Endo/Repro Exam 1: Osteoporosis and Treatment Modalities (Dr. Papas)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Define the following:
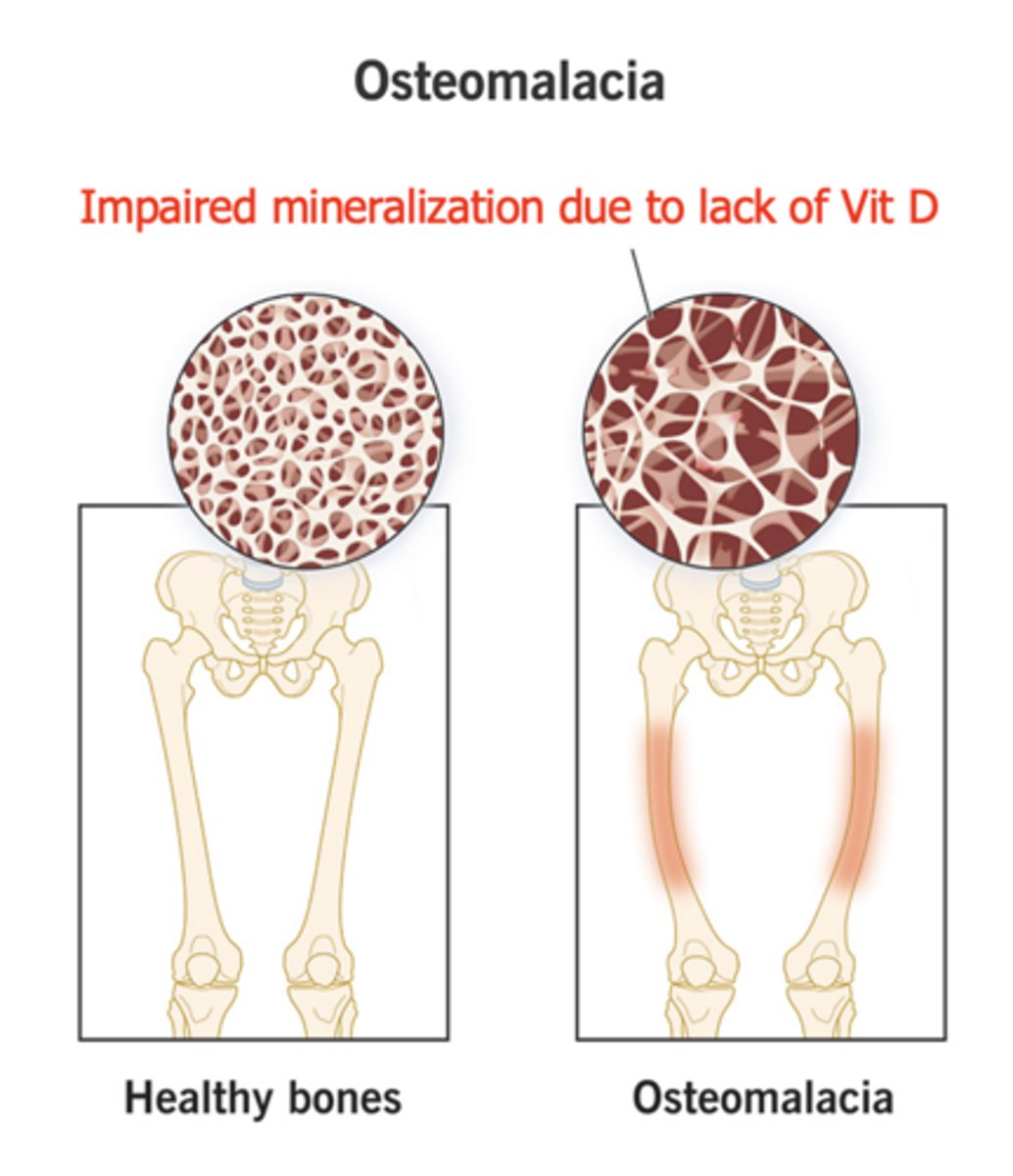
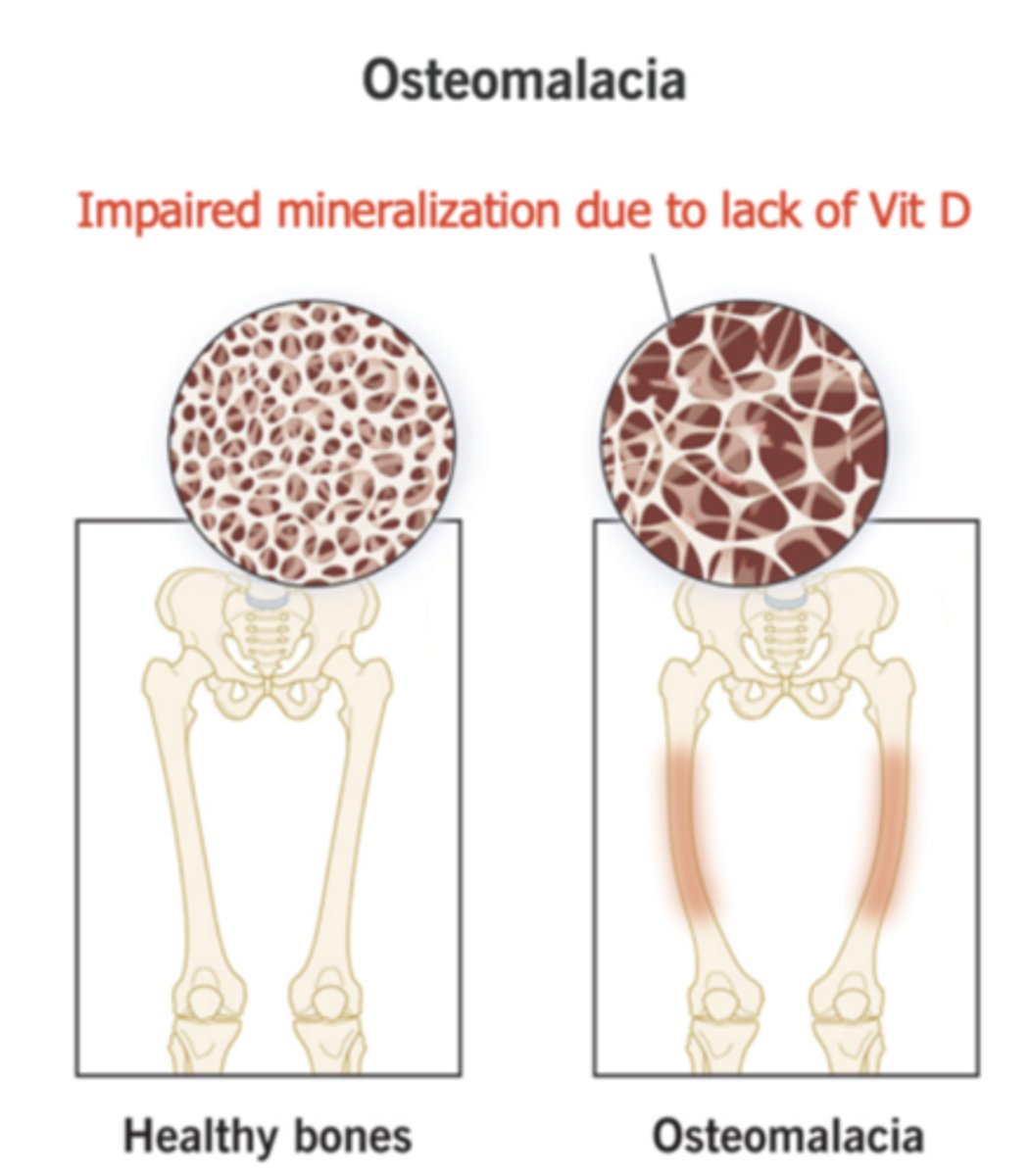
Impaired mineralization due to lack of vitamin D
Osteomalacia
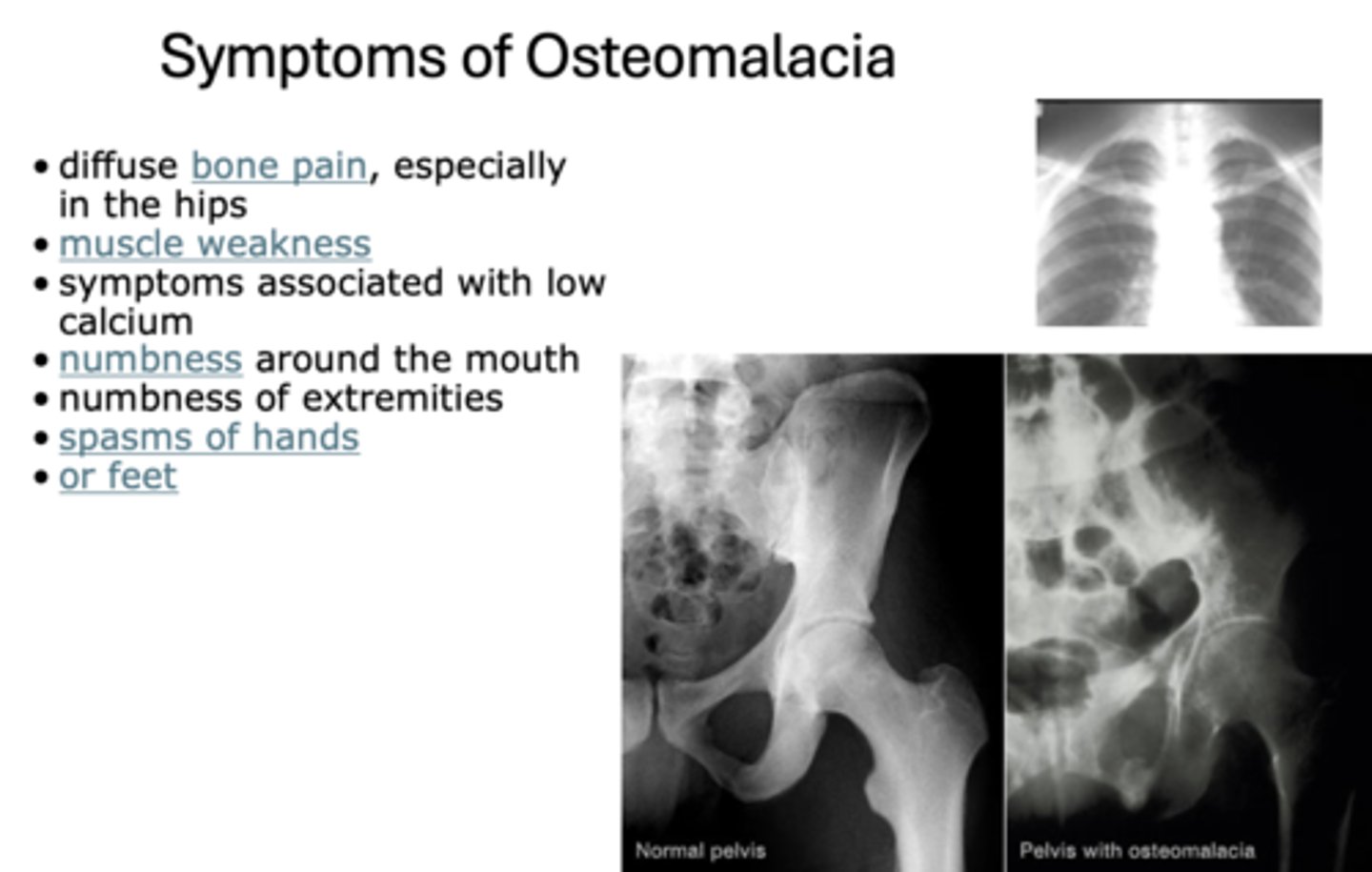
The following are symptoms of what?
