11-Industrial Revolution & Imperialism
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Industrialization
a rapid major change in an economy (as in England in the late 18th century) marked by the general introduction of power-driven machinery or by an important change in the prevailing types and methods of use of such machines
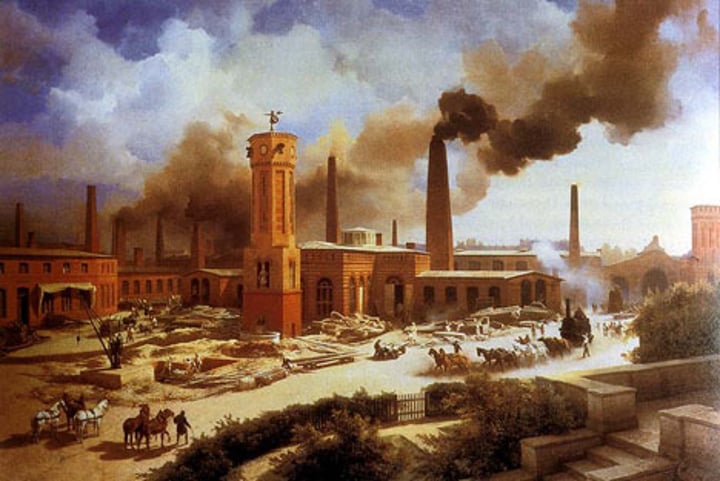

factors of production
the resources needed to produce goods and services that the Industrial Revolution required (land, labor, and capital)

Textile Industry
Industries primarily concerned with the design or manufacture of clothing as well as the distribution and use of textiles.

entrepreneur
a person who organizes, manages, and takes the risks of a business

urbanization
city building and the movement of people to cities

corporation
a business owned by stockholders who share in its profits but are not personally responsible for its debts

workshop
A room or building in which goods are manufactured or repaired

Laissez faire
economic policy of letting owners of industry and business set working conditions without interference, French for "let do", let people do as they please
capitalism
an economic system in which the factors of production are privately owned and money is invested in business ventures to make a profit

socialism
The factors of production are owned by the public and operate for the welfare of all

communism
a way of organizing a society in which the government owns the things that are used to make and transport products (such as land, oil, factories, ships, etc.) and there is no privately owned property

Unions
a voluntary labor association in which the unions speak on behalf of the workers

strike
refuse to work

power loom
invented by Edward Cartwright , it speeded up the production of textiles

spinning mule
A machine powered by water that could spin many threads at one time.
Adam Smith
Scottish philosopher, father of Capitalism. Wrote The Wealth of Nations

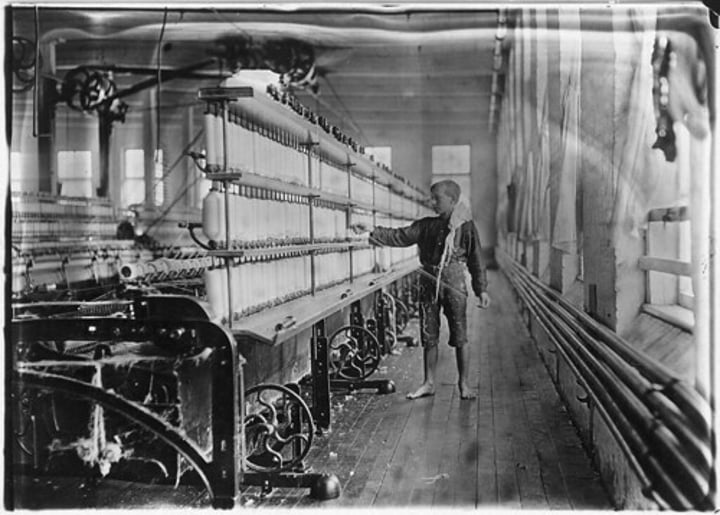
Industrial Revolution
A period of rapid growth in the use of machines in manufacturing and production that began in the mid-1700s. Began in Britain.

James Watt
Invented the steam engine

Reform Movement
Work to change society for the better. Focused on improving conditions for the poor, enslaved, imprisoned, women, and public education.

Assembly line
Production method that breaks down a complex job into a series of smaller tasks
Mass production
Process of making large quantities of a product quickly and cheaply
Proletariat
Marx's term for the exploited class, the mass of workers who do not own the means of production
Suffrage
the right to vote
Monopoly
Complete control of a product or business by one person or group
Social Darwinism
The application of ideas about evolution and "survival of the fittest" to human societies - particularly as a justification for their imperialist expansion.
Zionism
A policy for establishing and developing a national homeland for Jews in Palestine.
Cecil Rhodes
British entrepreneur and politician involved in the expansion of the British Empire from South Africa into Central Africa. The colonies of Southern Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) and Northern Rhodesia (now Zambia) were named after him. (p. 736)
Sphere of Influence
A foreign region in which a nation has control over trade and other economic activities.
Open Door Policy
A policy proposed by the US in 1899, under which ALL nations would have equal opportunities to trade in China.
Second Agricultural Revolution
Benefiting from the Industrial Revolution improved methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of farm products.
white mans burden
idea that many European countries had a duty to spread their religion and culture to those less civilized
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
Race for Africa
The competition between European nations to colonize African lands in search of natural resources and to create a larger market for goods.
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Panama Canal
Ship canal cut across the isthmus of Panama by United States, it opened in 1915.
Suez Canal
A ship canal in northeastern Egypt linking the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea
interchangable parts
uniform pieces that can be made in large quantities to replace other identical pieces
Sepoy Rebellion/Mutiny
an 1857 rebellion of Hindu and Muslim soldiers against the British in India
Opium War
1839-1842. Chinese attempted to prohibit the opium trade, British declared war and won against Chinese. Treaty of Nanjing, agreed to open 5 ports to British trade and limit tariffs on British goods.
Berlin Conference
A meeting from 1884-1885 at which representatives of European nations agreed on rules for the colonization of Africa
Marx and Engles
Authors of the Communist manifesto, Economic conditions determined the nature of everything in society. Class conflict will lead to a bourgeoisie revolution.
Fourier and Owen
Utopian socialists. Fourier (1772-1837) and Owen (1771-1858) wanted communities to be of an equitable society. They were to work together rather than as competitors, providing for all needs and educating children. Made many experimental societies under this model.
Queen Victoria
queen of Great Britain and Ireland and empress of India from 1837 to 1901 (1819-1901)