NSC 308 Chapter 14
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Which of the following minerals play a role in maintaining blood health?
Copper
Iron
Zinc
Almost two-thirds of body water is found in the ______ fluid compartment.
intracellular
A solute is a ______.
substance dissolved in a solution
When NaCl dissociates in solution, the resulting ions Na+ and Cl- are called ______.
electrolytes
Which electrolytes are generally present in intracellular fluid?
Potassium (K+) and phosphate (HPO42-)
Which of the following minerals play a role in maintaining fluid balance?
Sodium (Na+), potassium (K+) and chloride
Identify the two compartments where body water is found.
Intracellular compartment and extracellular compartment
What is the term for the passive diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane?
Osmosis
Solutions often contain dissolved substances known as ______.
solutes
The kidneys, brain, lungs, and liver all have important roles in maintaining ______ balance.
water
Electrolytes are ______.
ions that form when salts dissociate in solution
Which electrolytes are generally present in extracellular fluid?
Sodium
Chloride
In response to increased ______, the pituitary gland releases ADH, which signals the kidneys to retain water.
osmotic pressure
Examples of this process include pulling water out of strawberries by sprinkling them with sugar and crisping limp celery by placing it in water.
osmosis
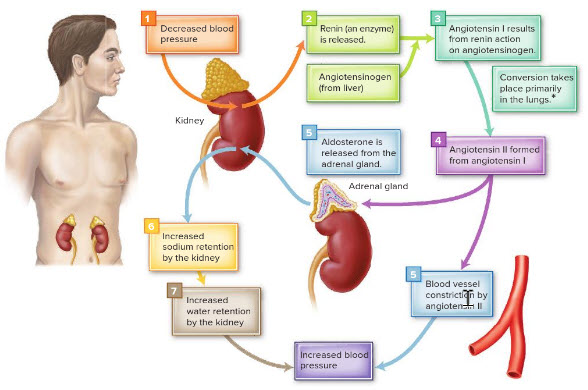
What effect does low blood pressure have on water balance?
It causes kidneys to increase water conservation.
Which of the following organs play important roles in water regulation?
kidneys
brain
When NaCl dissociates in solution, the resulting ions Na+ and Cl- are called ______.
electrolytes
The release of renin in the kidneys is initiated by ______.
falling blood pressure
What role does antidiuretic hormone play in relation to the regulation of water balance?
It signals the kidneys to retain water, reducing urine output.
What are the roles of angiotensin II?
Release of aldosterone
Constriction of blood vessels
Aldosterone is a hormone produced by the ______ that acts on the kidneys, causing them to retain sodium and water.
adrenal glands
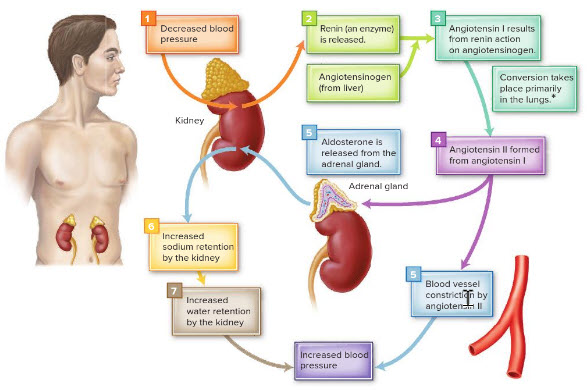
When blood pressure ______ the body triggers a series of fluid conservation measures.
falls
The production of saliva, keeping tissues moist, and the removal of waste products in the urine are all dependent on ______.
water
The enzyme formed in the kidneys that acts on a blood protein called angiotensinogen to produce angiotensin I is ________.
renin
Water ______ temperature changes, which helps the body regulate a safe body temperature.
resists
What is the term for the compound produced from angiotensin I that increases blood vessel constriction?
angiotensin II
______ is a hormone that acts on the kidneys, causing them to retain sodium and, therefore, water.
Aldosterone
How does sweat cool the skin?
Heat energy from the skin evaporates the sweat.
What is the nitrogen-containing by-product of protein metabolism excreted as a major waste product in the urine?
