S1.9 Endocrine System
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What does the Endocrine System do?
Messenger system comprising of feedback loops of Hormones that are released by Internal Glands and Target distant Organs. The Hypothalamus is the Neural Control center of ALL Endocrine System.
Endocrine System in Brain - Overview
Hypothalamus
Product the following, but stored in the Pituitary gland
Oxytocin (Store, not produce)
Causes increased contraction of the uterus during labor
Stimulate the release of milk into the ducts of the breasts.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) (Store, not produce)
Contricts blood vessels and controls salt in the body
Pineal Gland
Melatonin
Melatonin
Involved in the sleep-wake cycle
Pituitary Gland
Anterior
Growth Hormone
Promotes the growth of children
Prolactin (PRL)
Stimulate milk production in the mammary glands
Thyroid-Stimulating (TSH)
Activate the release of Thyroid Hormones
Follicle - StimulatingFollicle-Stimulating
Formation of Ova or Sperm
Luteinizing Hormone
Stimulate ovulation in Females and Androgen in Men
Adrenocorticorropiuc (ACTH)
Triggers the release of cortisol from the Adrenal Glands
Posterior (Does not produce its own hormone. It Holds Hormones made by the hypothalamus)
Oxytocin (Store, not produce)
Causes increased contraction of the uterus during labor
Stimulate the release of milk into the ducts of the breasts.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) (Store, not produce)
Contricts blood vessels and controls salt in the body
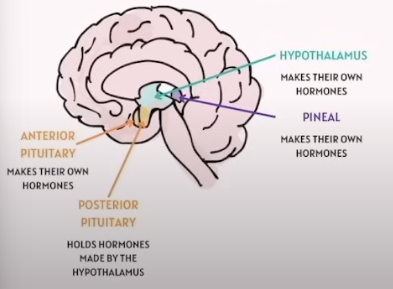
Endocrine System in the Brain - Quiz
Which gland produces oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH), though they are stored in the pituitary gland?
Which hormone causes increased contraction of the uterus during labor?
Which hormone stimulates the release of milk into the ducts of the breasts?
Which hormone constricts blood vessels and helps control salt and water balance in the body?
Which gland secretes melatonin?
Which hormone is involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle?
Which part of the pituitary gland produces its own hormones?
Which hormone promotes growth in children?
Which hormone stimulates milk production in the mammary glands?
Which hormone activates the release of thyroid hormones?
Which hormone stimulates the formation of ova in females and sperm in males?
Which hormone triggers ovulation in females and androgen production in males?
Which hormone triggers the release of cortisol from the adrenal glands?
Which part of the pituitary gland does not produce hormones but stores and releases those made by the hypothalamus?
Which two hormones are stored in the posterior pituitary gland?
Hypothalamus
Oxytocin
Oxytocin
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Pineal Gland
Melatonin
Anterior Pituitary
Growth Hormone (GH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Posterior Pituitary
Oxytocin and Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)

Endocrine System in Neck/Chest - Overview
Gland | Hormone | Function | Memory Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
Thyroid | Thyroxine (T4) | Increases the rate of chemical reactions in cells; helps control growth & development | 😊 |
Thyroid | Triiodothyronine (T3) | Stimulates the nervous system (wakefulness, alertness, responsiveness) | "T" for Thyroid = Both hormones turn up the metabolic rate |
Thyroid | Calcitonin | Lowers blood calcium | "Calci-tone it down" = Lowers down calcium in the blood |
Parathyroid | Parathyroid Hormone | Raises blood calcium | Parathyroid = Pushes it up (increases calcium in blood) |
Thymus | Thymosin | Helps make T cells | Thymosin = Thymus must stimulate immunity |
Endocrine System in Neck/Chest - Quiz
🟩 Questions
Which thyroid hormone increases the rate of chemical reactions in cells and helps control growth and development?
Which thyroid hormone stimulates the nervous system in wakefulness, alertness, and responsiveness to external stimuli?
Which two thyroid hormones help increase metabolic rate?
Which thyroid hormone lowers blood calcium levels?
What is the function of the parathyroid hormone?
Which hormone increases calcium levels in the blood?
Which gland produces a hormone that helps make T cells?
