drug discovery exam 3
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
library based drug discovery
screens many compounds against target to find hits
includes combinatorial chemistry
and parallel phase synthesis
what served as the start of library based discovery
automated peptide synthesis
what is automated peptide synthesis
uses a resin made out of polystyrene as a protecting group to act as a solid support
benefits of automated peptide synthesis
compound wont be dissolved in multiple layers
can use many reagents without worry of them washing away
no cross couplings would contaminate products
can sequentially perform multiple steps
split pool strategy
strategy of splitting up products and redistributing them
combinatorial chemistry
idea of making combinations of starting materials to generate a large number of products using solid phase synthesis.
problem with combinatorial chemistry
there is not a good method for separating the different products
RF tags
separate specific compounds of out of pools of products
By attaching RF tags to each resin bead and using a computer to track what compound is being built on each one, the instrument can read the tag and automatically determine which reaction flask that bead needs to go into for the next synthetic step
drawback to solid phase organic synthesis and why
compounds are cleaved with Friflouroacetic acid which leads to decomposition of product
inefficient removal of TFA leads to short shelf life
alternatives to solid phase organic synthesis
flourous technology
parallel organic synthesis
solution phase synthesis can mimic the benefits of using solid phase synthesis with
teabags
immobilized reagents
immobilized scavengers
can you pool solution phase synthesis
no
compounds made with solution phase have a greater ___ and do not require a ___
shelf life; cleavage step
convergent synthesis
converges multiple steps and cutes down on the number of steps
plays a role in the solution phase synthesis of new analogs
parallel organic synthesis
introduces modifications as late in the synthesis as possible, started as a way to made amide bonds. in solution phase.
can use automation
reactions are done seperately
advantages to the availability of a high number of analogs
removes synthesis as a bottleneck to progress
more confidence
access to SAR
reactions that introduce late stage diversity
parallel organic synthesis
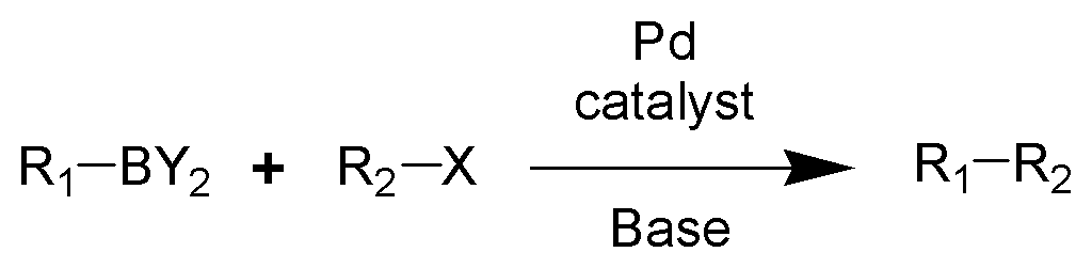
suzuki synthesis
suzuki coupling reaction synthesis
makes a carbon-carbon bond or a boronic acid (ester) without adding an H bond acceptor or donor and doesnt add to total PSA
buchwald hartwig reaction
makes an aryl bromide (C-N or C-O)
brings complex groups together
needs palladium
suzuki and buchwal rxn are good
work well on heterocycles
tolerant of typically reactive functionality
amendable to solid phase synthesis
dont need protecting groups
can be done on solid support
automation can speed up…
synthesis, purification, and analysis
lead optimization steps
1, confirm what is needed for activity
determine optimal distance between interacting groups-if flexible then make it rigid- avoid stereochemistry
knock out groups to see which is important
after optimal subst- reexamine prior optimizations
isostere
substances that are similar in properties because they have the same number of valence electrons in the same arrangement- not because they have the same number of atoms
biosisostere
substituents with similar properties that produce similar biological properties in a chemical compound
bioisostere example
replacing a hydrogen with a flouride or a CH3 with a CF3
amide bioisosteres
tetrazole replaces COOH
tetrazole replaces carboxylate
why is flouride replacing H good
C-F bond is not broken by CYPs- not metabolized
blocks oxidation of methyl group
downsides are greater MW, more lipophilic, inc logP
heterocycles
serve as bioisosteres of aromatic rings
can be proton donors or acceptors
mimic many functional groups
benzene can be replaced by
5 ring with sulfur
can replace peptide bonds with
heterocycles
PROTAC/TPD
