Unit 3_Transducers and the Beam
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
what is a transducer?
something that converts one form of energy to another
what do US transducers do?
convert electric energy into US (and vice versa)
Principle of Piezoelectricity states:
some materials, when deformed by an applied pressure, produce a voltage
the electric voltages applied to transducer are converted to _____________.
US echoes incident on the transducer and produce _____________.
ultrasound; electric voltages.
what do US transducers operate according to?
the Piezoelectric Principle
most common Piezoelectric material used?
PZT- lead zirconate titanate
Easily available and low cost
other names for Piezoelectric elements?
crystal
active element
transducer element
when a voltage is applied, what happens to the thickness of the element?
the thickness of the element increases or decreases depending on the polarity of the voltage
examples of natural Piezoelectric elements?
quartz, tourmaline, Rochelle salt
examples of synthetic (not naturally) Piezoelectric elements
lead zirconate titanate (PZT)
what is the Curie Point (number and definition)?
365 degrees Celcius
temperature at which material loses magnetic properties (aka dipoles can move freely)
explain process of how elements become Piezoelectric:
Heat material to Curie point (365°C)
Polarize dipoles with strong electric current/ field (alignment circuit).
Cool crystal below Curie point and remove from the alignment circuit.
The now aligned dipoles remain fixed parallel to each other and the material can exhibit its piezoelectric properties.
what occurs if an element is reheated to Curie Point?
Heating to Curie point again destroys piezoelectric properties
single element transducers take the form of _________.
disks
linear array transducers contain
numerous elements that have a rectangular shape
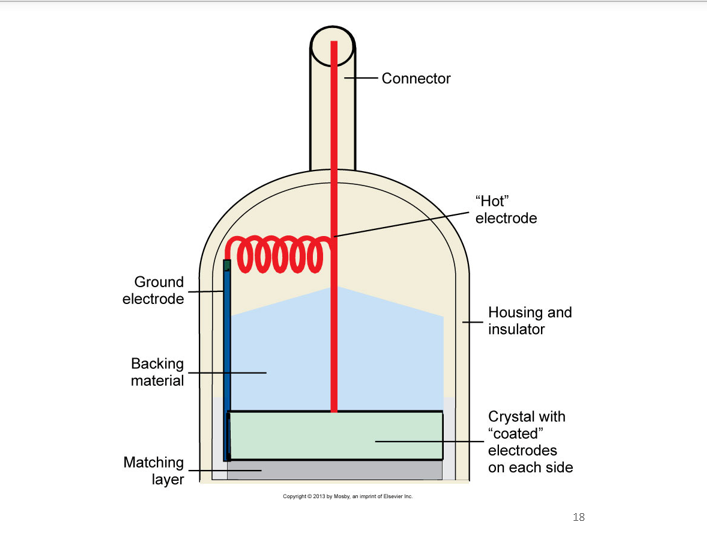
what describes a probe, scan head, or transducer assembly?
element with casing and damping and matching material
what are CMUTs?
capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
newer transducers that contain miniature elements with two electrically conducting layers facing each other
differences between CMUTs and PZT elements?
CMUTs have several advantages over PZT elements:
broader BW
improved detail resolution
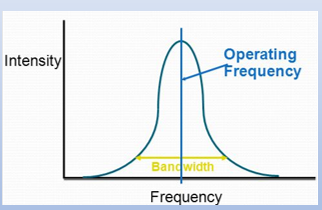
operating frequency definition?
natural frequency of operation for the element
what is operating frequency determined by?
Propagation speed of the element material
Thickness of the transducer element
equation for operating frequency?
ƒo = cPZT / 2 x cth
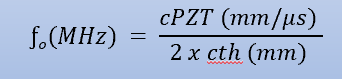
thickness and frequency relationship?
Thickness & frequency are inversely related
thinner elements operate at higher frequencies
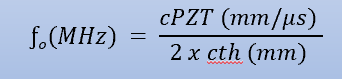
crystal thickness equation?
crystal thickness= wavelength / 2

other names for operating frequency?
resonant frequency
center frequency
typical diagnostic US elements are how thick? propagation speeds?
