10R Transport in animals
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Why do Multicellular organisms need a transport system?
To transport substances around the body of the organism
Why isn't it necessary for single-celled organisms (such as amoeba & paramecium)to have a transport system?
The movement of substances is facilitated through diffusion
What are the two circulatory systems in animals?
The blood vascular and lymphatic systems
What are the features of the blood vascular system?
It must have a circulatory fluid - blood
It must have tubes or vessels through which the fluid can circulate- blood vessels
It must have a contractile pumping device that propel the circulatory fluid around the body'- heart
What are the substances transported around the body?
Respiratory gases- such as O2, CO2
Hormones such as growth hormones, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, and adrenaline
Nutrients such as vitamins and minerals
Blood cells such as erythrocytes and leukocytes
Nitrogenous waste such as urea
Heat
What is blood?
This is the liquid tissue that transports substances around the body
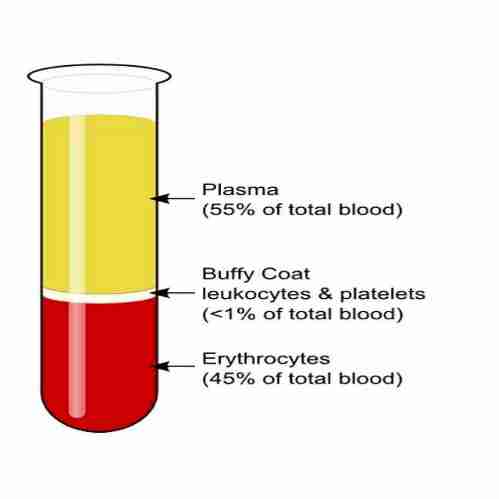
What are the components that make up blood?
55% of blood plasma and 45% of blood cells
What is blood plasma?
This is a pale yellow liquid consisting of 90% water and 10% various substances, including nutrients, heat, antibodies, hormones, and other clotting components in suspension and solution.
What are the types of blood cells present in the blood?
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) main types
Leukocytes (white blood cells) main types
Thrombocytes (platelets)
Where are erythrocytes produced?
These are produced in the marrow of long bones and are destroyed in the liver and spleen.
Describe the structure of the erythrocytes
It contains the red pigment Haemoglobin which is most numerous in the blood and gives it its red colour
They have a disc or biconcave shape which gives them a large surface area for diffusion
They lack a nucleus, live for about 120 to 160 days and are smaller than leukocytes.
What is the function of the erythrocytes?
They transport oxygen as oxyhaemoglobin from the lungs to the body cells.
