Astronomy DSST
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
277 Terms
heliocentric theory
places the sun at the CENTER of the solar system, states that all other bodies in the solar system orbit it.
This was in direct contradiction to Ptolemy's geocentric theory, that stated the earth was the center of the universe
Nicolaus Copernicus
widely credited as the father of the heliocentric theory (sun is the center of the universe)
he was not the first to propose the concept but his mathematical model was the first that correctly predicted the movement of the planets. Later he published a book that made the idea popular.
Hans Lippershey
usually credited as the inventor of the telescope (though it wasn't called that at first) he was a German-dutch lens maker who first applied for the patent of the "dutch perspective glass" it is important to note that, at the time, these were not used for astronomy until GALILEO
Galileo Galilei
the first to use the telescope for astronomical studies. Used the telescope to discover the four largest moons of Jupiter. Galileo was a firm believer in the heliocentric theory. Since most scientists of the time and (more importantly) the church embraced the geocentric theory, this caused Galileo much trouble and is why he was placed under house arrest until his death
Celestial Sphere Theory
similar to the geocentric theory, it said that we see in the sky what is was actually numerous spheres. (These spheres are like clear globes around earth with planets, comets and stars inside of them) some of these were thought to be in our own atmosphere and others farther away. even Copernicus (heliocentric theory) still believed in these spheres. His model of the universe had the stars at equal distance from the earth in one of the most distant spheres
tycho brahe
disproved the celestial sphere theory that all celestial objects were unmoving object's in the earth's sky. He demonstrated it was untrue through observation of a supernova, which he proved beyond the solar system and not a phenomenon within the Earth's atmosphere
Johannes Kepler
a mathematician who proposed the 3 laws of planetary motion. stated that the planets move in an elliptical orbit around the sun and mathematically proved it. His laws provided the building blocks for many future theories
first law of planetary motion
LAW OF ELLIPSES- the planet's orbits are elliptical in nature and that the center of the sun is a focus for those ellipses
second law of planetary motion
LAW OF EQUAL AREAS- describes how fast the planets are movingaround the sun., The closer the planets get to the sun, the faster it goes. As it moves farther away from the sun, it will slow down. HOWEVER the law also says that if we drew a line from the center of the sun to the center of the planet we would equally see that every 31 days the area covered by that line would be the same
third law of planetary motion
LAW OF HARMONICES- the orbital periods of different planets are related. SPECIFICALLY the ratio of the squares of the orbital periods to the cubes of the average distance from the sun are the same. SO: you take the length of time the planets takes to complete an orbit around the sun and square that number. THEN take the planet's average distance from the sun and cube it. the ratio between those 2 numbers will be the same no matter what planet you use the formula for
Isaac Newton
invented the first functional reflective telescope; proposed the three laws of motion and the universal law of gravitation
First law of motion
things at rest will remain at rest and things moving will remain moving until affected by an OUTSIDE force (LAW OF INERTIA)
second law of motion
mass is directly correlated to how much energy is going to be necessary to move an object. rocks take more force to move than feathers etc
third law of motion
every action holds an equal and opposite reaction: forces of two bodies on each other are always equal and directed in opposite directions
law of universal gravitation
everything in the universe has a gravitational field that affects other objects and how strong that field is depends on the objects mass and how close the two objects are to each other
max planck
German scientist, worked with Einstein, generally credited with creating Quantum Physics
- WOn Nobel prize in 1918
- Quantum mechanics- deals with matter on the atomic and sub-atomic level and is used in astronomy to explain the behavior and existence of many cosmic bodies which would otherwise be difficult to explain using normal physics
Edwin hubble
confirmed the existence of other galaxies outside our own in 1919.
- discovered the degree of doppler shift in those galaxies and how they increased the further the galaxy was from our own.
- led to Hubble's law, which allows the observation the universe expanding
Big Bang Theory
-explains the origin of all matter in the universe as the result of an original cosmic explosion and is constantly expanding
Arno Penzias and Robert WIlson
ACCIDENTALLY discovered cosmic microwave background radiation in 1964
- important part of necessary evidence for the Big Bang Theory
universal contraction theory
suggests that the universe will eventually begin to contract and ultimately the Big Bang will be reversed when the universe implodes on itself
panspermia
theory that life's building blocks are carried around the universe by meteors, comets, asteroids and planetoids. When one of these falls to a planet, life has the chance to begin evolving. Many scientists believe that this is how life began on earth and point out that the same process may have taken place on many other planets inner Universe.
