ISDS 3003 CH 1 - 4
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
228 Terms
Data
numeric, textual, visual, or audio information that describes real-world systems
Scope
amount of data produced & collected can vary
Format
data may be produced as numbers, text, images, audio, or video
Access
some data sources are private while other are made publicly available
Analog vs Digital
Analog: encoded as continuous variations on various physical media
Digital: encoded as 0s and 1s on electronic & magnetic media
Database
a collection of data in a structured format
Database System (aka Database Management System/DBMS)
software that reads and writes data in a database
Query
request to retriever or change data in a database
Query Language
specialized programming language designed specifically for DBMS
Database Application
software that helps business users interact with DBMS. Programmers write applications to simplify the user experience & ensure data access is efficient and secure
Database Administrator
responsible for securing the database system against unauthorized users – enforces procedures for user access and database systems availability
Database Designer
determines the format of each data element and the overall database structure
Database Programmer
develops computer programs that utilize a database
Database User
a consumer of data in a database. Database users request, update, or use stored data to generate reports or information
Large, complex databases with many users require:
Recovery
Rules
Authorization
Performance
Security
Transaction
a group of queries that must be either completed or rejected as a whole. Execution of them may lead to inconsistent or incorrect data
When processing transactions, database systems must:
Ensure transactions are processed completely or not at all
Prevent conflicts between concurrent transactions
Ensure transaction results are never lost
Architecture
describes the internal components and the relationships between components, which are similar at a high level
Query Processor
interprets queries, creates a plan to modify the database or retrieve data, and returns query results to the application
Performs query optimization to ensure the most efficient instructions are executed on the data
Storage Manager
translates the query processor instructions into low-level file-system commands that modify or retrieve data
Indexes
used to quickly locate data in large data sets
Log
a file containing a complete record of all inserts, updates, and deletes processed by the database; use log records to restore database if information is lost - stores queries processed by the database
Catalog (AKA data dictionary)
directory of and describes database objects like tables, columns, indexes
Relational Database
stores data in tables, columns, and rows, similar to a spreadsheet
Ideal for databases that require an accurate record of every transaction
SQL (Structured Query Language)
includes statements that read and write data, create and delete tables, and administer the database system
Big Data
massive volumes of online data
NoSQL
