MCAT Chem/Ochem
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What makes a good leaving group?
Weak bases + strong halide (I-, Br-, Cl-)
Increase in electronegativity (decrease in basicity), increase in size, increase in resonance.
Can stabilize after leaving
Does NOT want to share electrons.
Lewis acid
Accepts electrons
Lewis base
Donates electrons
Bronsted lowry acid
Loses H+
Bronsted Lowry base
Accepts H+
Arrhenius acid (aq.)
Dissociates to form H+
Arrhenius base (aq.)
Dissociates to form OH-
Strong acid + strong base
HCl + NaOH = NaCl + H2O
Strong acid + weak base
HCl + NH3 = NH4Cl
Weak acid + weak base
HClO + NH3 = NH4ClO
Weak acid + strong base
HClO + NaOH = NaClO + H2O
What makes a good nucleophile?
Negative species/ electron rich
Increase in basicity = decrease in electronegativity = increase nucleophilicity
Not sterically hindered
Has a lone pair or pi bonds
What makes a good electrophile?
POSITIVE species/ electron deficient
Essentially lewis acids (accepts e-)
Decrease in basicity = increase in electronegativity = increase in electrophilicity
Not sterically hindered
Has e- withdrawing group or polar pi bond
Example of a good nucleophile
OH-, CN-, Cl-, Br-, I-, NH3, amines
Examples of a good electrophile
Cl2, Br2 (easily polarizable), C=O, Alkyl halides R-halogen (electrophilic center, increases polarity).
Examples of good leaving groups
Conjugate bases of strong acids
Halides (I-, Br-, Cl-), water, sulfonates (TsO-)
SN1 reactions are ___molecular and ____- stepped
UNImolecular, two-stepped
SN2 reactions are ___molecular and ____- stepped
BImolecular, single-stepped
SN1 reactions favor: 3°, 2°, or 1° electrophiles
3° > 2° > 1°
SN2 reactions favor: 3°, 2°, or 1° electrophiles
3° < 2° < 1°
SN1 reactions are favored by
Polar protic solvents: OH/NH as nucleophile (water)
SN2 reactions are favored by
Polar aprotic solvents: Acetone, DSMO; allows nucleophile to be more reactive
SN1 reactions involve
LG leaves and forms a carbocation intermediate
Nucleophilic attack (either side)
Results in racemic mixtures
SN2 reactions involve
Nucleophile backside attack → LG leaves
An enzyme _____ to lower the activation energy
Stabilizes the transition state
Why do alcohols need to be protected?
To decrease reactivity of the alcohol, instead focusing reactivity on a different reaction involving strong bases/nucleophiles.
What kind of ether is useful as protecting groups?
TMS (trimethylsilyl)
What can remove protecting groups
Fl
Percent ionization
Extent to which a weak acid or base dissociates into ions
Weak acids = [H+] at equilibrium / [HA] initial
Weak bases = [OH-] at equilibrium / [B] initial
A single bond has ____ sigma bonds and _____ pi bonds
1, 0
A double bond has ____ sigma bonds and _____ pi bonds
1, 1
A triple bond has ____ sigma bonds and _____ pi bonds
1, 2
Intramolecular forces
Strong forces holding atoms together within a molecule
Intermolecular forces
Weaker forces that exist between molecules
Phosphorylation
Addition of a phosphoryl (PO3) group to a molecule
Oxidation of cysteine
Involves a reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
Can lead to formation of disulfide bonds and sulfenic acid (SOH)
With oxidizing agents
Reduction of cysteine
Breaks disulfide bonds, converting cysteine to thiol form (SH)
With reducing agents
How are disulfide bonds formed?
With oxidizing agents
How are disulfide bonds broken?
With reducing agents
CH bonds make a molecule:
more nonpolar and hydrophobic
OH and NH bonds:
Enable hydrogen bonding, making a molecule more polar and hydrophillic.
Lipases
Hydrolase enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of fats
Ion-exchange chromatography
Separation of molecules based on net surface charge.
