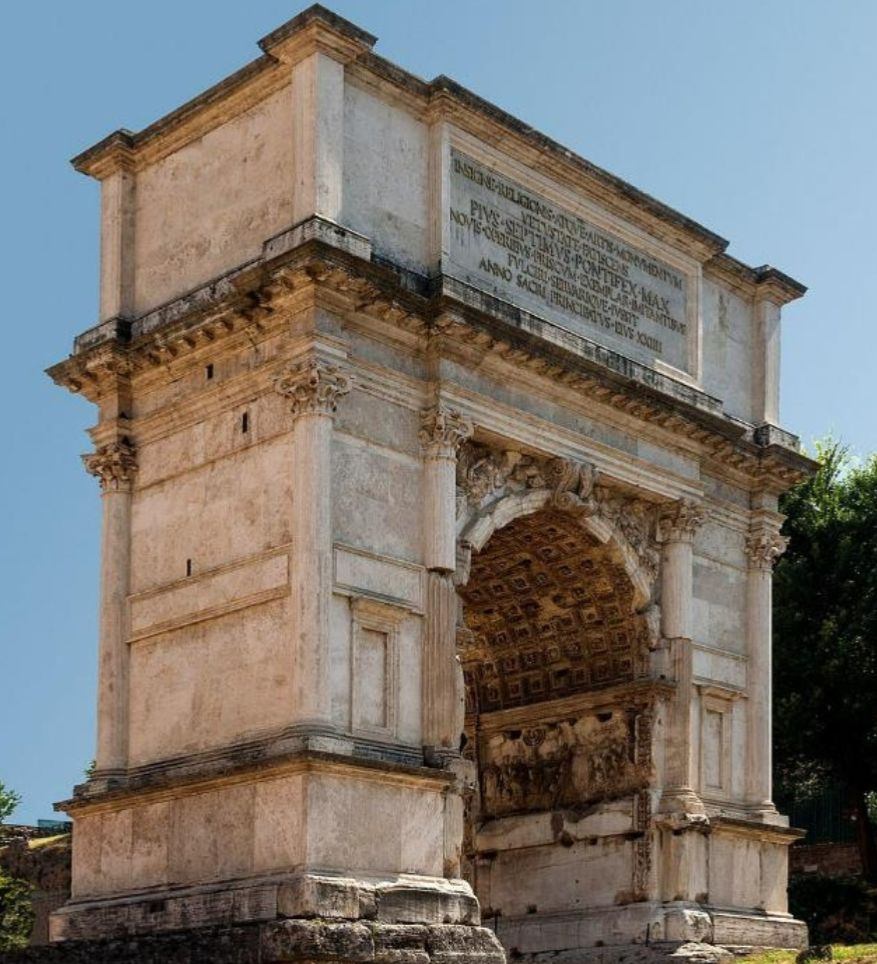

Arch of Titus; -; Rome, Italy; Roman Empire; 100 CE, triumphal arch
Utilized engaged decorative columns and archways
Relief panels depict the spoils of Jerusalem and the triumph of Titus
Major processions would go through the archway. Archway like a memorial of achievements