Accounting Outcome 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 5 accounting elements
Assets (current, non-current), Liabilities(current, non-current), Owners Equity, Revenue, Expenses
2
New cards
Asset
A present economic resource controlled by the entity as a result of past events that has the potential to produce future economic benefits
3
New cards
Current asset
Cash and other assets that are expected to be converted to cash within a year
4
New cards
Non-current asset
A company's longterm investments where the full value will not be realised within the accounting year
5
New cards
Liabilities
A present obligation of the entity to transfer an economic resource as a result of past events.
6
New cards
Current liabilities
A company's debts or obligations that are due within one year or within a normal operating cycle.
7
New cards
Non-current liabilities
Long-term liabilities, which are financial obligations of a company that will come due in a year or longer.
8
New cards
Owner’s equity
The residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting all its liabilities
9
New cards
The accounting equation
The formula that represents the format of the balance sheet. (Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s equity)
10
New cards
Balance Sheet
A financial report that details a business’s financial position by reporting its assets, liabilities and owner’s equity at a particular point of time.
11
New cards
Example of Assets
Cash at bank • Inventory • Accounts receivable • Vehicles • Equipment • Furniture • Fixtures and fittings • Machinery • Building
12
New cards
Revenue
Revenues are increases in assets or decreases in liabilities that result in increases of owner’s equity, other than those relating to contributions of the owner.
13
New cards
Expenses
Decreases in assets or increases in liabilities that result in a decrease of owner’s equity, other than those relating to distributions to the owner.
14
New cards
Net Profit
The total amount remaining after you subtract total expenses from total revenue
15
New cards
How do you calculate Net Profit
Revenue - Expenses = Net Profit
16
New cards
Example of Revenue
Fees – Service business • Sales – Trading business (Cash and credit sales) •
17
New cards
Example of Expenses
Advertising • Electricity • Insurance • Interest • Office Expenses • Rent • Telephone • Wages
18
New cards
When discussing an ethical decision what are the factors we need to consider
Financial (Pros and Cons) then either Social or Environment (Pros and Cons)
19
New cards
The accounting process
Business Documents → Data Input →Business Reports →Business Decision Making
20
New cards
Financial Data
a raw collection of facts
21
New cards
Financial Information
data put into a meaningful form for a particular use
22
New cards
Data is often recorded on…..
Business documents
23
New cards
Business documents
Source of raw financial data - receipts, invoices, EFT documents etc
24
New cards
Data input
Data is sorted into groups and then noted in financial records
25
New cards
Business reports
Financial reports providing useful information in summarised form
26
New cards
Accounting assumptions
Generally accepted rules of how a business should record their accounting information
27
New cards
Accounting Entity Assumption
The requirement that a business must keep the set of financial records seperate to the owners or other business’
28
New cards
Going Concern Assumption
The belief that a business is expected to operate into the future and will continue forever
29
New cards
Accural Basis Assumption
Revenues are reported in the period they are earned and expenses in the period they are incurred in order to determine profit (accounts payable/recievable)
30
New cards
The Period Assumption
Accounting take place over specific periods and that these set segments of time have an equal duration so that meaningful comparisons of progress can be made across the different periods.