0.2 mm thick
4-6 mm/ µs
what is bandwidth (BW)?
range of frequencies a transducer generates in addition to the operating frequency
what bandwidths are produced with short pulses?
broad BW
IMAGING
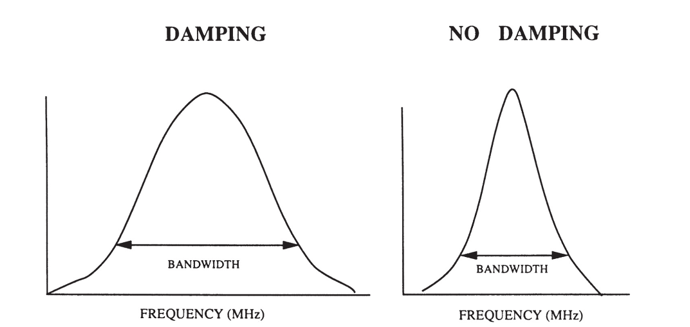
what bandwidths are produced with longer pulses?
narrow BW
DOPPLER
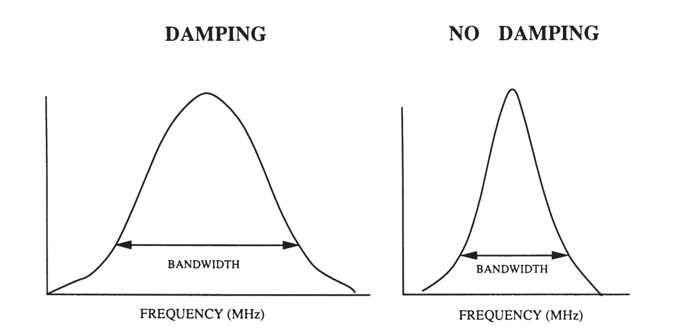
what does a broad/wide BW allow for?
imaging at multiple frequencies within BW range without changing transducers
harmonic imaging!!
what is damping (backing) material?
mixture of a plastic or epoxy resin attached to the rear face of the transducer element
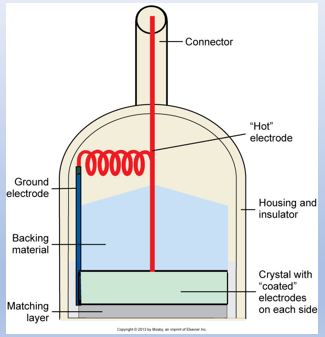
what does damping/ backing material do?
absorbs vibrations
reduces # of cycles/ pulse
broadens BW!
improves resolution (axial?)
reduces SPL
relationship between damping and PD?
inversely!
increased damping = decreased PD
this is because damping decreases cycles/ pulse and PD= T * cycles/ pulse
relationship between damping and SPL?
inversely!
increased damping = decreased SPL
this is because damping decreases cycles/ pulse and SPL= wavelength * cycles/ pulse
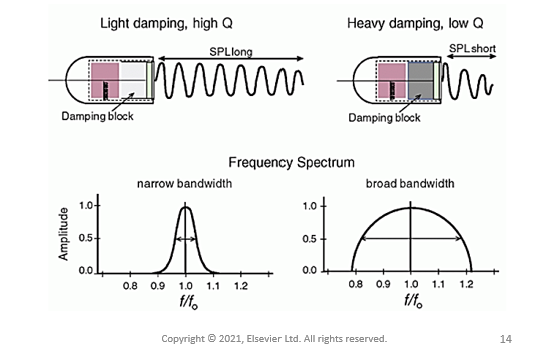
relationship between BW and QF?
inversely!
increased BW with more damping= decreased QF, sensitivity, and efficiency
what transducers are not damped?
CW because pulses are not used
how does damping material shorten pulses?
by allowing US energy to pass into it
CW transducers do not have ______________, which allows for….
backing material; all US energy to be reflected back into the patient
Con of Damping Material
reduces amplitude —>because not as much constructive interference
decreases efficiency and sensitivity
how are diagnostic imaging transducers damped?