What is the function of thymosin?
Thyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
Calcitonin
Raises blood calcium
Parathyroid Hormone
Thymus
Helps make T cells
Endocrine System in Abdomen/Plevin -Overview
Adrenal Gland
Pancreas
Gonads
Ovaries
Testes
Abdomen/Pelvin:
Region | Gland / Part | Hormone | Function | Memory Tip / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Adrenal Medulla | Epinephrine | Works on the heart; part of the fight-or-flight response | “Epi = No rush = Rush of both hormones during fight or flight” | |
Norepinephrine | Works on blood vessels; prepares body for fight-or-flight | Same as above | ||
Adrenal Cortex | Glucocorticoids | Steroid hormones are involved in glucose, protein, and fat metabolism | Example: Cortisol — “Cortisol Controls Stress” | |
Mineralocorticoids | Steroid hormones that help regulate salt and water balance | Example: Aldosterone — “Aldo Stores Na” |
Gonads - Ovaries/Testes
Gland | Hormone | Function | Memory Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
Pancreas | Insulin | Controls blood sugar and metabolism; turns food into energy | Insulin puts sugar IN |
Glucagon | Helps regulate blood glucose; raises glucose when it's low | GLUcagon raises GLUcose | |
Gonads | Estrogen | Develops female sex characteristics | — |
Progesterone | Creates healthy uterine lining for menstruation and pregnancy | — | |
Androgen | Develops male sexual reproduction and characteristics | — |
Endocrine
En = Enter
Releases hormones into their surroundings
No special ducts
Exocrine
Ex = Exit
A gland that makes substances and releases them thru a duct or opening to the body.
Ducts required
Endocrine System in Abdomen/Plevin -Overview
Endocrine System in Abdomen/Plevin - Quiz
✅ Questions
Which hormone controls blood sugar levels and helps turn food into energy?
Which hormone helps regulate blood glucose by increasing it when it drops too low?
What is the function of insulin in relation to blood sugar?
What is the function of glucagon in relation to blood sugar?
Which hormone develops female sex characteristics?
Which hormone creates healthy uterine lining for the menstrual cycle and pregnancy?
Which hormone develops male sexual reproduction and characteristics?
Which gland produces insulin and glucagon?
Which gland produces estrogen, progesterone, and androgen?
🟨 Answers
Insulin
Glucagon
Puts sugar into the cells (lowers blood sugar)
Raises glucose levels in the blood
Estrogen
Progesterone
Androgen
Pancreas
Gonads
Endocrine Function Cells
Term | What It Is | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
Gastrin | A hormone made by G-cells in the stomach | Stimulates the stomach to produce HCl (hydrochloric acid) and enzymes |
HCl Acid | A strong acid secreted by parietal cells | Helps digest food, kill bacteria, and activate digestive enzymes |
🧬 Relation to the Endocrine System:
Gastrin is a hormone, so it’s part of the endocrine system.
It travels through the bloodstream (like other endocrine hormones) to signal target cells (parietal cells).
Endocrine glands don’t use ducts — just like gastrin is released directly into the blood to act.
🧬 Endocrine vs. Exocrine System – Comparison Table
What they release?
Where they release?
Example of each?
Function of each?
What they target?
🔹 Feature | Endocrine System | Exocrine System |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Glands that release hormones into the blood | Glands that release substances through ducts |
Secretion Type | Hormones | Enzymes, sweat, saliva, oil, milk, etc. |
Secretion Path | Directly into the bloodstream | Through ducts to body surfaces (skin, mouth, etc.) |
Examples of Glands | Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas (endocrine part) | Sweat glands, salivary glands, pancreas (exocrine part) |
Target Area | Internal organs and tissues | External or specific local areas |
Function | Regulates body functions (growth, metabolism) | Aids in digestion, cooling, lubrication, etc. |
Hormones
A regulatory substance in an organisms and transported in tissue fluids to stimulate specific cells or tissue into action.
Hormones can come from varies biomolecules
Hormone Biomolecules:
Derived from Amino Acid (Polypeptides)
Derived from Lipids (Steroids)
Function:
Hormones bind to specific target cells and will cause some kind of action to occur.
The function of hormones really depends on the the receptor and target cell.