It contains iron
Describe the structure of leukocytes
They are larger than erythrocytes
They contain a nucleus and live for a long time
What are the types of leukocytes?
Lymphocytes and phagocytes
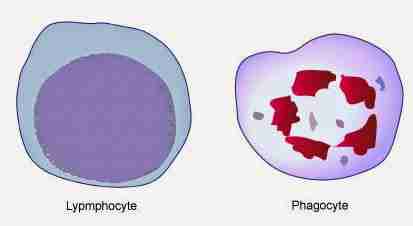
Describe the structure of lymphocytes
It has a large nucleus surrounded by a thin cytoplasm
It's divided into two main groups (T and B cells)
It has a fixed shape
They are larger than erythrocytes
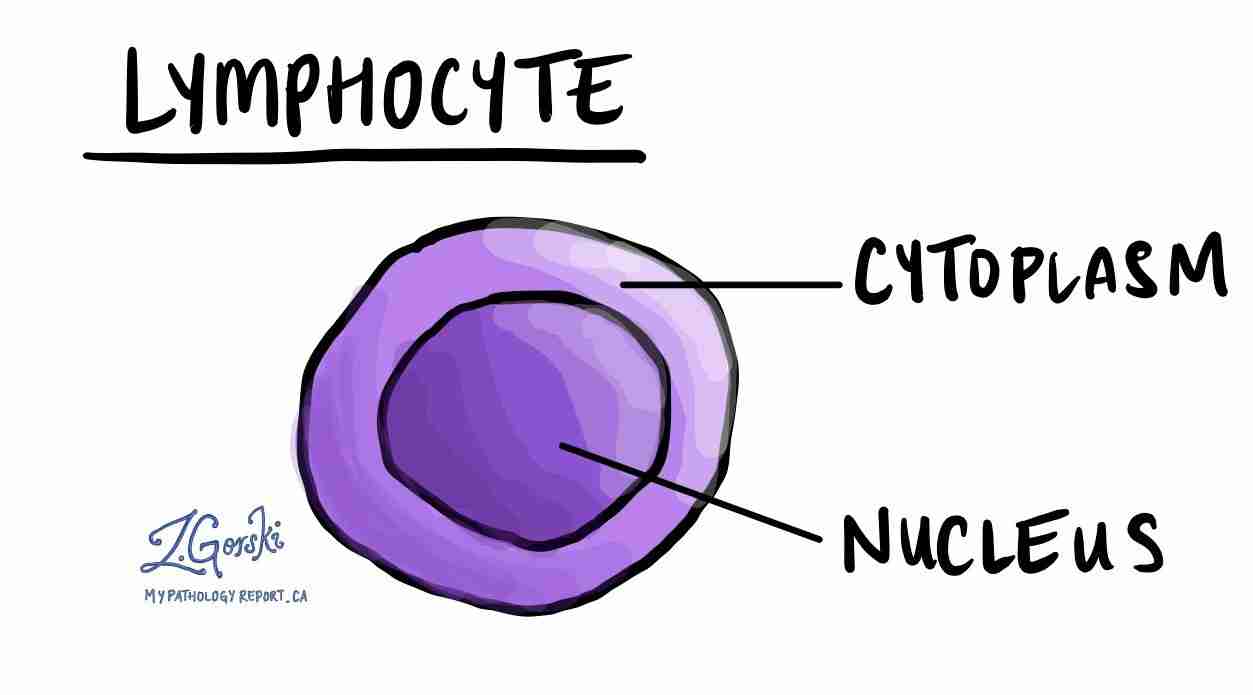
What is the function of lymphocytes?
These produce antibodies that clump and neutralize the pathogens.
Where are lymphocytes produced?
These are produced in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus gland and lymph nodes
Describe the structure of phagocytes
It has an irregularly shaped (lobed) nucleus and cytoplasm packed full of granules
It lives for a long time
It has an amoeboid shape- It can change shape/crawl
They are larger than erythrocytes

What is the function of phagocytes?
This engulfs pathogens in the bloodstream and tissue fluid by surrounding and ingesting them
Where are phagocytes produced?
These are produced in the bone marrow and remain in the blood stream
What are thrombocytes?
These are broken-off pieces of large blood cells (megakaryocytes) of the bone marrow
Describe the structure of thrombocytes
They are irregularly shaped
Lack a nucleus and are fragments of cytoplasm
They live for 5 to 10 days before being destroyed by the liver and spleen.
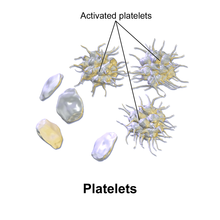
What is the function of thrombocytes?
These help form blood clots to stop or slow down bleeding and help to heal wounds
What are blood vessels ?
These are specialized tuɓes that transport blood around the body.
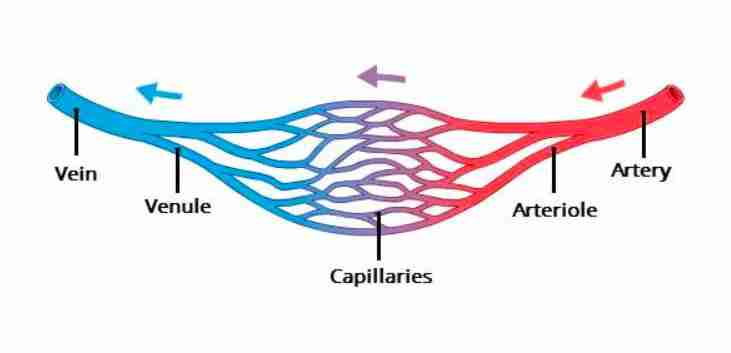
What are the types of blood vessels?
Arteries, veins, and capillaries
Describe the structure of arteries
They are the largest blood vessels in the body
They have a thick muscular elastic wall and are located deep in the muscles
They have a small lumen without valves, which transports blood under high pressure creating a pulse.
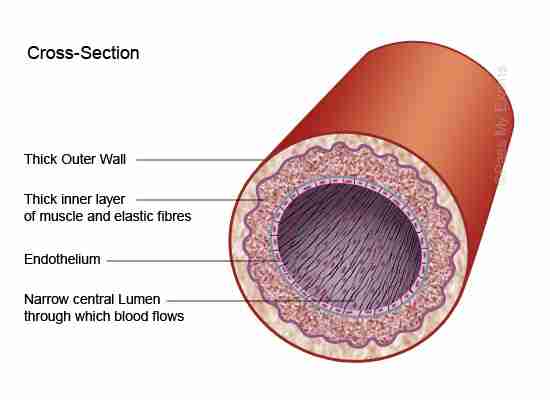
What is the function of an artery?
