Triangles of the Neck
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
what is the neck a conduit for?
conveying independent systems from the cranium to the thorax and vice versa
what does the investing fascia of the neck cover?
superficial muscles
(trapezius and sternocleidomastoid)
what does the pretracheal fascia cover?
surrounds the viscera
(thyroid, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, and trachea)
the part of the pretracheal fascia that covers the posterior surface of the pharyngeal muscles is called what?
buccopharyngeal fascia
what does the carotid sheath cover?
the neuromuscular bundle of the carotid arteries, internal jugular vein, and vagus nerve
how many carotid sheaths do we have?
2
what does the prevertebral fascia cover?
surrounds the epaxial (situated above axis of skeleton) muscles, prevertebral muscles, scalene muscles, and vertebra in a continuous sheath
prevertebral muscles include what spinal muscles?
longus capitis and longus colli
what is the clinical relevance of these fascial layers?
the various fascial planes between the compartments of the neck provide ideal pathways for the spread of infection from the oral cavity down into the thorax
one of the most important fascial planes is what?
the retropharyngeal space also known as the danger space
where is the retropharyngeal space located? what does it contain?
between prevertebral fascia and the buccopharyngeal fascia containing loose areolar tissue
what does the retropharyngeal space communicate with?
the superior mediastinum and gives route for infection from the neck to the thorax