newer non-relational system for "not only SQL" and are optimized for big data
Open Source
software that anyone can inspect, copy, and modify with no licensing fee
Query
a command for a database that typically inserts new data, retrieves data, updates data from a database
Query Language
a computer programming language for writing database queries
CRUD
four common queries sometimes referred to as CRUD operations –
Create
Read
Update
Delete data
Statement
a complete, executable database command
SQL "CREATE TABLE" statement
creates a new table by specifying the table and column names
Data Type
indicates the format of column; can be numeric, textual, or complex
INT stores integer values
DECIMAL stores fractional numeric values
VARCHAR stores textual values – string of variable length with specified maximum
DATE stores year, month, and day
FLOAT stores fractional values
CHAR store smaller set of characters that have little variation
Database Design
a specification of database objects (i.e. tables, columns, data types, and indexes)
Conceptual Design
Database requirements without regard to a specific database system
develops an entity-relationship model, capturing data requirements while ignoring implementation details
Important for complex databases with many users
Logical design
Phase implements database requirements in a specific database system – either a process or a design
converts the entity-relationship model into tables, columns, and keys for a particular database system
Physical design
Adds indexes and specifies how tables are organized on storage media
adds indexes and specifies how tables are organized on storage media
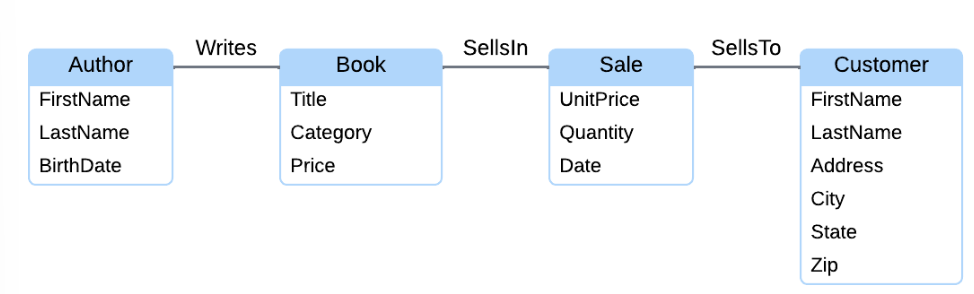
ER Diagrams
rectangles with round corners representing entities
Lines = relationships
Inside Text = attributes
Key
a column used to identify individual rows of a table
Table Diagram
used for logical design
Rectangles with square corners represent tables
Text within rectangles = columns
Bullets = key columns
Arrows between tables = keys
Tail – aligned with column
Arrow – points to table containing key
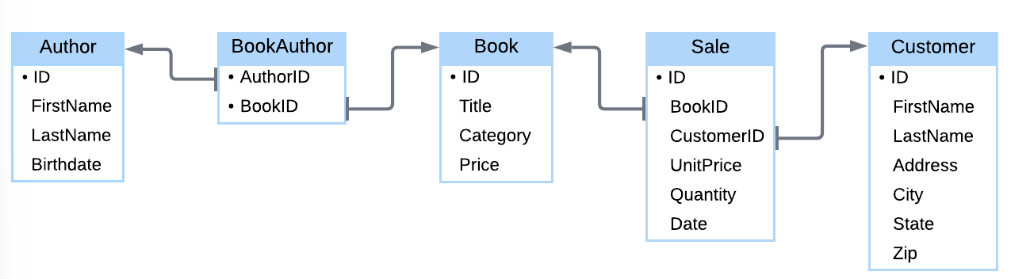
Schema
the logical design as specified in SQL and depicted in a table diagram
Data Independence
principle that physical design never affects query results
Application Programming Interface (API)
library of procedures or classes that links a host programming language to a database
MySQL
leading relational database system, sponsored by Oracle
MySQL Community
a free edition with a complete set of database services and tools – commonly used in university courses and training programs
MySQL Enterprise
a paid edition for managing commercial databases – includes MySQL Community and additional capabilities admirative applications
MySQL HeatWave
a commercial edition with additional capabilities for analytics and machine learning
MySQL Server
reference database system for the MySQL Community edition
SQL Sandbox
a zyBooks programming tool that runs on MySQL
Zybooksdb
an empty database used in most sandbox exercises
Sakila
a sample database maintained by MySQL – contains 16 tables with sample data, describing a video rental business
