Cog. Neuro: The Developing Brain (L4)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is the Nature VS Nurture debate?
The extent to which cognition & behaviour can be attributed to genes or environment.
Nature = Genetic blueprint
Nurture = Role of experiences
How did Piaget combine the Nature VS Nurture debate?
Considered development as a cyclical process of interactions between the child & their environment based on their progression through stages
What did Piaget define as the genetic contribution to development?
genetic contribution such as developing a brain that is ready to learn in certain ways
What did Piaget define as the environmental contribution to development?
Such as assimilating evidence via experience and then developing new mechanisms in light of feedback obtained
What is a more modern approach to Piaget combined theory of development?
Neuroconstructism.
Interactions between the environment & genetic factors. As the cognitive system matures & transforms, the brain goes through development changes.
What is the Blue print analogy of brain development?
Each connection in the brain is pre-determined
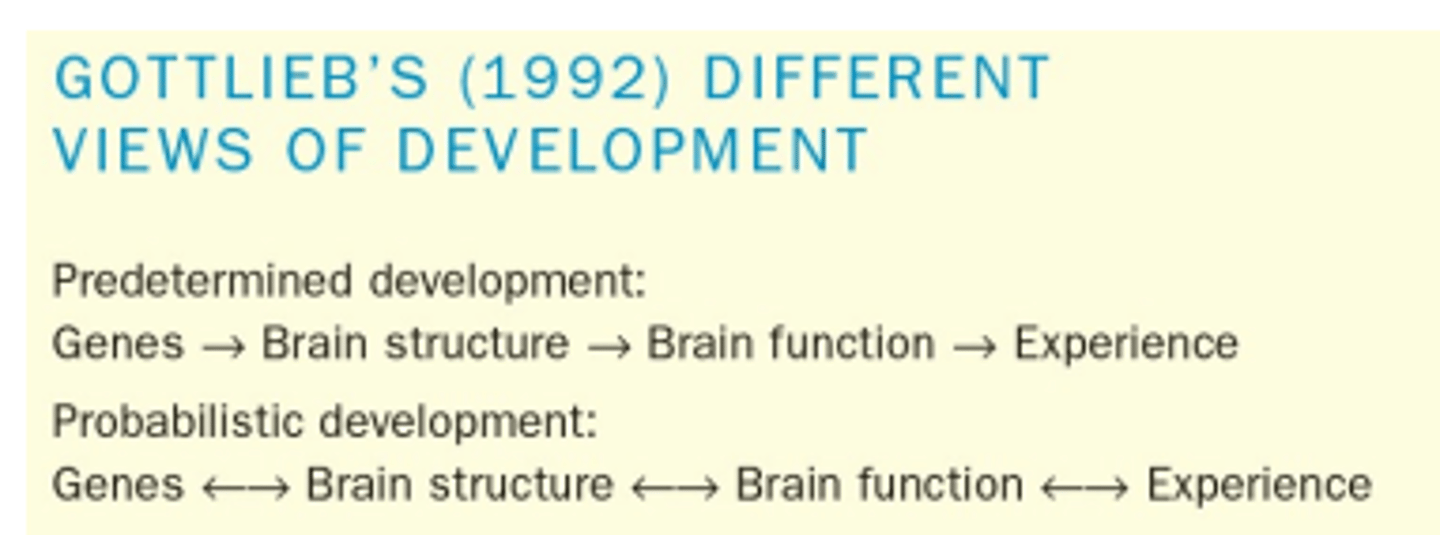
What are Gottlieb's different views on development?
1. Predetermined development: Structure is the same for everyone
2. Probabilistic development: Each stage influences each other
Name 3 stages of prenatal development
1. Cell division
2. Cell specialization
3. Neural tube formation
How many neurons are produced per minute during early development?
During early development, 250,000 neurons are produced per minute
What is Hebbian learning?
Spontaneous electrical activity enables networks to form (e.g. electric activity frm the retina helps to form visual pathways)
Describe how 2 structural features that emerge during early development
1. Folded cortex emerges from having lots of neurons
2. Pattern of gyri/sulci pulled into shape by tension of axon bundles
What is the weight of a new-born's brain VS adult brain?
Newborns = 450 grams.
Adult = 1400grams
What 3 processes help the brain increase in brain size?
1. Synaptogenesis
2. Myelination
3. Glial cell proliferation
synaptogenesis
Process of forming new synapses between neurons
myelination
formation of the myelin sheath around a nerve to allow for improved conduction
proliferation of glial cells
The multiplication or reproduction of glial cells by cell division, resulting in the expansion of their population
What is Plasticity?
Experience dependent change in neural functioning
How does gray matter increase?
Increased grey matter due to synapses, dendrites, axon collaterals & glia cells
What are critical or sensitive periods?
Opportunities for major reorganisation are time limited.
Describe the study into Konrad Lorenz into critical & sensitive periods
Studied how birds recognised their mothers during Filial imprinting (Process where young adults learn to recognize parent)
What are the 2 main features of critical & sensitive periods?
1. Learning takes place within a limited window
2. Learning is hard to reverse by later experience
What are the 2 possible explanations for critical & sensitive periods?
