AP Human Geo Unit 6
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Site Factors
Climate, landforms, availability of water etc. Ex. Cincinnati is on the north bank of the Ohio River and has a temperate climate and fertile soil
Situation Factors
Connections between sites. The relative location often dictates the function of the city. Ex. Cincinnati emerged as a river port after 1811 and was large in the steamboat industry.
Population Growth + Migration (Factor of Urbanization)
Rural to Urban migration
Favelas, squatter settlements a slums- households that can't provide on of the basic living characteristics. (Develop due to rapid population growth in developing countries)
Economic Development (Factors of Urbanization)
A city's economic function will have an impact on urbanization. Ex. Cancun due to tourism
Government Policies (Factors of Urbanization)
Governments seek to attract businesses and boost the economy through subsidies, incentives, zoning and special amenities
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people
Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
Urban Sprawl and Decentralization
Commercial developments expand outward from the city core due to greater access to the automobile. (Expansion is usually unplanned)
Suburbanization
The process of population movement from within towns and cities to the rural-urban fringe. (Less densely populated and developed due to transportation advancements)
edge cities
Community located on the outskirts of a larger city with amenities typically found in an urban center (not usually residential). Ex. Monticello, Forest Lake
Boomburbs
Suburb that has grown rapidly into a large and sprawling city with more than 100,000 residents
Exurbs
Community on the outside edge of traditional suburbs (function like a suburb but more rural and less connected to the central city)
Challenges of Decentralization (Examples)
Placelessness
Dependence on automobiles (leads to congestion and pollution)
Economically exclusive (poorer people tend to stay in the cores of cities)
World Cities
cities generally considered to play an important role in the global economic, cultural and/or political system ex. London or New York
urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements according to their size and economic functions. Explains the relative sizes and spatial organizations of cities
Rank-Size rule
Model that illustrates the relationship between population distribution in cities that are interconnected in the urban hierarchy. (Indicates even development) Population of 2nd largest city is 1/2 the population of the largest and so on
