cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis test
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
zygote
fertilized egg
gametes
sex cells
centromere
structure that connects the duplicate halves of the chromosomes
fertilization
the union of the sperm and egg
spindle
network of fibers that push and pull the chromosomes around in the cell during division
centrioles
organelle that organizes the construction of the microtubules for cell division
sperm cell
male gamete cell
egg cell
female gamete cell
reproductive cells
cells formed by meiosis
meiosis
process that has two divisions and reduces the chromosome number in half
diploid
chromosome number in all body (somatic) cells - full set of chromosomes - 2 of each kind of chromosomes
haploid
chromosome number in the gametes - half the chromosome number of body cells
23
human haploid number
46
human diploid number
tetrad
four sister chromatids in a homologous pair of chromosomes; forms during Prophase I; leads to crossing over
chromosomes
structures that carry the genetic information from one generation to the next
cleavage furrow
in a dividing animal cell, the indentation where cytoplasmic division will occur
cell plate
forms in plant cells to form new cell membrane and cell wall during telophase
when a cell grows too large, some problems that it faces includes;
too much demand placed on the DNA, obtaining enough food for the cell, and getting rid of wastes a large cell would produce
after mitotic division, how many chromosomes does each offspring cell contain as compared to the parent cell?
same number as parent cell
type of division where crossing over can occur
meiosis
used for growth and repair of cells, tissues, etc
mitosis
this division results in cells that are different from the parent cell
meiosis
type of division that cuts the chromosome number in half
meiosis
type of division of the nucleus in somatic cells
mitosis
metaphase
sister chromatids are lined up in the middle of the cell
prophase
nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear and the chromosomes coil and condense to become visible
anaphase
sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell
telophase
last phase of cell division, chromosome are in two new cells and nuclear membranes start to reform
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
Interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions;
G1, S, G2; cell spends the majority of time in this stage
G1 phase
stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions; double number of organelles
S phase
DNA replicates
G2
cell prepares for division
correct order of cell cycle
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis
phase of meiosis when crossing over occurs
Prophase I
offspring of this type of reproduction have a much better chance of adapting and surviving in a changing environment
sexual reproduction
mating is not required and offspring is identical to parent
asexual reproduction
involved egg, sperm, and fertilization
sexual reproduction
crossing over
increases the variety of genes in the chromosomes
How is cancer different from a normal cell in relation to the cell cycle?
A cancer cell does not follow normal cell division. The protein regulators that control the cell cycle are not functioning properly. Cancer cells will divide uncontrollably forming tumors that will invade healthy tissue.
How does crossing over occur during Meiosis?
During Prophase I, the homologous chromosomes are joined together and pieces of the sister chromatids can break off and reattach to their corresponding homologous chromsome. The genes exchange spots on the chromosomes.
Homologous chromosomes
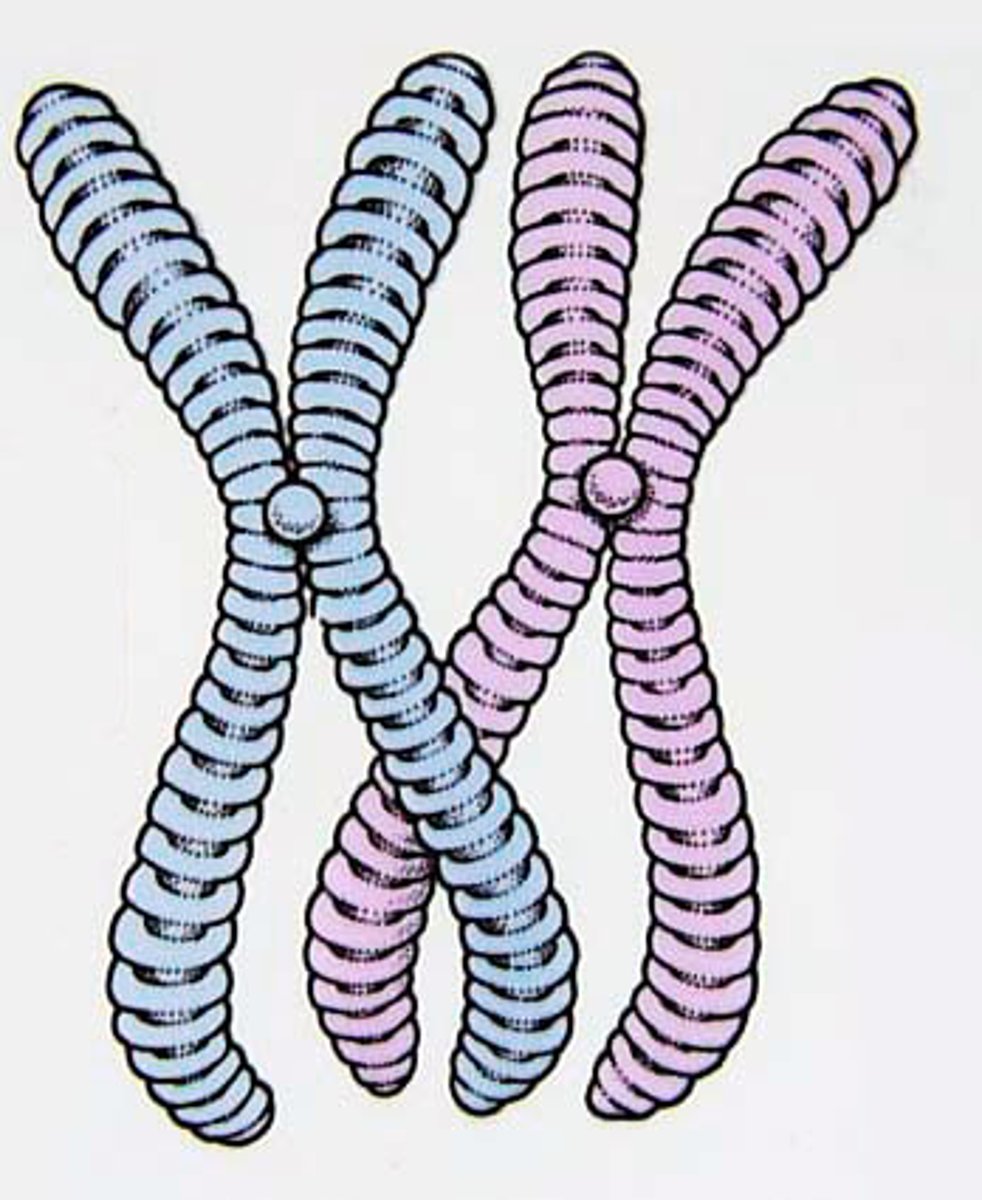
How does crossing over contribute to genetic variation in sperm and egg cells?
After crossing over occurs, the resulting chromatids will now have genes from their sister chromatid. There is an exchange of genes and this will increase the variation during the formation of the egg and sperm cells.