1. genetically programmed synaptogenesis followed by reduced plasticity
2. Closure of window could be initiated by learning itself (e.g. Environmental cue)
What is the Empiricism & Nativist view on innate knowledge?
- Empiricism = New-born's mind is a blank state
- Nativist = We are born with some knowledge
Name 2 ways we can investigate prenatal brain development
1. Prenatal Ultrasound: Different types of tissue (Skull, grey matter, white matter, CSF fluid) have different physical properties
2. Prenatal MRI: Show structure of the brain but still unsure what each component does
What is the Preferential looking paradigm?
If an infant consistently turns their gaze towards some forms more often than others, it must be able to perceive form.
Describe the study by Frantz (1961) & the visual interest test
Involved a looking chamber.
Found:
- 1 week to 3.5 months old = Differential interest in objects was based on pattern differences
- e.g. Turn gaze towards new forms more therefore able to perceive form
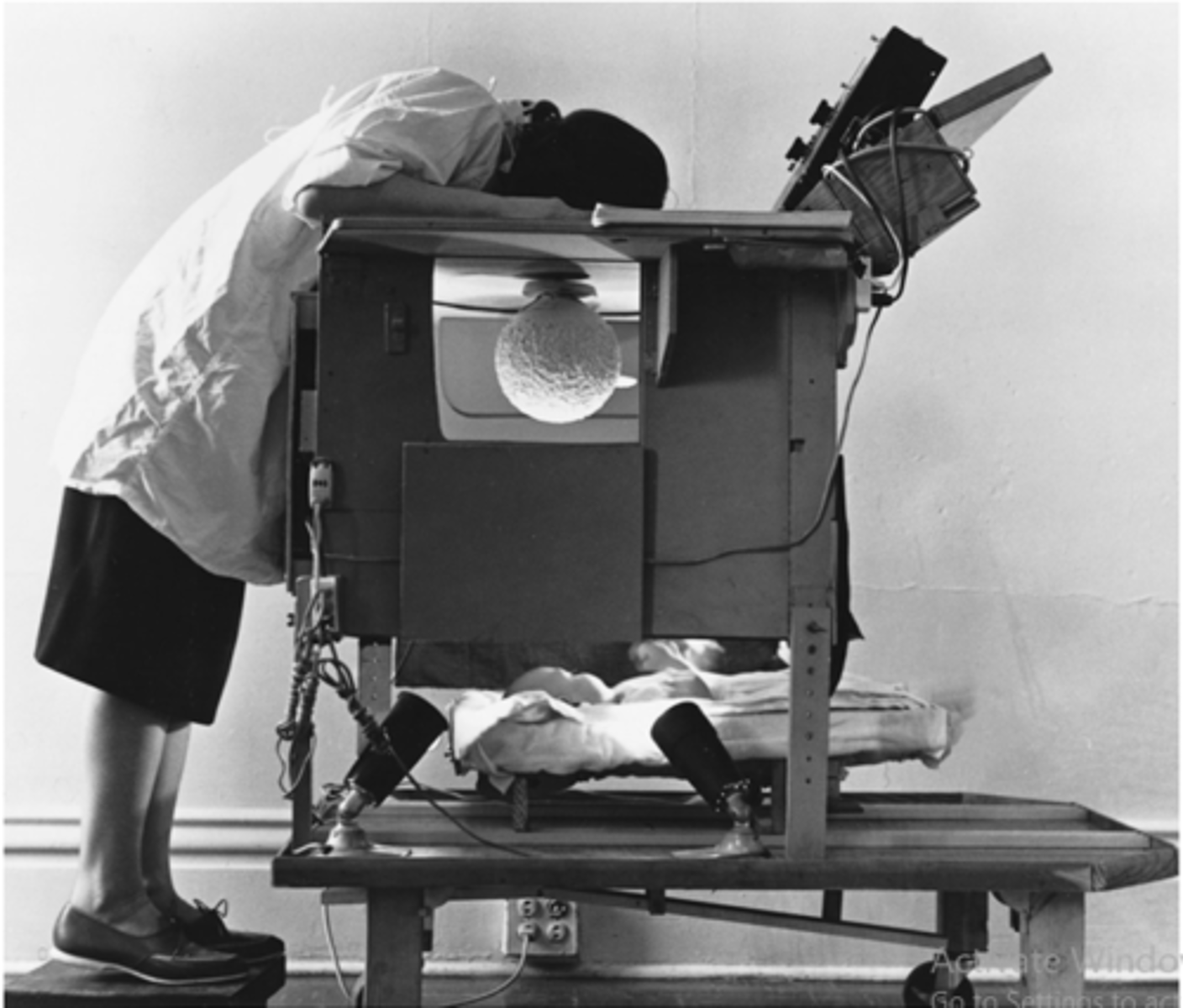
What is a Looking chamber?
