2.2 - Demand and PED (Price Elasticity of Demand)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Define demand.
The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price in a given time period.
Define effective demand.
When a desire to buy a product is backed up by an ability to pay for it.
Define latent demand.
Exists when there is a willingness to buy among people for a good or service, but where consumers lack the purchasing power to be able to afford the product.
Define derived demand.
Arises due to the demand for another product.
Define the law of demand.
For most goods and services, the quantity demanded varies inversely with its price.
As prices fall, consumer demand _________.
increases
As prices rise, consumer demand ________.
decreases
The demand curve is _________ sloping due to the _______ relationship between quantity demanded and price.
downwards, inverse
Define individual demand.
The demand for a good or service by an individual consumer.
Define market demand.
The total demand for a good or service, found by adding together all individual demands.
What is the cause of a movement along the demand curve?
A change in price.
What is a price increase on a demand curve?
Movement upwards along curve - causes contraction in demand.
What is a price decrease on a demand curve?
Movement downwards along curve - causes expansion in demand.
What is the impact of a contraction in demand on a consumer?
They are worse off, as they can’t afford to buy as many goods - reduces standard of living
What is the impact of a contraction in demand on a producer?
Sales and profits will fall, and market share will reduce, especially if competitors are not raising their prices
What is the impact of an expansion in demand on a consumer?
They are better off as they can afford to buy more goods, increasing social sustainability and standards of living
What is the impact of an expansion in demand on producers?
Sales and profits will rise. Competitors may be forced out of market if they can’t compete.
What is a shift of the demand curve?
When the whole demand curve shifts outwards (to the right) or inwards (to the left).
What mnemonic helps one remember the factors that cause a shift in the demand curve? What does it stand for?
Population
Advertising
Substitute (price of)
Incomes and the economic situation
Fashions
Interest rates and govt policies
Complements (price of)
PASIFIC
How does population cause a shift in the demand curve?
if population rises / falls, demand for goods and services may rise / fall
if there is a large proportion of the population in an age band, there may be more demand for relevant goods and services
If there is a larger proportion of the population that is one gender, there may be more demand in relevant goods and services
How does advertising cause a shift in the demand curve?
Increases demand for goods and services, by raising awareness
How does substitutes (price of) cause a shift in the demand curve?
Substitutes are goods and services that can be used in place of another good or service. If price for one product rises, demand will fall, as people change to buying the other one (demand for other one rises), e.g. PG Tips Yorkshire.
How does incomes and the economic situation cause a shift in the demand curve?
If incomes rise, consumers are able to buy more goods and services - causes outward shift of demand curve.
Inferior goods (lower-quality) may see fall in demand as consumers decide to buy better quality goods, because of their higher incomes
How does fashions cause a shift in the demand curve?
Most people prefer to buy goods and services that are in taste and trendy - demand for these goods and services rise
How does interest rates and govt policies cause a shift in the demand curve?
Banks may change interest rates, making cheaper / more expensive to borrow money - this could lower demand.
Governments may pass laws making some goods or services compulsory, increasing demand for those goods or services.
How does complements (price of) cause a shift in the demand curve?
Complements are goods and services that go together, e.g. fuel and cars, or fish and chips. If demand for one rises, the demand for the other is likely to rise too.
A leftward shift of the demand curve means that people want ____ of a good, whatever it’s _____.
less, price
A rightward shift is good news for producers who are to ____ and ____ more of their goods. In making more goods, producers may be able to benefit from economies of scale where average _____ fall as output _____. This increases producers’ _______ and provide them with more funds to ______.
make, sell, costs, profits, invest
A leftward shift is very worrying for firms as sales ________ will fall and so will _______. At worse, this could even threaten the ________ of a firm and cause a firm to go out of ________.
revenue, profits, survival, business
Define price elasticity of demand.
Measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in a product’s own price.
Define elastic demand,
When the %change in quantity demanded is more than the %change in price.
Define inelastic demand.
When the %change in quantity demanded is less than the %change in price.
What is the formula for PED?
%change in quantity demanded / %change in price
What is the formula for working out a %change?
difference / original
If PED of a product = -0:
What does this mean
What term is given to the product
Give an example of a product that is described like this
Means demand does not change whatever the change in price
perfectly inelastic
Hard drugs
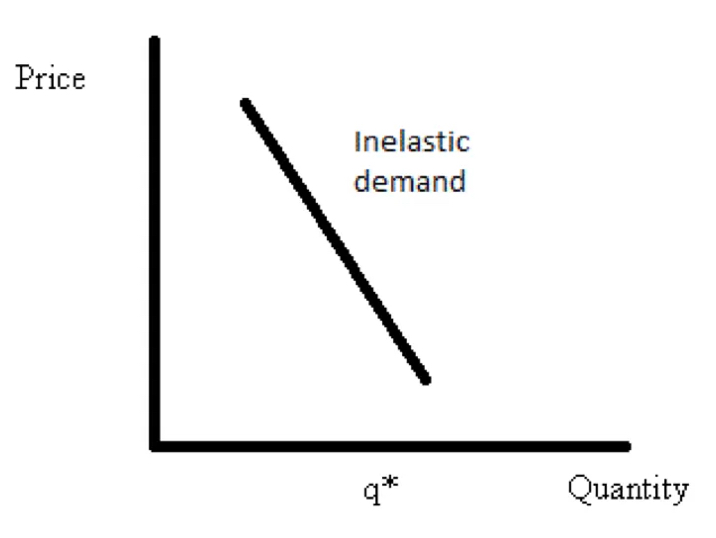
If PED of a product is from -0 to -1:
What does this mean
What term is given to the product
Give an example of a product that is described like this
%change in demand is less than the %change in price
Price inelastic
Petrol, cigarettes
If PED of a product = -1:
What does this mean
What term is given to the product
Give an example of a product that is described like this
%change in demand is equal to the %change in price
Unitary elastic
Most goods and services
If PED of a product is from -1 to -infinity:
What does this mean
What term is given to the product
Give an example of a product that is described like this
%change in demand is more than the %change in price
Price elastic
Designer clothes, holidays, etc.
