5A Acids and Bases
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is molarity dependent upon?
moles and volume
What happens at equivalence points in a titration?
When a species has one of their hydrogens dissociated
Every time ur increasing by 10 dB, you’re effectively ______ to the difference in intensity
Adding another zero.
Stronger acids _____ so Ka is ___.
What are the levels for Ka in strong and weak acids?
Completely dissociate
HIGH
SA: Ka>1
WA: Ka<1
What are the common strong acids? What about the common strong bases?

What is Kw at 25 degrees Celsius? What is it also equal to?
Kw = 1 × 10-14
Kw= Ka x Kb
If [H+] increases, pH ____.
Decreases
A SA has a ___ Ka and a ____ pKa.
High
Low
If we are given pH and solution concentration, how do we solve for the Ka?
Write out Ka as alike any other equilibrium constant (products/reactants)
Replace missing concentrations with “x” as that is the change which is also subtracted from our initial solution concentration
Assume “x” is small at the bottom
Since we know [H+] based on the pH and both H and A- are equal to x, they both will be equal to H concentration
![<ol><li><p>Write out Ka as alike any other equilibrium constant (products/reactants)</p></li><li><p>Replace missing concentrations with “x” as that is the change which is also subtracted from our initial solution concentration</p></li><li><p>Assume “x” is small at the bottom</p></li><li><p>Since we know [H+] based on the pH and both H and A- are equal to x, they both will be equal to H concentration</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d2f0c2c5-0339-49b6-b856-d478bc2ce0f5.png)
What is the formula fro normality and how do we get it?
equivalents (eq/L)

What is the formula for gram-equivalent weight? What is the unit?
g/eq

If we know we are dealing with a titration and are asked what the concentration of the unknown is, what do we do?
Use MV=MV with the titrant known concentration and volume with analytes unknown volume and unknown concentration as a variable
Fill dis out