31
New cards
What does the entity assumption mean for the business
This assumption enables users of accounting reports to make decisions based soley of the performance of the business
32
New cards
What does the going concern assumption mean for the business
Allows business to recognise transaction that span over the course of one accounting period (like credit transactions) and enables businesses to distinguish between an asset and expense (expense is consumed within a reporting period whereas an asset has the ability to provide future economic benefit)
33
New cards
What does the accural basis assumption mean for the business
Allows for profit to be calculated based on the revenue earned and expenses incurred for a particular reporting period
34
New cards
What does the period assumption mean for the business
Reporting periods should be consistent over the life of a business so comparisons can be made between reports
35
New cards
Qualitative characteristics definition
Standards that must be met when preparing financial reports so the information they contain is useful for decision making
36
New cards
What are the qualitative characteristics
timeliness, understandability, faithful representation, verifiability, comparability, relevance
37
New cards
Timeliness
A qualitative characteristic that requires financial information to be available for decision makers in time to be capable of influencing their decisions. The older the information, the less useful
38
New cards
Understandability
A qualitative characteristic that requires financial information to be presented without any missing information, no misleading information. The report must be concise, clear in presentation with headings and subheadings. Making the report easy to navigate and cross reference. The report must be able to be understood with those who have a basic knowledge of finance
39
New cards
Faithful Representation
A qualitative characteristic that requires financial information contained in the reports to be complete, free from bias and without error
40
New cards
Verifiability
A qualitative characteristic that requires two or more independent observers to reach the same conclusion of the accounting report, that they are faithfully represented and the actual events of the business
41
New cards
Verifiability (details)
Upheld through referencing and maintaining source documents as evidence for transactions (checked through auditing) If the reports are not verifiable then the information has not been faithfully represented
42
New cards
Comparability
Information in the accounting reports can be useful when it is compared to previous reports and with similar information from other entity’s reports
43
New cards
What does comparability allow for
Identify and understand similarities and differences among reports. Display changes in accounting procedures over time
44
New cards
Auditing
an official financial inspection of a company and its accounts
45
New cards
Relevance
Information available is capable of influencing decisions, helps confirm information and form predictions for future outcomes