- Diffuse bone pain, especially in the hips
- Muscle weakness
- Symptoms associated with low calcium
- Numbness around the mouth
- Numbness of extremities
- Spasms of hands or feet
Osteomalacia
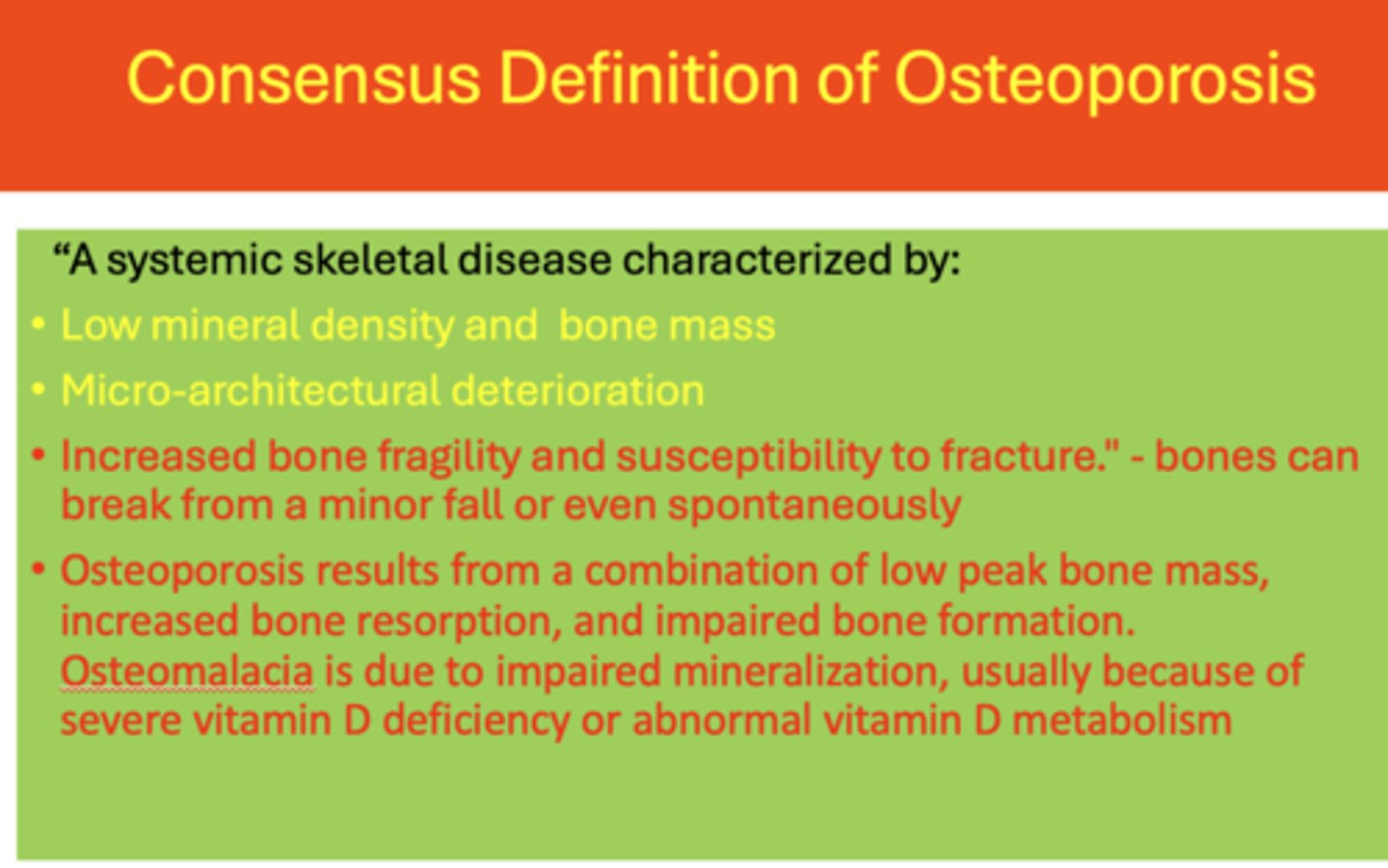
Define the following:
A systemic skeletal disease characterized by:
- Low mineral density and bone mass
- Micro-architectural deterioration
- Increased bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture. - Bones can break from a minor fall or even spontaneously
Osteoporosis
_____________ results from a combination of low peak bone mass, increased bone resorption, and impaired bone formation
Osteoporosis
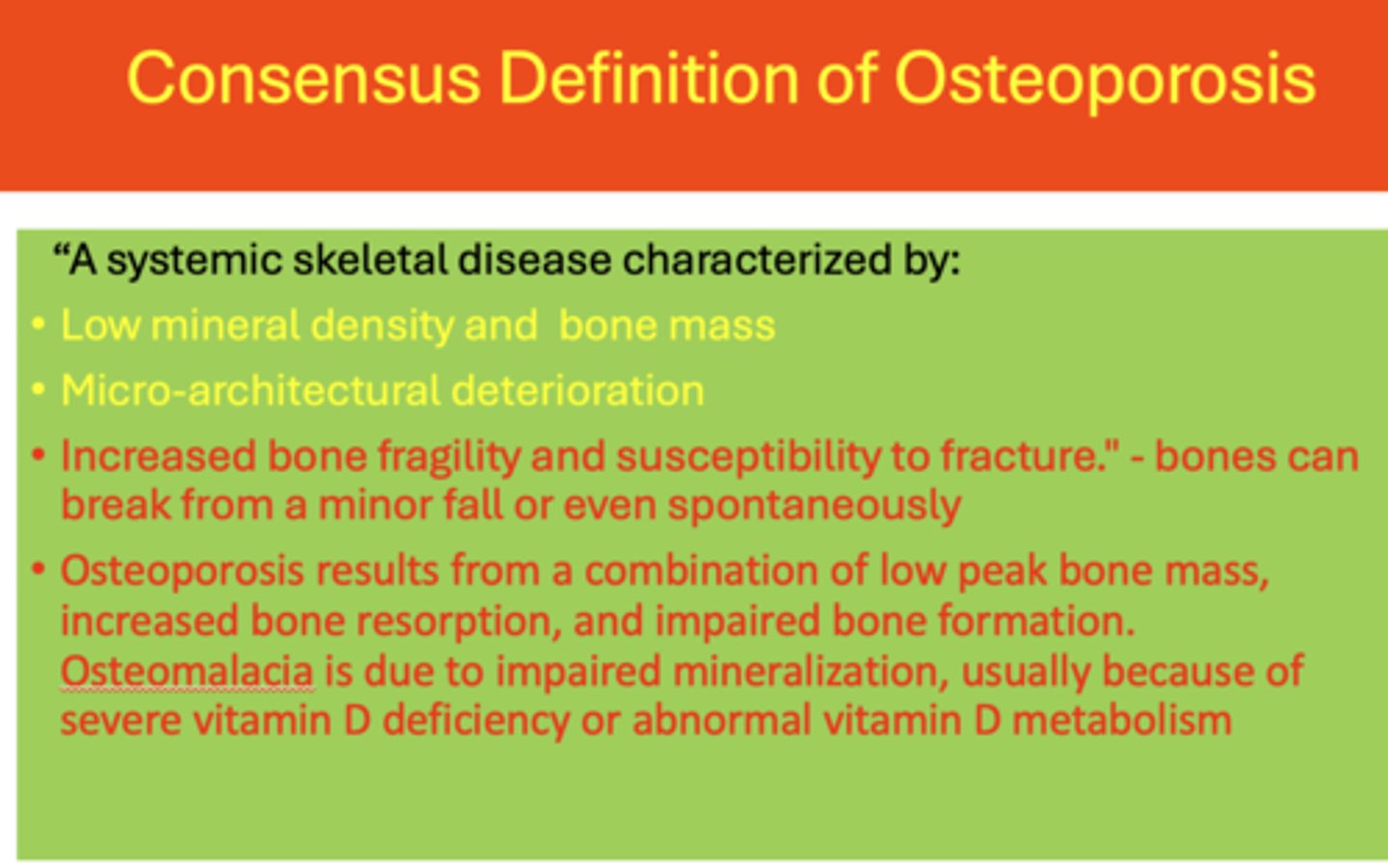
_____________ is due to impaired mineralization, usually because of severe vitamin D deficiency or abnormal vitamin D metabolism
Osteomalacia
What is the lifetime risk of osteoporosis for women?
44%

Bone is living tissue that is constantly turning over. ____________ occurs when the creation of new bone doesn't keep up with the loss of old bone.
