UT High School Health 1 Final Exam Review
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
What are the 6 areas of health?
1. physical
2. social
3. emotional
4. spiritual
5. environmental
6. mental
What is physical health?
the way in which the body works
What is emotional health?
ability to express emotions in a healthy manner
What is social health?
relationship with others
What is mental health?
ability to handle the everyday stress and demands of daily life
What is spiritual health?
relationship that you have with a power that is bigger than yourself
What is environmental health?
relationship with the world around you
What influences your health?
heredity, environment, family, friends, culture, media
What is heredity?
the passing of traits from biological parents to children
Examples of inherited traits
- skin color
- eye color
- hair color,
- body type and size
- growth patterns
- likelihood of getting certain diseases
What is a risk behavior?
actions or choices that may harm you or others
What is a cumulative risk?
related risks that increase in effect with each added risk
What does subjective mean?
comes from person's own views and beliefs
What does objective mean?
based on facts
What is a good method for solving disagreements?
cooperative problem solving
What are the 4 types of influences on health?
heredity, cultural, environmental, social
What are the two categories of defense responses in the immune system?
innate immune response and adaptive immune response
5 areas of non-specific immune responses
- skin and mucous membranes
- inflammatory response
- temperature
- proteins
- white blood cells
Why is a rise in temperature a good defense for the body?
as temp. increases, growth of organisms decrease causing body to fight off infections
List the two specific immune responses
humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity
What is an antigen?
stimulates the production of an antibody
What scientist first introduced the idea of immunizations?
Edward Jenner
List four disorders of the immune system
Immunodeficiency, Autoimmune, Allergic, Cancer
List three types of autoimmune disorders
Lupus, Junior Rheumatoid Arthritis, Scleroderma
What is another name for white blood cells?
leukocytes
List two types of leukocytes, and explain what they do
Phagocytes(chew up invading organisms), Lymphocytes(allow body to remember, recognize, and destroy invaders)
List three types of immunity
innate, adaptive, passive
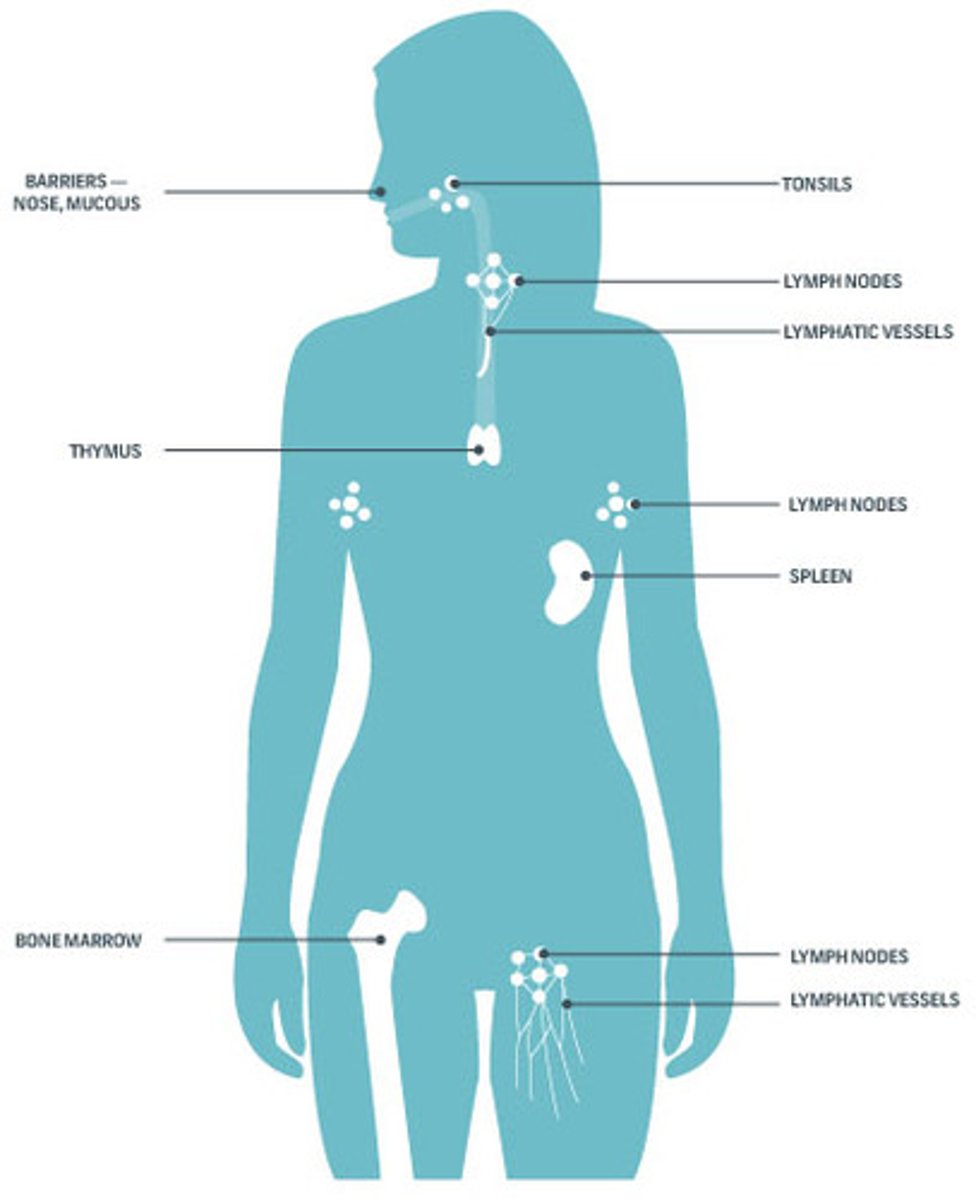
List main components of the immune system
adenoid, tonsil, thymus, spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes
Chicken Pox
Definition: contagious viral infection caused by varicella-zoster virus
Method of Spread: direct contact with infected person/airborne transmission
Symptoms: rash, fever, fatigue, and headache
Onset of symptoms: 10-21 days after exposure
Complications: bacterial skin infection, pneumonia, encephalitis, and reactivation of virus
Fifth Disease
Definition: viral infection caused by parvovirus B19
Method of Spread: respiratory droplets, blood transfusion, or organ transplants from infected person
Symptoms: low-grade fever, "slapped face" rash, rash on body
Onset of symptoms: 1-4 days after onset of rash
Complications: joint pain, anemia, complications for pregnant women and individuals with weakened immune system
Hepatitis A
Definition: viral infection caused by hepatitis A virus
Method of Spread: personal contact with infected person, ingesting food/water contaminated with fecal matter with virus
Symptoms: fatigue, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, jaundice, and dark urine
Onset of symptoms: 15-50 days after exposure
Complications: liver failure, acute liver inflammation, complications for those with pre-existing liver conditions
Hepatitis B
Definition: viral infection caused by hepatitis B virus
Method of Spread: contact with infected blood/body fluids, childbirth
