4.3 & 4.5: Muscles
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
forehead
Frontalis
temples
Temporalis
eyes
Orbicularis Oculi
cheeks
Buccinator
jaw
Masseter
mouth
Orbicularis Oris
shoulder
Deltoid
Pectoralis
Pectoralis
front of arm
Bicep
Abdominals
Abdominals
side abs
Oblique
neck
Trapezius
back of arm
Tricep
back
Latissimus Dorsi
butt
Gluteus
back to knee
Sartorius
front of thigh
Quadricep
back of thigh
Hamstring
back of calf
Tibialis
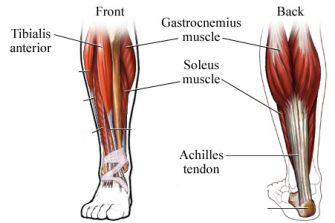
back of calf
Soleus
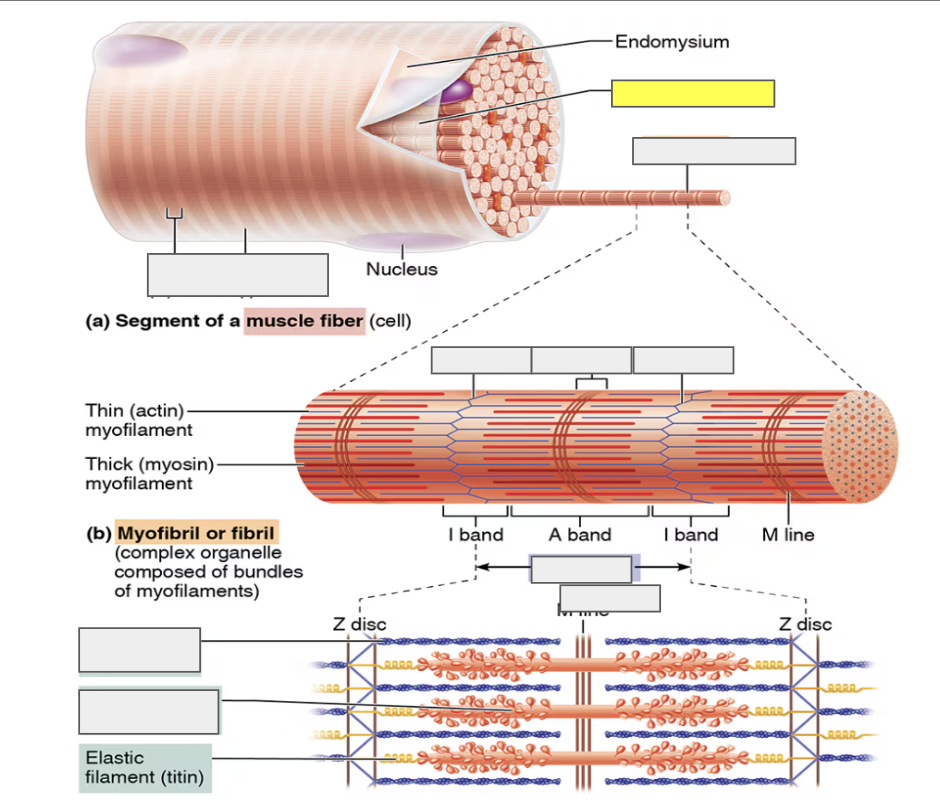
identify
Sarcolemma
identify
Myofibril