This transports oxygenated blood from the heart to body cells, except for the pulmonary artery which transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Describe the structure of veins
These are smaller than arteries but larger than capillaries
These have thin elastic walls and are located close to the surface of the muscles.
They have a large lumen with valves to prevent the backflow of blood. Blood is pumped under low-pressure
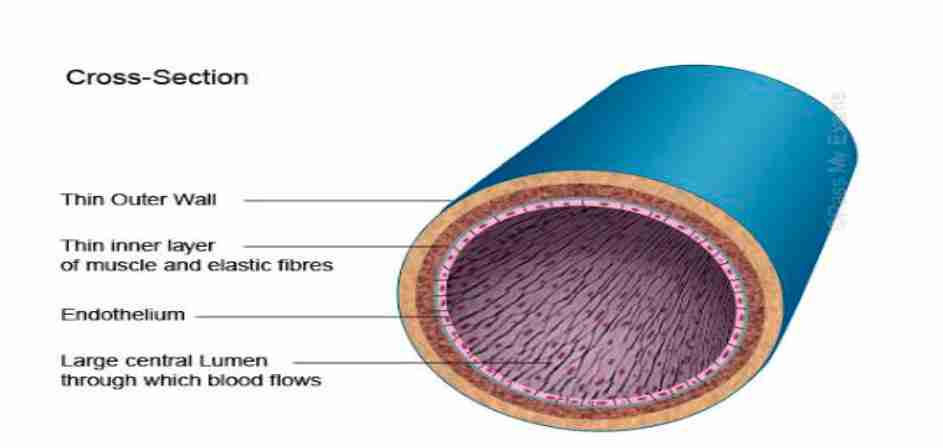
What is the function of a vein?
These transport deoxygenated blood from body cells to the heart with the exception of the pulmonary veins which transports oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Describe the structure of a capillary?
These are the smallest and most numerous blood vessels in the body
They are composed of one layer of cells which facilitates diffusion of substances in and out of the cell.
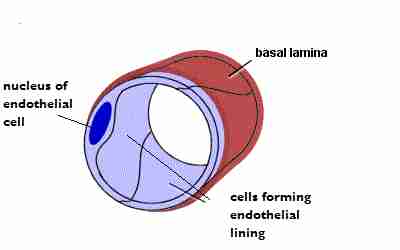
What is the function of a capillary?
These facilitate the exchange of materials between the blood and tissue cells
Where is the heart located?
This is located in the centre of the thoracic cavity between the lungs and is tilted slightly to the left. It is protected from external injuries by the sternum

What is the function of the coronary artery?
This supplies glucose and oxygen to the tissues of the heart which is needed for respiration
Which artery supplies blood to the head and which vein takes blood away from the head?
The carotid artery and the jugular vein
Which artery supplies blood to the arms and which vein takes blood away from the arms?
The subclavian artery and the subclavian vein
Which artery supplies blood to the lungs and which vein takes blood away from the lungs?
The pulmonary artery and the pulmonary vein
What is a blood clot and why is it formed?
This is the result of the skin being cut and causing a blood vessel to brake. It is formed to prevent further blood loss and the entry of disease-causing organisms. .
Describe the process that leads to blood clotting after a cut is formed on the skin
When blood is exposed to air, platelets, along with calcium ions and vitamin K, convert prothrombin an insoluble blood protein into thrombin. Thrombin then turns fibrinogen another insoluble blood protein into fibrin, whose insoluble fibres trap red blood cells and forms a clot.
Define haemorrhage
This is the loss of blood from a vessel
What surrounds and protects the heart internally?
The pericardium which is a tough sac consisting of two membranes
What are the two membranes of the pericardium?
The outer membrane and the inner membrane
Describe the structure of the outer membrane of the pericardium
This is made up of white elastic fibrous tissues attached to the sternum by ligaments.
What is the function of the outer membrane of the pericardium?
This protects the heart against blunt force and sudden external pressure changes.
Describe the structure of the inner membrane of the pericardium
This is made up of loose elastic connective tissues.
What is the function of the inner membrane of the pericardium?
This produces pericardium fluid which reduces the friction between the heart wall and surrounding tissues when the heart beats.
What is the function of the pericardium?
This prevents the heart from being overstretched or overfilled with blood.
What are the four Chambers of the heart?
The right and left atria and the right and left ventricles
Describe the structure and function of the atria
This has thin walls and collects blood
Describe the structure and function of the ventricles
These have thick muscular walls and pump blood away from the heart.
Which of the ventricles have the thickest muscular walls?
The left ventricle because it pumps blood all around the body.