Water resources Terms
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
scientific methods
cycle of hypothesis testing to generate conclusions
Water Quantity
amount of water present
Water Quality
Total Global Water
About 8.4 million Liters
Total Global Freshwater
2.5% of total water
Plagiarism
using someone else’s words as your own work
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation for a phenomenon made as a starting point for further investigation
Theory
Sustained explanation acquired through the scientific method and repeatedly tested and confirmed through observation and experimentation
Socio-ecological System
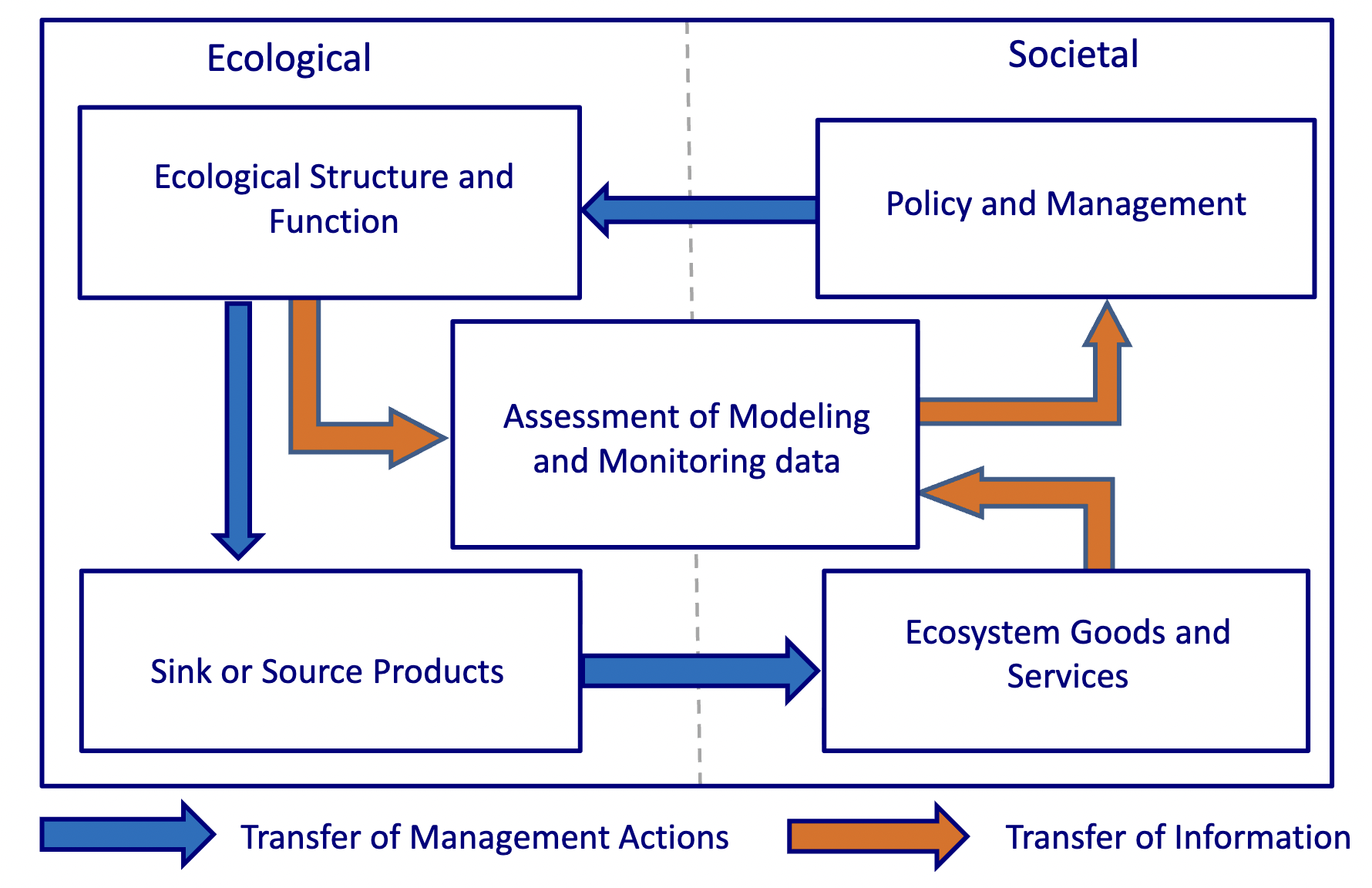
Water Budget
water entering and leaving a watershed or basin, how much is there and how much can you use?