Cation/anion
Cation exchange chromatography
Ion-exchange: negatively charged ion exchange resin with affinity for molecules with a net positive charge
Anion exchange chromatography
Ion-exchange: positively charged ion exchange resin with affinity for molecules with a net negative charge
Column chromatography
Ion-exchange, size-exculsion, affinity
Size-exculsion chromatography
Separates molecules based on size: biggest elute the fastest
Affinity chromatography
Isolates and purifies specific molecules based on binding interactions and molecular properties: identifies protein of interest
Melting temperature of nucleotides
Temp at which 50% double-stranded DNA is changed into single-stranded DNA
Ksp
Solubility product constant: equilibrium between the solid form of an ionic compound & its ions in solution.
Lower Ksp =
less soluble compound
Indicator’s pKa
Represents the pH at which HALF of the indicator molecules exist in their acidic form, and the remaining half in their basic form.
The pH at which an indicator changes color is dependent on:
pKa of the indicator
Good insulator
No freely moving e-
Insulator
Poor conductor of electricity and heat: resist e charge and thermal energy
No e- movement
Conductor
Allows electricity and heat to flow through them easily with low resistance
Empirical formula
Lowest whole-number ratio of molecular formula
Isoelectronic species have the
same number of electrons
Gas that is _____ in molar mass will diffuse more quickly
lower
Zwitterion/dipolar ion
Inner salt molecule containing an equal number of positively and negatively charged functional groups.
Turns in proteins
Gamma (3) → Beta(4) → Alpha (5) → Pi (6 residues)
i + 2 → i + 3 → i + 4 → i + 5
Pi turn
H bond between carbonyl O i and amide hydrogen of i + 5
6 residues
Gamma turn
H bond between i and i + 2 residues
3 residues
Beta turns
H bond between i and i + 3
4 residues
Alpha turns
H bonds between i and i + 4
5 residues
Great Brains Always Plan
Paramagnetic
Materials with unpaired electrons
Weak attraction to the magnet
Oxygen, titanium, aluminum
Dimagnetic
Materials with all electrons paired in atomic orbitals
Induce a field in opposite direction (repels against magnet)
Copper, silver, gold
Salt bridge
Strong non-covalent interactions between oppositely charged amino acid side chains in proteins
Often involves basic + acidic aa residues
Dipole-dipole forces
Occurs between polar, uncharged amino acids that contain electronegative atoms
Reagent for an acylation reaction
Acid chloride (RCOCl) or acid anhydride
Friedel Crafts acylation
Addition of acyl group to an aromatic compound with an acyl chloride (RCOCl) acting as a catalyst
Ether extraction
Uses different solubilities of compounds in 2 immiscible solvents (ether + water)
Molarity units (M)
mol/L
Chiral carbon definition
Must be bonded to 4 different groups
No double bonds
sp3 hybridized
Formula for fatty acids
CH3(CH2)nCOOH
Beta plus decay
Adds a positron
+1 to atomic # (+ 1 proton)
Beta minus decay
Adds an electron e-
-1 to atomic # (-1 proton)
Atomic number
Number of protons
Mass number
Number of protons + neutrons
Isotopes differ in number of:
Neutrons (atomic mass # changes)
Which molecules can cross the selectively permeable cell membrane?
Small, NP, lipid-soluble, hydrophobic
Diffusion
Water
Osmosis
Small, polar, hydrophillic
Slow diffusion
Which molecules cannot cross the selectively permeable membrane?
Large, polar
Facilitated diffusion, AT, endocytosis
Ions
AT, ion channels
Macromolecules
Endo/exocytosis
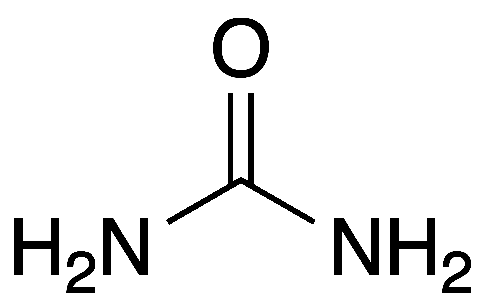
Urea structure (carbamide)
CO(NH2)2