HIGHLY damped
2-3 cycles/pulse
how are PW Doppler transducers damped?
LESS damped
5-30
what does QF do?
determines sensitivity
ability to detect weak echoes
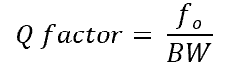
lightly damped transducers have what kind of BW?
narrow BW
high QF, more sensitivity and efficiency
what is the matching layer?
material places on transducer face (front)
typically two layers are used but in some cases two or three can be used
what does the matching layer do?
improves sound transmission across element-tissue boundary
by reducing reflection
impedance matching is intermediate between transducer element and tissue
reduces reflection, improves transmission
matching layer equation?
wavelength / 4

what would occur without the matching layer?
majority of emitted intensity reflected at the skin boundary
what occurs due to air between the transducer and skin surface?
reflection of virtually all sound and prevention of any penetration into the sound tissue
what does a coupling medium do?
aka gel
eliminates air layer between transducer and skin
facilitates passage of sound into and out of tissue
what occurs to a pulse as it travels away from the transducer? what causes this?
width of pulse changes
superposition of waves
constructive interference
destructive interference
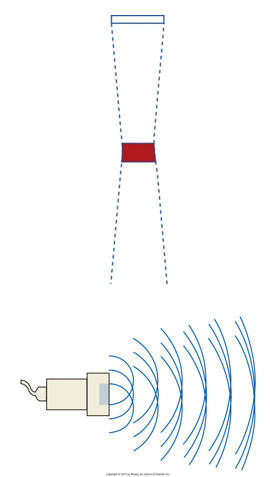
ultrasound waves follow what principle?
Huygen’s Principle
what is Huygen’s principle?
sound beam is a combination of all sound arising from different point like sources on a transducer crystal face
what determines lateral resolution?
width in scan plane
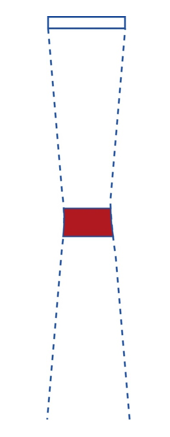
what is not uniform throughout the beam?
intensity (not uniform in space or time)
Intensity= power/ area
therefore, as beam gets smaller, intensity gets larger because the area is smaller.
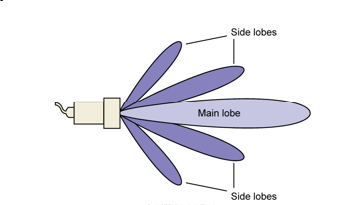
what are side lobes?
additional beams that travel out in some directions NOT included in the beam
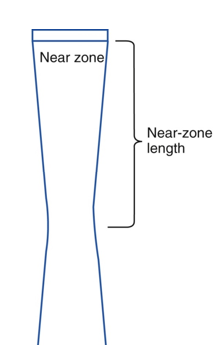
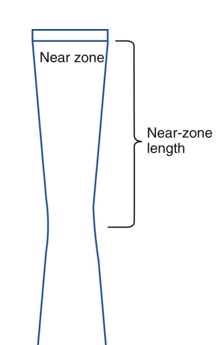
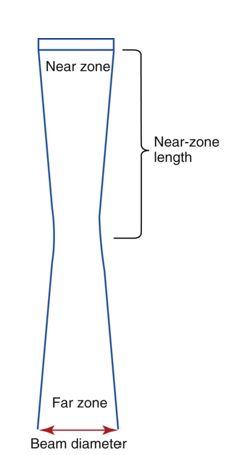
other names for Near Zone?