- Objects attached to ceiling of looking chamber
- Researcher sees infant's eyes through a peephole in the ceiling
- When image of one object is mirrored in the centre of infants eye, the infant is looking directly at it
- Time infant spends looking at each object is measured
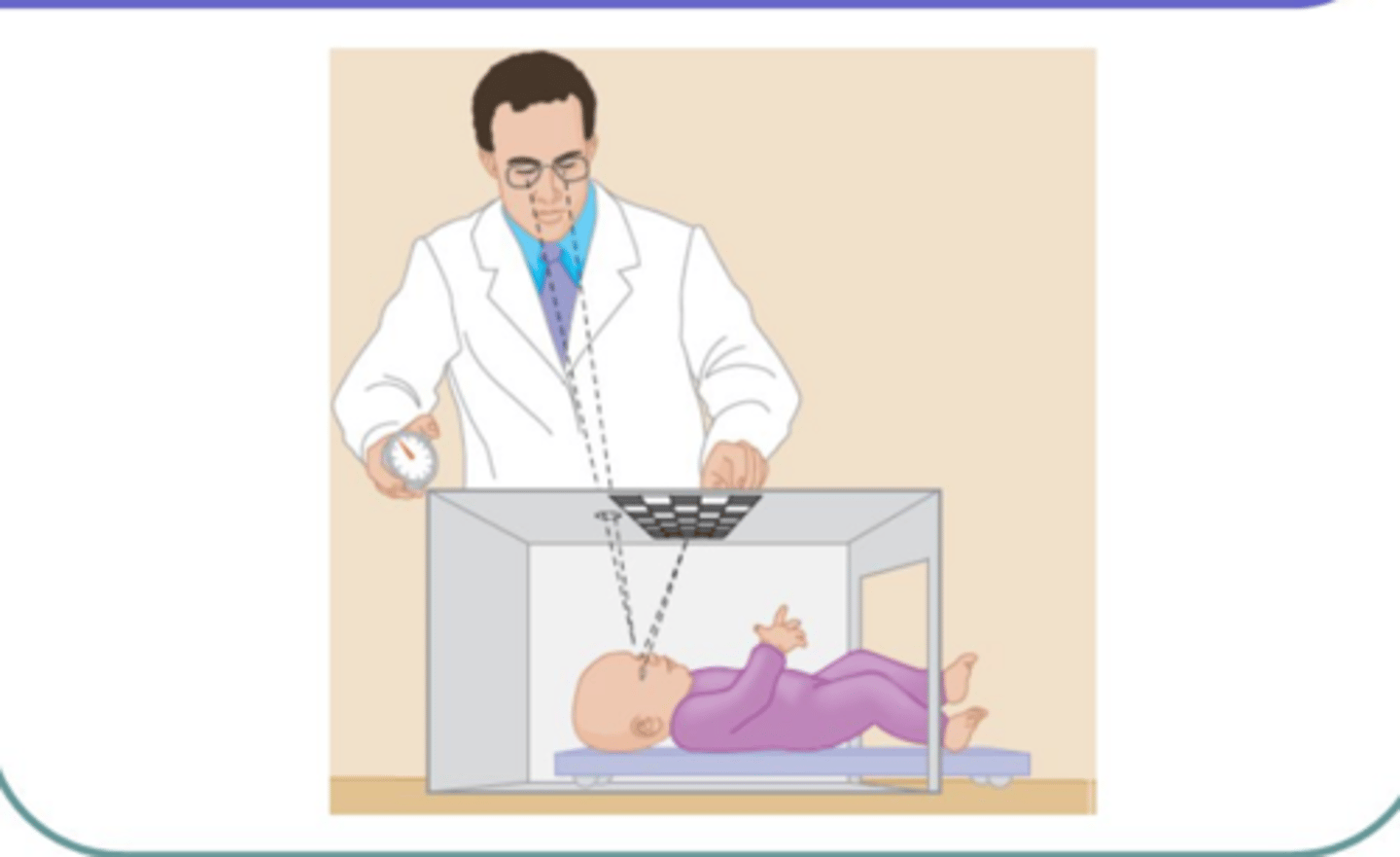
What is the Visual acuity threshold and what was found?
The width of the stripes of the finest pattern was preferred to grey which provides an index to visual acuity.
Found: Width of finest striped could be distinguished decreased as the age of the infant increased.
Therefore, the eye, visual nerve are poorly developed at birth
Describe how we use preferential looking paradigm in a more modern way?
Use video cameras and present stimuli on the screen.
Use infrared eye-tracking to measure where P is looking at screen.
What is the Habituation paradigm?
Infants prefer novelty (aka prefer to see something new)
- Infants are made bored with stimulus A and then it is paired with another stimulus.
- Infants look more at the new stimulus therefore have discriminated the 2 stimuli from each other
Infant ERPs
some adult ERP peaks are present in infants but delayed, like the N1 and N290, but some ERP components are only present in infants
Negative Central Peak
Typically peaks between 300- 700 ms after stimulus onset, with a larger peak reflecting higher attention
fNIRS (functional near-infrared spectroscopy)
Uses blood oxygenation to track brain activity, but unlike fMRI it uses near infrared spectrum of light
Cons of fNIRS
Lower spatial resolution, only surface of cortex can be imaged, only a few sensors are need
Pros of fNIRS
portable, and more tolerant of movement