Urea
Water has many functions. These functions include ______.
regulating body temperature
acting as a solvent
forming specialized fluids throughout the body
Water has a high heat capacity, or _______ heat, which aids in body temperature regulation.
specific
What is the Adequate Intake for total water intake per day for adult women?
11 cups
During exercise or hot weather, ______ is secreted through the skin pores.
sweat
In all cases of dehydration, fluid intake ______ fluid loss.
does not match
Most unwanted substances in the body are water soluble and can leave the body via the ______.
urine
Which of the following are functions of sodium? More than one answer may be correct.
It aids in water balance.
It helps in the absorption of glucose in the small intestine.
The production of saliva, keeping tissues moist, and the removal of waste products in the urine are all dependent on ______.
water
Which of the following are the most abundant dietary sources of sodium?
Restaurant food
Processed foods
Which of the following are functions of potassium?
Transmits nerve impulses
Maintains fluid balance
Contracts muscle
What is the Adequate Intake for daily water consumption for men?
15 cups
Which type of major mineral is most often found in unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, milk, whole grains, dried beans, and meats?
Potassium
______ can be caused by diarrhea, vomiting, fever, heavy exercise, hot weather, dry environments, and even high altitudes. It occurs when fluid intake does not match fluid loss.
Dehydration
Which mineral is required for normal muscle and nerve function and aids in water balance?
Sodium
The salt shaker at home, processed foods, and food consumed at restaurants are all common sources of which mineral?
Sodium
Chloride is an essential nutrient and the main anion in the ______ fluid.
extracellular
Which major mineral is thought to blunt the effects of a high salt intake and help keep blood pressure normal?
Potassium
Which of the following foods are good sources of potassium?
Dried beans
Broccoli
Bananas
Which of the following are functions of chloride?
Aids in the transmission of nerve impulses
Used during immune responses
Is a component of the acid produced in the stomach for food digestion
Which of the following are functions of sodium? More than one answer may be correct.
It aids in water balance.
It helps in the absorption of glucose in the small intestine.
Chloride is known as a(n) ______ nutrient.
essential
Table salt consists of sodium and ______.
chloride
______ are blood cells that are involved in the body's immune system and help fight infection.
Leukocytes
When the number of normal red blood cells is lower than normal the condition called ______ occurs.
anemia
______, along with sodium, helps maintain extracellular fluid volume and balance.
Chloride
Globally, ______ percent of women ages 15-49 years have anemia, with about half of all cases due to iron deficiency.
30
Which of the following foods contain chloride?
Seaweed
Lettuce
Table salt
Which blood component is vital for normal blood clotting?
Platelets
Within the mitochondria, ______ is a component of cytochromes that carry electrons to oxygen in the electron transport chain.
iron
Causes of anemia include:
limiting the synthesis of red blood cells.
blood loss.
an increased breakdown of red blood cells.
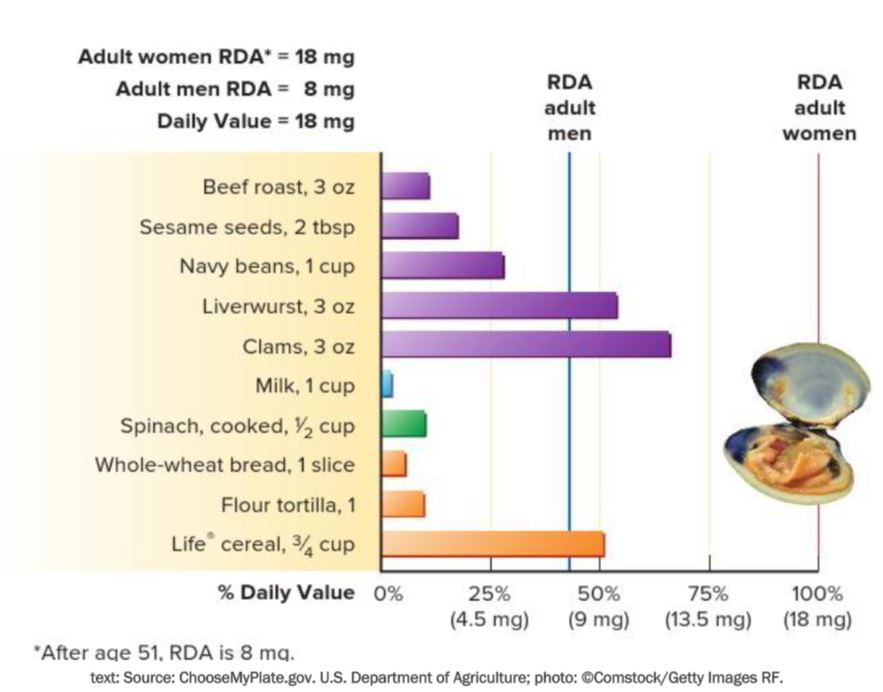
Which of the following are good sources of iron?