you can mark proteins with ubiquitin to inhibit it since its being marked for degradation to target protein-protein intxns
prodrugs
when the active substance is not the drug
animal models
xenografts (animal to person)
immunodeficient mice to study tumors
biomarkers are responses measured from living organism
ways to measure efficacy (does it do what we want)
rat paw edema test
rat flick test
mental state (forced swim test)
disease progression
progression free survival
waterfall plot (tumor growth)
how to know if statistically significant
if two standard deviations above
biologics
substance derived from animal products for treating/preventing disease
not orally bioavailable
ab suffix
biologic/antibody
umab
humaized antibody
imab
from primate
biologics can be generated using
recombinant DNA tech for antibodies
why can biologics not work
bc proteins undergo post translational modification or folding
biologics pros
hyperspecific
low toxicity/adverse effects
biologics cons
poor PK-IV only
expensive
IND
investigational new drug application- filed to get permission from the FDA to start human trials. where drug generic and normal name is decided and approved.
IND requires
protocols used to analyze compound
plans and protocols to be used during trials
details about drug candidate
details about how and where compound will be prepared and purity
details about pharmacology and toxicology
companies must follow guidelines for
GLP- laboratory
GMP- manufacturing
GCP- clinical
physiochemical details required
structure
MW
MP
pka, logP, logD
optica rotation
proof of structure
form
stability
salt selection study
counterion of drug plays large role in PK
form of drug studied via X ray powder diffusion (XRPD or XRD)
allows for identification of diff polymorphs- ability of solid material to exit in more than one form
drug must be tested against (physical)
light
heat
mechanical
hygroscopidity
florida test- drug sits in oven for 24 hrs
CMC group
chemical manufacturing and control- optimizes synthesis of drug on large scale
good to avoid what in large scale synthesis
reactions w low temps
slow controlled additions
chromatographic purifications
cGMP facilities have (certified GMP)
record of thorough documentation and compliance
all reaction components are of documented quality
components can be reliably supplied
how to limit costs
do only the last step in a cGMP facility by making other intermediates available from other sources. Give up some IP, but saves money.
what detail needs to be provided for each reactant
source
purity
grade
methods of detecting impurities
triple qudrapole mass spec
NMR w other nuclei
elemental anlysos
chemical derivization
FDA purity
every impurity that exists above 0.05% or one that they would be exposed to above 1.0mg/day must be accounted and tested for
what is used to study toxicology
MBI (mechanism based inhibition) of CYPs
hERG
maximally tolerated dose (>100g)
Ames test for mutagenicity
Ames test
if drug reverses bacterias mutation that allows growth in histidine deficient medium, then flagged as a potential mutagen
IB
investigators brochure- info provided to the clinicians who will be studying the compound. includes pertinent safety data and drug characterization
Phase 1
first in humans
PK profile- multiple dose
single clinic
determines safety and MTD (max tolerated dose)
adverse events (1-5) are graded
IND specifies what would be considered MTD
at singular site
determine SAE (seriou adverse effects)
phase 2
examines effiacy
multiple GCP facilities
many IND apps are written as a combo of phase I and II
participants are aware of the study and role
if very good- will be approved
IND of combo phase I and II risks and why it is necessary
necessary to find number of people to participate in risky study (cancer)
complicated bc studying efficacy before safety
can cloud SAE cause
phase 2 parts
IIA- dose range finding
IIB- can statistical efficacy be seen
RDT
new type of phase 2 trial- randomized discontinuation trial that tries to overcome phenonomen of positive thinking in trials. Patients who show efficacy are switched from test to control group.