MySQL Workbench
a desktop application with a graphical interface, available with MySQL Server – it's powerful but complex
MySQL Command-Line Client
a textual programming tool, also available with MySQL Server
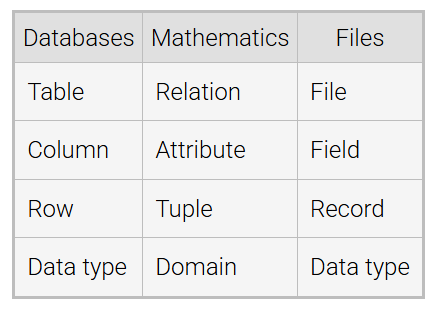
Database Model
a conceptual framework for database systems, with 3 parts:
Data structures – prescribe how data is organized
Operations – manipulate data structures
Rules – govern valid data
Relational Model
a database model based on a tabular data structure
Relational Operations
Select selects a subset of (or all) rows of a table
Project selects one or more columns of a table
Product lists all combinations of rows of 2 tables
Join combines 2 tables by comparing related columns
Union selects ALL rows of 2 tables
Intersect selects rows common to 2 tables
Difference selects rows that appear in 1 table but not another
Rename changes a table name
Aggregate computes functions over multiple table rows (I.e. sum, count)
Relational Algebra: these operations as a collective
Relational Rules
part of the relational model and govern data in every relational database
Unique primary key
Unique columns names
No duplicate rows
Set
an unordered collection of elements enclosed in braces
Tuple
an ordered collection of elements enclosed in parentheses - i.e. (a, b, c) or (c, b, a)
How data is organized:
Table – has a name, fixed tuple of columns, + varying set of rows
Column – has a name + a data type
Row – unnamed tuple of values; each value corresponds to a column and belongs to the column's data type
Rows are NOT ordered so sets are not ordered
Data Type – named set of values, from which column values are drawn
Business Rules
based on business policy + specific to a particular database
All rows in a particular column must have known values
Values may not repeat in different rows
When a row is deleted, all related rows should be deleted
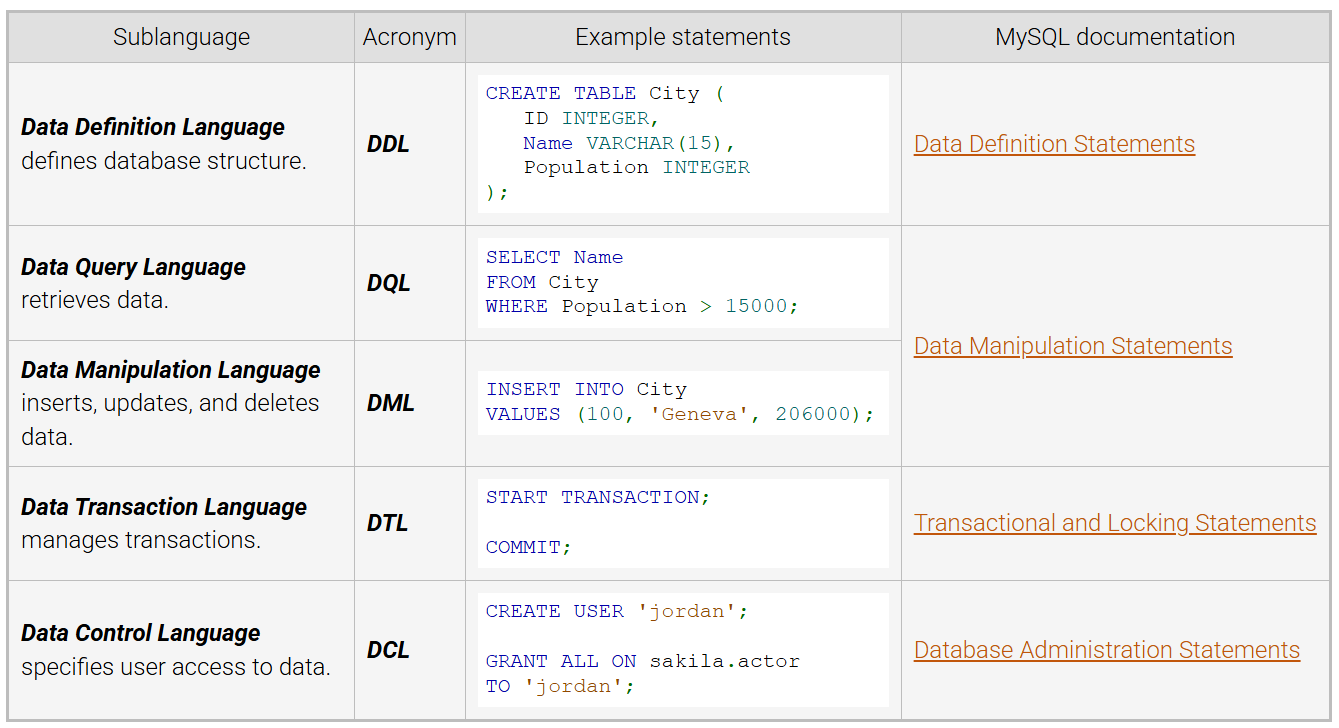
SQL Sublanguages:
SQL Language Elements:
Literal: explicit value
Keyword: word with a special meaning for the language processor
Identifier: name of a database object
Expression: sequence of literals, identifiers, and operations that evaluate to a single value
Comment: text that is ignored by the language processor
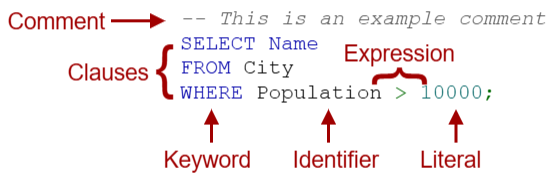
Statement
a complete, executable instruction, ending with a semicolon – consists of one or more clauses
Clause
begins with a keyword, followed by additional language elements
SQL Standard:
specifies the official syntax and behavior of SQL statements
Database System Instance
a single executing copy of a database system
CREATE DATABASE Database Name
creates a new database
DROP DATABASE DatabaseName
deletes a database
USE DatabaseName
selects a default database for use in subsequent statements
SHOW statement
provides information about databases, tables, and columns:
SHOW DATABASES lists all databases in the database system instance.
SHOW TABLES lists all tables in the default database. The optional clause FROM DatabaseName lists tables in a named database.