Symptoms: fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice, and joint pain
Onset of symptoms: 45-160 days after exposure
Complications: chronic liver infection, cirrhosis, liver cancer, complications for those with weakened immune system
Hepatitis C
Definition: viral infection caused by hepatitis C virus
Method of Spread: contact with infected blood/body fluids, childbirth
Symptoms: (mostly asymptomatic), fatigue, fever, nausea, loss of appetite, and jaundice
Onset of symptoms: 2 weeks to 6 months after exposure
Complications: chronic liver infection, cirrhosis, liver cancer, complications for those with weakened immune system
Impetigo
Definition: bacterial skin infection caused by Staphylococcus/Streptococcus
Method of Spread: direct contact with sores/nasal discharge of infected person
Symptoms: red sores, itching, pain, swollen lymph nodes
Onset of symptoms: 4-10 days after exposure
Complications: cellulitis, ecthyma, glomerulonephritis, and scarring
Infectious Mononucleosis
Definition: viral infection caused by Epstein-Barr virus
Method of Spread: close contact with saliva, blood transfusions, or organ transplants of infected person
Symptoms: severe fatigue, fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes & tonsils
Onset of symptoms: 4-6 weeks after exposure
Complications: enlarged spleen, liver inflammation, anemia, complications for those with weakened immune system
Influenza
Definition: contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza virus
Method of Spread: respiratory droplets of infected person, touching surfaces with virus and then touching mouth, eyes, or nose
Symptoms: high fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, body aches, headaches, fatigue, vomiting/diarrhea
Onset of symptoms: 1-4 days after exposure
Complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, sinus & ear infections, worsening of chronic medical conditions, complications for those with weakened immune system/underlying health conditions
Meningitis
Definition: inflammation of protective membranes covering brain & spinal cord caused by bacterial/viral infections
Method of Spread: close contact with infected person, touching contaminated surfaces
Symptoms: high fever, severe headache, stiff neck, sensitivity to light, nausea, vomiting, confusion, seizure/coma
Onset of symptoms: 2-10 days(bacterial)/3-7 days(viral) after exposure
Complications: hearing loss, brain damage, seizures, shock, and death
Strep Throat
Definition: bacterial infection caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria
Method of Spread: close contact with infected person, touching contaminated surfaces
Symptoms: sore throat, difficulty swallowing, red & swollen tonsils, white patches of pus on tonsils, swollen lymph nodes, fever, and headache
Onset of symptoms: 2-5 days after exposure
Complications: rheumatic fever, scarlet fever, kidney inflammation, and abscess formation around tonsils
Types of communicable diseases
bacteria, virus, fungi, and protozoa
Examples of communicable diseases
Influenza, Measles, Tuberculosis, Hepatitis
Bacteria
Definition: one-celled organisms that multiply and produce toxins that damage cells in tissue they invade
Examples: tuberculosis, cholera, and pneumonia
Virus
Definition: one-celled organisms smaller than bacteria that multiply, take over cells, and destroy them
Examples: polio, aids, and common cold
Fungi
Definition: single-celled organisms larger than bacteria
Examples: ringworm and other skin infections
Protozoa
Definition: single-celled organisms that enter through food and water
Examples: malaria
Examples of non-communicable diseases
asthma, allergies, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer
Symptoms of asthma
wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath due to inflamed airways
Symptoms of allergic reaction
itchy, watery eyes, sneezing, coughing, dark circles under eye, difficulty breathing, swelling of lips, dizziness, loss of consciousness