what is the most common cause of infection transmission down the retropharyngeal space?
abscessed tooth
what does the sternocleidomastoid do?
divides the neck into the anterior and posterior triangles
what are the boundaries of the posterior triangle of the neck?
Anterior: Posterior border of sternocleidomastoid
Posterior: Anterior border of Trapezius
Base: superior border of clavicle
Roof: investing fascia of deep cervical fascia
Floor: Prevertebral fascia covering splenius capitus, levator scapulae, and scalene muscles
The posterior triangle is farther subdivided into two smaller triangles by what? what are these triangles called?
subdivided by the inferior belly of the omohyoid into occipital triangle (larger) and supraclavicular triangle (smaller)
what is located within the posterior triangle?
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus
- inferior belly of omohyoid
- thyrocervical trunk
- subclavian artery/vein within supraclavicular triangle
what are the boundaries of the anterior triangle of the neck?
- anterior border of sternocleidomastoid
- inferior border of mandible
- medial plane of the neck
the anterior triangle of the neck is further subdivided into what triangles?
- Submental triangle (unpaired)
- Digastric triangle (paired)
- Muscular Triangle
- Carotid Triangle
what are the boundaries of the submental triangle?
- Apex: Chin
- Base: Hyoid
- Legs: right and left anterior belly of digastric
- Floor: mylohyoid
what is located in the submental triangle?
submental lymph nodes
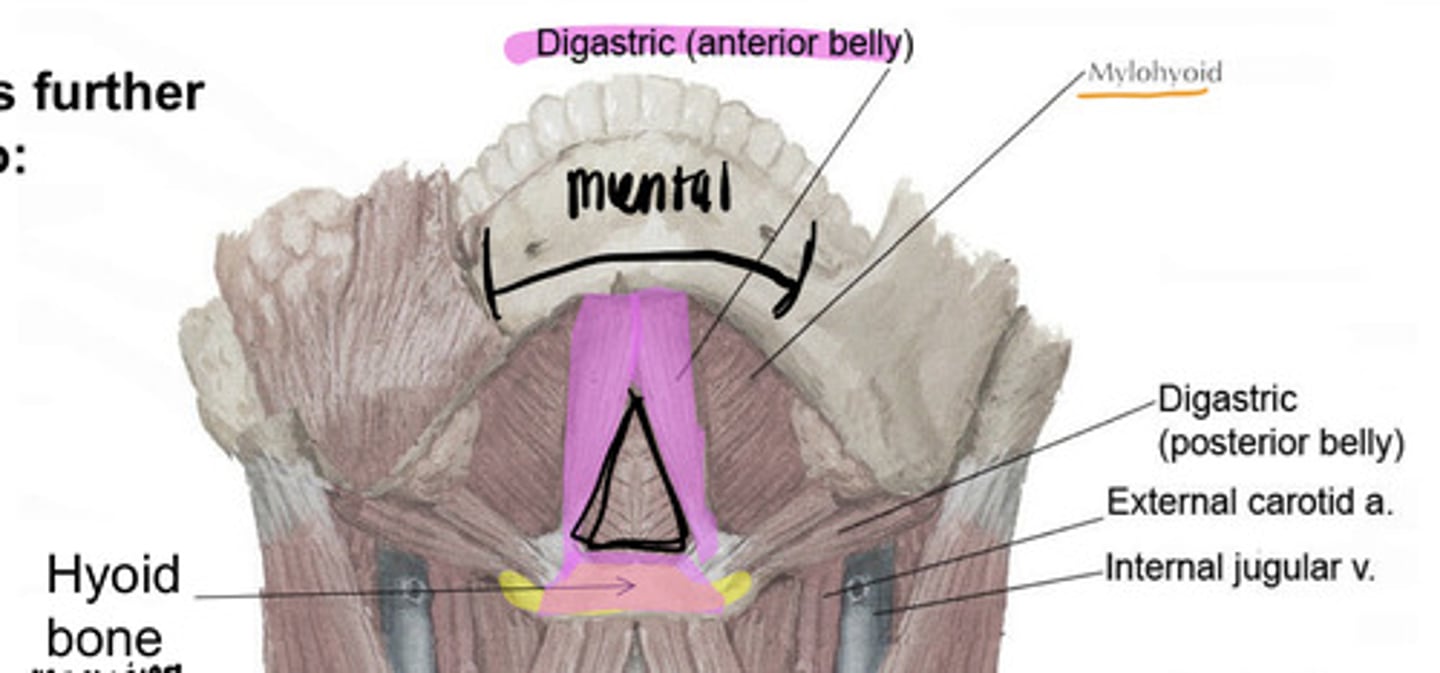
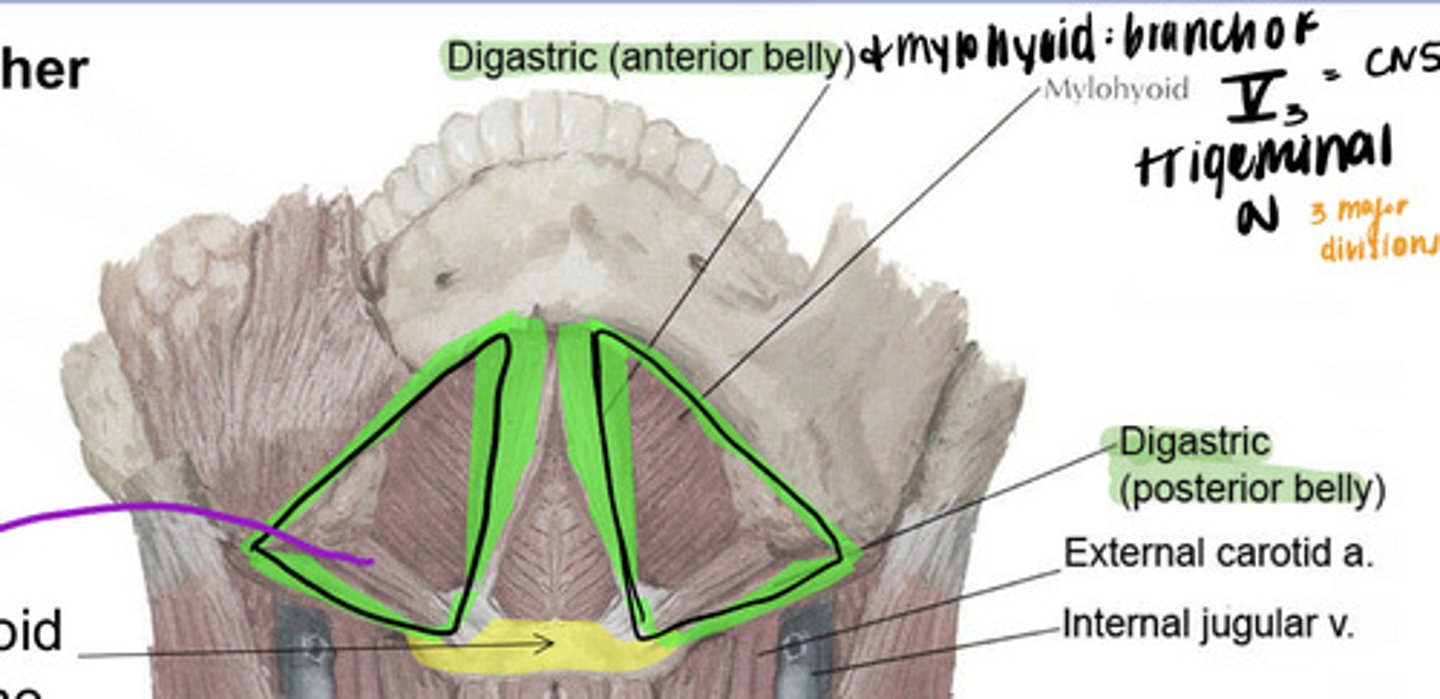
what are the boundaries of the digastric triangle?