Primate City
Model that illustrate disproportionate population distribution. (One city is extremely large in terms of population size AND economic, political or cultural influence)
Gravity Model
Model that illustrates the spatial relationship/amount of interaction between locations of different sizes (larger cities interact more with other large cities. Small cities are drawn to the influence of larger cities)
Christaller's Central Place Theory
Model that illustrates the hierarchical spatial patterns/order of cities and settlements (The "central place" is the large city that provides the most goods and services for the surrounding areas. Model is in hexagons to assure that no surface is left out or overlapped)
Threshold
The number of people needed to support a good or business
Range
The distance that someone is willing to travel for a good or service
High Order Goods and Services
Expensive, desirable or unique- large threshold and range. Typically found in major cities. Ex. Sports arenas, specialty doctors, concerts and universities
Low Order Goods and Services
Inexpensive, common, everyday needs. Smaller threshold and range. Typically found in towns and villages. Ex. Grocery stores, salons, barber shop and gas stations
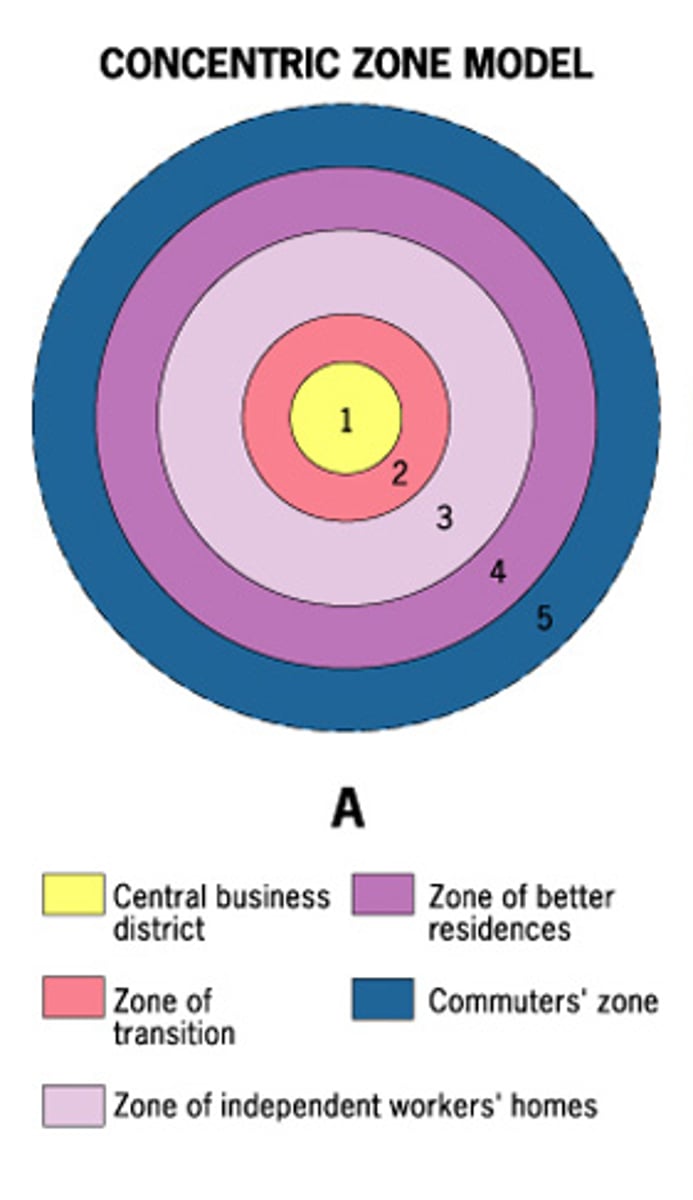
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
Rings used to classify each type of land use pattern. CBD in center followed by a zone for factories and industry, then low income housing with high population density. Finally, high income housing on the outskirts
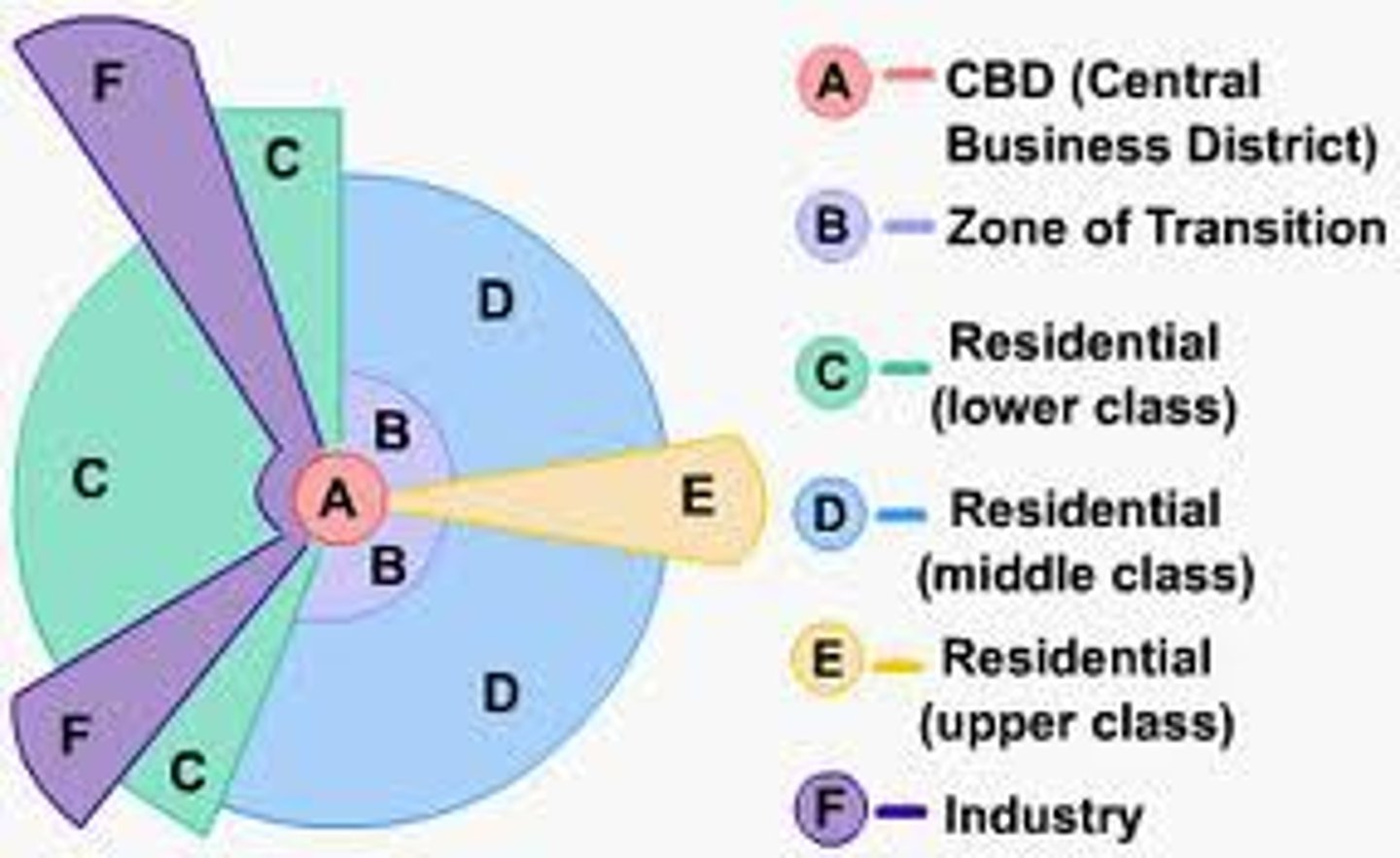
Hoyt Sector Model
Use of sectors/wedges to classify each type of land use pattern. Sectors develop along transportation routes. CBD still centrally located.
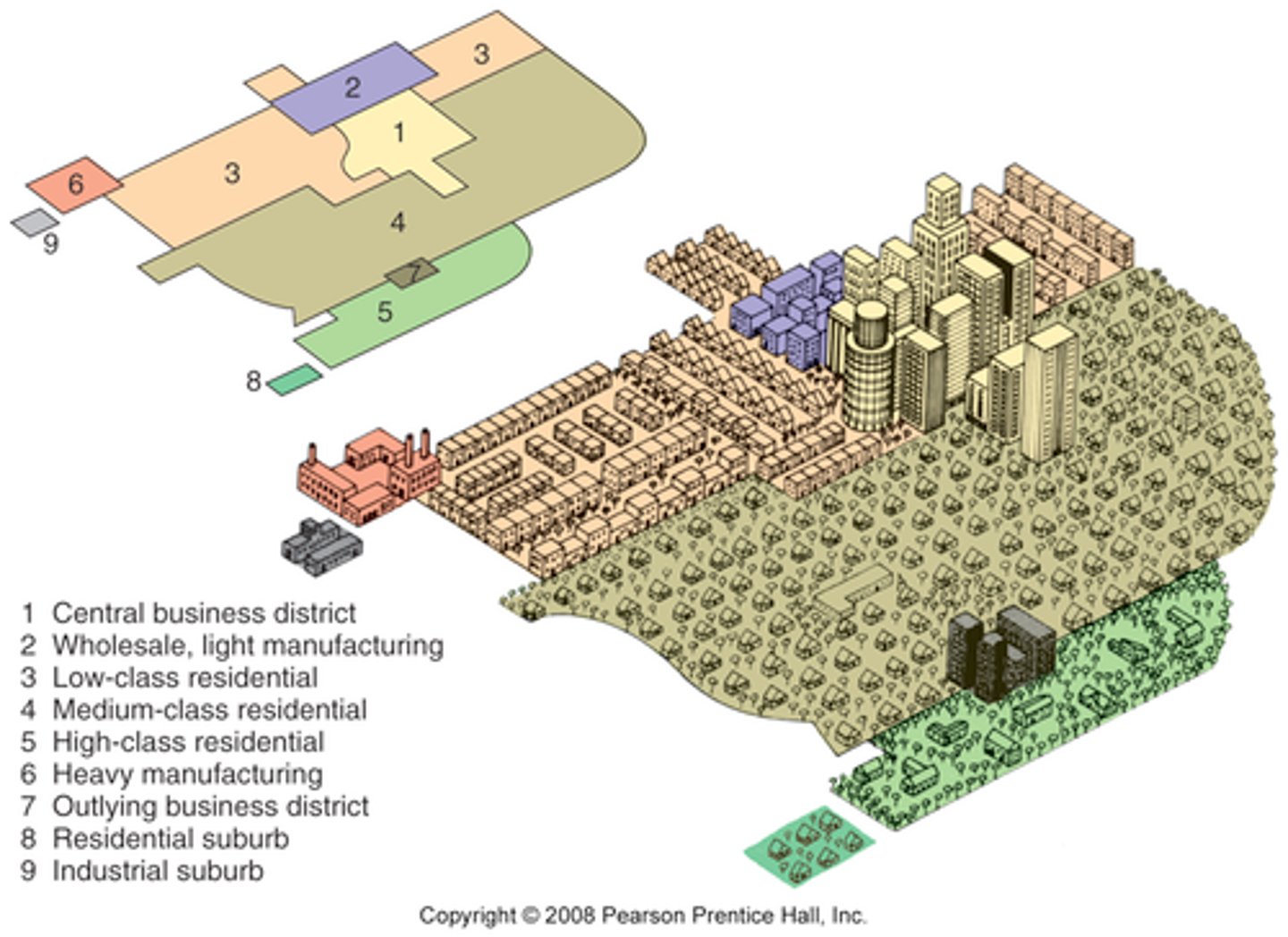
Multiple Nuclei Model
Cities develop around multiple focal points and build outwards to create a functional region. Site and situation factors influence land-use patterns. (Use of smaller business districts- not just one CBD)
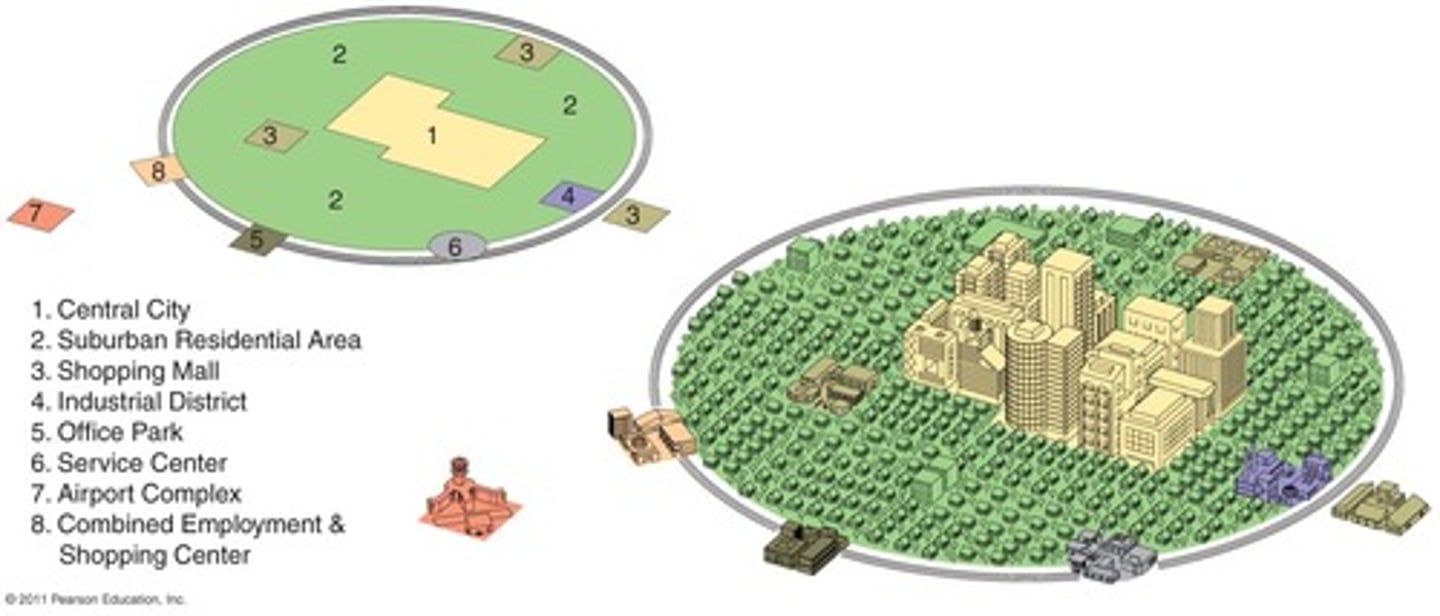
Galactic City Model
Focuses on the decentralization and suburbanization of urban environments. Includes edge cities which are like mini CBDs, typically located along transportation routes
Latin American City Model
Shares structures of concentric and sector city models. Characterized by the "spine" that runs from the modernizedCBD in the center, through wealthy housing and connects to a secondary urban called the mall.