Fresnel Zone or Near field
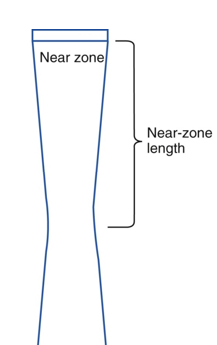
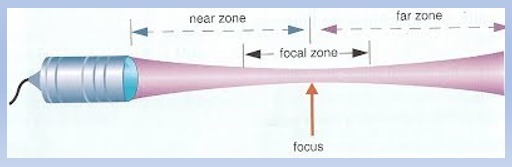
what is the near zone?
region extending from the transducer to the minimum beam width
in the near zone, beam width decreases as….
distance from the transducer increases
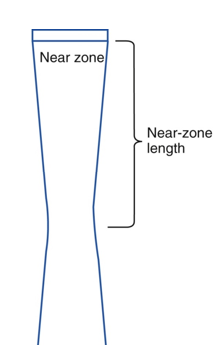
what is Near Zone Length?
distance between transducer and minimum width of beam
what is the NZL determined by?
size and operating frequency of the element or group of elements
for equation relationship with frequency, note that frequency and wavelength are inversely related
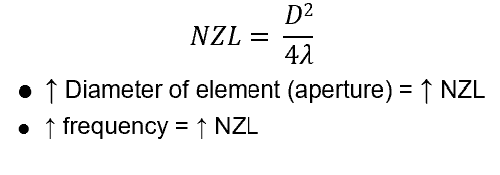
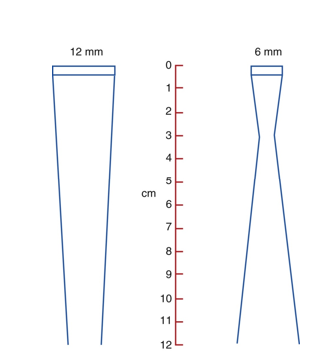
if aperture size increases, NZL ___________
NZL increases
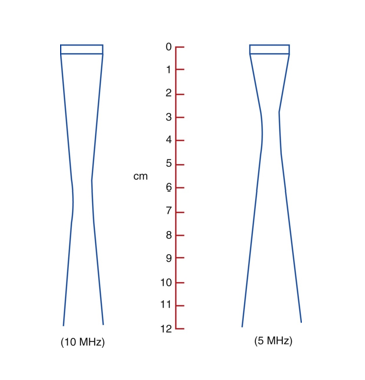
if frequency increases, NZL ___________
increases
NZL equation?
NZL= D2/4λ or D2f /4c
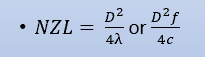
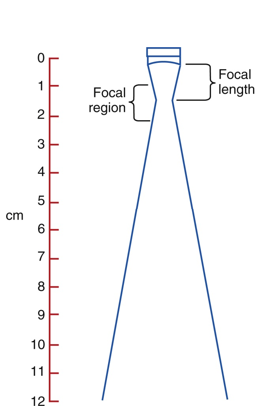
what is the focal zone
where the beam is focused on each side of the focal point
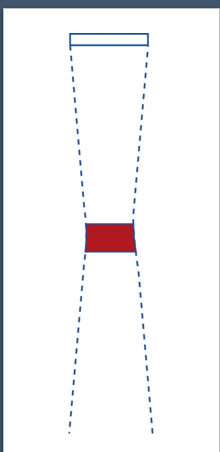
where is the best resolution?
focal zone, due to narrowest beam width
focal zone equation?
beam diameter at natural focus= D/2
other names for far zone?
far field or Fraunhofer zone
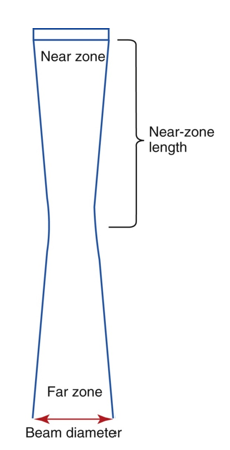
what is the far zone?
region after natural focus
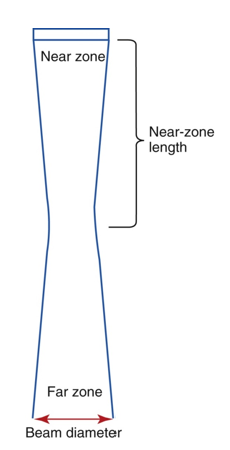
what is divergence of the beam?
beam width increases with increasing distance from the transducer
far field divergence equation?