- there is some scientific evidence pointing towards this conclusion as there have been meteors originating from Mars that seem to show signs of microorganisms having once lived there. The debate about this is still ongoing
solar mass
way of determining the size of celestial bodies
- one solar mass= the size of our sun
-this is used to have a frame of reference to the size of other stars.
astronomical unit
-way of measuring distance in astronomy
- equals about 93 million miles (the distance between the sun and the earth)
-this is used to determine the distances when a light year is too large a unit of measurement
-Jupiter is 5au from the sun, so its 5x farther than the earth
light year
the distance light travels in one year; roughly 6 trillion miles, 10 trillion KM or 63,000 AU
parsec
a unit of measurement in astronomy
-equals 206,00 AU/3.2 light years
absolute magnitude
measure of intrinsic brightness used for celestial objects
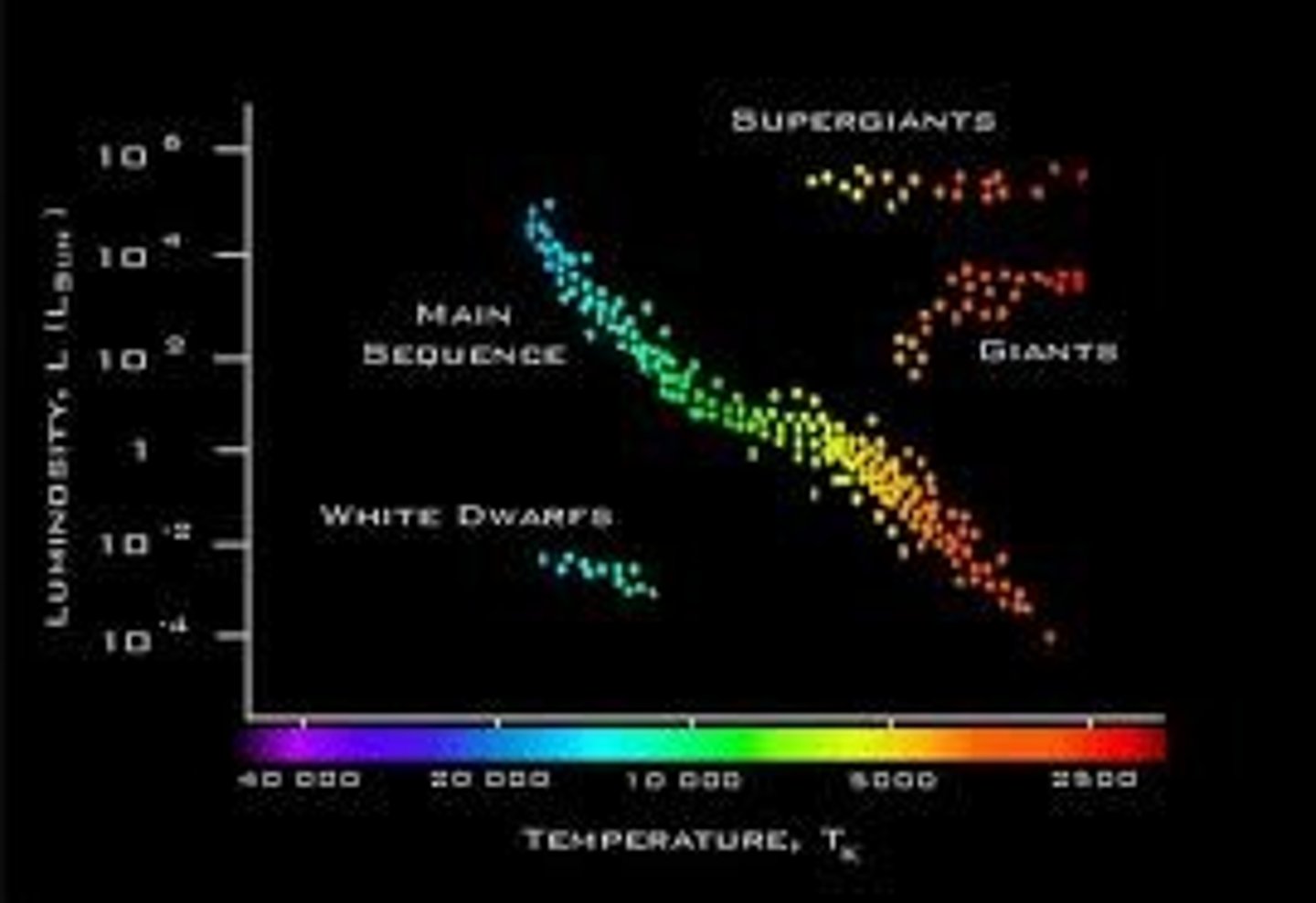
Hertzsprung Russell Diagram
determines the relationship between a star's absolute magnitude, type and temp. in a scatter-graph form. the two sides show the value of luminosity and color(which is linked to temperature) against each other.