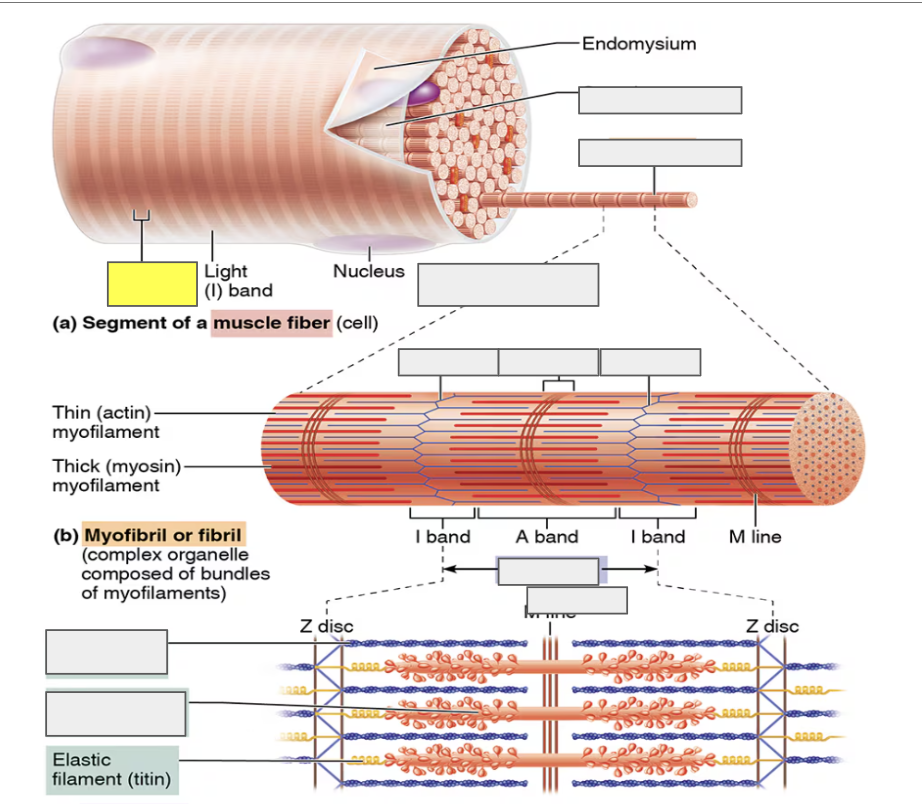
identify
alternating Dark A bands
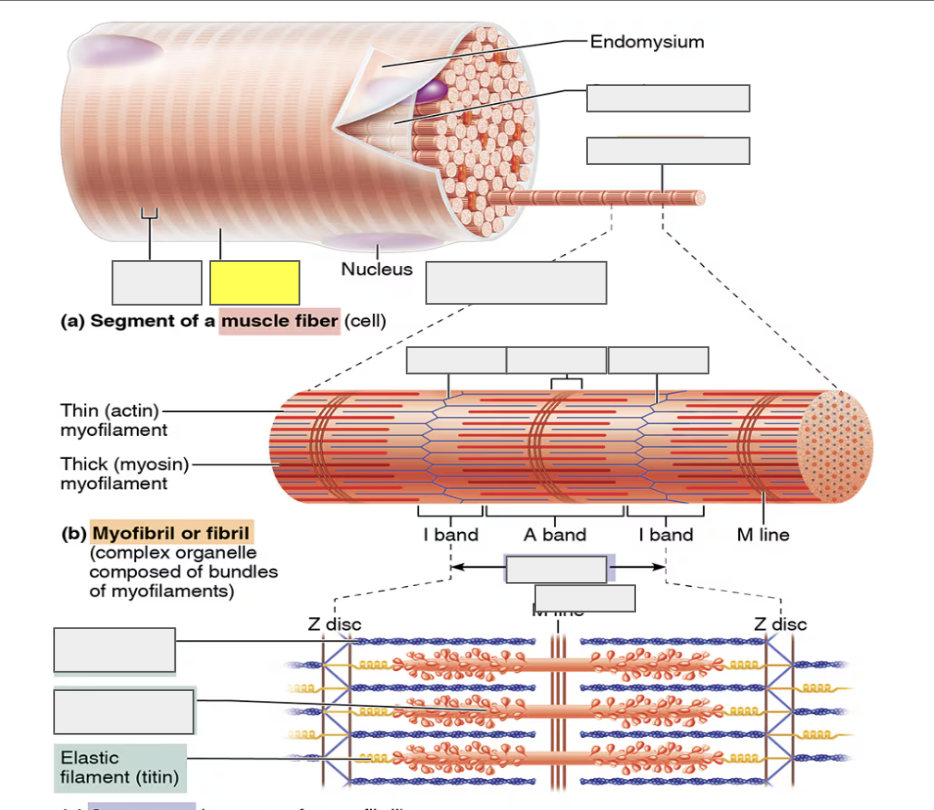
identify
alternating Light I bands
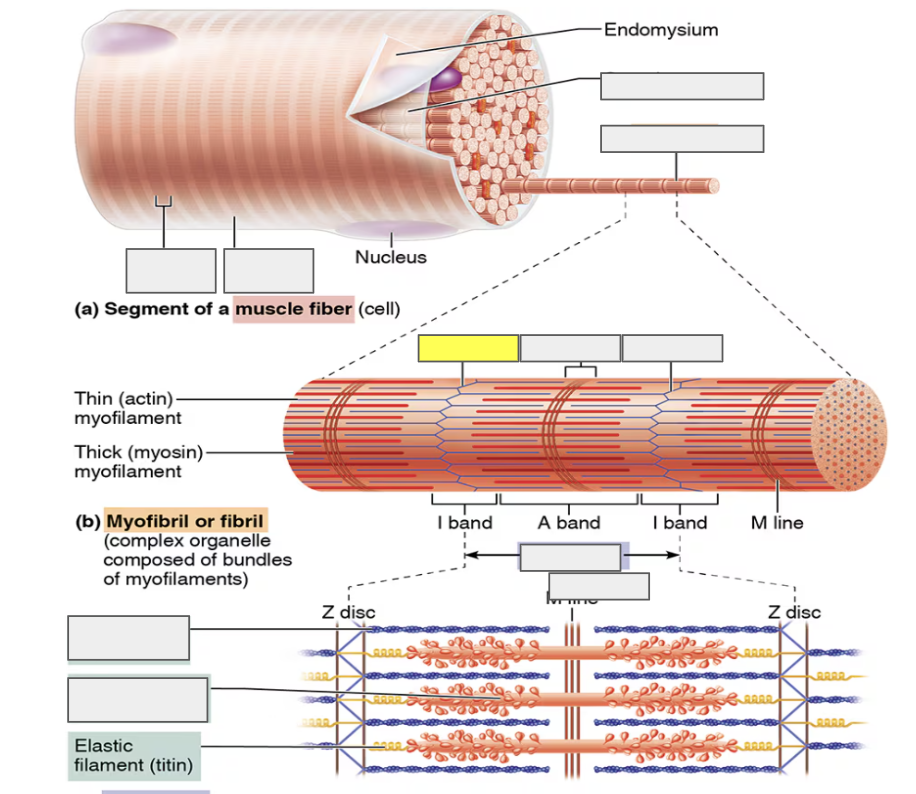
identify
Z disc (I)
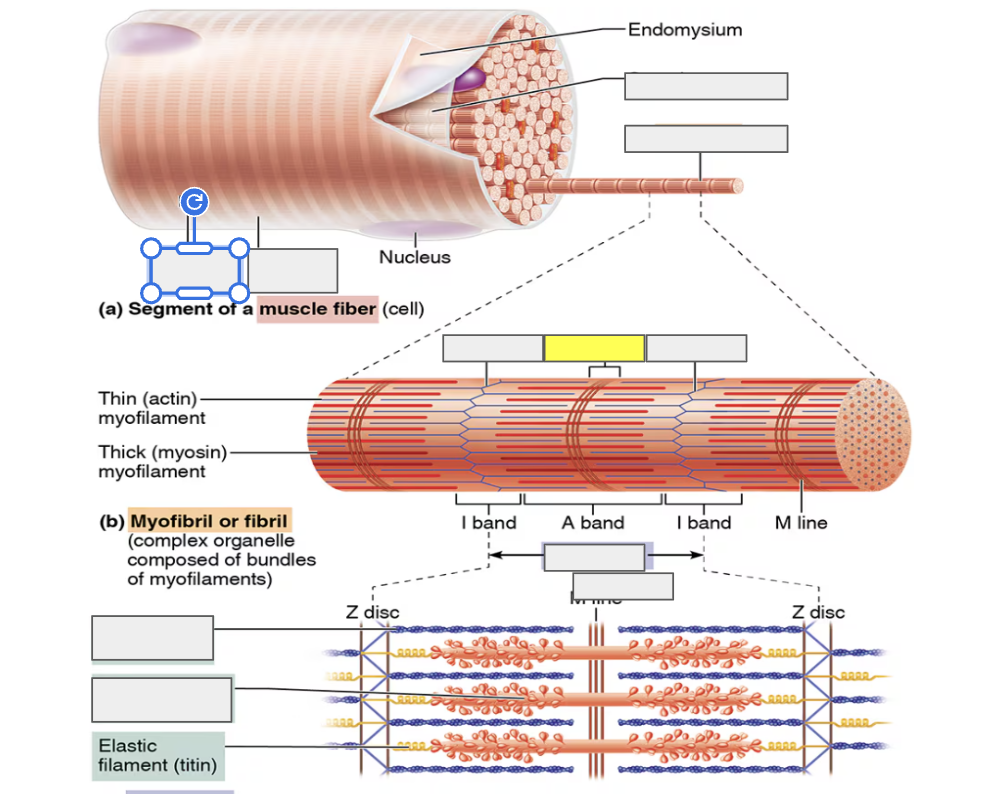
identify
H zone (A)
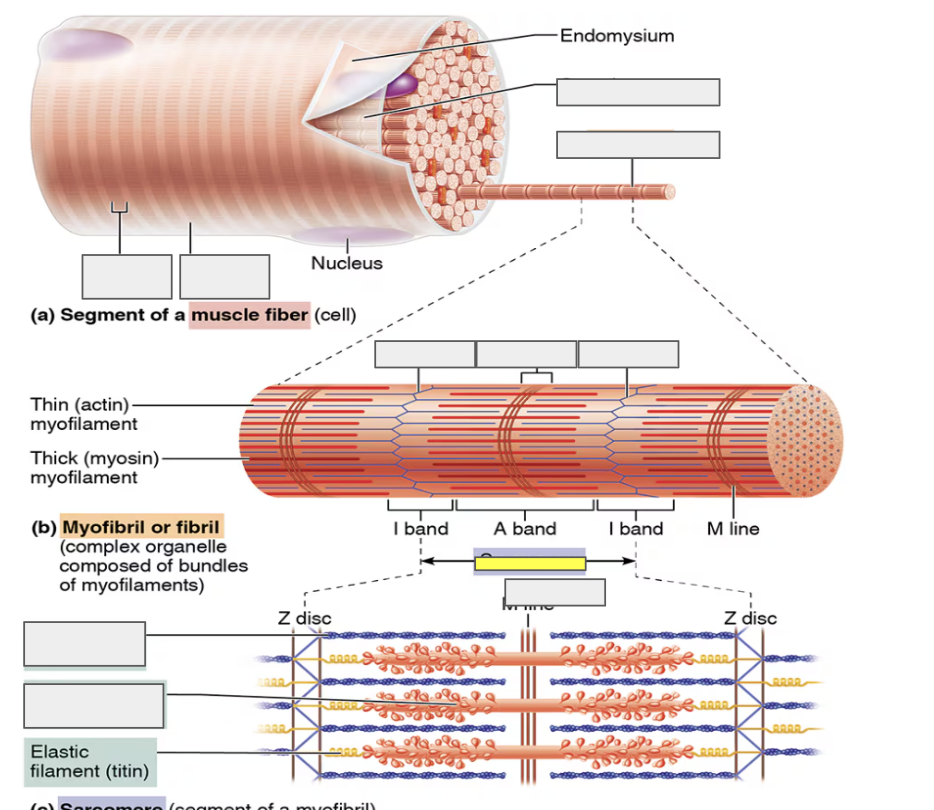
identify
sarcomere
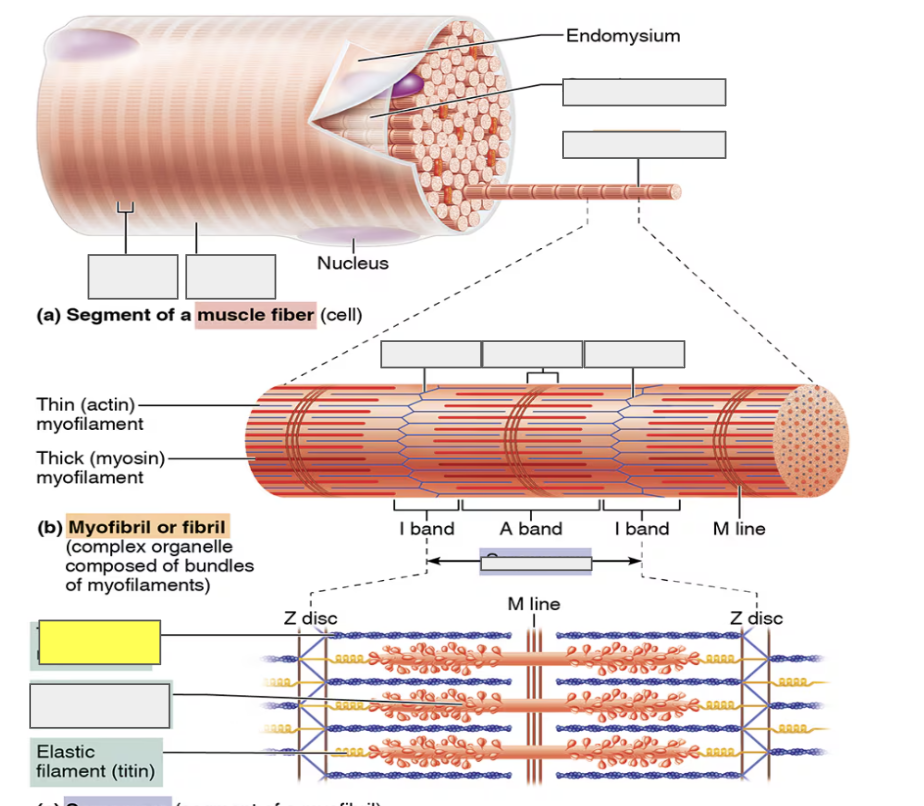
identify
actin (thin myofilament)
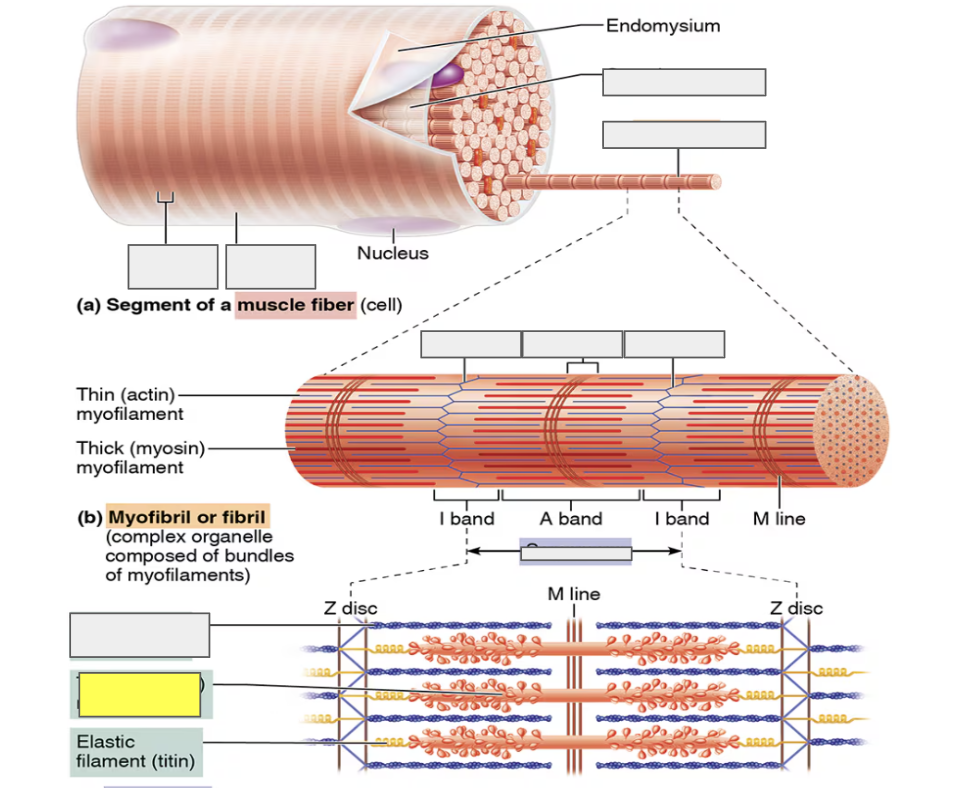
identify
myosin (thick myofilament)
Muscles can only ___
PULL
What happens when a nerve sends an impulse to muscle fibers?
Calcium ions are released.