Osteoporosis

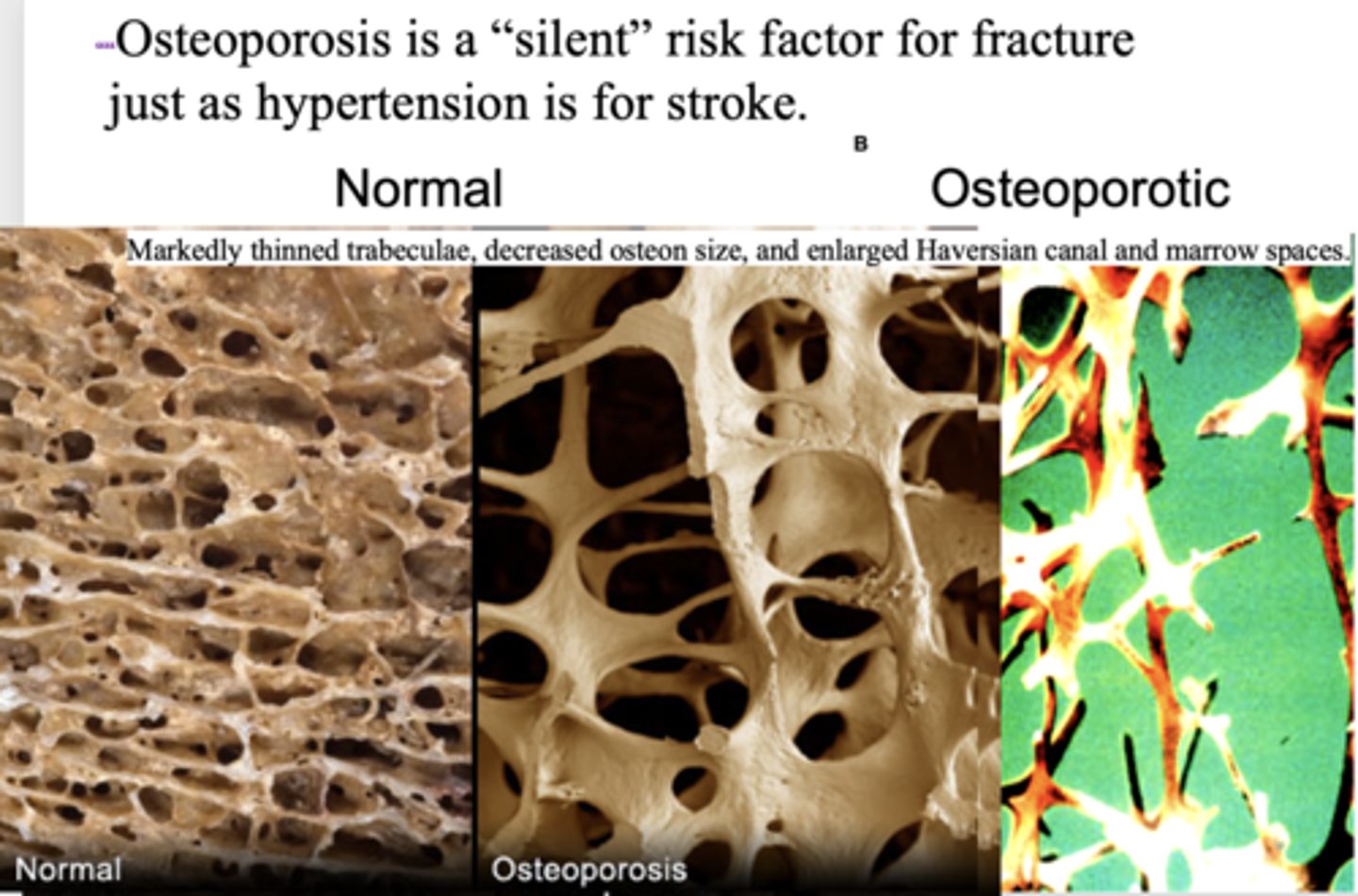
___________ is a "silent" risk factor for fracture just as hypertension is for stroke.
Osteoporosis
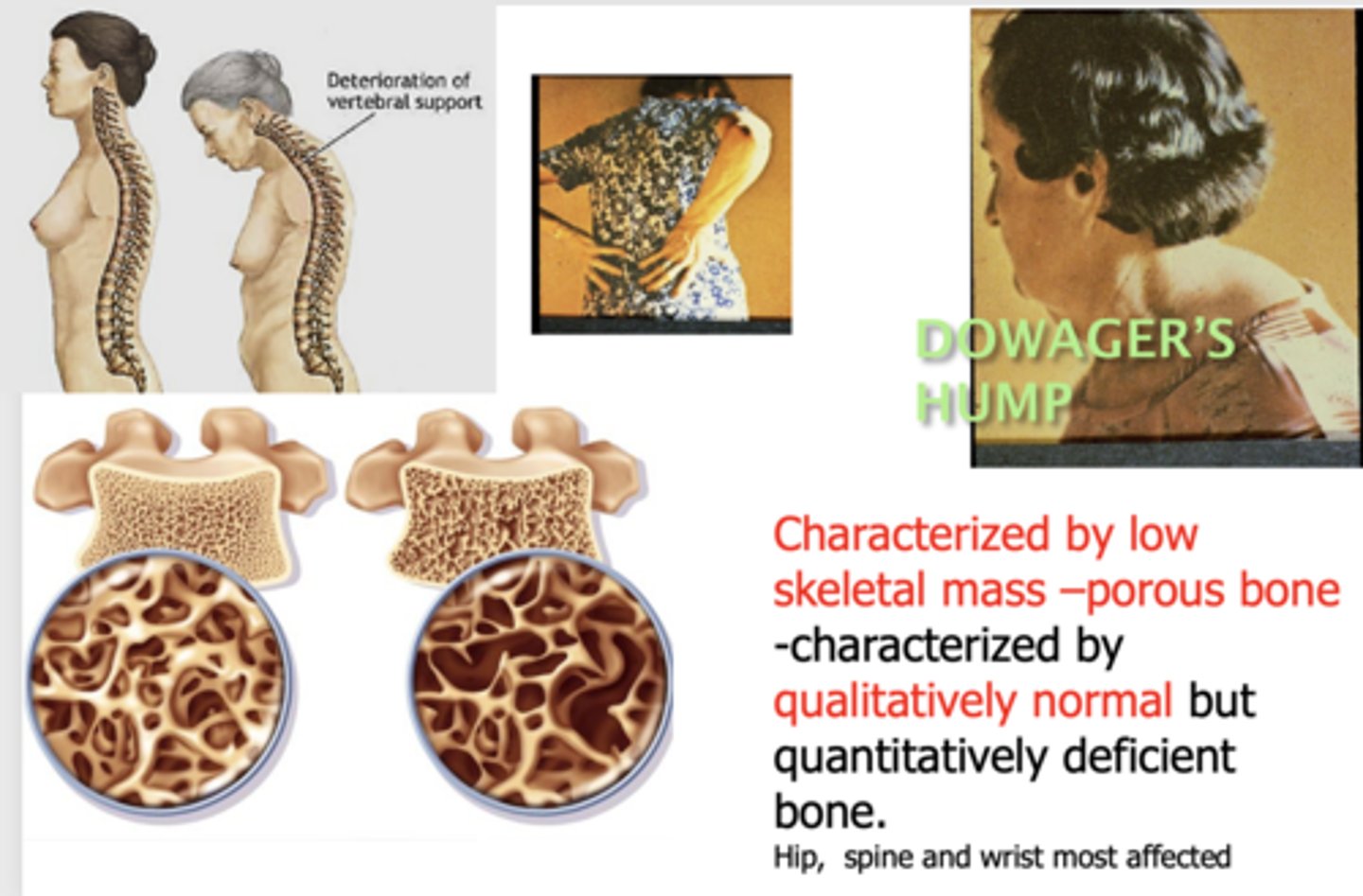
What has the following characteristics?
- Characterized by low skeletal mass –porous bone
- Characterized by qualitatively normal but quantitatively deficient bone.
- Hip, spine and wrist most affected
Osteoporosis
T/F: Osteoporosis often is not evident until it is too late
True

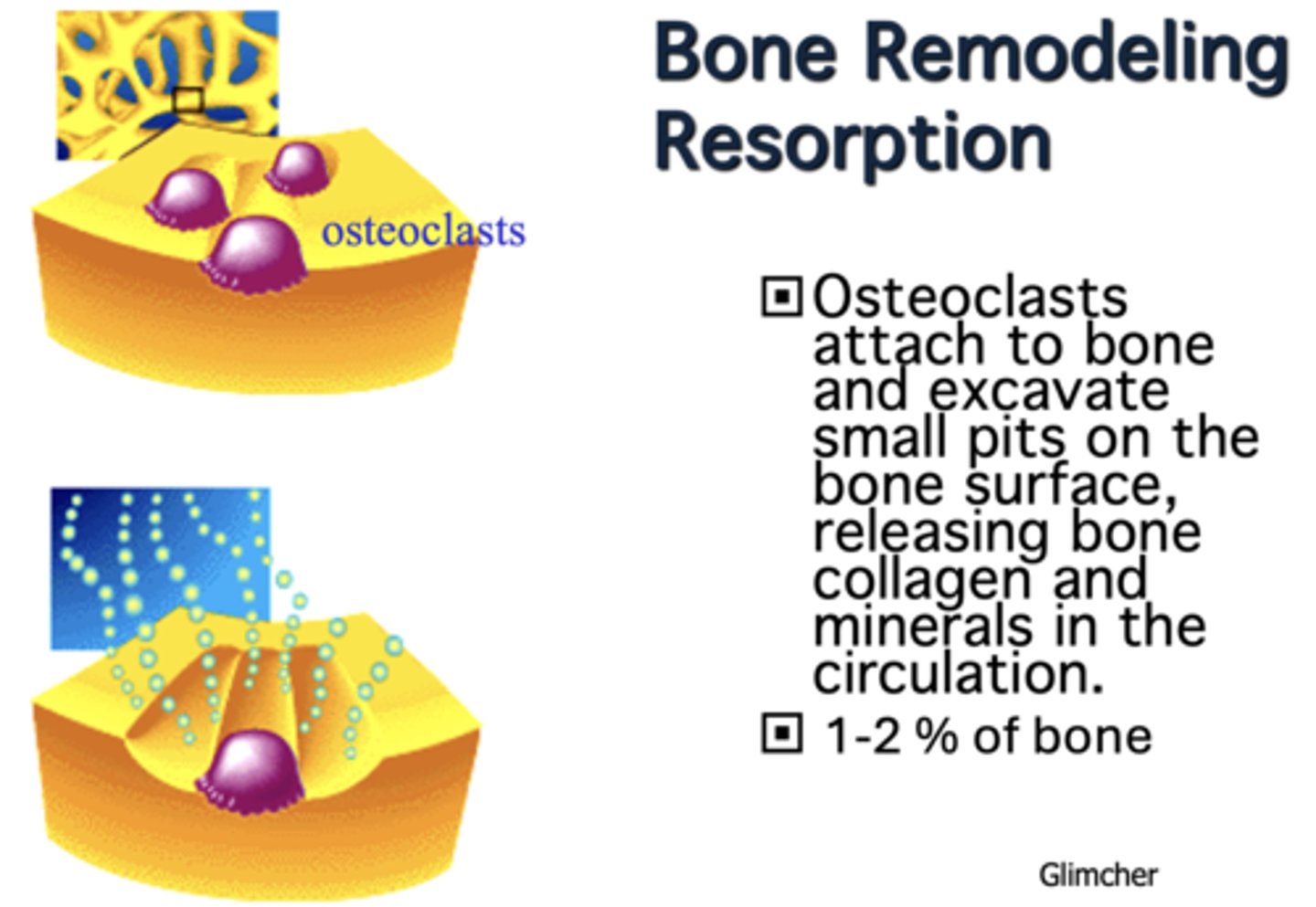
During bone remodeling and resorption, ____________ attach to bone and excavate small pits on the bone surface, releasing bone collagen and minerals in the circulation.