SIMPLY- diagram allows a comparison of many types of stars based on colors, temp, and brightness. this can show at a glance where most stars fall in brightness and temp. as well as color.
Astronomers use this to see trends and spot stars that fall from outside the norm
spectroscope
used to measure light over the electromagnetic spectrum; often means it breaks down the light into its individual wavelengths, like a prism breaks sunlight down into individual colors
-useful for indentifying what objects are composed of based on their visible spectrum
absorption lines
- analyze chemical composition of celestial bodies
-when a certain shade of color on the strip is black, indicating that a particular frequency of light has been blocked.
- lines are used to tell more about the makeup by what wavelengths of light are blocked,
- BLOCKED
emission lines
indicates the emission of a particular wavelength of light (rather than absorption) it shows up as a bright line on a spectrum\
-PRESENT
angstrom
used to measure wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation and named after ANDERS ANGSTROM
- radio waves have the longest wavelength and gamma rays have the shortest
doppler effect
- describes how a wave's frequency changes based on the motion of the observer in relation to the source of the wave
-a source of light getting closer to earth has a higher frequency which shows the BLUE SHIFT
- as the source moves away, the wave lengthens towards the red end of the spectrum known as the RED SHIFT
- an object showing redshift is moving away from us, an object showing blueshift is coming closer to us
- USING THIS astronomers can detect the relative motion of celestial objects and even determine their speeds
radial velocity-
the speed at which an object moves toward pro away from the viewer here on earth
- one way that astronomers determine whether stars have exoplanets
- if it does have an exoplanet, the radial velocity of the star will change when the planet's gravity affects its orbit
- how astronomers know that the universe is expanding, by measuring the radial velocities of galaxies as they move away from us
parallax
apparent shift in the position of an object when the angle of viewing is changed
- as you make small changes to your location, the objects closest to you will appear to move more than those farther away
triangulation
how parallax is used to measure distance to stars
how? 1) note the dangle of the star 2) wait a period of time and then take the angle of the star again
-since the earth has moved around the sun during this time, the angle is completely different
- using some trig the can accurately determine the distance by computing the difference of the two angles;
- WORKS ON STARS UP TO 400 LIGHTYEARS AWAY
-all measurements of astronomical distance depend on this
proper motion
movement of the star itself rather than the observer
- measured by taking the angle of the star's movement over time compared to the center of the solar system
-like this, stars will often seem to move to different constellations over time, the more the angle changes, the closer the star can be assumed to be
telescope
device used to see distances far beyond normal eyesight
- the first telescope (developed in the Netherlands in 1608) was refractive and not used for astronomy
refracting telescope
- the use of the telescope for astronomy (pioneered by Galileo) operates by having two lenses (objective and eyepiece) that focuses the light from an image so that the viewer can see it more clearly
- downside is that you can't see the entire spectrum of light because the of the glass and the fact that the size of the lens is limited
- issues were mainly solved with the invention fo the reflective telescope
reflective telescope
- uses curved mirrors to reflect gathered light and form an image
-light enters the telescope and is then reflected towards an eyepiece through a series of mirrors
-first one was built by NEWTON
- allows much larger lenses to be used since the entire mirror can be supported instead of just the edges of the lens
-maximum useful magnification is between 50-60 times the diameter of the lens or mirror
-most telescopes used by pro astronomers today are reflective
radio telescope
used to see celestial bodies in the radio spectrum but cannot be used where there is a lot of radio interference
-usually placed away from cities and inside valleys to avoid the interference
-radio waves have extremely long wavelengths so tis important to collect as many as you can
- because of this radio telescopes have very large dishes
-able to see past physical obstructions and are therefore very useful for seeing into places like the galaxies core where stellar dust and other light sources may block conventional telescopes
xray telescope
- able to see beyond the visible spectrum and identify objects that may otherwise be obscured
- usually required to be either in the upper atmosphere or space-based as the earth's atmosphere absorbs x-rays
- used to look at black holes
galaxy
- group of stars and stellar matter held together by gravitational forces
- can contain anywhere from 10 million to 100 trillion stars
-usually classified by their shape
types: spiral, elliptical, and irregular
spiral galaxy
shaped like a spiral, like water going down a drain
- usually have two arms but my have more
usually made of younger stars and many globular clusters
-the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy
elliptical galaxy