What does calcium do in muscle contraction?
Releases acetylcholine (ACh)
What does acetylcholine (ACh) trigger on the sarcolemma?
It activates the sodium-potassium pump until an action potential is reached.
What happens after the action potential is reached?
The action potential causes muscle contraction.
What stops the muscle contraction?
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) breaks down ACh.
What happens in the sarcolemma?
Actin & myosin bind together until the muscle is fully contracted
Graded response
Each muscle fiber’s all or nothing response
What happens during ADP Phosphorylation?
Creatine phosphate donates a phosphate to ADP, forming ATP.
Does ADP Phosphorylation need oxygen?
No, it does not require oxygen.
How long does ADP Phosphorylation last?
It depletes quickly.
What happens during Aerobic Respiration?
Forms 32 ATP.
Is Aerobic Respiration fast or slow?
It’s slow but lasts the longest.
What happens during Anaerobic Glycolysis?
Forms 2 ATP.
How long does Anaerobic Glycolysis last?
It depletes quickly
What happens when a stimulated muscle can’t contract?
It’s experiencing muscle fatigue
What causes muscle fatigue?
Lack of oxygen prevents oxidation of lactic acid buildup.
Why is recovery time important between workouts?
It allows cells to replenish oxygen.
What is true muscle fatigue?
When the body shuts down from extreme exhaustion.
What does constant movement create in muscles?
Muscle tone — fibers stay slightly contracted from daily activity.
What happens with inactivity?
Muscles weaken.
What does aerobic exercise (like cardio) do?
Increases blood flow, stores more oxygen in muscles, and improves digestion and coordination.
What does anaerobic exercise (like lifting) do?
Strengthens muscle fibers and connective tissue by forcing strong contractions.