patients per phase
I- tens
II- hundreds
III- thousands
phases 2 and 3 are ___ studies
efficacy
phase 3
new IND
comparison to standard of care
multiple GCP facilities
test and control group
double blind
22% improvement must be met
unblinded when certain conditions are met
DSMB
data an safety monitering board
established for each trial
reviews data and evaluates safety and efficacy
reports findings after data is unblinded
can stop trial for a group or the whole thing
tuskegee trial
study that enrolled african american men eith syphilis but never told them even if they infected others. Study lasted 40 years. led to various changes in clinical trials
changes made after the tuskegee study
informed consent of all participants
accurate communication of any diagnoses
DSMB establishment
establishment of IRB for all clinical trials
clinical trials cost
$150k/patient for each trial
50 for phase 1
500 for phase 2
5,000 for phase 3
why is it impossible to complete clinical trials for cancer and alzheimers
the length of time
average time to go from IND application to completion of phase 3 trial
8 years
success rates for clinical trials
phase 1- 63%
phase 2- 31%
phase 3- 58%
adds up to 10% success rate
NDA
new drug application, used when phase 3 trial is complete. contains all data to make case on why drug should be approved. more than 10k pages
SPA
special protocol assessment. Establishes what would be considered statistical significance before the trial begins. If fda agrees then drug is automatically approved after completion of the NDA.
FDA advisory commitee
meetings are public, they advise the FDA on what they should do.
if approved, FDA makes restrictions about…
labeling and claims (black box label)
off label use
what do most phase 3 trials do
they are for drugs that have already been approved in other therapeutic area
can a drug be prescribed for any use
yes, but might not be covered by insurance
emergency use authorization
drug can be approved without FDA approval beforehand in emergencies. Was used for covid and before that for diagnostic tests.
PDUFA
prescription drug user fee act to get expedited review. 4 million dollar fee charge for fda to consider new drugs for approval
phase 4 trials
for drug/drug interactions
translational medicine (other effects it might have)
how long to go from concept to clinic approval
10 years
hatch-waxman act
alt name: drug price competition and patent term restoration act
did two things
any new molecular entity is given 5 years of exclusivity
established ANDA- a bioequivilant drug should be approved as a generic component
incentivizes people to break patents
what does bioequivilance mean
same bioactive component is in the same concentration as the approved drug.
only needs phase 1 trial
least expensive
no PDUFA fee
ANDA
abbreviated new drug application (for generic drugs)
hatch waxman act incentives for generic drugs
gov cover legal costs of patent challenges for first group to file ANDA
180 dat exclusivity for first successful ANDA
how do generic drugs come to be
use a route not protected by a patent- changes not considered obvious
6 reqs for patentability
usefulness
novelty
nonobviousness
written desc
enablement
best mode
greatest challenge to patents
best mode for synthesis
how do large countries have low per capita sales
do not respect intellectual property, and companies that fight it end up with many charges
advantage of biologics over molecules
immune to generics
disadvantages for discovering a drug for an orphan disease
helps few amt of people
limited opportunity to recover costs
limited patient pop for clinical trials
orphan disease
disease that affects less than 200,000 people in the US
OOPD
office of orphan products development-governs orphan designations
orphan drug act and benefits
incentivized companies to find drugs for orphan diseases
tax credit equal to 50% of clinical testing costs
access to federal assistance to pay for clinical testing (loss of confidentiality)
7 years of exclusive rights to market drug for orphan indication
regulatory guidance for clinical trials (removes possibility of failure)
what drugs have mainly been approved for orphan diseases
those that target diseases with veryyy low infectious rates
how has the ODA been exploited
companies had failed drugs- folded- were sold to big pharma that used the tax credits for profit
running out of antibiotic agents
new antibiotics will be held out
incentive is hospital subscription to medicines
CDER
center for drug evaluation and research
evaluates prescription drugs and other claims