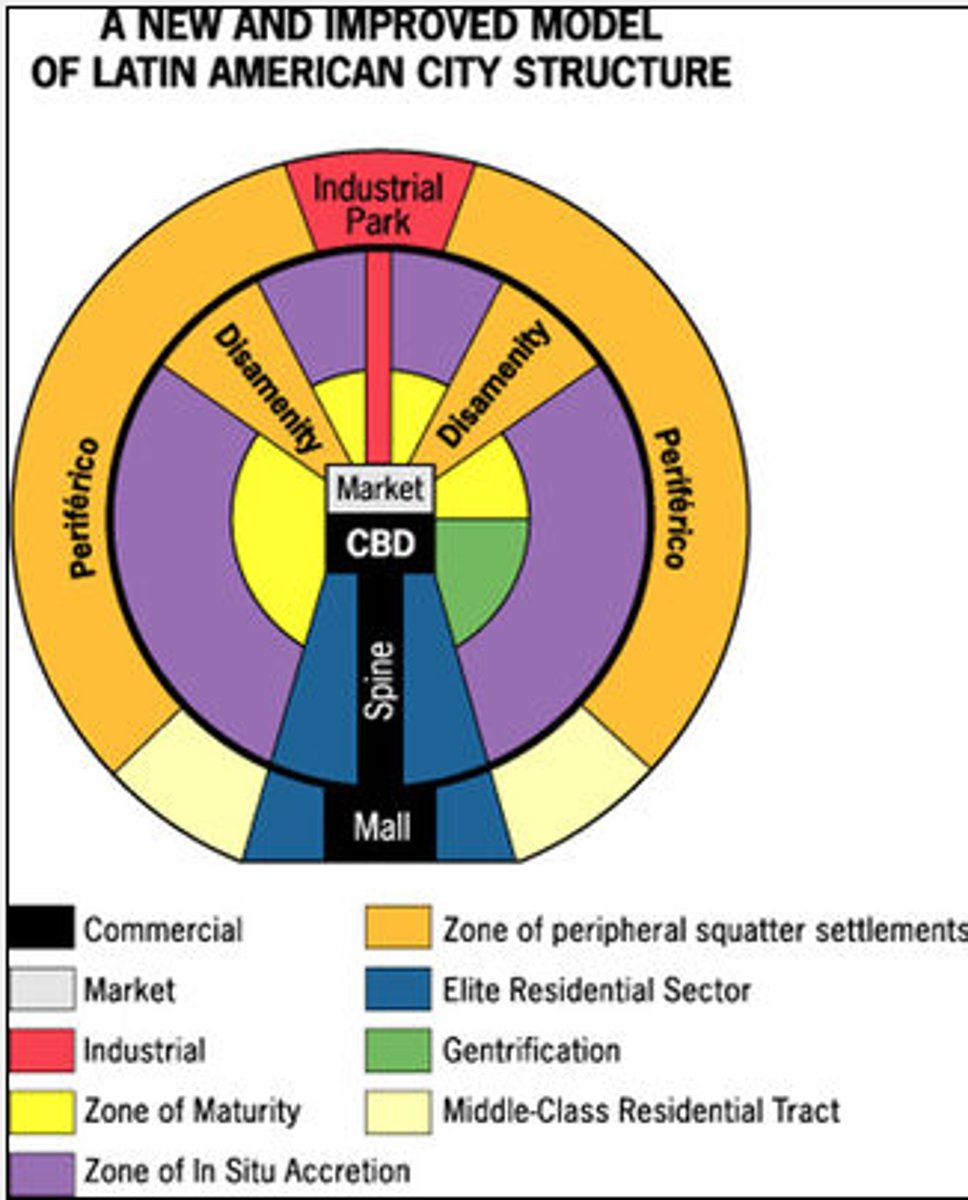
Disamenity Zones (Latin American Model)
Locations that are typically steep, mountainous and dangerous terrain that are not connected to city services (squatter settlements form here)
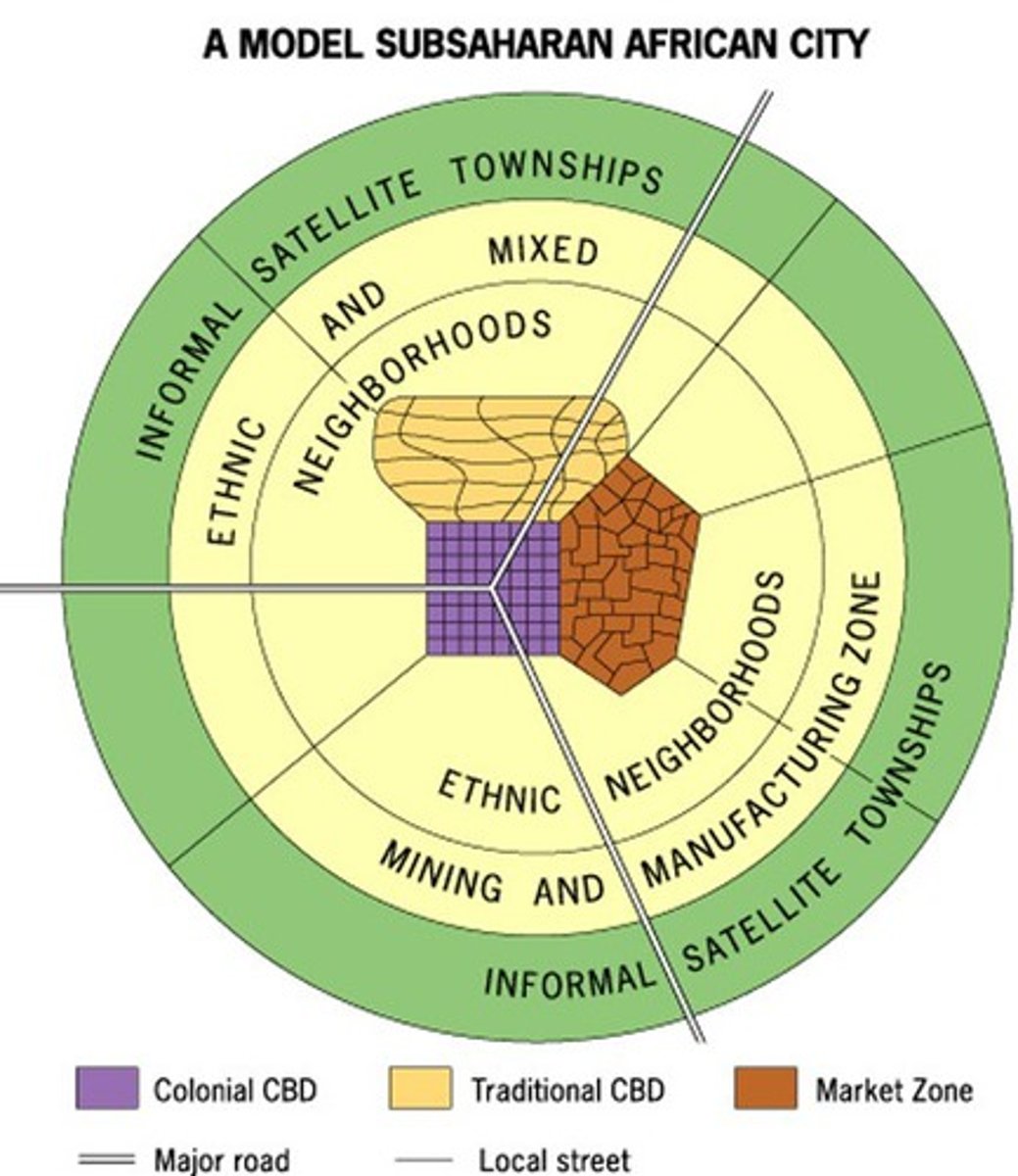
African City Model
Characterized by 3 CBDs and reflects the influence of colonialism throughout the continent
- Mostly outdated but can be seen on the cultural landscapes
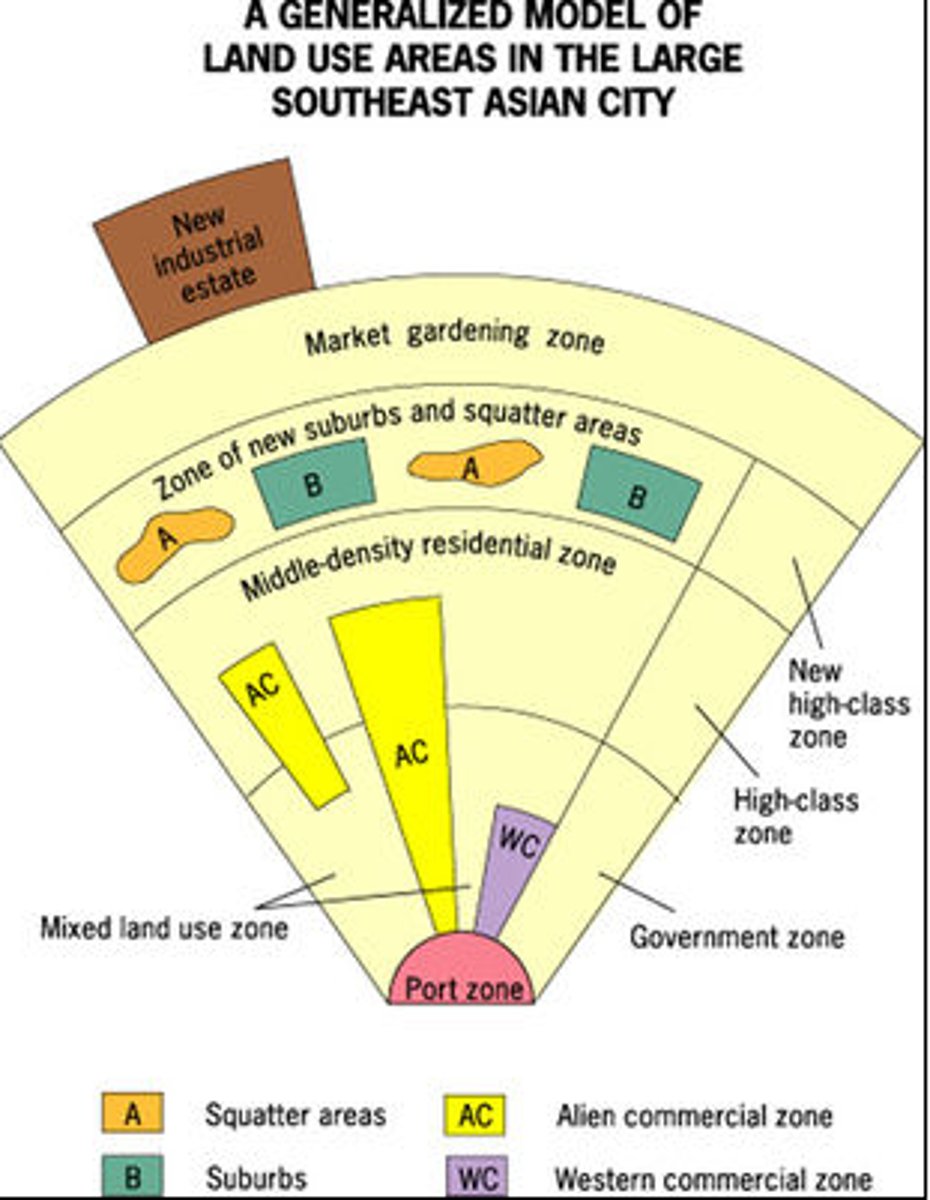
Southeast Asian City Model
Characterized by a port zone, which was the center of commerce in colonial SE Asia- export oriented, so no CBD. History of colonialism
Population Density
The amount of people that occupy a specific unit of land
Historical Residential Land Use
Older cities would place housing, businesses and services within walking distance of one another because they didn't have the transportation technology that we do today
Contemporary Residential Land Use
Newer cities were developed around transportation technology that allowed people to travel longer distances from their homes to work or services
Zoning
A regulation about what type of development of land use can occur in a specific location
Infilling
Redevelopment of vacant land to improve the surrounding area. Ex. Previous industrial areas change to offices, housing and entertainment venues. (Increases density and changes land-use pattern)
Infrastructure
The basis support systems need to keep a society and economy running smoothly ex. Transportation, Wi-Fi, sewage, schools, healthcare , police/fire departments
Sustainable City
- Reduces the city's impact on the environment
- Livability, high quality of life with opportunity and stability
Smart Growth and New Urbanism
