Multi-Store Model
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Who made the MSM?
Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968,71)
How does the MSM suggest memory is made up of?
Sensory register, STM, LTM
How does the MSM describe how memory is stored?
Information transfers from one store to another through processing
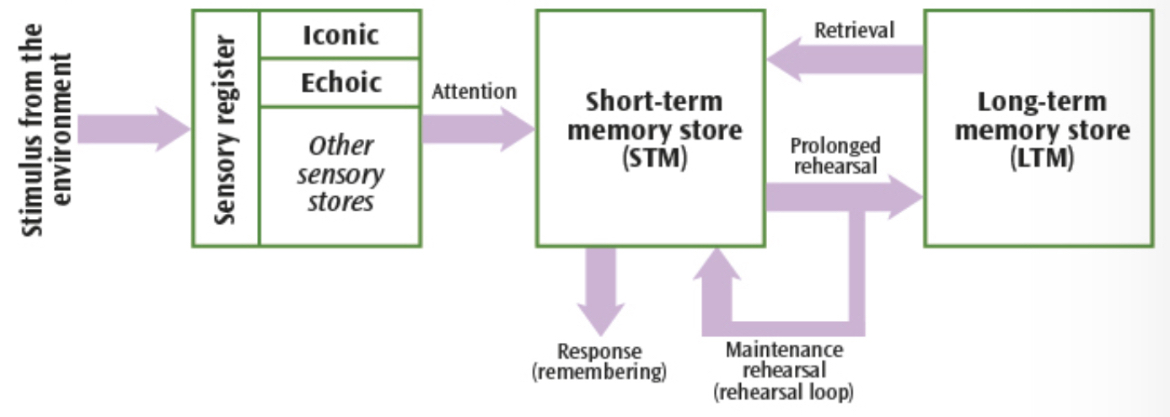
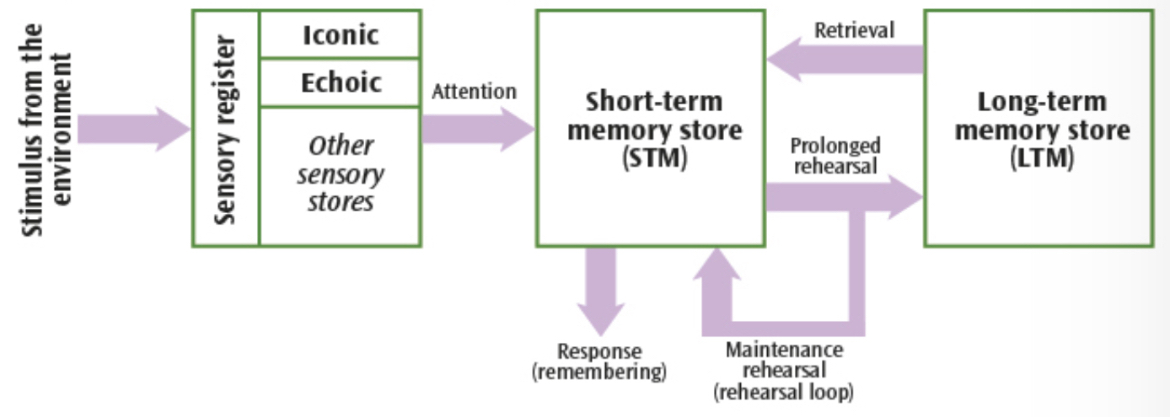
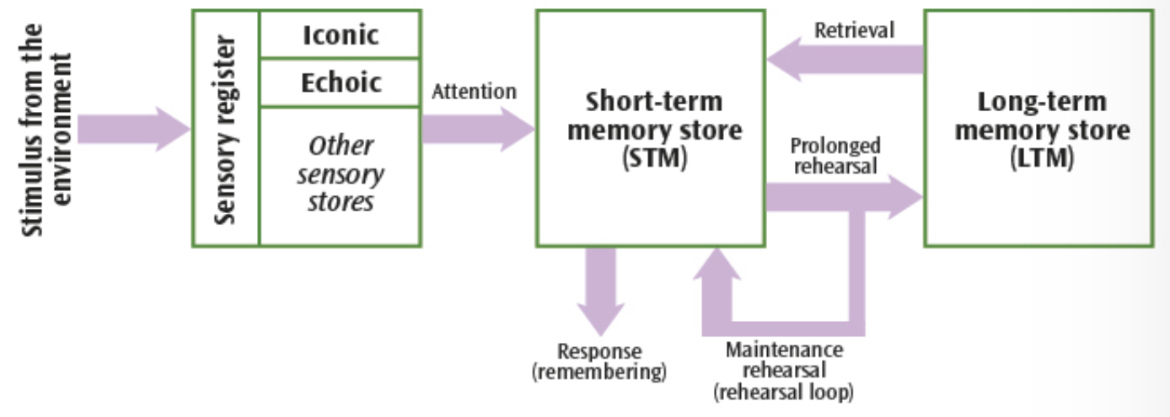
What is the sensory register?