Superior: Mandible
Inferior: Posterior belly of Digastric
Medial: anterior belly of digastric
Floor: Mylohyoid
what are the contents of the digastric triangles?
- stylohyoid muscle
- facial artery and vein
- submandibular gland
- submandibular lymph nodes
what innervates the anterior belly of the digastric and the mylohyoid?
branch of V3 (Trigeminal)
what innervates the posterior belly of digastric and the stylohyoid?
Cranial N 7 (facial N)
what makes up the muscular triangle?
- median plane of the neck
- superior belly of omohyoid
- sternocleidomastoid
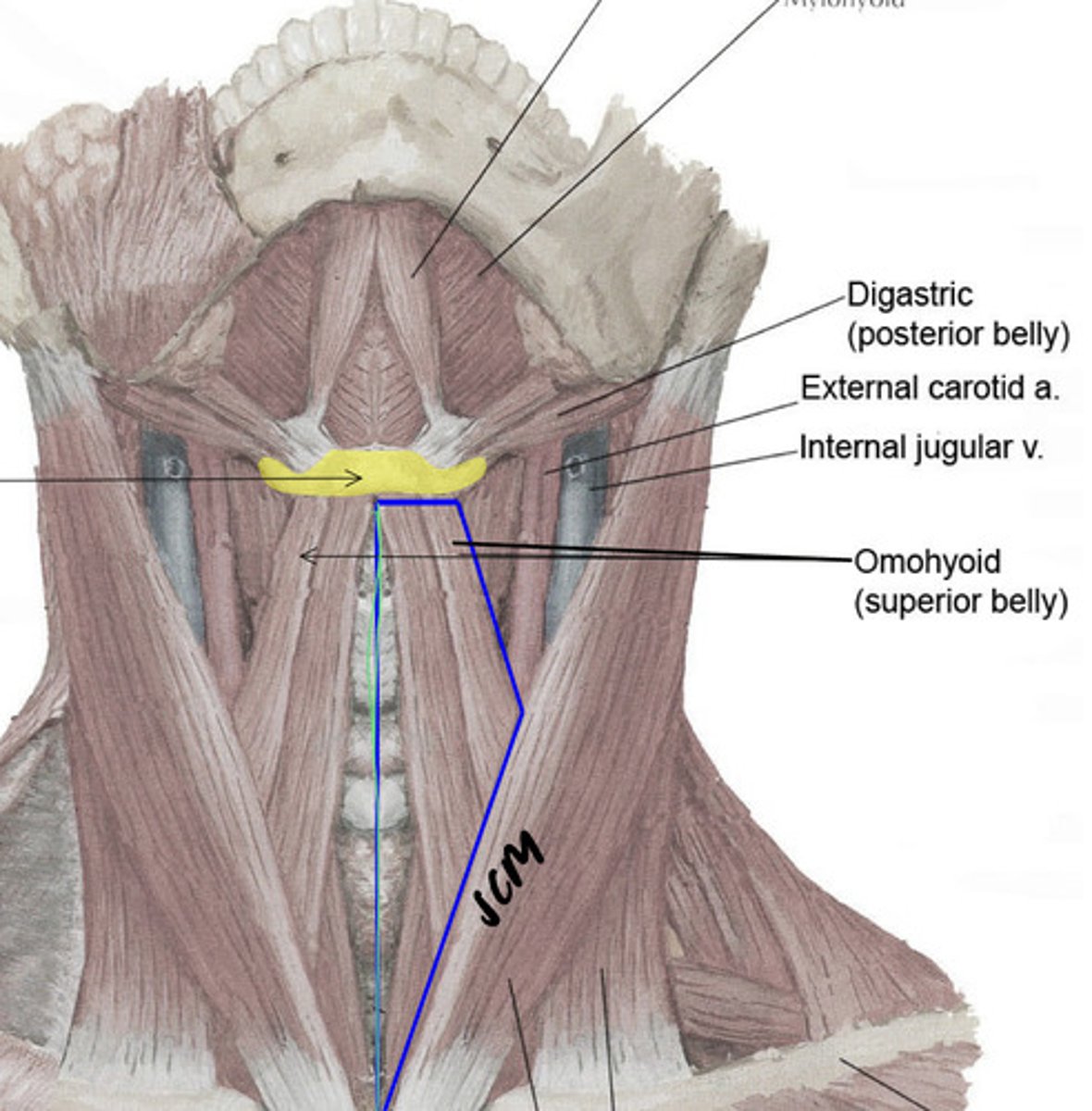
what are the contents of the muscular triangle?