Osteoclasts
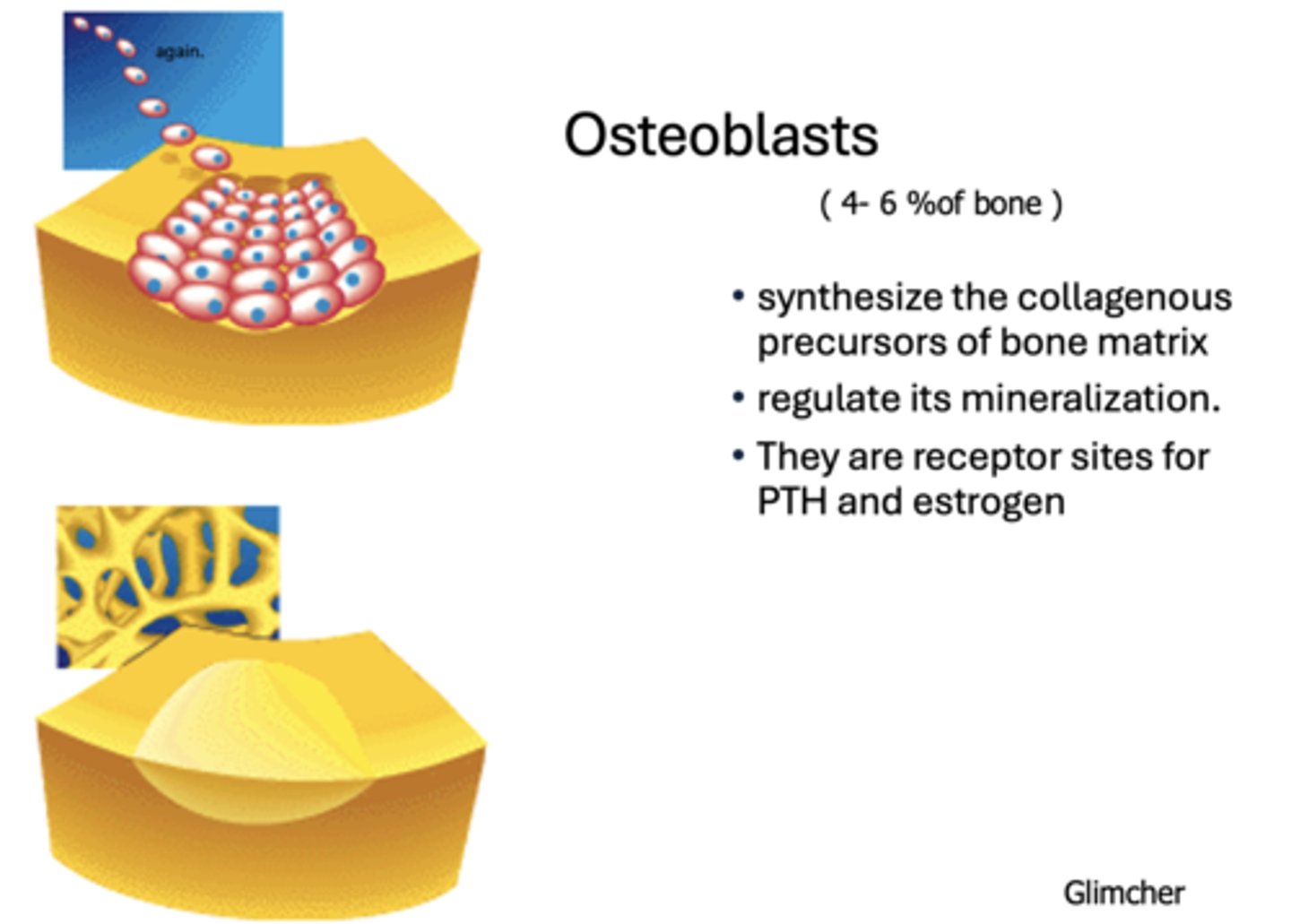
What has the following characteristics?
- Synthesize the collagenous precursors of bone matrix
- Regulate its mineralization.
- They are receptor sites for PTH and estrogen
Osteoblasts
What age is the peak bone mass in males and females?
30-40
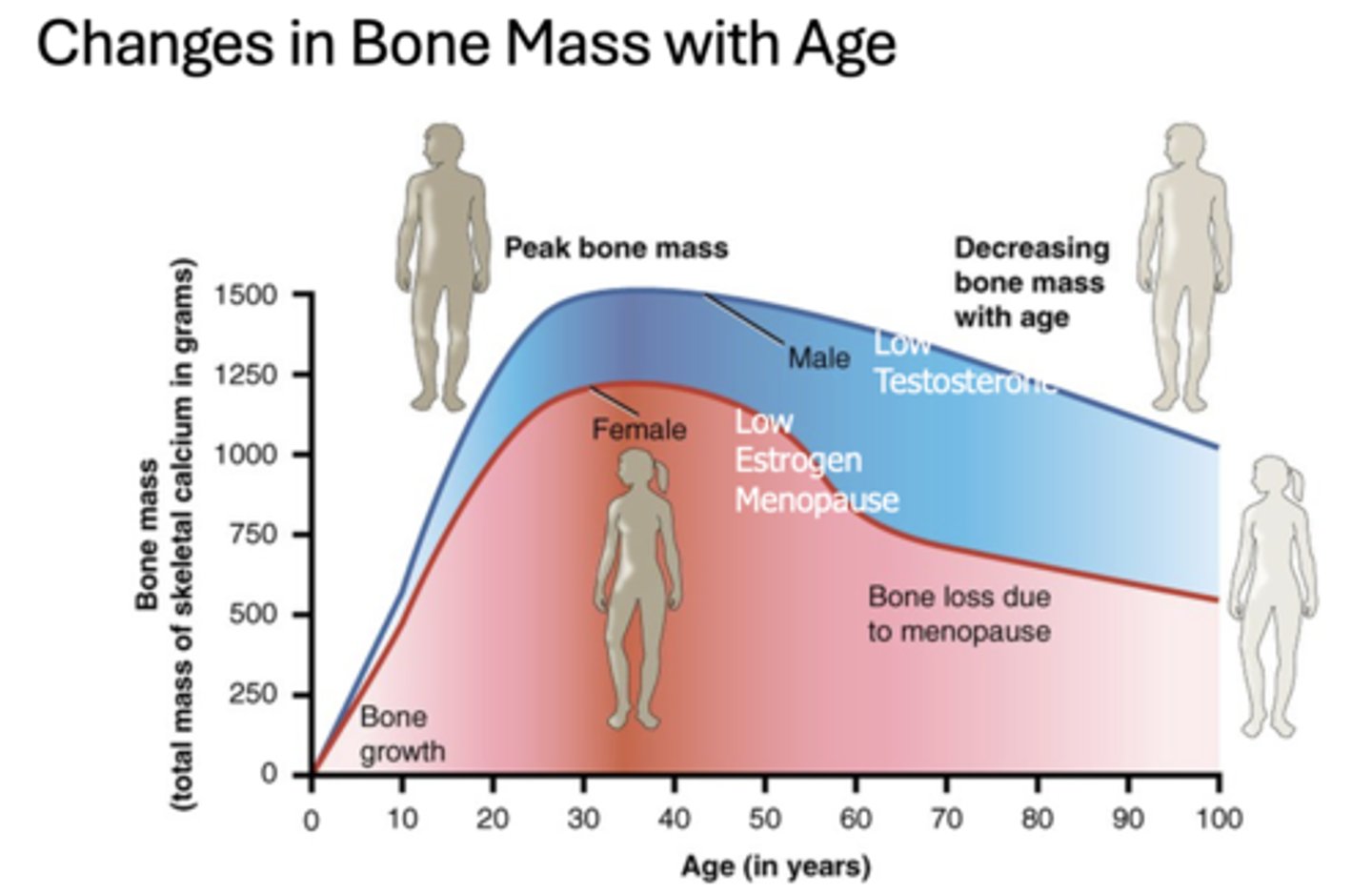
What causes males bone mass to decrease with age?