-spherical shaped and may be larger than spiral galaxies
-usually filled withholder stars and open clusters
irregular galaxy
- a galaxy that does not fall into one of the other two classifications
-usually due to interactions with other stellar objects like collision between two galaxies
quasar
- most distantly observed and luminous objects in the universe
- according to high redshift, they are the most distant objects observed
- the fact that they are observable from so far shows the power of their luminosity
- one quasar has the luminosity equivalent to a trillion suns
- astronomers believe they are the result of supermassive black holes in the center of some of the earliest formed galaxies in the universe
supermassive black hole
believed there is one of these in the middle of the Milky Way and most other galaxies, forming a gravitational center that the other stars in the galaxy revolve around
galaxy groups
a large group of galaxies (usually at least 50) which are gravitationally connected
galaxy clusters
larger than a galaxy group, usually between 50 and 1,000 galaxies inch cluster
local clusters
the collection of galaxies in which our own Milky Way is a part of
-numbers roughly 53 galaxies with the Milky Way and the Andromeda galaxy being two of the largest
nebula
birthplace of stars
-cloud of interstellar gas or dust
- large collections of hot gasses and dust are interstellar nurseries where stars are born
protostar
a precursor to a star which is born in a nebula. the dust and gas condenses and begins to heat up. Once it condenses enough, the hydrogen fuses to form helium and it turns into a main sequence star. If the mass of dust and gas isn't large enough to begin this fusing process, it forms a BROWN DWARF instead
main sequence star
- a star in which the hydrogen is fusing to form helium
-for example, the sun in its current form
-the smaller the star the longer it burns
- a star with one solar mass takes almost 10 billion years to complete the transformation of all its hydrogen into helium
-larger stars fuse their hydrogen much more quickly and therefore end the main sequence stage sooner
red giants and blue giants
main sequence star which has fused all of its hydrogen into helium
- as the hydrogen disappears, the star begins to swell and cool
- as it swells, it will begin to lose gases around the white dwarf core in the form of a planetary nebula
white dwarf
comparable in size to earth but in mass to the sun
- instead of a nuclear fusion like a main sequence star, they are powered by the leftover energy remaining in the core
-less luminous than the sun and usually take several billion years to fade
supergiant
-byproduct of a star with larger mass
- larger stars become supergiants instead of red giants
-with a rapidly expanding shell of gases around the core, they can be up to 1000 times the diameter of our sun
-difference between a supergiant and a red giant is size and how they die
-supergiant tends to die in a violent explosion as the core collapses upon itself in less than a second (SUPERNOVA)
supernova
an event that occurs when a massive star undergoes a gravitational collapse
-resulting supernova explosion produces extreme luminosity which can temporarily outshine an entire galaxy
- if the core survives the explosion, it forms a neutron star or black hole
- flares up to hundreds of millions of times its former brightness
neutron star
- smallest and densest star
remnants of a star that dies through particular types of supernova gravitational collapses
-very small and very dense
- generally have less than 3 solar masses
-anything larger than three solar masses and the core will collapse onto itself forming a black hole
black hole
gravitational vacuum from which even light cannot escape
- formed after a supernova when the core collapses upon itself
-consume nearby matter which may include stars or even other black holes
pulsar
type of neutron star which emits radiation that appears as a pulse when observed from Earth
- this happens because the star is rapidly spinning and emitting energy
- when the roaring points it towards earth, we see the energy released as a pulse
binary star
star system made up of two stars orbiting around a common center point
- many of the stars seen in the night sky might be a binary star system
- the two stars are so close that the light appears to be coming from a single point
blue stars
"class O stars"
- the hottest of the main sequence stars
- a blue supergiant, which can have the surface temp of around 40,000 degrees kelvin or higher, is one of the hottest types of stars known to exist
-blue star burns HOTTER than a red star
cepheids
-pulsating variable stars
- change luminosity at very regular intervals and by very regular amounts
-this makes them excellent standard candles and they are useful for determining distances in space
metallicity classification
- the population 1, 11, and 111 classification system indicated the metallicity of stars
- important because it is believed that through it we can tell the age of a star
population 111 stars
lowest in metal content and thus the oldest
- when formed, there wasn't much metal in the universe
-still unobserved since it is believed most of them went supernova soon after the universe's creation
population 11 stars
- oldest of today's observed stars and were formed from the metallic remnants of the population 1 stars
population 1 stars
youngest and highest in metal content, recycling metal that was formed by other stars and stellar events before them