Cardiovascular disease
leading cause of death in US, risk factors include smoking, lack of physical activity, and poor nutrition
Diabetes
Definition: lifelong condition where body doesn't produce/properly use insulin
3 conditions occurring in diabetes
Hypoglycemia, Hyperglycemia, Ketoacidosis
3 major types of diabetes
Type 1: little or no insulin
Type 2: improper use of insulin
Gestational: high blood glucose in pregnancy
Cancer
uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells, symptoms include fever, chills, night sweats, weight loss, loss of appetite, fatigue, malaises
Tests to detect cancer
CT scan, complete blood count, blood chemistries, biopsy of tumor, bone marrow biopsy, chest x-ray
Information about health screening
Mayo Clinic, NIH
Information about health screening for young adults
labtestonline.org
Information about mental health screening
nbsalliance.org
BRUH
BRUH
What 3 things should be included as disclaimers on health site?
statement(limitations, purpose, scope, authority, currentness), source, statement that it is general health advice not medical advise
How often should children see doctor?
0-6 months(every month), 6-18 months(every 3 months), 2-21 years(every year)
How often should adults see doctor?
every 2 years
How should adults select a doctor?
based on gender and any risk factors
Goal of preventative care
checks for diseases before symptoms develop
Periodicity Schedule
detailed summary of what questions/tests will doctor review during each visit
Benefits of preventative child care
prevent illness through discussions about nutritions/vaccinations, track development of children, parents letting know of concerns, creating trust between families and healthcare
Adult Preventative Care Timeline
summarizes what tests occur in which individuals and at which test
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Screening
Screening Eligibility: men aged 65-75 who have ever smoked
Disease Prevention: aneurysm
Frequency: one-time screening for eligible individuals
Alcohol Misuse Screening
Screening Eligibility: adults aged 18 or older
Disease Prevention: alcohol-related health issues
Frequency: routine healthcare visit/individual risk factors
Blood Pressure Screening
Screening Eligibility: adults aged 18 or older
Disease Prevention: blood pressure issues
Frequency: every 2 years for normal BP, frequent for high BP
Cholesterol Screening
Screening Eligibility: adults aged 20 or older
Disease Prevention: cholesterol issues
Frequency: 4-6 years for normal levels, frequent for high levels
Colorectal Cancer Screening
Screening Eligibility: men aged 50-75 with risk factors/history
Disease Prevention: colorectal cancer
Frequency: various screening & colonoscopy every 10 years
Depression Screening
Screening Eligibility: adults, pregnant, & postpartum women
Disease Prevention: depression
Frequency: routine healthcare visits/individual risk factors
Diabetes (Type 2) Screening
Screening Eligibility: overweight/obese adults aged 40-70, young individuals with risk factors
Disease Prevention: type 2 diabetes
Frequency: every 3 years for normal results, frequent for risk factors
Hepatitis B/C Screening
Screening Eligibility: those with high risk/history
Disease Prevention: hepatitis B/C
Frequency: 1-time screening/periodic screening for high risk
Obesity Screening and Counseling
Screening Eligibility: all adults
Disease Prevention: obesity
Frequency: routine healthcare visits
Tobacco Use Screening
Screening Eligibility: all adults & adolescents
Disease Prevention: cancer & lung disease
Frequency: routine healthcare visits
Social wellness checklist
make connections(protects health & lengthens life), take care of yourself(stress takes toll on health), get active together(positive health habit and connection), shape family's health(role model for healthy habits), kids bond(builds relation and confidence, manage feelings), build healthy relationships(improve wellbeing)