Using mixed-zoning policies in order to increase the use of already existing urban structures while maintains a sense of place. (Typically build up instead of out to prevent urban sprawl)
Mixed-Use Development
Planned urban development that includes multiple uses such as retail, residential, educational, recreational and businesses
Greenbelts
An area of green space such as a park, agricultural land or forest around an urban area intended to limit urban sprawl
Positives of Sustainable Urban Design
-Reduction of sprawl
- Improved walkability, transportation and liveability
- Improved and diverse housing options
reduction in the negative environmental impact of cities
Negatives of Sustainable Urban Design
-Increased housing costs
-De facto segregation (low income families and people of color can no longer afford to live in the cities core)
-Potential loss of historial character. Placelessness
Qualitative Data
Data that involves descriptive depictions or characteristics of a research topic, often based on peoples perceptions or opinion
Quantitative Data
Data which involves numbers and statistics- can be measured
Redlining
Housing discrimination maintained by banks- starting in the 1930s, refusal to grant home loans in certain areas because of the ethnic or racial composition
Blockbusting
Housing discrimination maintained by the real estate industry- white families were encouraged to rapidly sell when African-American families moved into neighborhoods (partially caused White Flight to the suburbs)
Affordability (Cause of Housing Issues and Discrimination)
Rising mortgage rates, expensive home prices low inventory and inflation have made it more difficult for the average American family to afford a home
Access to Services (Effect)