SHOW COLUMNS FROM TableName lists all columns in the TableName table of the default database.
SHOW CREATE TABLE TableName shows the CREATE TABLE statement for the TableName table of the default database.
Table
a name, a fixed sequence of columns, and a varying set of rows
Must have at least one column and zero rows
Rules Governing Tables:
Exactly one value per cell
No duplicate column names
No duplicate rows
May be used in temporary tables but deleted once moved to a permanent tables
No row order
Column
a name and a data type
Row
an unnamed sequence of values – each value corresponds to a column and belongs to the column's data type
Cell
a single column of a single row
Data Independence
rule #4, allows database administrators to improve query performance
The result of a database query is not affected by the physical organization of data on storage devices
CREATE TABLE
statement creates a new table by specifying the table name, column names, and column data types
DROP TABLE
deletes a table, along with all the table's rows, from a database
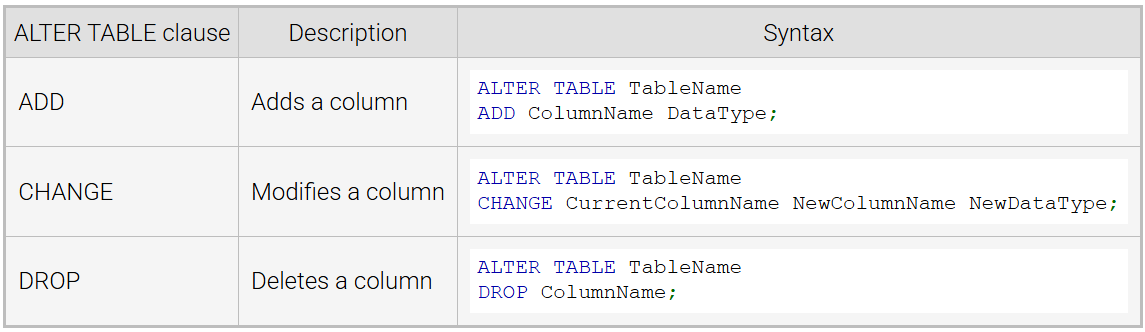
ALTER TABLE
adds, deletes, or modifies columns on an existing table
data type
a named set of values from which column values are drawn. In relational databases, most data types fall into one of the following categories
Integer
data types represent positive and negative integers.
INT, implemented as 4 bytes of storage
SMALLINT, implemented as 2 bytes.
Decimal
data types represent numbers with fractional values. Decimal data types vary by number of digits after the decimal point and maximum size
FLOAT
DECIMAL.
Character
data types represent textual characters
CHAR, a fixed string of characters
VARCHAR, a string of variable length up to a specified maximum size
Date & Time
data types represent date, time, or both
DATE
TIME
DATETIME
TIMESTAMP.
Binary