Low testosterone
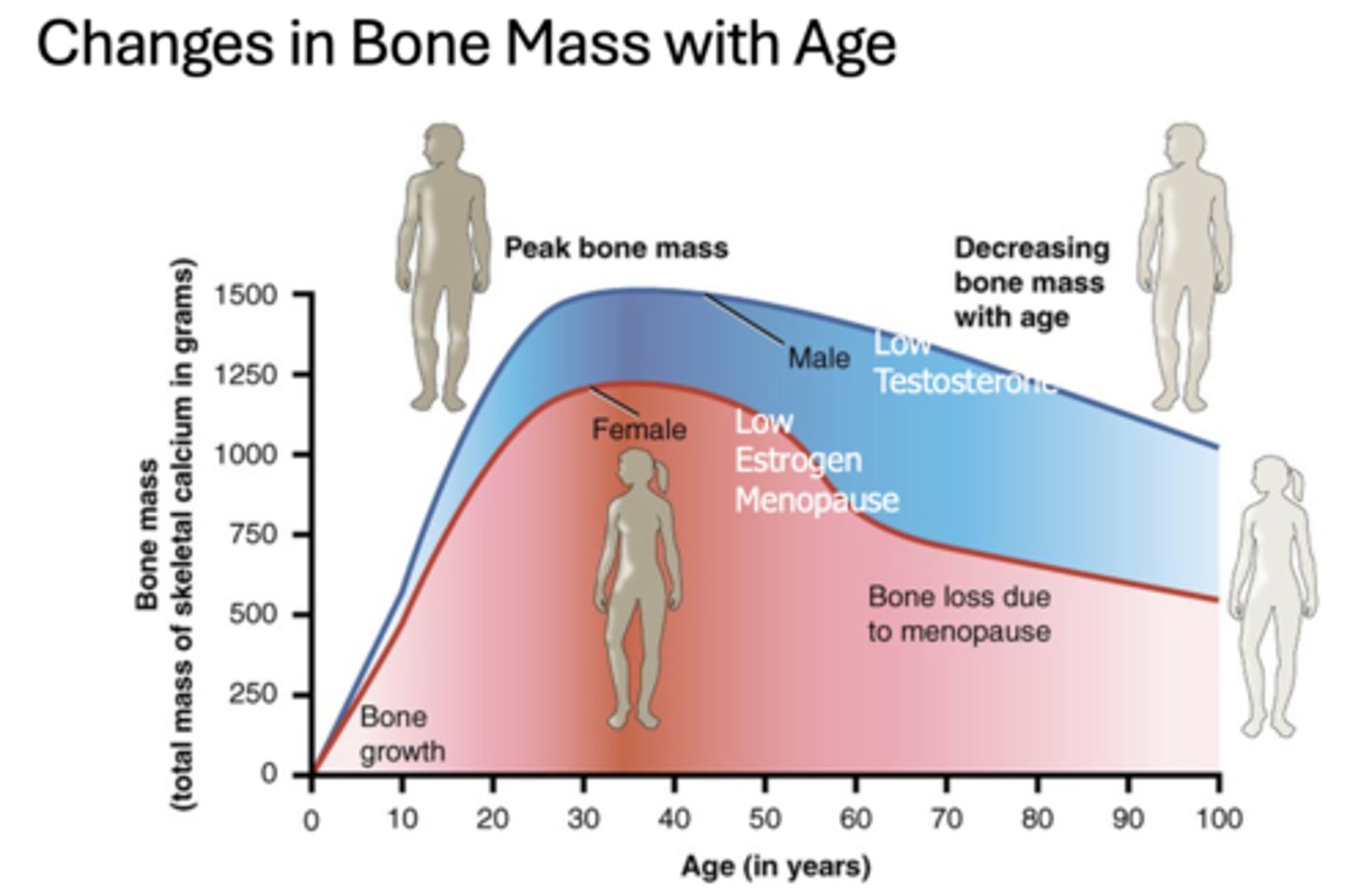
What causes females bone mass to decrease with age?
Low estrogen with menopause
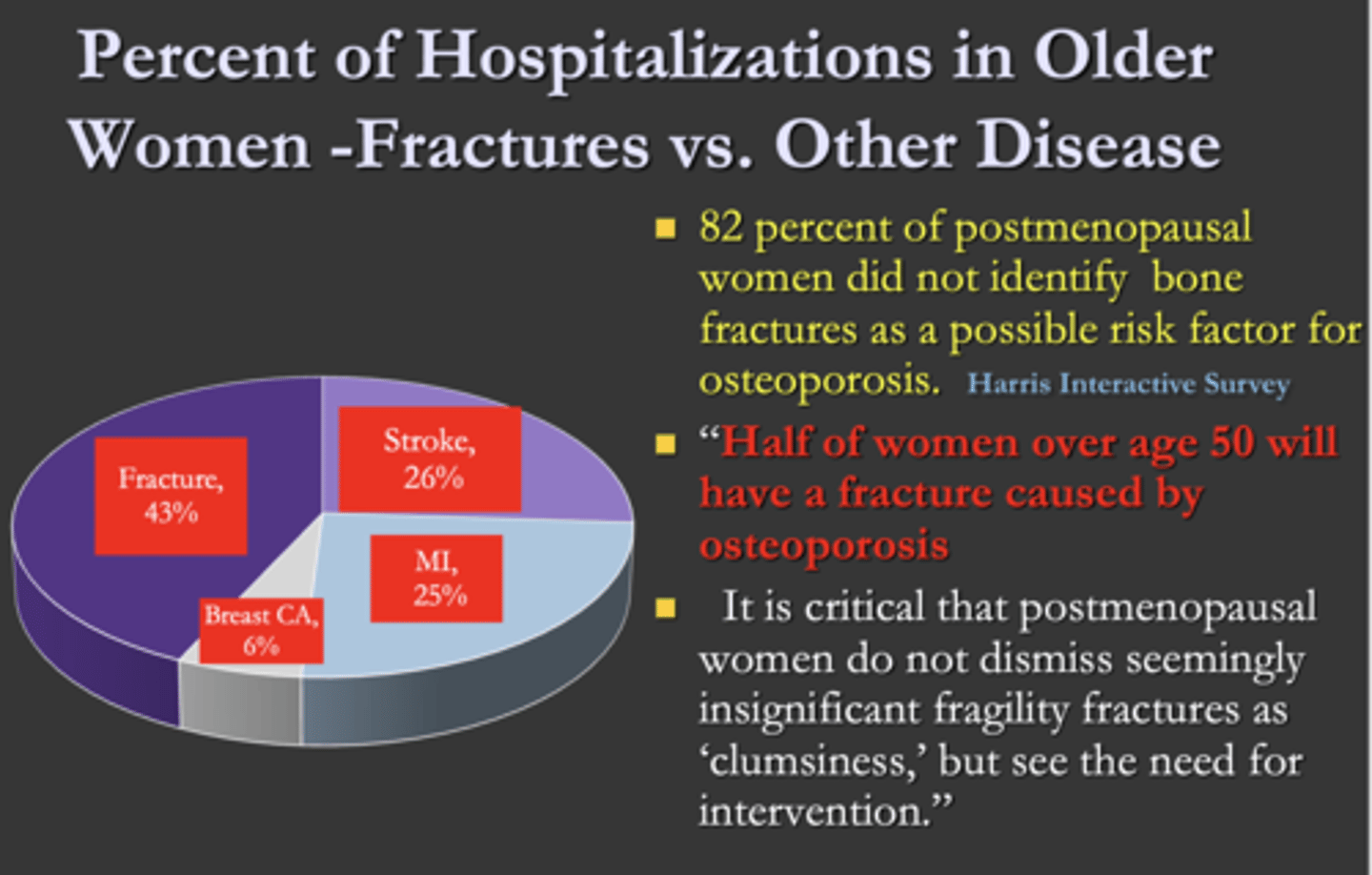
What is the major reason for older women to be in the hospital?
A. Fractures
B. Stroke
C. MI
D. Breast cancer
A. Fractures
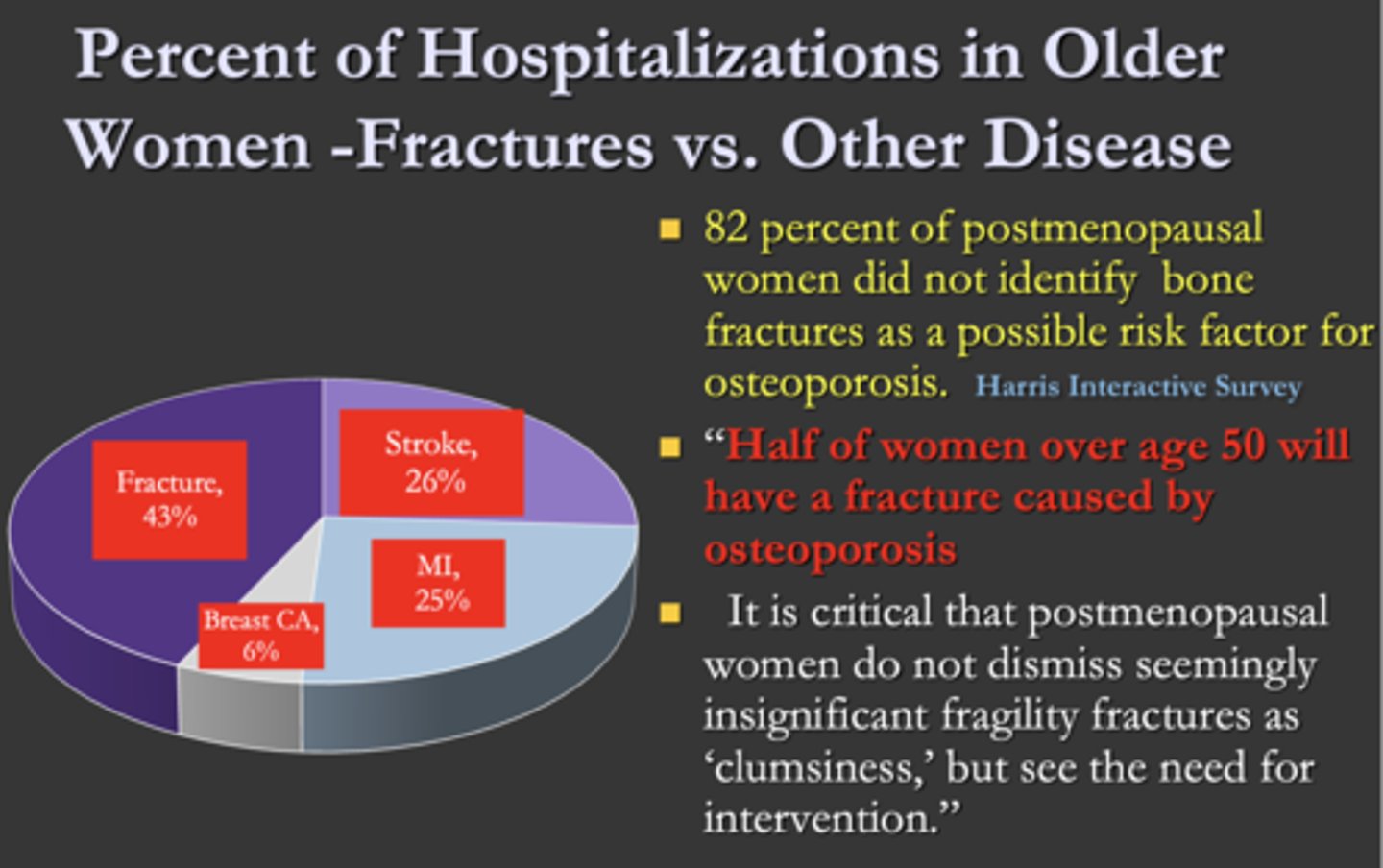
T/F: A high percentage of postmenopausal women did not identify bone fractures as a possible risk factor for osteoporosis
True (82%)
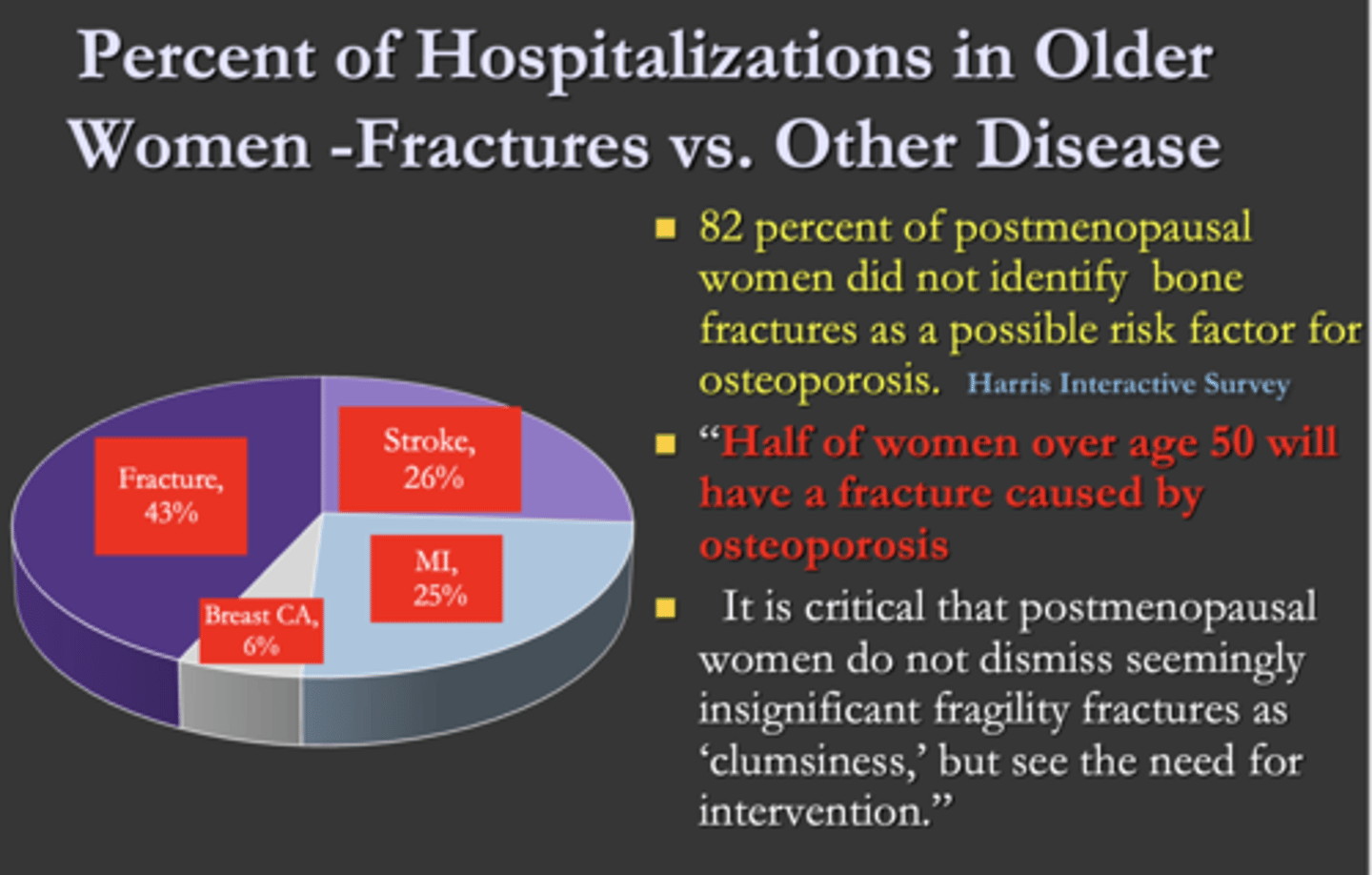