Services are more difficult to access in urban areas with primarily low-income populations that lack transportation (cars=$$)
Food deserts
Locations where residents' access to AFFORDABLE healthy food options (especially fresh fruits and vegetables) is restricted or nonexistent due to the absence of graocery stores within convenient
Rising Crime (Effects)
When people are economically and racially segregated in urban areas, crime increases. (factors that impact include: lack of jobs, resources and infrastructure, criminalization of homelessness and isolation)
Environmental Injustice (Effects)
Communities of color and the poor are more likely to be exposed to environmental burdens such as air and water pollution
Growth of Disamenity Zones
Locations that are typically physically unsafe with dangerous terrain that are not connected to city services (high crime, high poverty, flood-prone, homelessness)
Inclusionary Zoning (Response)
Areas where city governments require that developers must include low and medium income housing options in their projects to obtain building permits
Local Food Movements (Response)
Using city owned land or abandoned areas to plant community, urban gardens to provide fresh fruit and vegetables to people living in food deserts
Urban Renewal (Responses)
Programming funded by federal government grants after WWII intended to redevelop and modernize blighted, abandoned and/or industrial urban areas
Gentrification
They process by which higher income residents or professional developers buy buildings in abandoned, blighted and/or industrial areas for a low cost and renovate, restore and rebuild the property
Positives of Urban Renewal (Examples)
-Improved housing and increased property values
-attract new businesses (stimulate economic growth)
-Infrastructure improvements