- infrahyoid muscles (below hyoid bone)
- larynx
- thyroid gland and parathyroid glands
- trachea
- esophagus
what makes up the carotid triangle?
- superior belly of omohyoid
- posterior belly of diagastric
- sternocleidomastoid
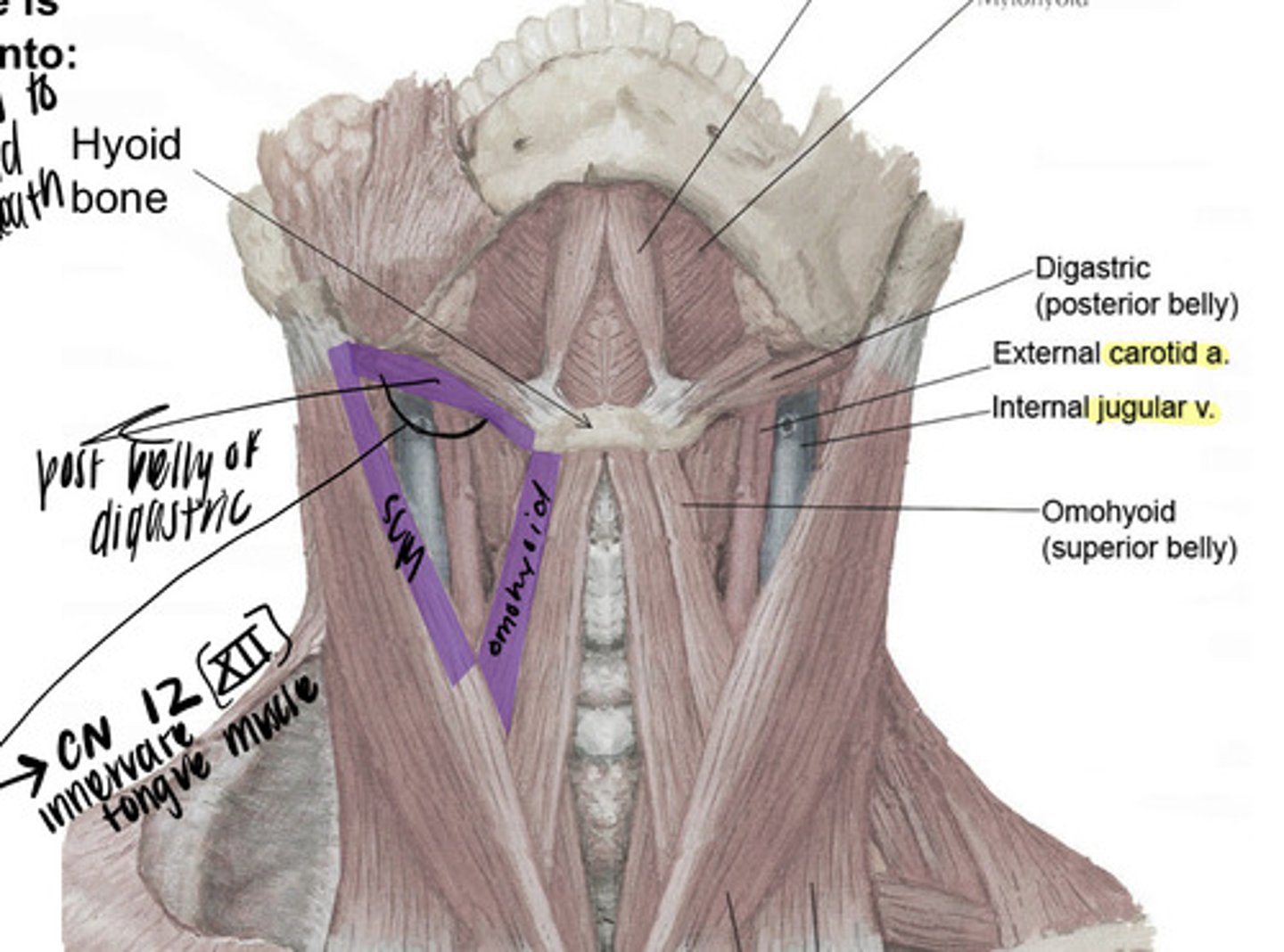
what are the contents of the carotid triangle?