Life cereal
Navy beans
Liverwurst
What mineral deficiency is considered a leading global health risk by the World Health Organization?
Iron
Sally is very tired and having trouble concentrating in school. Her fatigue most likely is a result of low energy production due to poor oxygenation of her tissues. She could be suffering from what disease?
iron deficiency anemia
Vitamin K affects bone health by ______.
affecting synthesis of specific bone proteins
What are some functions of iron within the human body?
Drug and alcohol transformation
Energy metabolism
Part of many enzymes
Which vitamin can be synthesized by bacteria in the large intestine?
Vitamin K
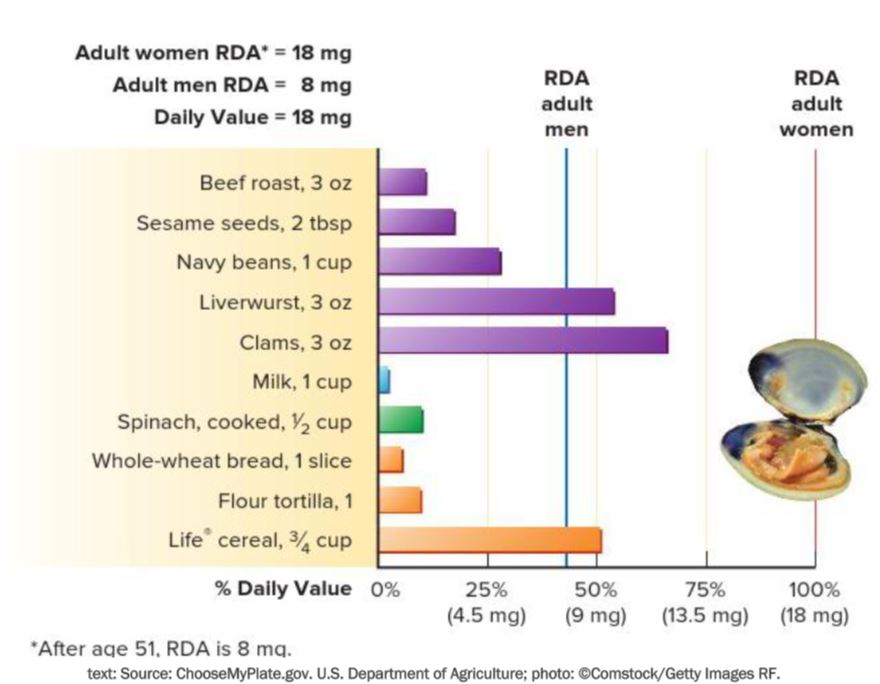
Select the highest source of iron.
Clams, 3 oz
Which vitamin is given as an injection to infants at birth?
Vitamin K
What are the symptoms of iron deficiency anemia?
Impaired energy metabolism
Fatigue
Depressed immunity
An action of vitamin K that may decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease is ______.
the prevention of blood vessel calcification
One of iron's main functions is to ______.
aid in oxygen transportation
Identify the sources of vitamin K.
Green leafy vegetables
Canola oil
Broccoli
Infants are given an injection of vitamin K at birth because ______.
their intestines lack sufficient bacteria to produce Vitamin K
Vitamin K affects bone health by ______.
affecting synthesis of specific bone proteins