-Rehabilitation of historic buildings
-Decreased crime rates
Negatives of Urban Renewal
-Displacement of long-time residents
-Demolition or alteration of historic buildings by new businesses (think Placelessness)
Suburban Sprawl (Challenge to Sustainability)
With greater access to the automobile and roads, commercial and residential development have expanded outward from the city core (higher congestion and pollution, destruction of habitats)
ecological footprint
Uses land as currency to measure how fast we consume resources and generate waste compared to how fast nature can absorb our waste and generate new resources
Sanitation (Challenge to Sustainability)
Across the world, sanitation issues such as open defecation and lack of sewage systems prevent cities from having access to healthy water
Climate Change and Energy Consumption (Challenge to Sustainability)
Urban areas consume massive amounts of energy-moss in fossil fuels which cause the emission of greenhouse gases that impact the ozone layer and cause climate change
Regional Planning (Responses)
Seeks to coordinate the development of housing, transportation, urban infrastructure and economic activities at a regional scale
Remediation and Redevelopment of Brownfields (response)
Decontamination of brownfields, which reduces health and safety hazards and then redevelopment can occur (turns into mixed using development, green spaces or affordable housing)
Brownfield
Large, abandoned industrial sites in central cities and suburbs due to the shift from manufacturing to service-based economies. Typically unsafe and polluted
Establishment of urban Growth Boundaries (Response)
Intended to limit sprawl and encourage the conservation of agricultural land, forests and other natural areas