Immediately processing stimuli from the environment - compromised of five different stores, one for each sense
What is the coding for the sensory register?
Modality-specific: depends on sense → eg echoic memory store is coded acoustically
What is the sensory register’s capacity?
Very high - eg over 100million cells in one eye each store data
What is the sensory register’s duration?
Less than ½ a second
How is information transferred to and from the sensory register?
To: Stimuli from the environment
From: Further into the memory system if you pay attention to the information
What is STM?
The information we have retained from paying attention
How is STM coded?
Acoustically
What is STM’s capacity?
5-9 items
What is STM’s duration?
18 seconds
How can you extend the duration of STM?
Rehearsal of information
How is information transferred to and from STM?
To: Paying attention to information
From: Prolonged rehearsal of information long enough passes it into LTM.
How does information stay in the STM?
Maintenance rehearsal
What is LTM?
Potentially permanent memory store for information that has been rehearsed for a prolonged period
How is LTM coded?
Semantically
What is LTM’s capacity?
Practically unlimited
What is the duration of LTM?
Potentially up to a lifetime
How is information transferred to and from the LTM?
To: Prolonged rehearsal
From: Retrieving the information transfers it back to STM
Strengths of MSM
Research support for LTM and STM being seperate x2
Research support on sensory register
Limitations of MSM
Meaningless stimuli
Case of KF disproves MSM
Lack of clarity over how LTM works
Oversimplified model
What research support is there for the MSM?
Baddeley (1966) found that we tend to mix up words that sound similar when using the STM, and words with similar meanings using LTM
Demonstrates them to be separate, independent, memory stores
What other research support is there for the MSM?
HM underwent brain surgery to relieve his epilepsy
His hippocampus was removed from both sides of his brain (procedure was in its infancy, not fully understood → now we know that this is central to memory function)
He thought it was 1953 when it was 1955, and 27 years old when he was 31
He couldn’t form new long-term memories, but still performed well on tests of immediate memory span (measure of STM)
Shows STM and LTM to be separate and independent memory stores
What supporting research is there for the duration of the sensory register?
Sperling (1960) showed participants a tachistoscope of digits and letters for 50 milliseconds
They were asked to write down as many items as they could remember, and afterwards they heard a tone that would correspond to a row and after the exposure they should write down the row indicated.
Their recall of the whole thing was poorer than when asked to give one row
Whole report: 42% (5/12 items)
Partial report: 75% (3/4 items)
Supports MSM as it shows the sensor register has a short duration → partial results were higher as they had less to write down
Why is meaningless stimuli a limitation?
Many studies that support MSM use artificial stimuli: Jacobs’ using digits, Baddeley using words, and Peterson & Peterson using consonant syllables
This shows MSM to not be a valid model of how everyday memory works with more meaningful information to remember
How does the case of KF show limitations to the MSM?
Shallice and Warrington (1970)’s client KF had amnesia
KF’s STM for digits was very poor when they were read to him, but his recall was good when he read them to himself.
Suggests MSM is wrong in claiming there is just one STM store processing different types of information
How does the MSM lack in explaining how LTM works?
Craik and Watkins (1973) found that the type of rehearsal is more important than the amount.
Elaborative rehearsal, linking information to existing knowledge, is needed for LTM
This means prolonged rehearsal isn’t required → suggests MSM does not fully explain how LTM storage is achieved
How is the MSM an oversimplified explanation of memory?
Atkinson and Shiffrin based the MSM on research evidence available at the time that showed STM and LTM to be separate and independent
However, there has been lots of research to show that STM and LTM are not separate, or that there are more memory stores.