Overview of Cardiac Physiology and Conduction System
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Cardiomyocyte
Heart muscle cell with unique structural features.
Cardiac conduction system
Network of cells initiating heart contractions.
Action potentials
Electrical signals triggering muscle contraction.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Graphical representation of heart's electrical activity.
Systole
Phase of heart contraction and blood ejection.
Diastole
Phase of heart relaxation and filling with blood.
Cardiac cycle
Sequence of events during one heartbeat.
Intercalated discs
Connections between cardiomyocytes for synchronized contraction.
Desmosomes
Protein structures linking adjacent cardiac cells.
Gap junctions
Channels allowing electrical signal passage between cells.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
Organelle storing calcium ions in muscle cells.
T tubules
Extensions of cell membrane facilitating calcium entry.
Calcium ions (Ca2+)
Key regulator of cardiac muscle contraction strength.
Epinephrine
Hormone increasing heart contraction force via calcium.
Isradipine
Drug blocking calcium channels, slowing heart rate.
Mitochondria
Organelles producing ATP through cellular respiration.
Aerobic respiration
Oxygen-dependent ATP production method in cardiomyocytes.
Anaerobic respiration
ATP production without oxygen, less efficient.
Autorhythmic fibers
Self-excitable cells generating heart rhythm.
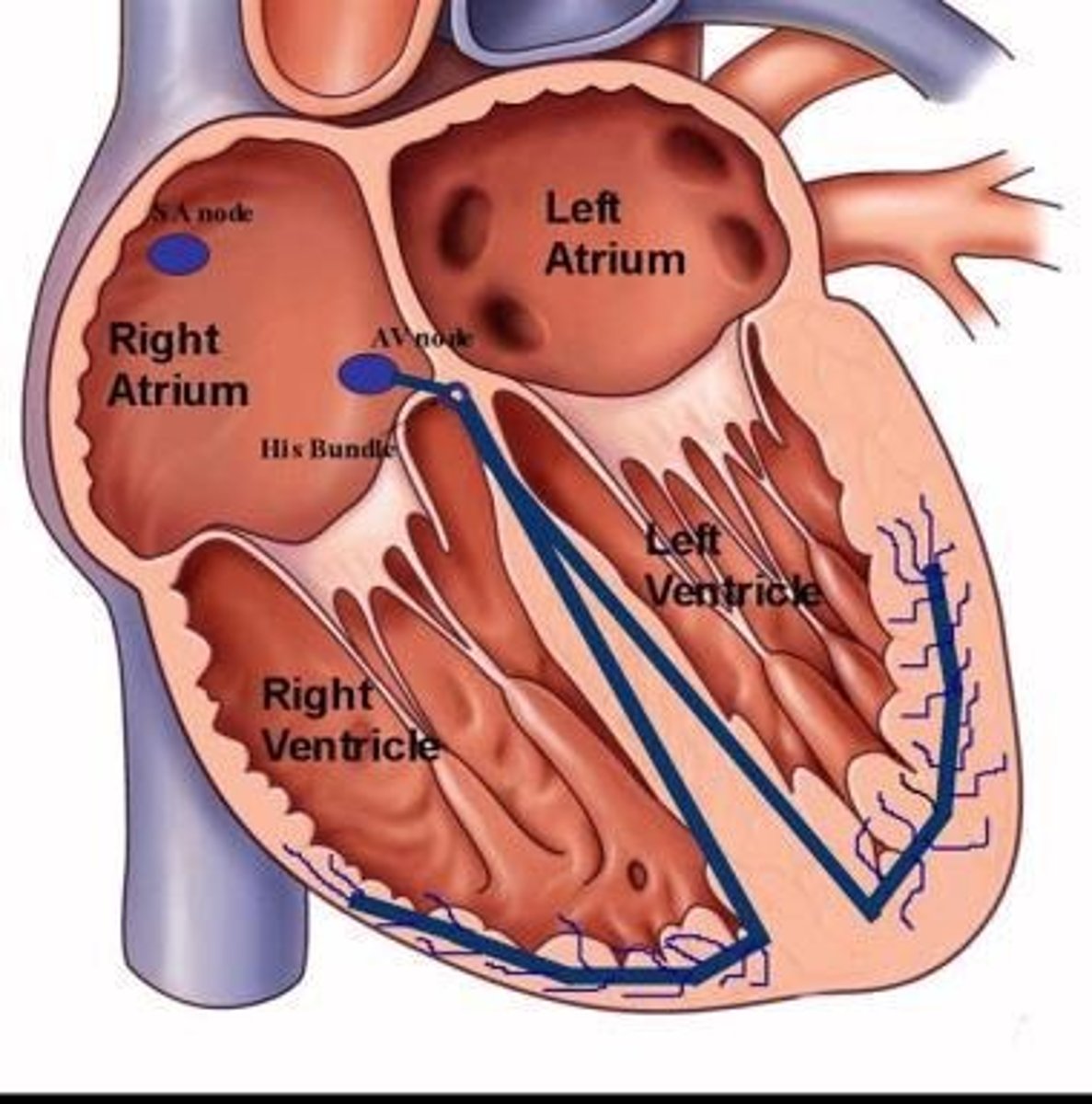
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Primary pacemaker located in right atrium.
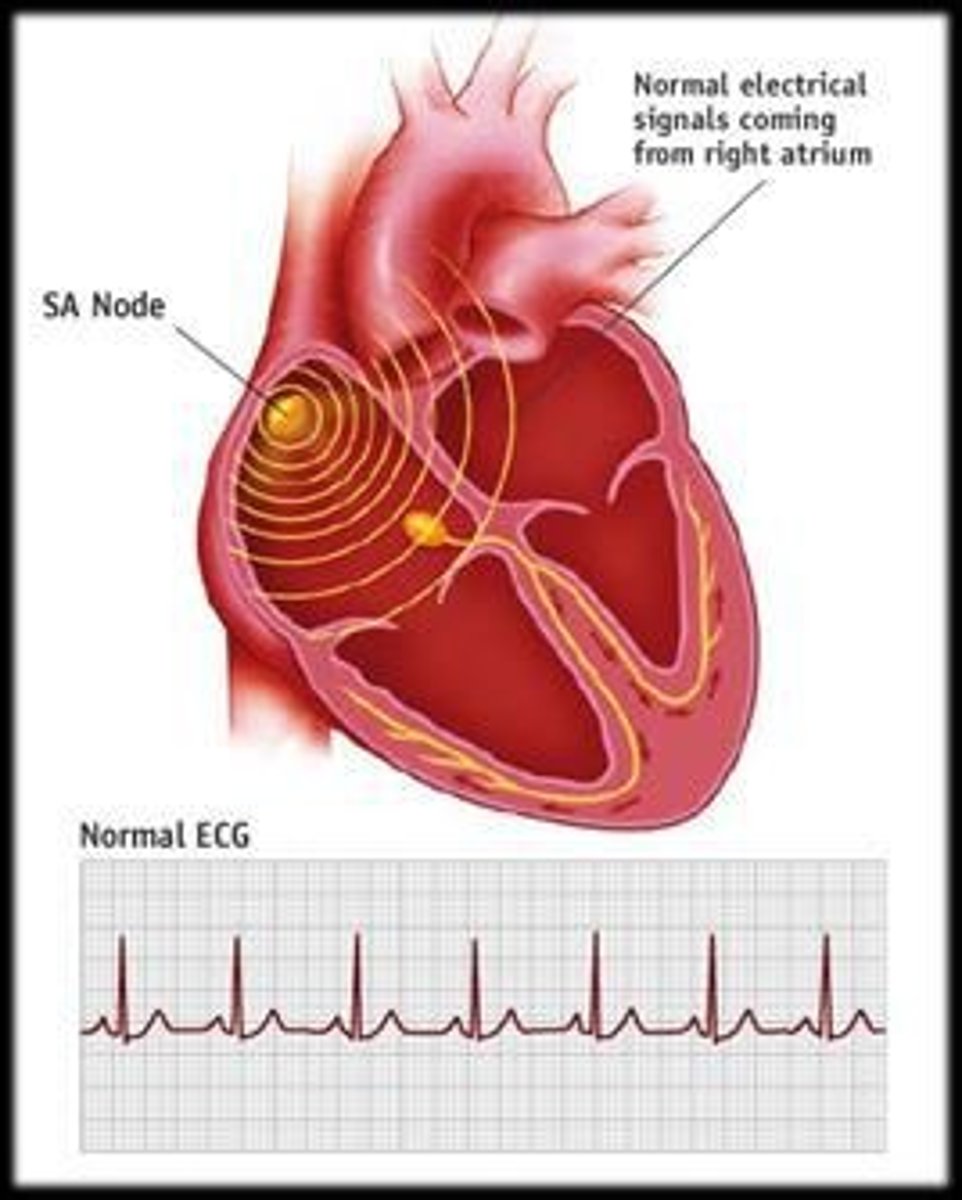
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Node transmitting signals from atria to ventricles.