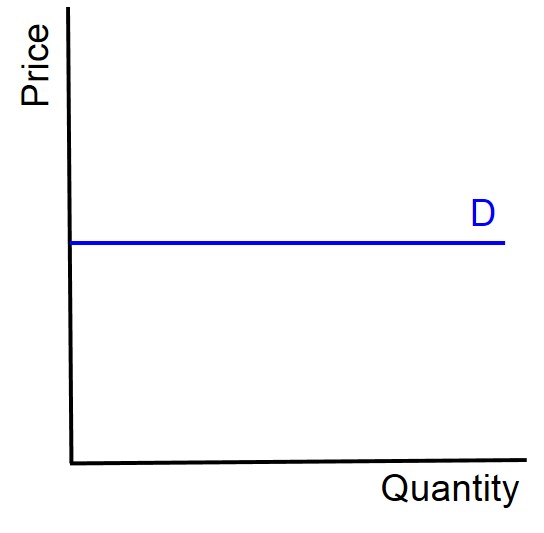
If PED of a product = -infinity:
What does this mean
What term is given to the product
Give an example of a product that is described like this
if firm increased price, demand would fall to zero. If firm decreased price, demand would rise to infinity
Perfectly elastic
No real world examples
What does the demand curve for perfectly inelastic demand look like?

What does the demand curve for price inelastic demand look like?
What does the demand curve for unitary elastic demand look like?
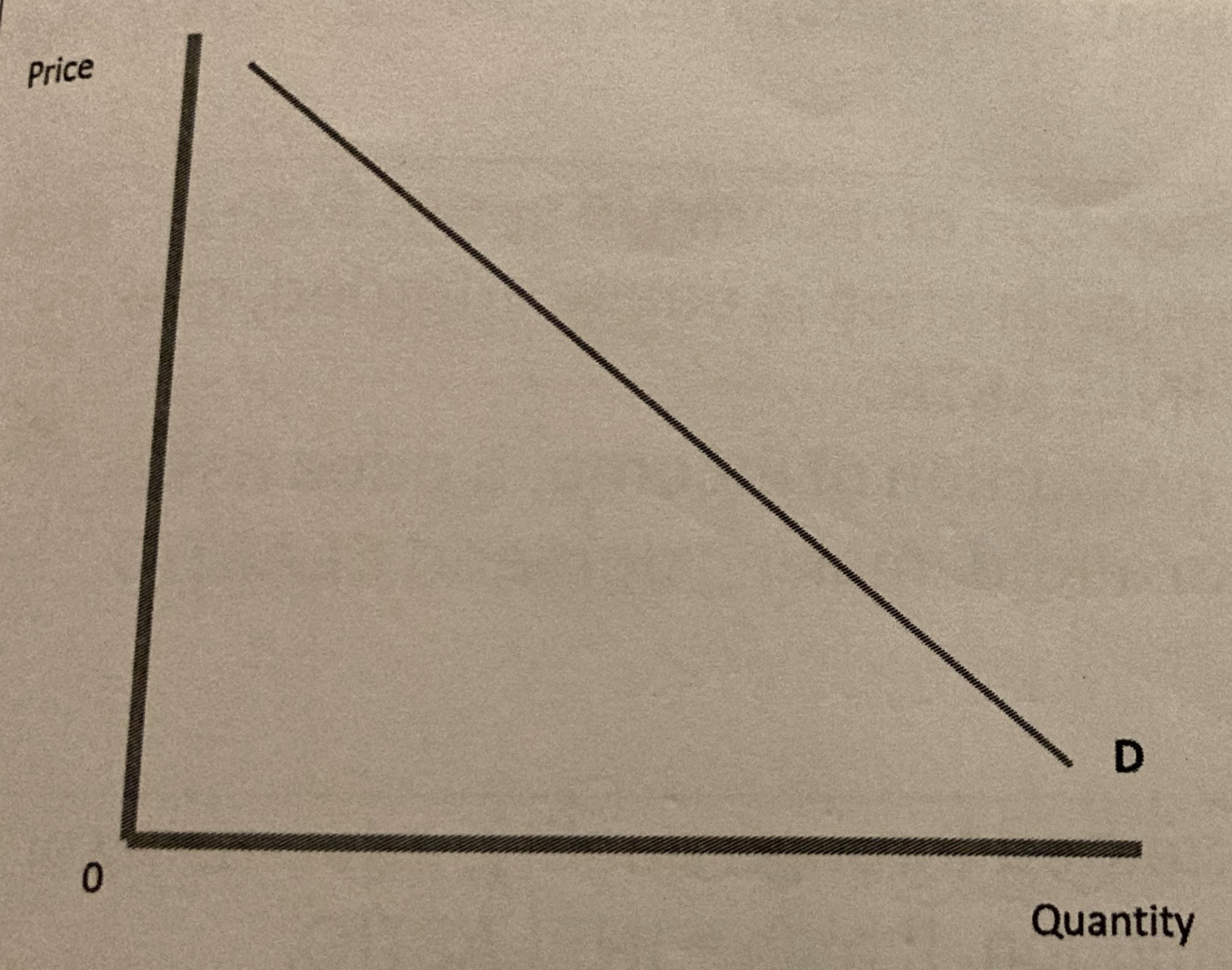
What does the demand curve for price elastic demand look like?

What does the demand curve for perfectly elastic demand look like?