- the sun= population 1 star
star cluster
- group of stars gravitationally bound
- 2 primary forms of star clusters which are globular clusters and open clusters
globular cluster
- contains very old (pop 11) stars
-can contain several million stars in a. very small region; tightly bound
-usually yellow stars and red stars are present with the very rare blue star
-found in galactic halo
open cluster
- made up of young stars which re usually brighter and burning hotter than their globular cluster counterparts
- blue stars are more common though there are nowhere near as many stars in an open cluster as there are in a globular cluster
-open clusters usually last for only a few hundred million years before being dispersed by gravitational affects of other stellar bodies
fusion
-powers the sun and the stars
-process by which starts convert their hydrogen into helium
- provides the luminosity and heat by which the stars are classified
-two types of fusions primarily seen are the proton-proton chain reaction for smaller stars like the sun and the CNO cycle for larger stars
Proxima centauri
-closest star to our own
"only" 4.2 light years way from the sun
- the Proxima in its name is latin for "nearest to" which is an easy way to remember it
age of our solar system
the currently accepted estimates place the age at about 4.578 billion years old
Orion arm
location of our solar system in the Milky Way galaxy
comet
a ball of ice, rock and dust which usually originates in the kulper belt or Oort Cloud
- orbits the sun, burning of gasses the closer it gets to the sun during its orbit
kuiper belt
- area past the orbit of Neptune that is filled with icy bodies mostly gaseous in nature (frozen methane, water)
- it is believed tcome from this area
Oort Cloud
a hypothetical cloud of many billions of icy objects on the outskirts of the solar system
- we don't have any firm proof of its existence, models of solar system formation agree that it must be there
- it is believed that many of our solar systems long-period comets do oringinate from this cloud
planets
eight planets are currently in the solar system
MVEMJSUN (in order from closest to the sun)
ringed planets
Jupiter, saturn, Neptune and Uranus all have rings
- the last 4 in the solar system
- Saturn's rings are the largest
gaseous surface
the last 4 have gaseous surfaces
-the last 4 have rings, are the largest, and are gaseous
rocky surfaces
first 4 have rocky surfaces
Venus and mercury
the only two planets in our solar system with NO natural orbiting moons
venus
has an atmosphere of about 95% carbon dioxide that acts as a greenhouse
- because of its proximity to the sun and its atmosphere, it is extremely hot with surface temps between 800 and 900 degrees Fahrenheit
earth's age
approx 4.54 billion years old
great oxidation
scientists use this term to explain the formation of oxygen in the earth's atmosphere, believe it occurred roughly 2.5 billion years ago and was due to algae booms
earth's rotation
takes 23 hrs and 5t6 minutes for earth to rotate completely on its axis
earth's seasons
affected by the orbit of the earth around the sun in combo with its tilt (23.5 degrees) on its axis
- results in different parts of the world being colder/warmer at different parts of the year
-
precession
the tilt of the earth makes a small circle, like a top spinning
- takes earth 26,000 years to make one full ":wobble" or precession cycle
- caused by the gravitational forces of the sun nd our moon pulling on the earth
- so now the Polaris is the North Star but in a few thousand years there will be another start that takes its place as the earth's precession causes the night sky to move
celestial sphere
- tool used by astronomers
- an imaginary sphere around earth which allows observers to attribute celestial objects to particular places on the sphere
- it is divided by an equator which matches earth's equator and has its own celestial north and south poles
equinox
twice a year occurrence where the earth is tilted neither towards nor away from the sun
- at the moment of the equinox, the center of the sun appears to be directly overhead a person who is standing on the earth's equator
-geometric center of the sun is above the horizon for 12 hours
vernal equinox
- the equinox that occurs in march (beginning of spring in northern hemisphere)
autumnal equinox
equinox that occurs in September (the beginning of fall in the north)
solstice
twice a year occurrence when earth is tilted mostly towards the sun
- opposite of the equinox
the beginning fo summer in the north is accepted as the summer solstice (the sun is farthest north in the sky)
- the first day of winter is the winter solstice (sun is farthest south)
meteoroid
a piece of Ricky or metallic debris smaller than an asteroid which travels through the solar system
meteor
name given tot the visible path of a meteoroid as it enters the atmosphere of the earth
meteorite
surviving remnant of a meteor on the surface of earth
asteroids
- bodies of solid rock and metal which are relatively small compared to the planets
- most of the rocky asteroids in the solar system are found in the asteroid belt between mars and Jupiter
mars
has an atmosphere of 95% carbon dioxide but also has very low density so the gas DOESNT have a greenhouse effect like it does on Venus
Olympus mons
found on mars
-highest mountain in the solar system
asteroid belt
main belt of asteroids in our solar system between mars and Jupiter