Emotional wellness checklist
build resilience(cope with difficulties), reduce stress(boosts resilience), quality sleep(think clearly, quicker reflexes, focus better), be mindful(be aware), cope with loss(healthy grieving), strengthen connections
Social determinants of health
safe neighborhoods & transportation, discrimination & violence, access to education & job, access to nutritious food & physical activity, pollutants, language & reading skills
Conflict-Resoultion Skills
understanding how conflict feels, listening to other side, speak directly and assertively
Forms of Communication
assertive, passive, aggressive
List Maslow's 4 physiological needs
food & water, rest, clothing & shelter, reproduction & health
List Maslow's 5 Hierarchy of Needs
physiological needs, safety needs, love & belonging, esteem, self-actualization
Explain Maslow's safety needs
need of safety for personal survival
Explain Maslow's social needs
needs related to interaction with others
Importance of Maslow's Hierarchy
helps to improve ourselves and others based on needs
Why are emotions important?
help communicate with others
Why is it important to communicate emotions?
necessary to enhance message, convey authenticity, and develop trust
What is healthy self-concept?
ability to know yourself & recognize strengths and weaknesses
Difference between self-concept and self-esteem
self-concept is description while self-esteem is evaluation
Characteristics of people with poor esteem
self-critical, ignores positive qualities, use negative words, blames self for wrongdoing
Causes of poor self-esteem
unhappy childhood, poor academic performance, chronic health issues, mental illness
Anxiety disorders
Overview: abnormal amount of anxiety
Symptoms: sweating, pounding heart, rigid body structure
Risk Factors: shyness, stress exposure, history, medication/condition
Treatment: psychotherapy, medications, support group, stress techniques
Borderline Personality Disorder
Overview: can't manage emotions
Symptoms: mood changes, avoid abandonment, unstable relationships
Risk Factors: family history, brain structure, surrounding factors
Treatment: psychotherapy, medications, therapy for caregivers/family
Bipolar Disorder
Overview: illness where there are unusual shifts in person's mood, energy, activity levels, & communication
Symptoms: increase/decrease of energy, trouble concentrating, low self-esteem
Risk Factors: brain structure/function, genetics
Treatment: psychotherapy, medications
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Overview: abnormal amount of anxiety
Symptoms: sleep problems, having headaches, difficulty controlling worry/concentration
Risk Factors: shyness, stress exposure, history, medication/condition
Treatment: psychotherapy, medications, support group, stress techniques
OCD
Overview: uncontrollable behavior with urge to repeat task
Symptoms: fear of imperfection, excessive tidiness, arranging in precise way
Risk Factors: brain structure/function, genetics, environment
Treatment: psychotherapy, medications
Panic Disorder
Overview: abnormal amount of anxiety
Symptoms: sweating, chest pain, feeling of doom/out of control
Risk Factors: shyness, stress exposure, history, medication/condition
Treatment: psychotherapy, medications, support group, stress techniques
Types of depression
Major Depression: severe depression lasting for 2 weeks
Persistent Depressive Disorder: less severe depression lasting for 2 years
Prenatal Depression: depression before & after pregnancy
Seasonal Affective Disorder: depression related to seasons
Psychosis: severe depression with hallucinations/ delusions
Types of anxiety disorders
social anxiety disorder, phobias, separation anxiety disorder
Schizophrenia
disorder which affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, includes psychotic, negative, and cognitive symptoms