T/F: Half of women over age 50 will have a fracture caused by osteoporosis
True
Approximately ______% of patients with a hip fracture die within a year and more than ______% never completely regain function.
20%, 50%
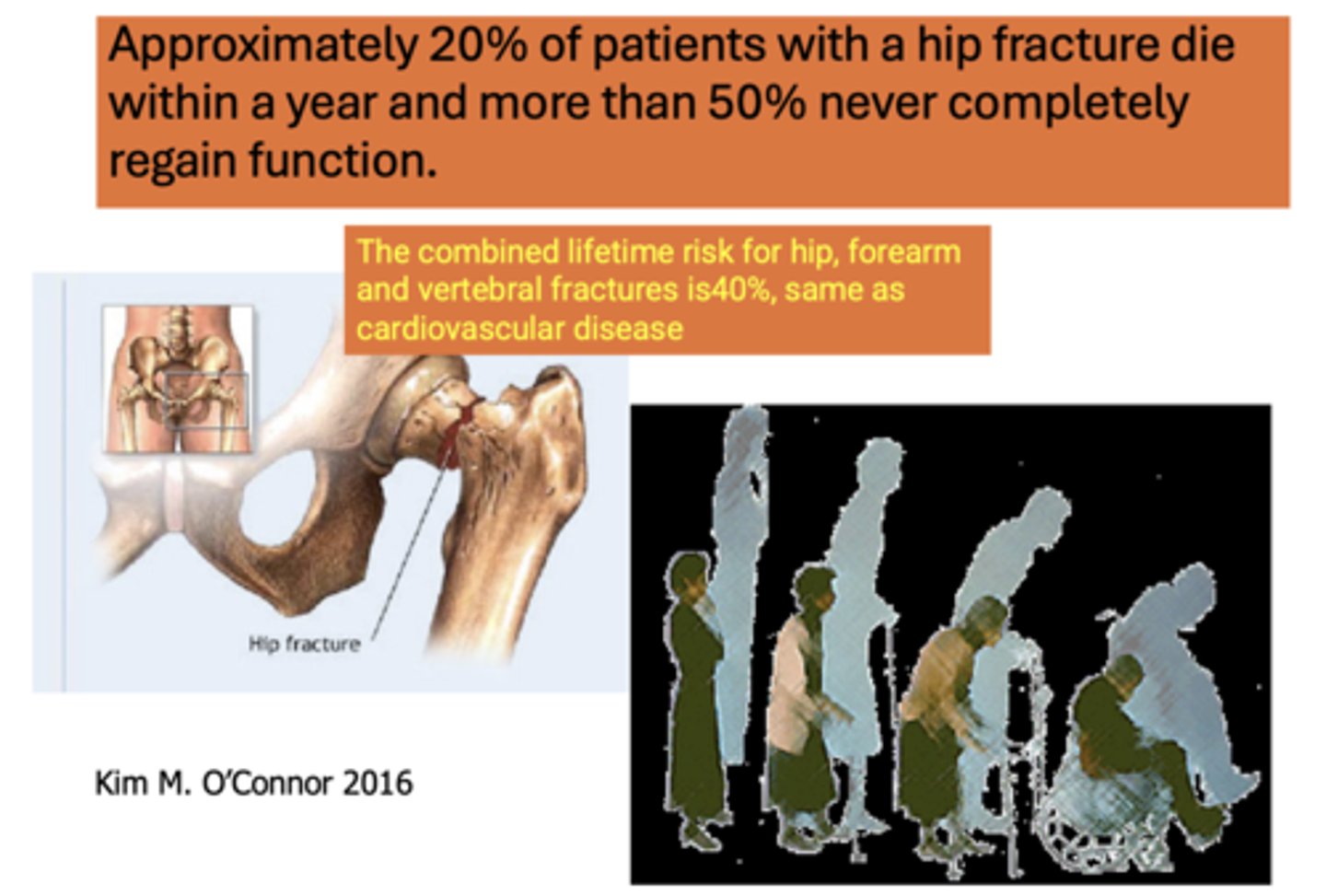
The combined lifetime risk for hip, forearm and vertebral fractures is _____%, same as cardiovascular disease
40%
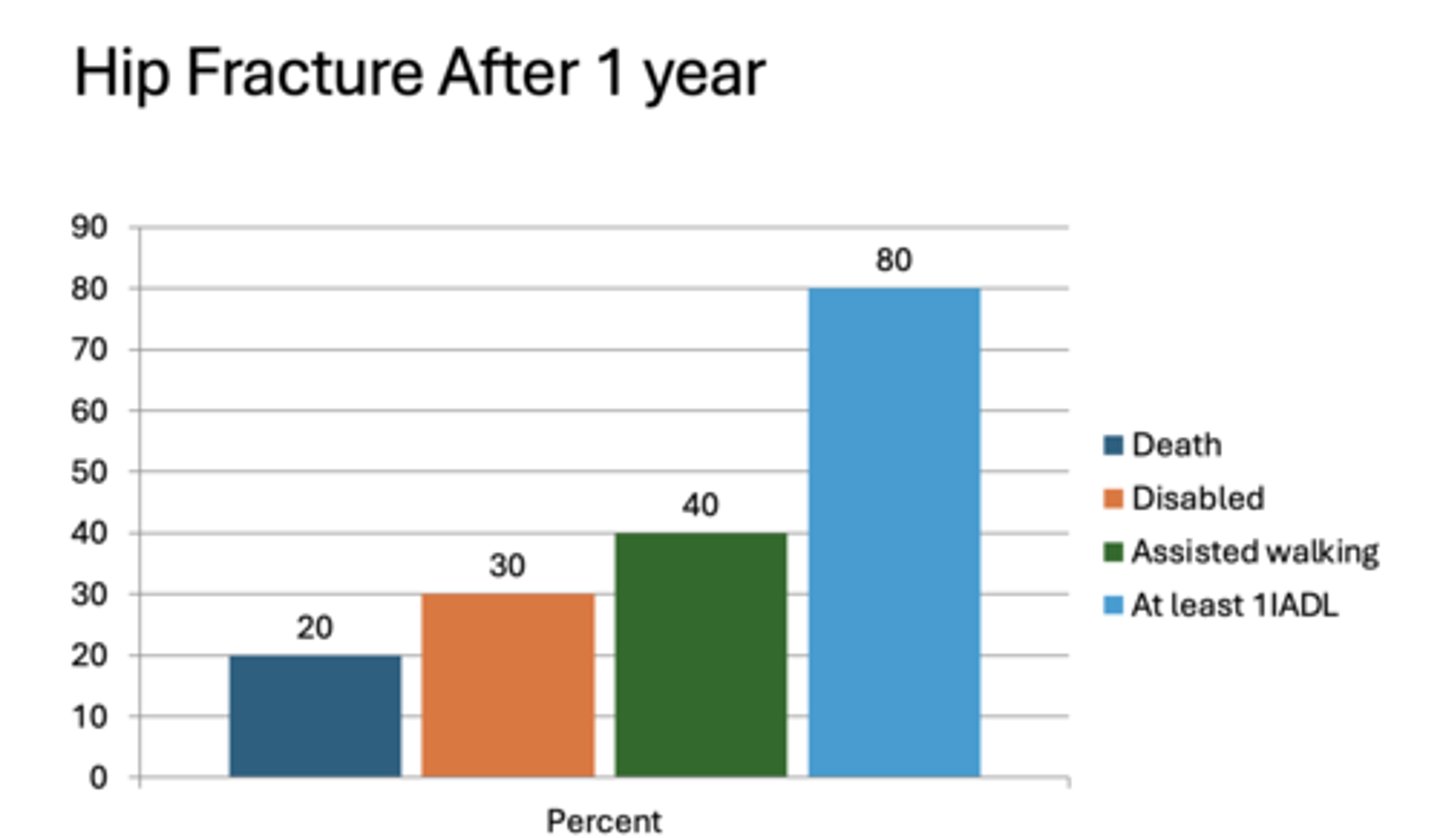
What percent of people 1 year after a hip fracture cannot participate in at least one activities of daily living?