- bifurcation of common carotid into the external and internal carotid arteries
- carotid sinus
- carotid body
- vagus nerve (X)
- hypoglossal N (XII)
- Internal Jugular Vein
what makes a suprahyoid muscle syprahyoid?
its attached to related to the superior aspect of the hyoid bone
what are the suprahyoid muscles?
- posterior belly of digastric
- stylohyoid
- anterior belly of digastric
- mylohyoid
what are the posterior belly of digastric and stylohoid innervated by?
Facial N (CN VII)
what are the actions of the posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid?
- elevate, retract, and fix the hyoid in place
- for speech and swallowing!
what are the anterior belly of digastric and mylohyoid innervated by?
Branches of Trigeminal N V3
what are the actions of the anterior belly of digastric and mylohyoid?
- depress mandible (poorly)
- Elevate and fix the hyoid in place
- for chewing, swallowing, and speech!
what is a suprahyoid muscle deep to the mylohyoid?
geniohyoid
is the geniohyoid a part of the submental triangle?
no!
what is the innervation of geniohyoid?
C1 (spinal nerve, ventral rami of C1)
what makes an infrahyoid muscle infrahyoid?
a strap muscle that attaches to the interior side of the hyoid bone (so found under hyoid)
what are the infrahyoid muscles?
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies)
- sternohyoid
- sternothyroid
- thyrohyoid
which two infrahyoid muscles are found in the same plane next to each other?
superior belly of omohyoid and sternohyoid
if we reflect the superior omohyoid and sternothyroid, what other deep infrahyoid muscles can be found?
sternothyroid and thyrohyoid
what is the action of the infrahyoid muscles?
depress or fix the hyoid in place during swallowing
what is the innervation of the infrahyoid muscles? whats the exception to this?
all infrahyoid muscles are innervated by ansa cervicalis except for the thyrohyoid innervated by C1
what is thyrohyiod innervated by?
C1 (spinal nerve ventral rami)
how is the common carotid branched?
into external and internal carotid arteries
what does the external carotid supply?
face and neck (scalp)
what does the internal carotid supply?
brain and orbit
when does the internal carotid branch?
inside the cranial cavity
at the branching of the internal carotid artery from the common carotid artery there is a swelling known as what?
the carotid sinus
what is the carotid sinus? what doe this mean?
it is a baroreceptor, meaning it regulates blood pressure of the cerebral arteries
what is a small mass of tissue located at the bifurcation of the internal/external carotid that lies in close relation to the carotid sinus?
the carotid body
what is the carotid body? what does this mean?
this is a chemoreceptor meaning its responds to changes in CO2 levels
what are the branches of the external carotid artery?
- superior thyroid artery
- superior laryngeal artery
- lingual artery
- facial artery
- maxillary artery
- superficial temporal artery
DEEP:
- ascending pharyngeal
- occipital
- posterior auricular
what does the superior thyroid artery supply?
the thyroid gland - it actually pierces the thyroid gland
what branches off of the superior thyroid artery?
the superior laryngeal artery
what does the superior laryngeal artery pierce through to supply what?
it pierces through the thyrohyoid membrane to supply the larynx (voice box)
what does the lingual artery supply?
tongue and parts of oral cavity
what does the facial artery pass deep to?
the submandibular gland
what does the facial artery supply?
the external face and oral cavity (may arise in common with lingual artery)
what are the branches of the facial artery?