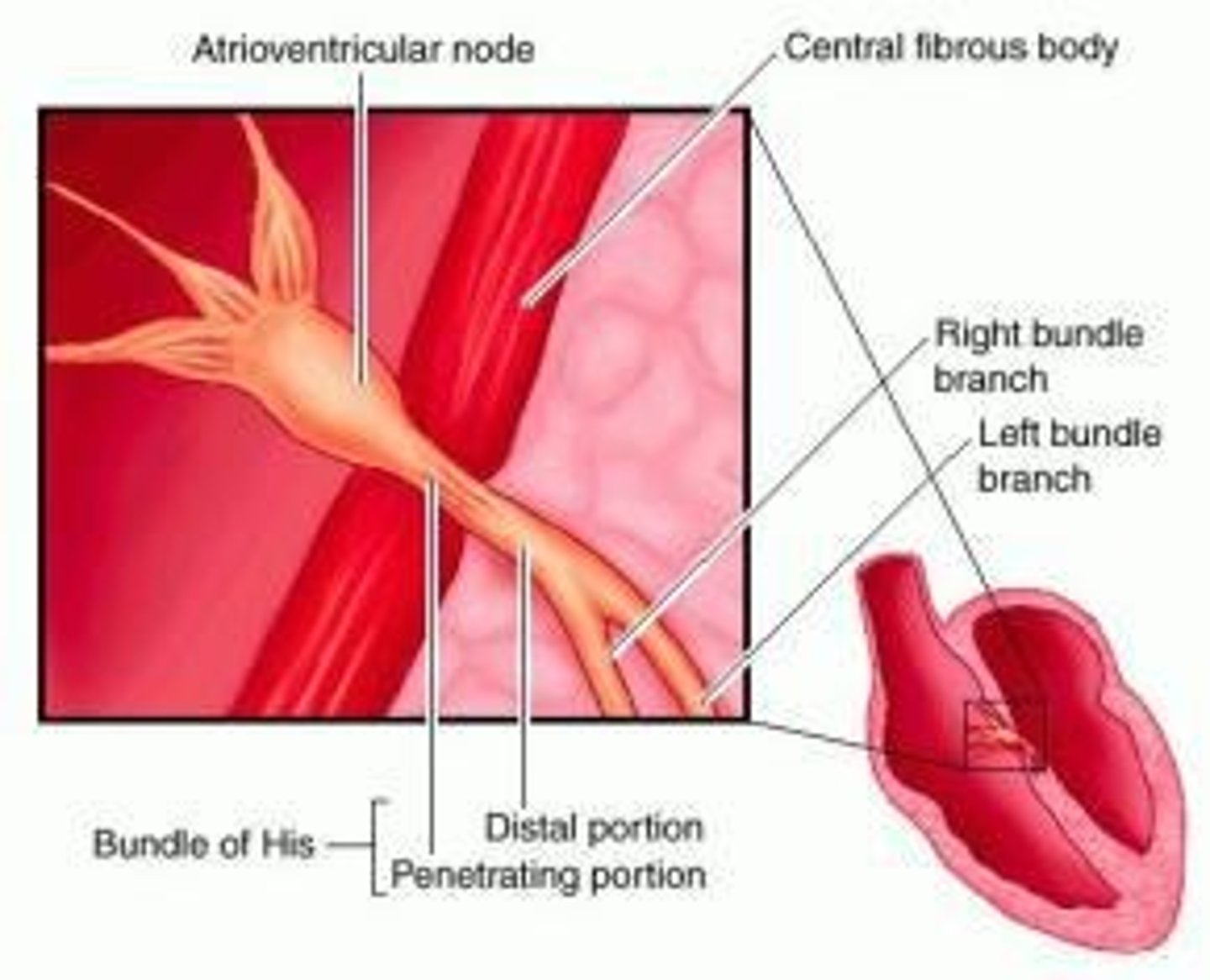
Bundle of His
Pathway conducting impulses from AV node to ventricles.