sinθ=1.22λ/D
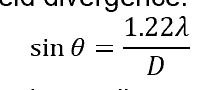
relationship between far field divergence and diameter
inversely related
increase in Diameter
decrease in beam divergence
relationship between far field divergence and frequency?
inversely related
increase in frequency
decrease in beam divergence
what does focusing improve?
lateral resolution
ONLY IN THE NEAR ZONE
beam width is decreased in …
the near zone and focal region
beam width is increased/ widened in…
the far zone
what is focal length?
same thing as near zone length
the distance from the transducer to the center of the focal region (distance from a focused transducer to Spatial Peak Intensity)
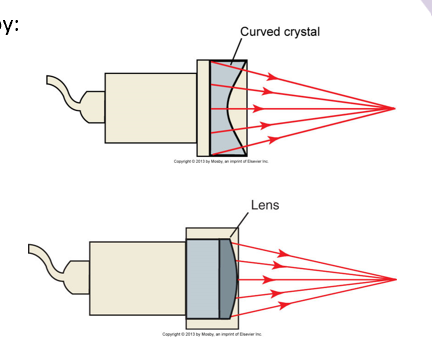
sound may be focused by:
curved transducer elements
using a lens
phased arrays
define frame
a complete scan of the US beam
what does real time sonography do?
presents images (frames) in a rapid sequential format
electronic scanning is performed with…
arrays
automatic scanning of the sound beam is performed how??
electronically
automatic scanning provides a means for…
sweeping the sound beam through the tissues rapidly and repeatedly
how are arrays operated?
in two ways:
sequencing
phasing
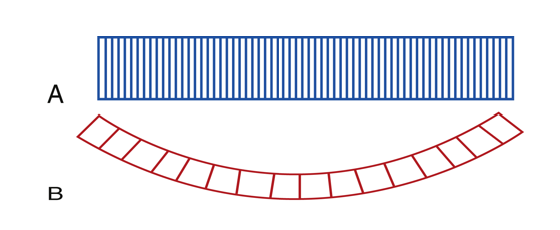
how are elements arranged?
in a straight (linear) or curved (convex) line
what is sequencing?
sweeping of the beam to allow for real-time scanning
what is phasing?
beam steering and focusing
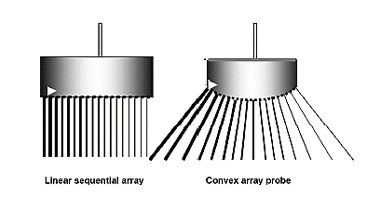
what is linear sequenced array?
aka sequencing (which is sweeping the area)
straight line of rectangular elements
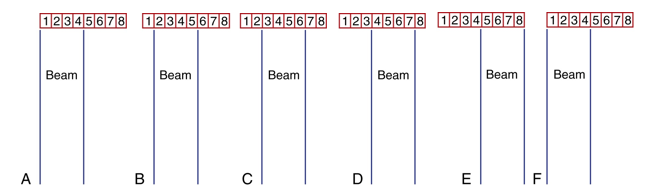
how is linear sequenced array operated?
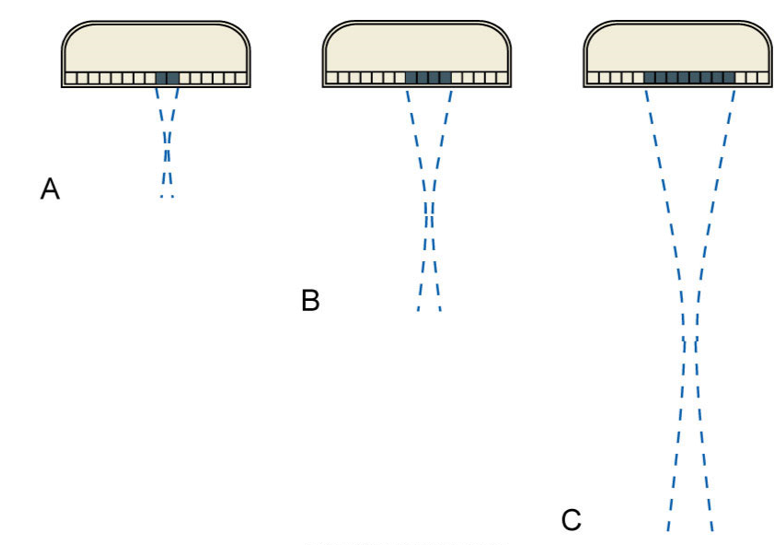
by applying voltage pulses to GROUPS of elements in succession
what does linear sequenced array do to image quality?