data types store data exactly as the data appears in memory or computer files, bit for bit. The database manages binary data as a series of zeros and ones
BLOB
BINARY
VARBINARY
IMAGE.
Spatial
data types store geometric information, such as lines, polygons, and map coordinates.
POLYGON
POINT
GEOMETRY
Document
data types contain textual data in a structured format such as XML or JSON
Signed
may be negative
Unsigned
cannot be negative
Operator
a symbol that computes a value from one or more other values, (operands) - may be numeric, character, and other data types
Arithmetic: compute numeric values from numeric operands
Comparison: compute logical values TRUE or FALSE
Logical: compute logical values from logical operands
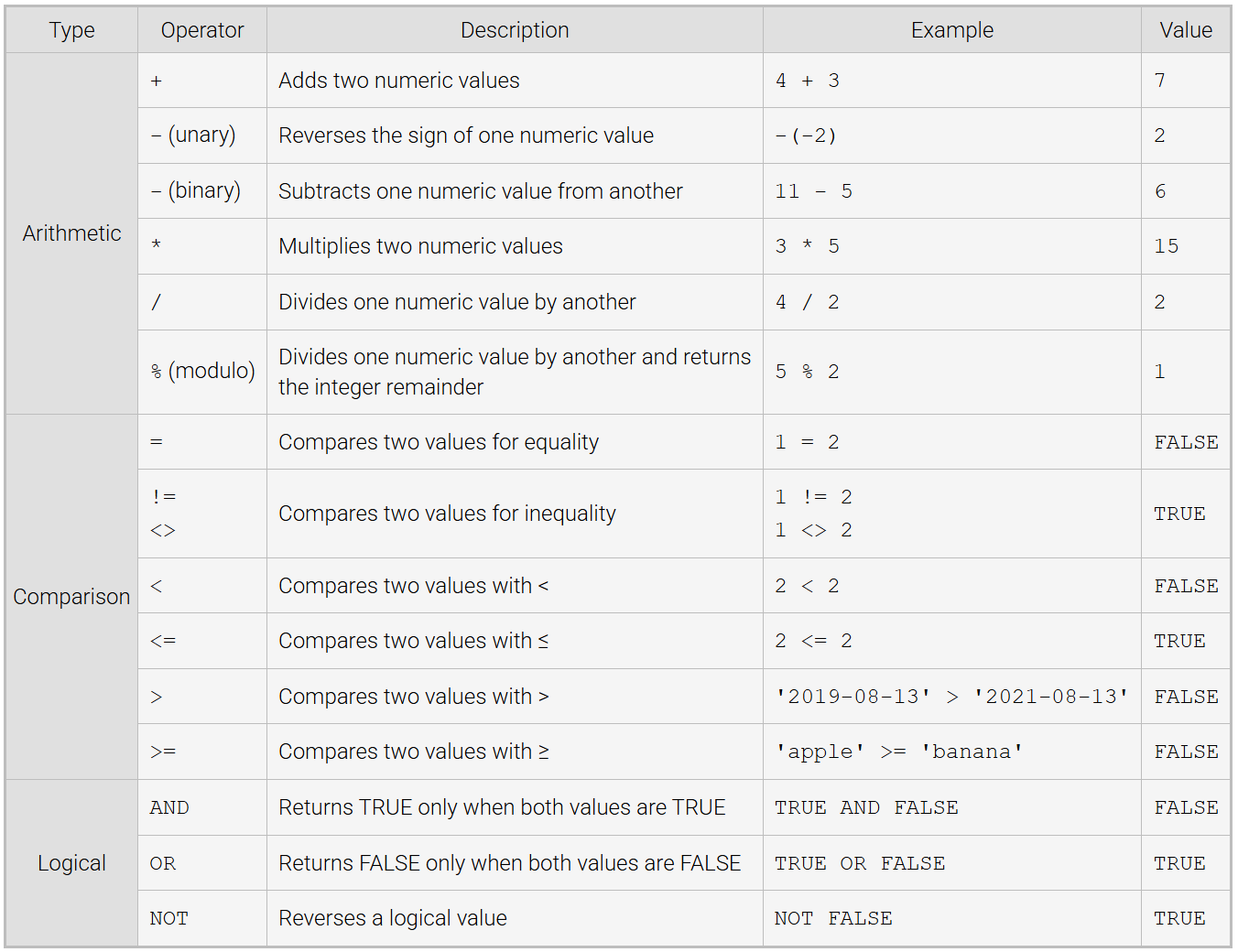
Unary
operator has one operand
Binary
operator has two operands
Expression
a string of operators, operands, and parentheses that evaluates to a single value
Operator Precedence
the way operations in an expression are evaluated in order
SELECT / FROM
statement selects rows from a table
SELECT clause and FROM clause
SELECT clause: specifies one or more expressions, separated by commas, that determine what values are returned for each row
FROM clause: specifies the table from which rows are selected
Result Table: the SELECT statement returns a set of rows called the result table
LIMIT
a clause that limits the number of rows returned by a SELECT statement
Condition
an expression that evaluates a logical statement
WHERE
an optional clause in the SELECT statement that specifies condition for selecting rows
TRUE – row is selected
FALSE/NULL – row is omitted
NULL
a special value that represents either unknown or inapplicable data – NOT the same as zero
IS NULL and IS NOT NULL may be used to select NULL values (proven as true)
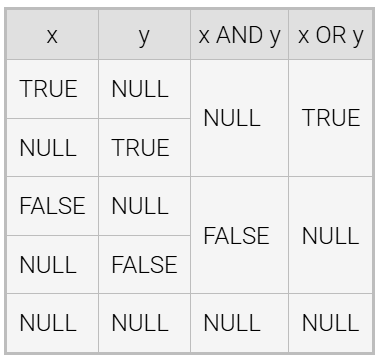
Truth Tables
the value of logical expressions containing NULL operands