Purkinje fibers
Conduct action potentials rapidly in the myocardium.
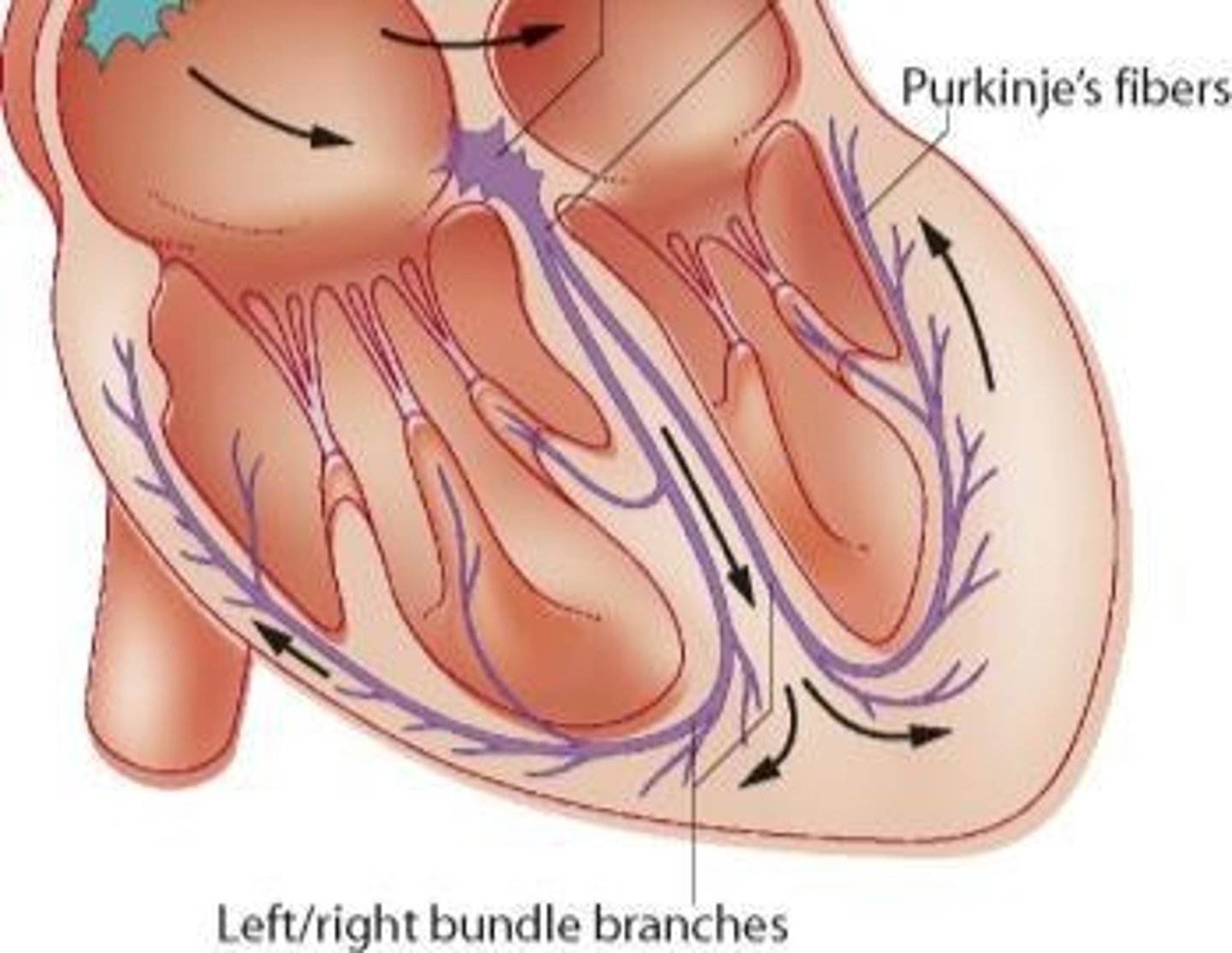
Apex contraction
Contraction starts at heart's apex via Purkinje fibers.
SA node
Primary pacemaker, initiates action potentials every 0.6 sec.
Normal sinus rhythm
Regular heart rhythm established by SA node.
AV node
Slows action potentials before reaching ventricles.
AV bundle
Transmits action potentials with smaller diameter fibers.
Cardiac action potentials
Initiated by SA node, excite contractile fibers.
Phase 0
Rapid depolarization due to Na+ channel opening.
Phase 1
Slight dip in AP from K+ outflow.
Phase 2
Plateau phase; balance of Ca2+ and K+ channels.
Phase 3
Repolarization phase with K+ channel opening.
Phase 4
Resting membrane potential at -90 mV.
Refractory period
Interval preventing second contraction during phases.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Records electrical activity of the heart.
P wave
Depolarization of both atria in ECG.
QRS complex
Depolarization of both ventricles in ECG.
T wave
Repolarization of both ventricles in ECG.
Lead II trace
Shows cardiac cycle events in ECG.
Cardiac cycle duration
One complete heartbeat lasts about 0.8 seconds.
Heart rate at rest
Adult heart beats approximately 75 times per minute.
Calcium's role
Increased Ca2+ triggers contraction in cardiac AP.
Tetanus in cardiac muscle
Would prevent normal rhythmic contractions.
Contractile fibers
Working cardiomyocytes that contract during AP.
