Electromagnetic Waves
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5 and 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Waves
A disturbance in any medium (such as water) which transports energy from one place to another without causing any permanent change in the medium
Transverse waves
Displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of wave travel
Longitudinal or Compressional Waves
Displacement of the medium is parallel to the direction of wave travel
Perpendicular
transverse waves have _________ displacement
Parallel
Longitudinal waves have _______ displacement
water
example of transverse waves
sound waves
examples of longitudinal waves
Speed, Amplitude, Wavelength, Frequency
4 characteristics of all waves
amplitude
The maximum displacement of the medium
strong
amplitude is associated with how ____ the transverse waves are
transverse waves
which waves are specific to x-ray
perpendicularly
transverse waves travel
parallelly
longitudinal waves travel
compression/longitudinal wave
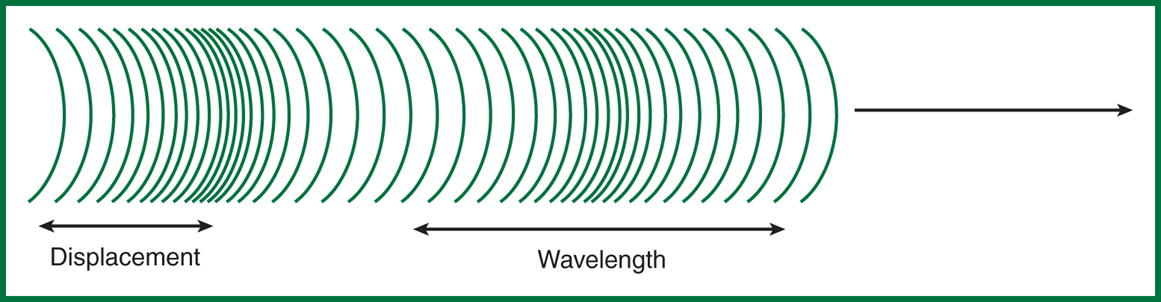
amplitude
displacement can also be referred to as
True
T or F: amplitude can change
transverse waves
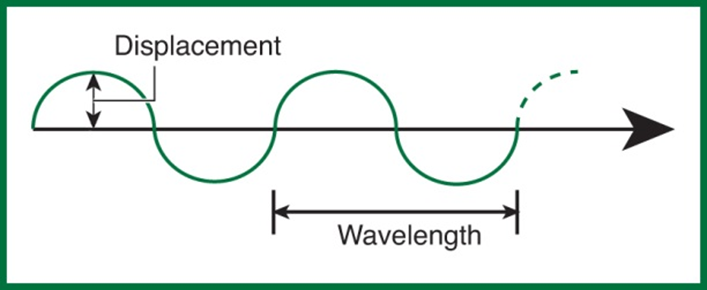
1/2
For transverse waves such as water waves, amplitude is _____ of the distance from trough to crest
expansion, compression
For compressional waves such as sound, amplitude is the distance from the middle of an _________ to the middle of a __________
sound waves
example of compressional waves
water waves
example of transverse waves
inverse square law
amplitude follows the
wavelength
Distance measured between two like points along the wave form
prevent it from spreading it
how do you preserve the amplitude of a wave
height/strength
increasing amplitude increases the ____/___ of the wave
crest
top of a wave
trough
bottom of a wave
crest to crest
For transverse waves, _____ to ______, or beginning point to beginning point
middle, middle
For compressional waves such as sound, this is the distance from the _________ of an expansion to the ________ of the next expansion
cycle
One completion of the wave form
pulses
Each cycle consists of two ______, one positive and one negative
cycle
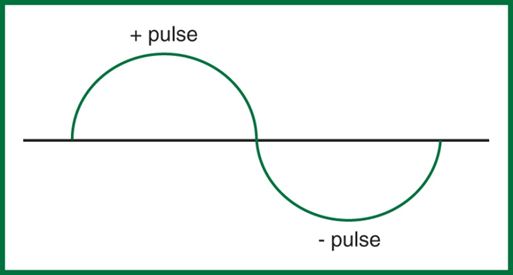
this represents a
circle
For a transverse wave, superimposition of the two pulses creates a
frequency
The number of cycles (waves) that pass by a given point each second
hertz
unit for frequency is
Hz
abbreviation for hertz
speed, or wavelength
Changing the ______ or the _______ will alter the frequency of a series of waves
frequency
increasing the speed increases the
increased
if the wavelength is shortened the frequency is
short
x-rays are short or long waves
wave formula
v = fλ is the
velocity/speed
v represents
frequency
f represents
wavelength
lambda represents
directly proportional
velocity and frequency are _____ _____ to each other in the wave formula
twice
if you are traveling at twice the speed _____ as many waves will strike you per second
no
is velocity constant in the wave formula
directly proportional
velocity and wavelength are ______ _______ to one another in the wave formula
inversly proprtional
frequency and wavelength are ______ _______ to each other in the wave formula
wave formula
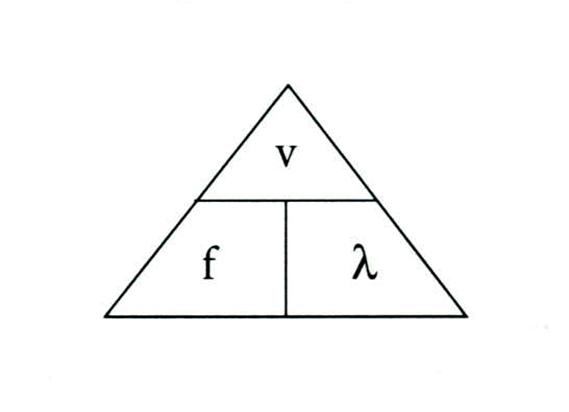
this is a mehtod for
waves per second
hertz is defined as
constant
in electromagnetic wave formula v is
3×10^8 m/s
what is the speed of light
c
abbreviation for the speed of light rather than v
same
Differ from water waves in that electromagnetic waves always travel the ____ speed in a vacuum such as outer space
seconds
For electromagnetic waves such as x-rays, unit conversions are often unnecessary because the speed of light is usually given per second and the unit for frequency is Hertz or cycles per second, so the ______ cancel each other out
electromagnetic wave
we utilize which formula in x-ray
Plank Formula
E = hf represents the
A particular shade of green light has a wavelength of 5 X 10-7 meters. How many waves of this green light strike you each second, i.e., what is its frequency in hertz?
0.6 X 1015 Hz
The frequency of red light is 460 trillion cycles per second, or 4.6 X 1014 hertz. What is the wavelength of this electromagnetic wave?
0.65 X 10-6 meters
who is the father of quantum theory
Planck
in Planck’s fomorula, wavelength is _________ _________ to frequency
inversely proportional
energy is represented by
volts
for Planck’s formula the higher the voltage the ________ the wavelength
shorter
the Planck formula relates wavelength to
enery
h x c=
12.4
What is the minimum wavelength of an 80 kVp x-ray beam?
0.15 Angstroms
What is the kV of a single x-ray having a wavelength of 0.2 Angstroms?
62 kV
the ____ __ represents only the shortest wavelength in the beam
peak kV
the peak kV represents the
shortest wavelength
The push and pull of electric charges and magnets are so similar because they are
different manifestations of the same force
electromagnetic force
the x-ray beam is a __________ beam
divergent
polyenergetic means
many energies
the magnetic field is always ____________ to the electrical field
perpendicular
do electrons have to be traveling down a wire in the form of electricity in order to possess a magnetic field
no