80%
All of the following are environmental factors leading to what?
- Smoking
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Low calcium diet
- Medications such as anti-convulsives, steroids, SSRI, blood thinners, proton pump inhibitors, and some cancer medications
- High salt diet
- Low protein
- Low vitamin D / little exposure to sun
- More than 3 drinks a week
- More than 3 coffees a day
Bone loss

All of the following are risk factors leading to what?
- Low sex hormone
- History of anorexia nervosa
- Small and thin framed (below 127 lbs)
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Being a Caucasian/Asian woman
Bone loss

What is a method to measure bone density?
DXA-dual energy xray absorptiometry
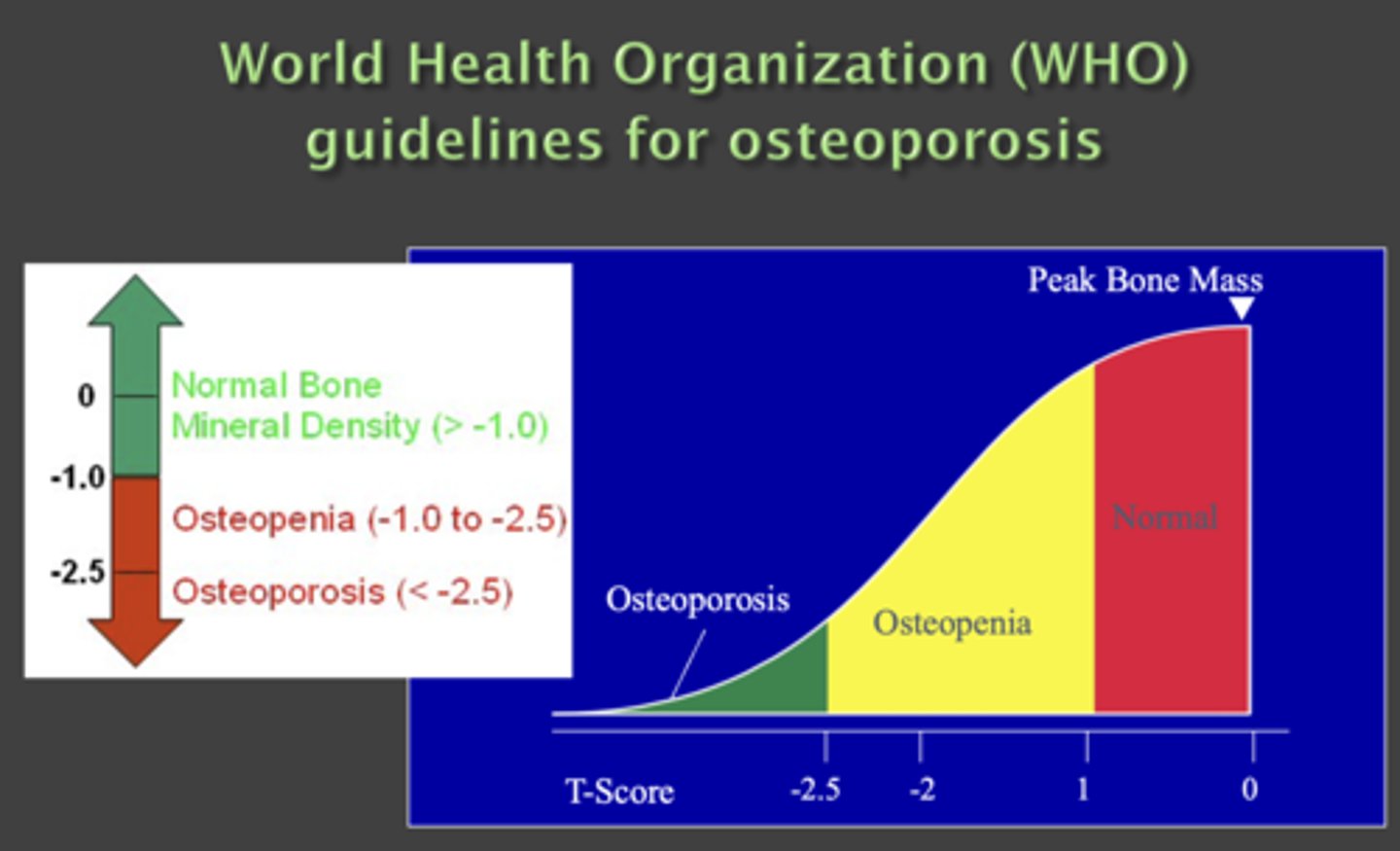
What is the T score for osteoporosis?
< -2.5
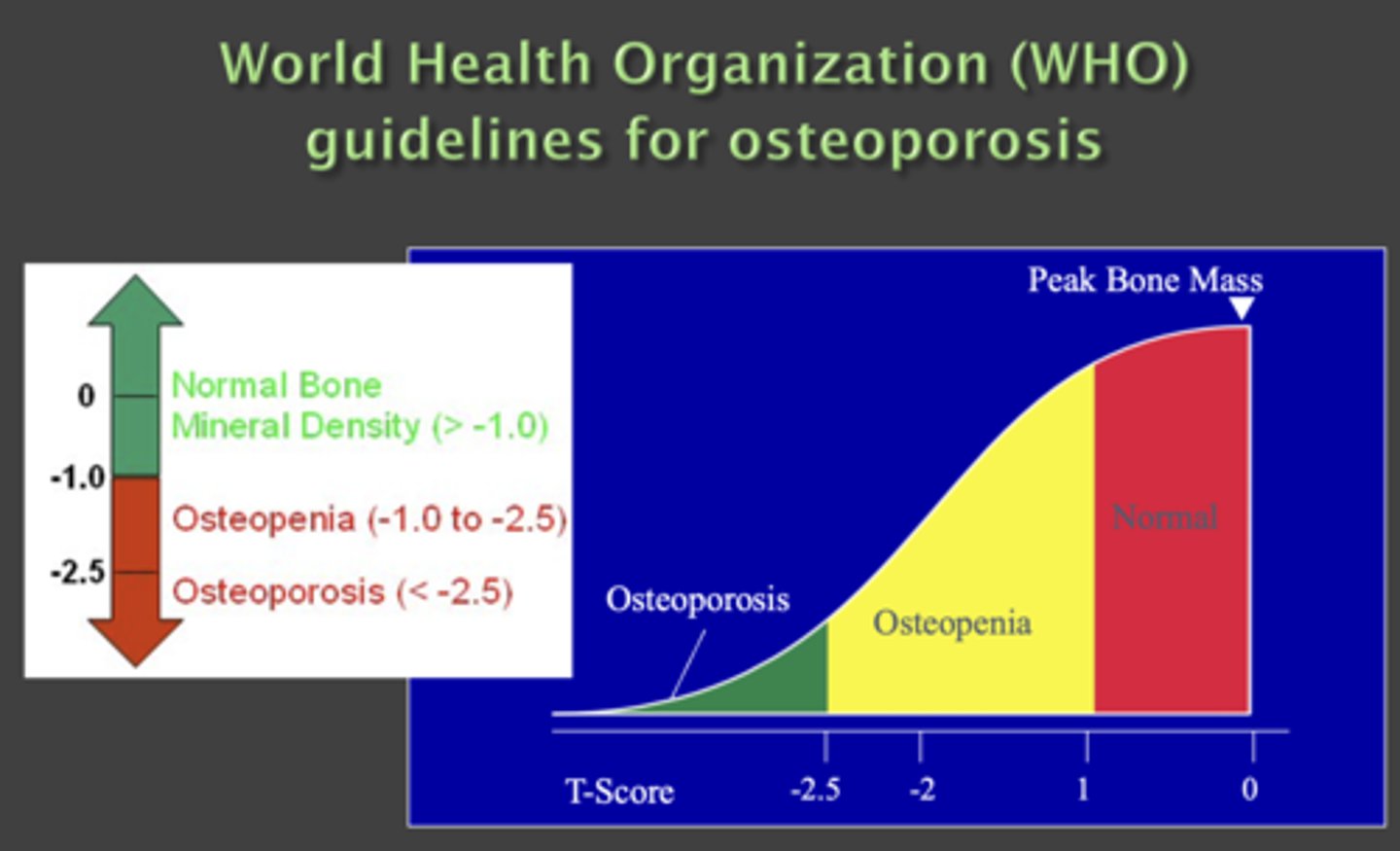
What is the T score for osteopenia?