Hydrologic Unit Code
HUC, ranges from 2 to 12, Region, Subregion, basin, sub-basin, watershed, subwatershed
Internal Basin
Water is stuck inland, never makes it to the ocean
Continental Divide
defined by ridgeline, which way water goes
Watershed
land area that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins or seas
Orographic Precipitation
rain and snow fall
Dependent Variable
y- axis, relies on the x-axis
Independent Variable
x-axis, doesn’t necessarily rely on the y-axis
Dewpoint
temperature where relative humidity is at 100%
Relative Humidity
amount of moisture in the air vs. the air can “hold” at that temp
Vapor Pressure
how much water vapor is in the air
Leaf Stomata
opening in leaf that cointrols water intake
Transpiration
uptake of water through vegetation and evaporated through their leaves
Evapotrasnpiration
precipitation and transpiration, water + heat,
100 year flood
1 percent AEP, 1 in 100 chance of being equaled or exceeded in 1-year, average recurrence interval of 100 years (IS NOT ALWAYS 100 YEARS BETWEEN)
bed load
rolling sand and gravel from high energy areas
dissolved load
dissolved components, solids that are dissolved in the water then carried fro a long time
ephemeral stream
only flow in response to storms
erosion
Hydraulic Action, force of water moving against bends and breaking off rocks
floodplain
geomorphically, overland maginitude of the floods, where the rivers move back and forth
gaining stream
hydrograph
graph that shows discharge(y) over time(x)
intermittent stream
flows seasonally, fed by groundwater
recurrence interval
Find Maximum daily average
list every year
Rank (m) them across the period of record (n)
calculate the exceedance probability (%)
n= number of years
m/(n+1)
suspended load
fine particles and particulate sediment
water year
Novemebr 1st to October 31st
delta
4 dimensions of a river
Longitudinal- Down Stream, Lateral- in and out of floodplain, Vertical- into the hyporheic and groundwater, Temporal- change over time and movement within the channel migration zone
alluvation
the cut and fill of a river and the land around it
alluvium
round rocks, deposited sand and silt
colluvium
angular not tumbled rocks
avulsion
creation of oxbow lakes
stream order
variable source area
small portions of the landscape, can contribute disproportionately to runoff and peak flow during storm events
losing stream
lake stratification
the separation of layers by temperature and chemical differences
lake turnover
hypolimnion grows and the wind blows causing the lake to turnover, the oxygen levels change densities
wetland
where the water table is at the surface
lake
very slow moving body of water in a depression of ground, not in contact with the ocean
pond
same as lake but not as deep, don’t have limnetic zones
limnetic zone
area greater than 2m deep
littoral zone
zone of aquatic plants
lacustrine
lakes
palustrine
freshwater wetlands
epilimnion
top layer of the lake around 20°C with typically more oxygen
hypolinion
lower layer of lake with typically less oxygen around 5°C
seiche
the rocking of the Epilimnion and the Hypolimnion when the wind blows, can sometimes cause a flip
dimictic
Turnover of lakes that happens twice a year in the Spring and Fall
cirque lakes
a lake formed in a gouged out area (by glaciers) at a high elevation
sinkhole lake
forms in the remains of a sinkhole
facultative
FAC, oxygen levels, aerobic vs. anaerobic bacteria
riverine wetland
driven by flood conditions
lacustrine fringe wetland
overbank flow from lake
wetland function
happen whether they have value or not, remove contaminants, remove sediments, ecosystems, setting for cultural activities, store surface waters, reduce energy of surface water, recharge groundwater, discharge groundwater, stabilize soils, remove and transform nutrients
wetland value
large
aquitard
a restrictive layer
aquifer
a geologic formation that can store and transmit water in amounts useful to humans. All of the pore spaces or fractures are filled with water
artesian aquifer
water is confined between impermeable earth and rock layers, under pressure because it’s connected to a distant recharge area
cone of depression
conical depression of the water table that can extend beyond the well itself, created by pumping well
confined aquifer
same as artesian
consolidated rock
sedimentary rock
crystalline rock
basalt, granite, other igneous and metamorphic rock, veyr dense, cannot host groundwater unless it’s fractured
Darcy’s law
Q= KiA, Q is flow(volume/time) K
Drawdown
induced by piping well
Groundwater
exists in and moves through geologic material, but not all is equal
Groundwater discharge
to springs, beds of gaining streams, wetlands
Groundwater mining
consumptively using groundwater at a rate exceeding the recharge rate
Groundwater recharge
by infiltration of rain/snowfall and possibly from losing streams
hydraulic conductivity
the volume of water flowing through a given a cross-section of geologic media in a given period of time
hydraulic gradient
change in head per length (head = elevation of water in a well casing)
Limestone
easily dissolves in water
Permeability
ability of porous material to transmit water
Porosity
volume of the void space as a proportion of the total volume, porosity is the highest when grains are all the same size
Sandstone
Sedimentary rock
consolidated by heat and pressure from overlying rock over the ages, shale, limestone, sandstone, coal, siltstone, conglomerate, expect for shale can store and transport groundwater
shale
spring
points where aquifers intercept ground surface and discharge to the land, if aquifer is confined water may jet into the air (artesian spring)
unconfined aquifer
aquifer above an aquitard
unconsolidated rock
clay, silt, sand, gravel, cobble
unsaturated zone
vadose- infiltration area
water table
surface, not volume of water, often changes with the seasons
well yield
the volume of water per unit of time achieved by pumping at stable drawdown
consumer
something that eats something else to survive
decomposer
an organism that decomposes organic material
ecosystem
organisms interacting with their physical environment
eutrophication
change in the structure and function of aquatic ecosystems in response to excess nutrients
food web
the way diffrent food chains interact with eachother
habitat
invasive species
oligotrophic
organism