increases line density= improved image quality
another name for convex sequenced array?
curved array
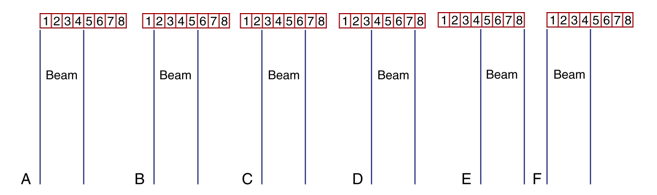
what is convex sequenced array?
curved line of elements that created a sector image
difference between convex sequenced array and linear sequenced array?
operate similarly except pulses travel out in different directions from different points across the curved surface
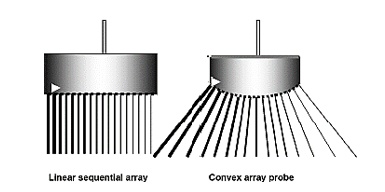
what is phased array also known as?
linear phased array
how is phased array operated?
by applying voltage pulses to most or all of the elements (not groups) but with small time differences (delays) between them
resulting sound pulse is sent out in a specific path direction
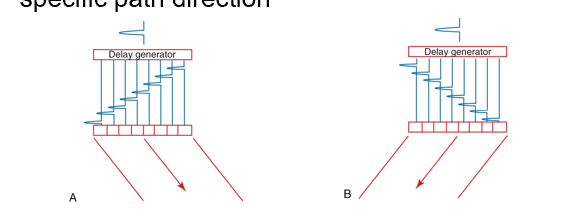
what is beam steering?
phasing is applied to arrays to steer the beam by sending out several pulses from each group with different phasing
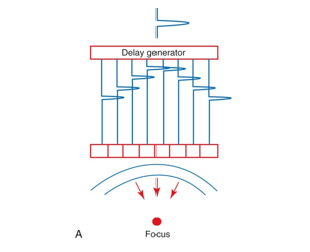
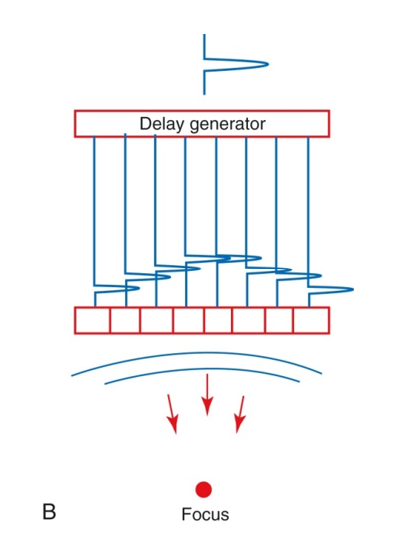
what is electronic focusing?
phased array can also focus the beam
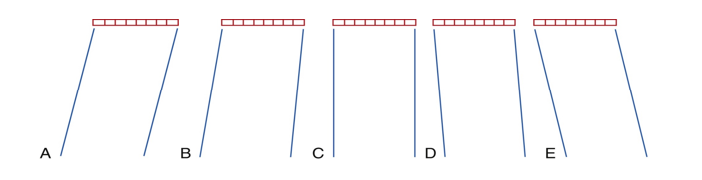
a greater curvature would place the focus…
closer to the transducer
less curvature moves the focus….
deeper
what does aperture focusing do?
varies the number of crystal activated to focus the beam
what groups of aperture focusing are used for short focal lengths?
smaller groups
what is the dimension perpendicular to the scanning plane known as?
slice/ section thickness dimension