Conduction system
Initiates heart contraction sequence.
Atria contraction
First phase of heart contraction.
Ventricles contraction
Follows atrial contraction in sequence.
Volume changes
Alteration in chamber sizes during contraction.
Pressure changes
Result from volume changes and valve actions.
High pressure
Drives blood from ventricles to body.
Systole
Phase of heart contraction.
Diastole
Phase of heart relaxation.
Ventricular filling
Phase where ventricles fill with blood.
Atrial contraction
Phase where atria contract to push blood.
Isovolumetric contraction
Phase with closed valves and no volume change.
Ventricular ejection
Phase where blood is expelled from ventricles.
Isovolumetric relaxation
Phase with closed valves and decreasing ventricular pressure.
End-diastolic volume
Volume in ventricles before contraction, ~130 ml.
Passive ventricular filling
Blood flows into ventricles without atrial contraction.
Atrial depolarization
Electrical activity leading to atrial contraction.
Ventricular depolarization
Electrical activity leading to ventricular contraction.
QRS complex
Represents ventricular depolarization on ECG.
T wave
Represents ventricular repolarization on ECG.
AV valves
Valves between atria and ventricles.
SL valves
Semilunar valves between ventricles and arteries.
Pressure gradient
Difference in pressure driving blood flow.
Atrial systole
Atrial contraction phase in cardiac cycle.
Ventricular systole
Ventricular contraction phase in cardiac cycle.