46
New cards
Cash receipt
A document containing financial information, that provides evidence that a financial transaction has occurred (a receipt verifies a business has received cash)
47
New cards
Electronic funds transfer (ETF)
A document containing financial information, that has been issued when an EFTPOS sale. This confirms that funds will be taken from the account and deposited into the business account on behalf of the customer (quicker and can be processed online at any time)
48
New cards
Cheque butt
A source document used to verify the details of a cash payment made by cheque
49
New cards
Bank statement
A source document issued by the bank as a record of all transactions affecting the bank account over a period of time
50
New cards
Sales invoice
A source document containing financial information of goods and services sales on credit. This means the business has provided a good or service but is awaiting payment. An accounts receivable is created
51
New cards
Tax invoice
Verifies the details of a credit transaction
52
New cards
Statement of account
A source document issued by a business to its credit customers summarising the purchases and payments between the customer and the business over a period of time
53
New cards
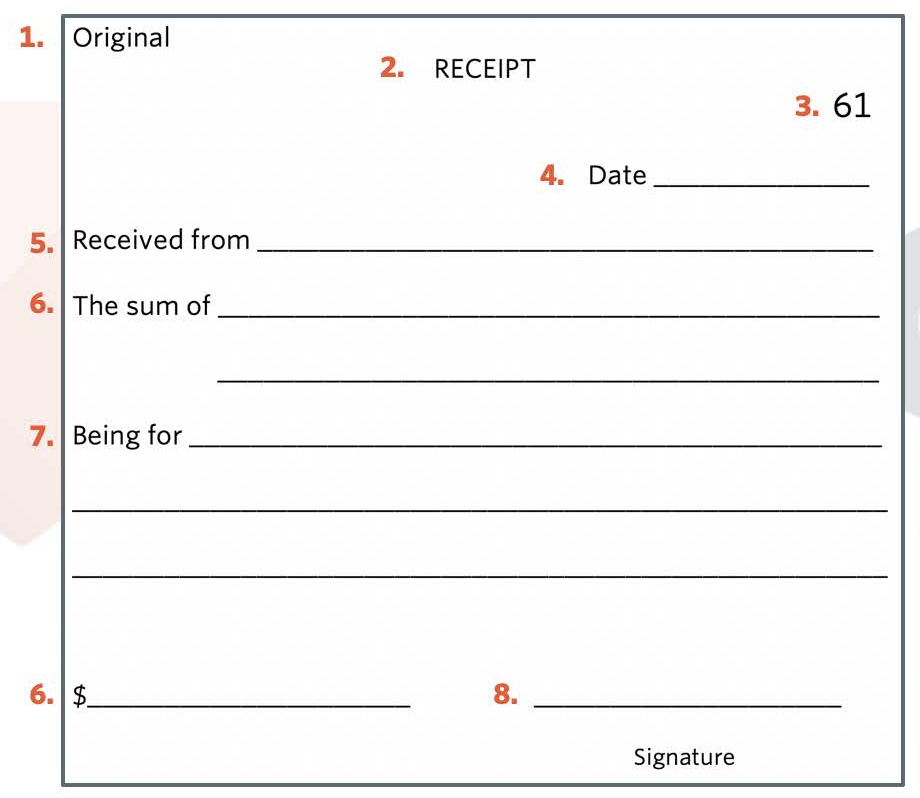
What source document is this
Cash Receipt
54
New cards

What source document is this
EFT receipt
55
New cards
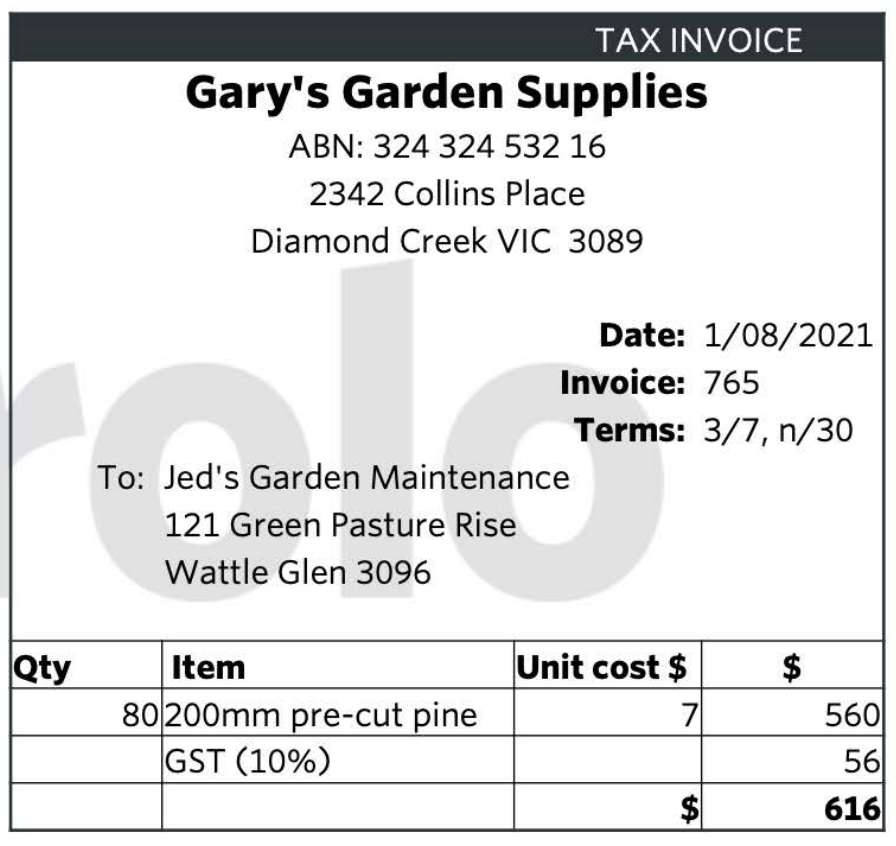
What source document is this
Sales invoice
56
New cards
