angiosperms
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what were angiosperms 3 key innovations
more efficient xylem
flowers
fruits
describe angiosperms evolution of xylem
cells with modified ends
complete perforations without primary or secondary wall
makes conducting way easier
which innovation of angiosperm lead to its adaptive radiation
flowers!
special mechanisms for pollination
directly associated with their rapid speciation
single mutations can lead to large changes in flower morphology
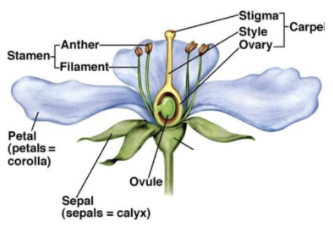
what are the different male/female reproductive organs
female (carpel): stigma, style, ovary (tissue around ovule), ovule
male (stamen): anther, filament
later plants enclose carpels and stamen in sepals and petals
what is outcross pollination
pollen and stigma on different plants
how do plants spread their pollen effectively
80% of angiosperms use animal pollinators
have evolved to coop unrelated species to carry their gametes
need animals to visit the plant, contact the anther, then the stigma of a compatible plant
what is the main purpose of flowers
attract good pollinators
deter non-pollinating visitors
manipulate visitor behaviour to maximize pollen transfer
traits that affect pollination:
shape
colour
scent
markings (uv markings animals can see)
position
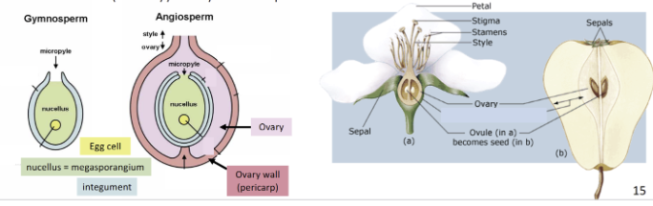
what are fruits
after fertilization, ovary tissue ripens and becomes the fruit
that tissue has diversified into different forms and functions
functions: protect developed seed, seed dispersal
how do fruits disperse seeds?
not all fruits are meant to be eaten
dandelions - wind
burs - fur
some animals eat fruit, seeds pass through gut and gets pooped out somewhere else
testament to modularity of plants
humans and flowers
eat them: grains, spices, vegetables
radiation of angiosperms responsible for culture and cuisine
global trade and auctions
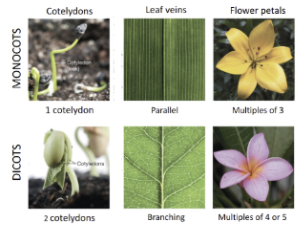
what are the two big groups that angiosperms are divided into
monocotyledons (monocots)
dicotyledons (dicots)
what are the differences between monocots and dicots
monocots:
1 cotyledon
parallel veins in leaf
flower petals in multiples of 3
dicots:
2 cotyledons
branching veins in leaves
flower petals in multiples of 4 or 5