- inferior and superior labial with a terminal branch of angular artery
what does the maxillary artery supply?
the infratemporal fossa, nasal cavity, and teeth
what does the superficial temporal artery supply?
the temporal region of scalp and side of the head
what does the deep ascending pharyngeal artery supply?
the larynx and pharynx as it arises within the branching of the internal and external carotid
what does the occipital artery supply?
posterior region of the scalp
what does the posterior auricular artery supply?
the region of the ear
what are the branches of the subclavian artery?
- Vertebral artery
- Thyrocervical Trunk
- Inferior thyroid artery
- Transverse Cervical Artery
- Ascending Cervical
- Suprascapular
where does the vertebral artery go?
its deeply located where it passes through transverse foramina on its way to the brain to eventually join and make the basilar artery
what does the thyrocervical trunk supply?
blood to the thyroid, neck, and shoulder
what are the branches of the thyrocervical trunk?
- inferior thyroid artery
- transverse cervical artery
- ascending cervical artery
- suprascapular artery
what are the major veins of the neck?
- internal jugular vein
- external jugular vein
- vertebral vein
what does the internal jugular vein drain?
- superficial face, deep face, and neck
what are the tributaries of the internal jugular vein?
- sigmoid sinus
- inferior petrosal sinus
- retromandibular vein
- facial vein
- lingual vein
- superior thyroid vein
- middle thyroid vein
the internal jugular vein joins with what to form what?
it joins with the subclavian vein to join the brachiocephalic vein which later merges to make the superior vena cava
what vein lies superficial to the sternocleidomastoid?
external jugular vein
what does the external jugular vein drain?
scalp, posterior regions of neck/shoulder, portions of superficial face and deep face
where does the external jugular vein empty into?
the subclavian vein lateral to the internal jugular vein
what are the tributaries of the external jugular vein?
- suprascapular vein
- anterior jugular vein
- retromandibular vein
the retromandibular vein is formed deep within the parotid gland by what?
maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein
the retromandibular vein forms an inverted Y that has branches that drain into where?
the posterior branch drains into the external jugular vein while an anterior branch drains into the internal jugular vein
what comprises the thyroid gland?
2 lobes connected by an isthmus
what does the thyroid gland overly?
the 2nd and 3rd tracheal rings
what embryonic development may be present on the thyroid gland?
pyramidal lobe
what is the thyroid gland associated with?
metabolic regulation
what is the blood supply to the thyroid gland?
- superior thyroid artery from the external carotid artery
- inferior thyroid artery from the thyrocervical artery from the subclavian artery branch
what is the venous drainage of the thyroid gland?
multiple veins draining into the internal jugular vein and the brachiocephalic vein
what nerve travels posterior to the thyroid gland? what does this mean clinically?
the recurrent laryngeal nerve, so clinically if you do surgery on the thyroid gland you want to be careful not to cut this nerve or your patient will be hoarse forever
what are the sympathetic ganglions of the neck?
- superior cervical ganglion
- middle cervical ganglion
- inferior cervical ganglion
what is the terminal ganglion of the sympathetic chain located at the base of the skull anterior to the atlas?
superior cervical ganglion
what does the superior cervical ganglion supply?
sympathetic innervation to the head and neck
what is the last stop for sympathetic synapse?
superior cervical ganglion
the middle and inferior cervical ganglion are much smaller than superior, and they are responsible for innervation to where?
heart and thyroid
the inferior cervical ganglion is often fused with the first thoracic sympathetic ganglion and is called what?
a stellate ganglion
T1-L2 has what fibers?
pre-ganglionic sympathetics
what type of sympathetic fibers are found in the head/brain?
post ganglionic sympathetic
the vagus nerves descend in the carotid sheath and enter the thorax via what?
superior thoracic aperture
in the thorax, the recurrent laryngeal nerves hook around what?
the subclavian artery on the right, the arch of the aorta on the left
what is the final common pathway for lymphatic drainage of the head and neck?
through jugular trunks that drain into the thoracic duct or right lymphatic duct
what are the regional groups of lymph nodes for the head and neck?
Expect a question like "which one of these are not a lymph node of the head and neck" on the exam.
- occipital
- mastoid
- parotid
- buccal
- submandibular
- submental
- superficial cervical
- laryngeal
- tracheal
what is found along the carotid sheath adjacent to the internal jugular vein?
the deep cervical group