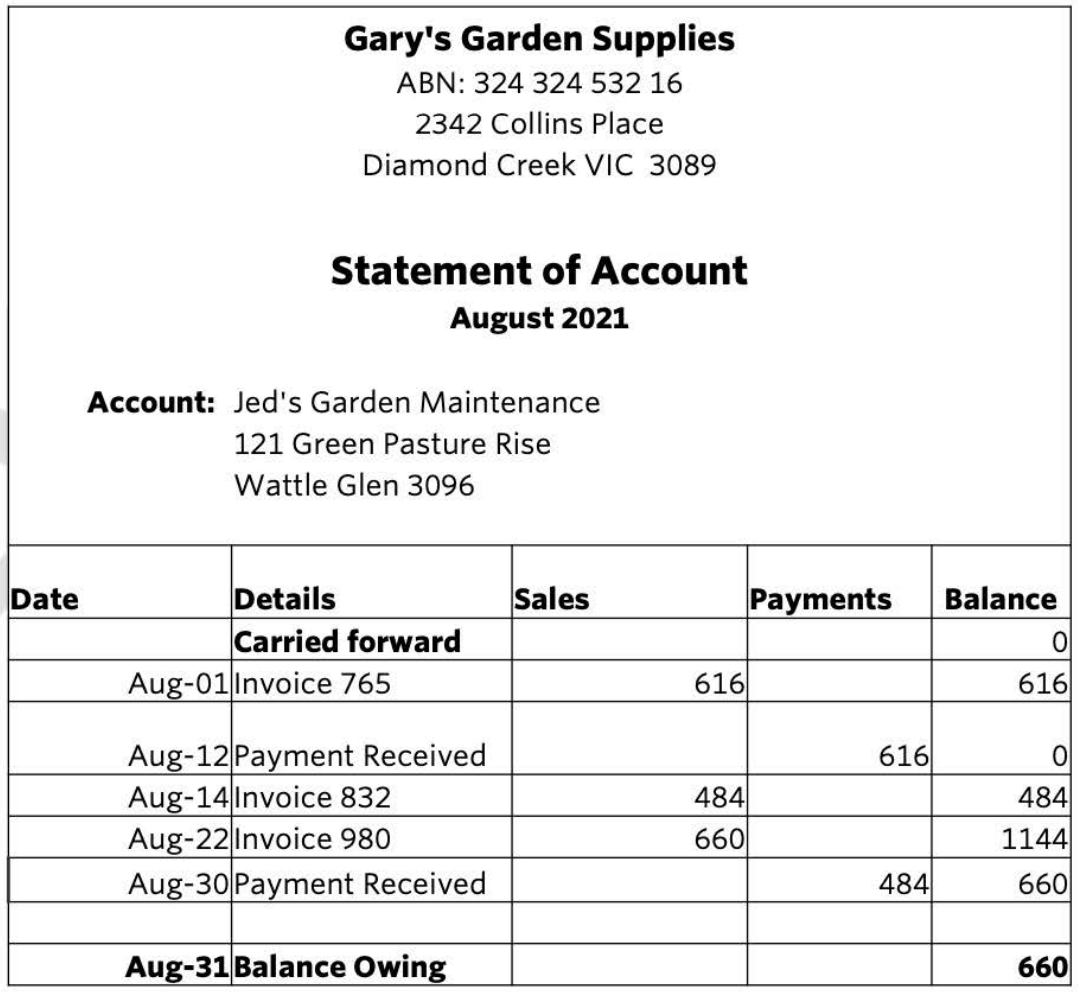
What source document is this
Statement of account
57
New cards

What source document is this
Cheque/Cheque butt
58
New cards
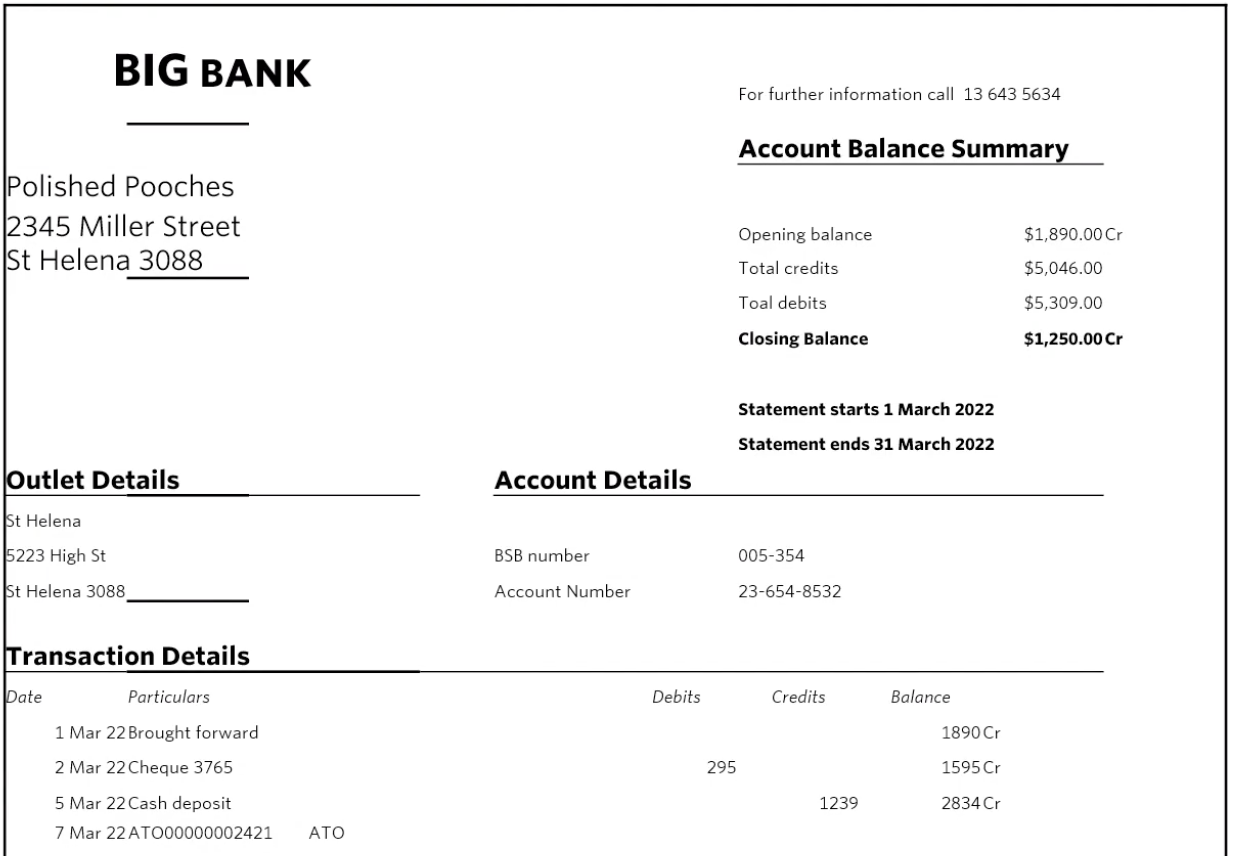
What source document is this
Bank statement
59
New cards

What source document is this
Memo
60
New cards
Source document
Evidence a financial transaction has occurred,
61
New cards
To calculate capital
capital = assets - liabilities
62
New cards
T-form balance sheet
an accounting report showing assets on one side and liabilities and owners equity on the other
63
New cards
Narrative form balance sheet
an accounting report prepared in a vertical fashion down the page, highlighting the owners equity in the business
64
New cards
Layout of narrative form
Owners equity (capital) → is represented by: → Assets (current/non-current) → Less: Liabilities (current/non-current) → Net assets
65
New cards
A classified balance sheet allows for what qualitative characteristic
Understandability
66
New cards
How to calculate Owners Equity
OE = A - L
67
New cards
How to calculate Working Capital
Working Capital = Current Assets - Current Liabilities
68
New cards
How to calculate Working Capital Ratio
Working Capital ratio = Current assets/Current liabilities
69
New cards
Liquidity
the ability of a business to meet its short-term obligations as they fall due
70
New cards
Single entry accounting
a simple accounting system in which one entry is made for each transaction
71
New cards
Cash journal