Fill dis out
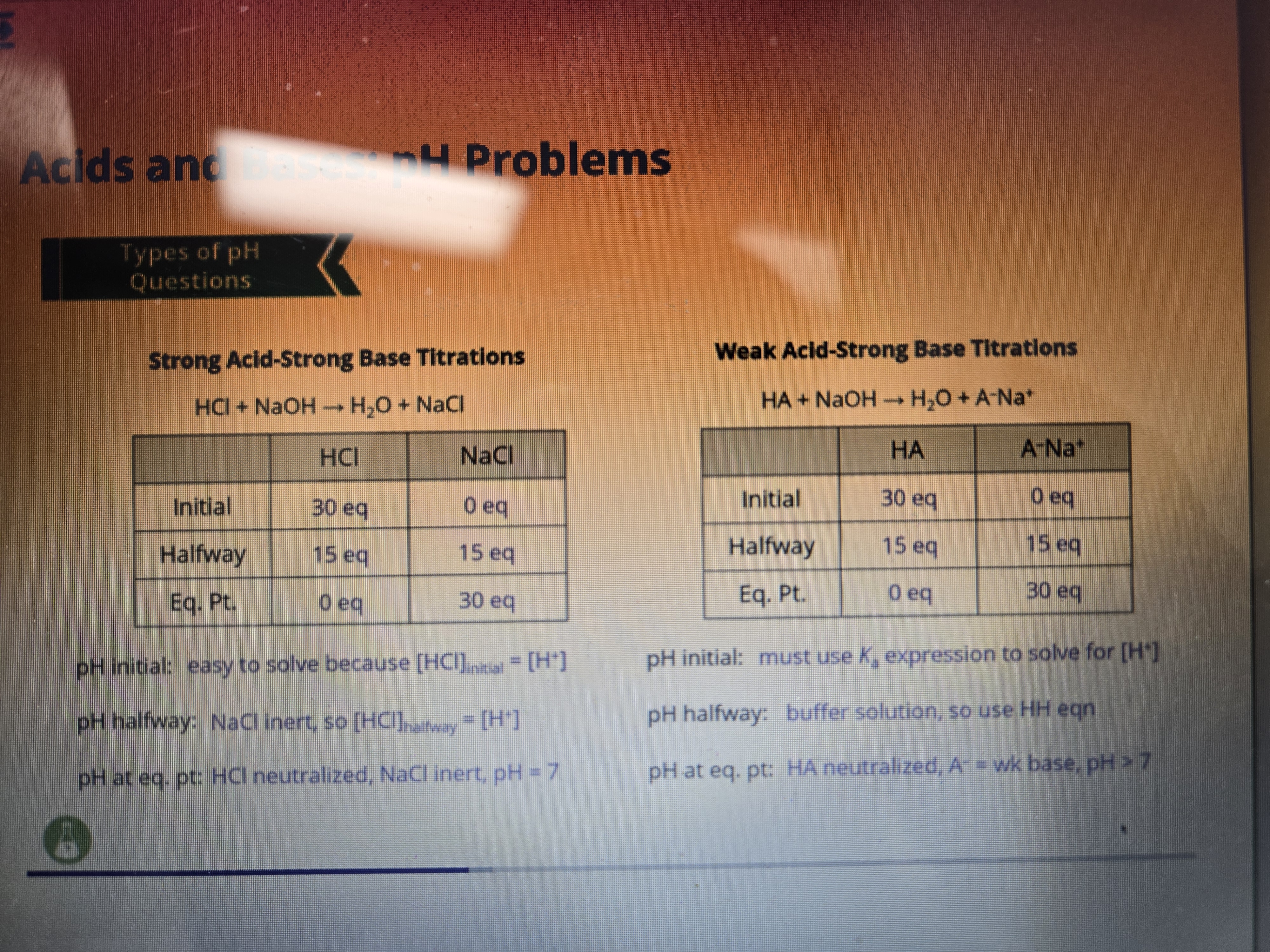
What is the pH of a 10-3 M HCl solution when titrated with NaOH at:
Initial:
Half eq:
Eq pt:
Initial: 3
Half eq: 3.5
Eq pt: 7 (because we end up just making water and salt)
How would we find the number of Cl ions at equivalence point with a titration involving HCl and NaOH?
Cl- will stay the same throughout the titration so use the concentration of Cl- from the concentration of HCl and its volume and use Avogadro’s number!
What is the pH of a 10-3 M CH3COOH (pKa =5) solution when titrated with NaOH at:
Initial:
Half eq:
Eq pt:
Initial: 4
Half eq: 5
Eq pt: pH>7
Lets say that 40 mL was needed to reach the equivalence point, if we just add 20 mL instead, we are ____.
At half equivalence!
How do you know to use the common ion effect and Ksp to solve a solubility question like this one?
"Solid silver chloride (Ksp = 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰) was added to the vascular fluid to increase osmotic pressure. Assuming the vascular fluid is approximately 1.6 × 10⁻² M NaCl, what is the maximum amount of silver chloride that can be added before a precipitate forms?"
🧪 Use the Ksp + common ion strategy when:
You’re dealing with a sparingly soluble salt (like AgCl).
The solution already contains a common ion (Cl⁻ from NaCl).
The question asks for the maximum amount that can dissolve without precipitation.
🧠 Strategy Steps:
Write the dissociation equation:
AgCl(s) ⇌ Ag⁺ + Cl⁻Use the Ksp expression:
Ksp = [Ag⁺][Cl⁻]Plug in [Cl⁻] from NaCl:
Ksp = (x)(1.6 × 10⁻²) = 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰
Solve for x = [Ag⁺] = max solubilityThis x is the maximum [Ag⁺] that can be added before AgCl starts to precipitate.
Weak electrolytes are characterized by their ____.
Weakly Polar covalent bonds
If something is accepting protons from water and creating hydroxide ions in solution, it is a ___ Bronsted Lowry __.
Strong
base
If a question asks for the ratio of a species with one less hydrogen to one with one more hydrogen, what is it most likely asking us to do?
Use HH equation using a pH and pKa given somewhere in the passage
What does interpolation involve when dealing with concentrations?
Interpolation brings something towards the standard, so if we are measuring concentration and some species is way above the normal, we interpolation by diluting the sample.
If given a pKa and we are asked for a buffer which pH would be suitable?
A pH that is ± 1 pH
So if pKa is 8 we can’t use pH 6 but we can use pH 7 or pH 8.5!
If we are asked to consider whether the keto or enol version of something is preferred at a certain pHand has previously mention pKa, what is it actually asking?
at that pH, and considering their pKa would the species be protonated or deprotonated?
If the pKa is higher than the pH it is more likely protonated, so choose the version that has more H!
How do we know when a substance is more soluble in an SA like HCl versus a SB like NaOH?
A base would react with the acidic H+ of HCL
An acid would react with a basic OH- of NaOH
This is mostly due to Le Chatlier principle as any consumption of these ions would most likely pull the reaction to the right
What is Ki?
It is similar to Km but refers to the concentration of INHIBITOR in order to get to ½ Vmax, so be careful!
If pH is raised which group deprotonates first?
The most acidic
If we want to analyze some precipitate through titration, what does it require?
We first need to characterize that questioned species as acidic or basic
If its basic we should dissolve it in strong acid
We then titrate with strong base!
What is an easy way to figure out the pI of a polypeptide and we’re given pKas?
Determine what charge each has ionized and start raising the pH from the lowest pKa that will bring us from 0—> -1 and seeing from there when we get neutral. Then we just average the lowest pka and the highest (to get a neutral molecule)
Which additional AAs should we use in our pI calculations and what are their ionized charges?
Cys- (-)
Tyr- (-)
His- (+) (unless at physio pH)
When a question asks about a residue what is it looking for?
A specific amino acid at a specific position within a polypeptide chain.
Tertiary structure is determined by the interactions between ___.
Secondary structures
What’s the difference between Arrhenius and Bronsted
Arrhenius talks about increasing hydroxide or hydronium while bronsted is about proton donation