a multi-column record used to record the daily receipts or payments of cash over a period
72
New cards
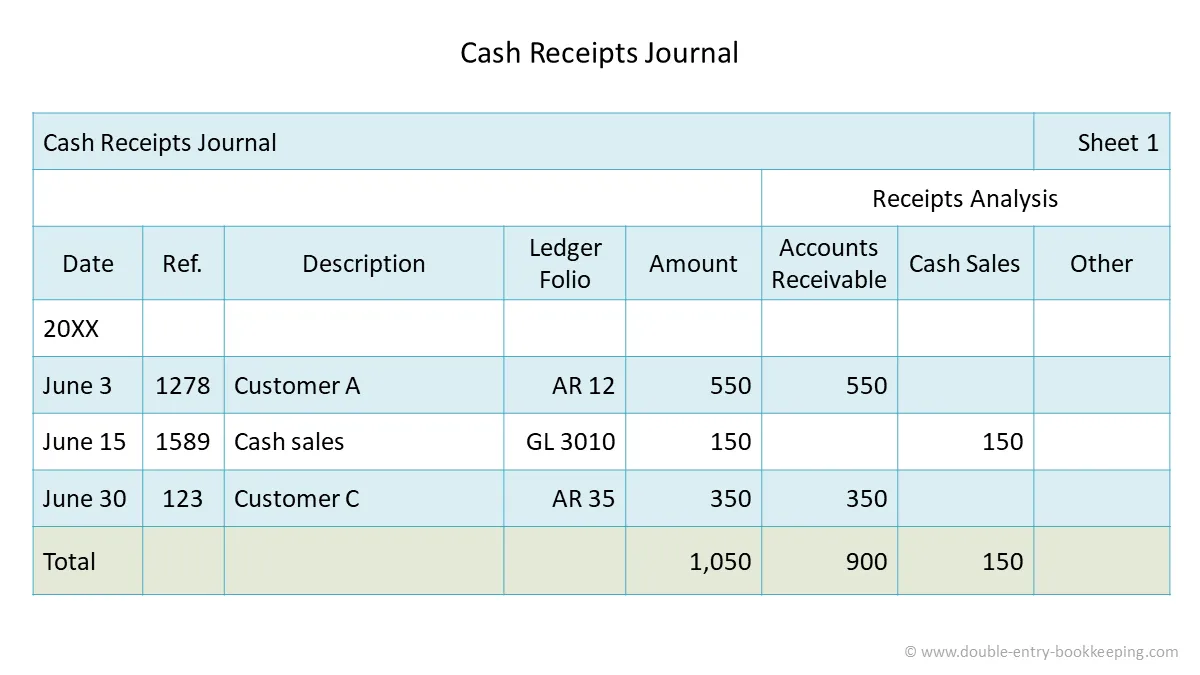
What is this
Cash Journal
73
New cards
EFTPOS terminal
a machine rented by a business owner from a bank to make EFTPOS transactions
74
New cards
Purchase Order
a document used to confirm a request to a supplier to provide goods or services. (pro: firm has a record of goods ordered, which can be cross-checked with goods delivered). Includes description of goods, quantity, size, colour, range etc plus desired delivery date
75
New cards
Delivery Dockets
a document that may come with goods when they are delivered, that the purchaser is required to sign to acknowledge delivery has occurred. Includes, a description of goods and quantity supplied. Not recorded in the accounting system
76
New cards
Statement of Accounts
a document that informs a business’s customers of all transactions over the previous month.
77
New cards
What is this business document
Delivery Docket
78
New cards
What is the document flow diagram
Order form ( from business to supplier) → Delivery Docket (to business) → Invoice (to business) → Cheque/EFT payment (to supplier) → Statement of account (to business)
79
New cards
What factors do you consider in terms of making ethical decisions to a business
Cost of a decision to a business, Potential benefits to the business, effect on the reputation of the business, potential environmental damage of business decisions, Financial and emotional effect on individuals (including owners, managers and consumers)