-2.5 to -1
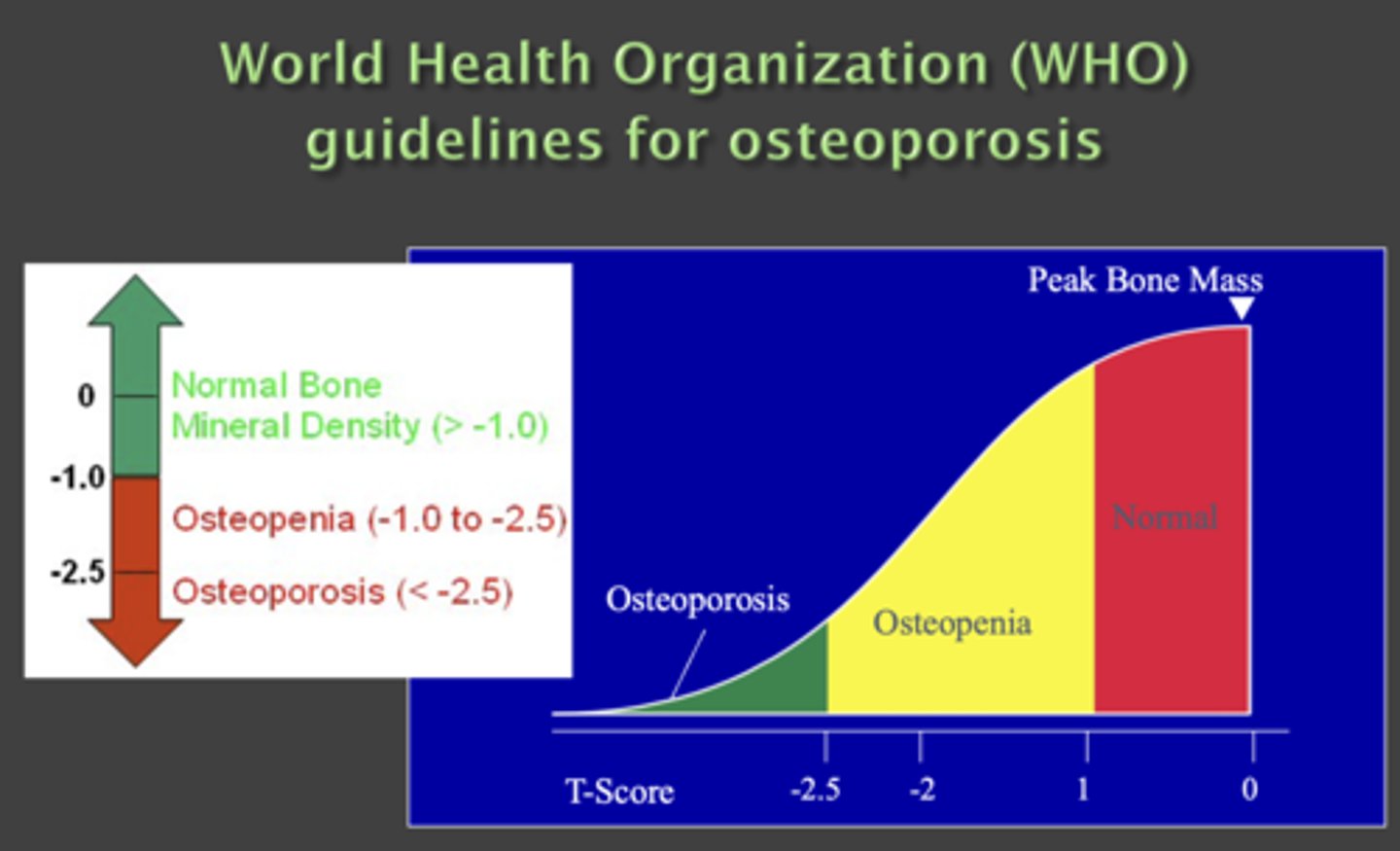
What is the T score for peak bone mass?
> -1
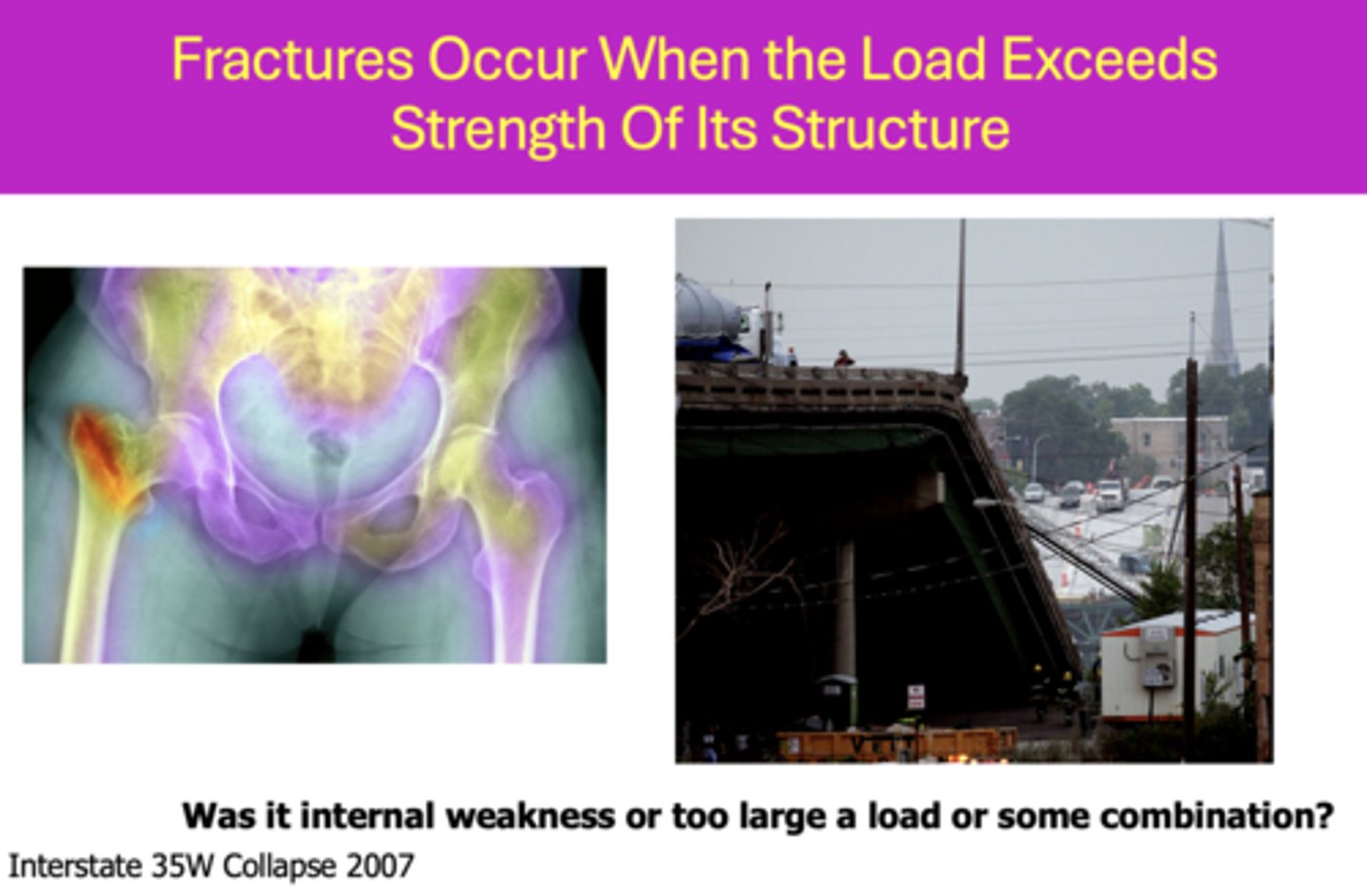
When do fractures occur based on loads?
When the load exceeds strength of its structure
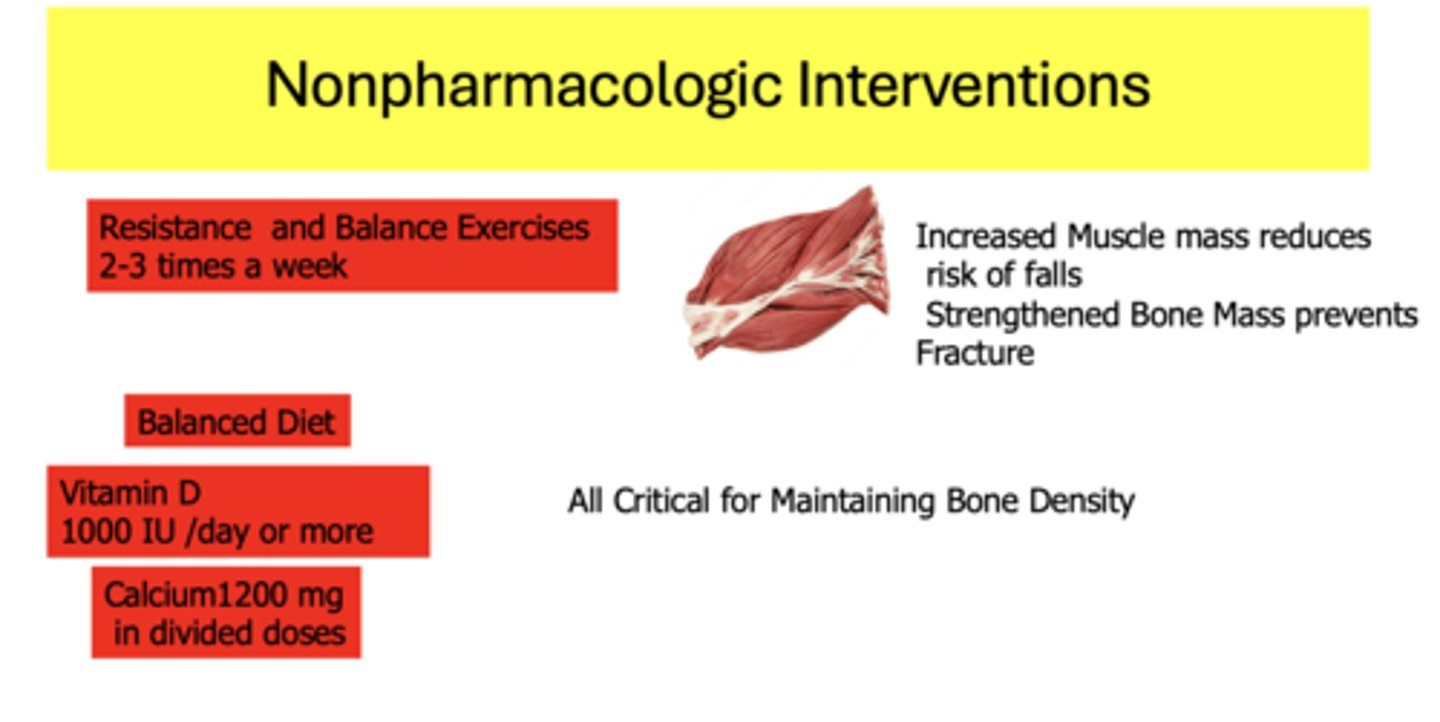
What are nonpharmacologic interventions to maintain bone density?
- Resistance and balance exercises 2-3 times a week
- Balanced diet
- Vitamin D 1000 IU /day or more
- Calcium 1200 mg in divided doses
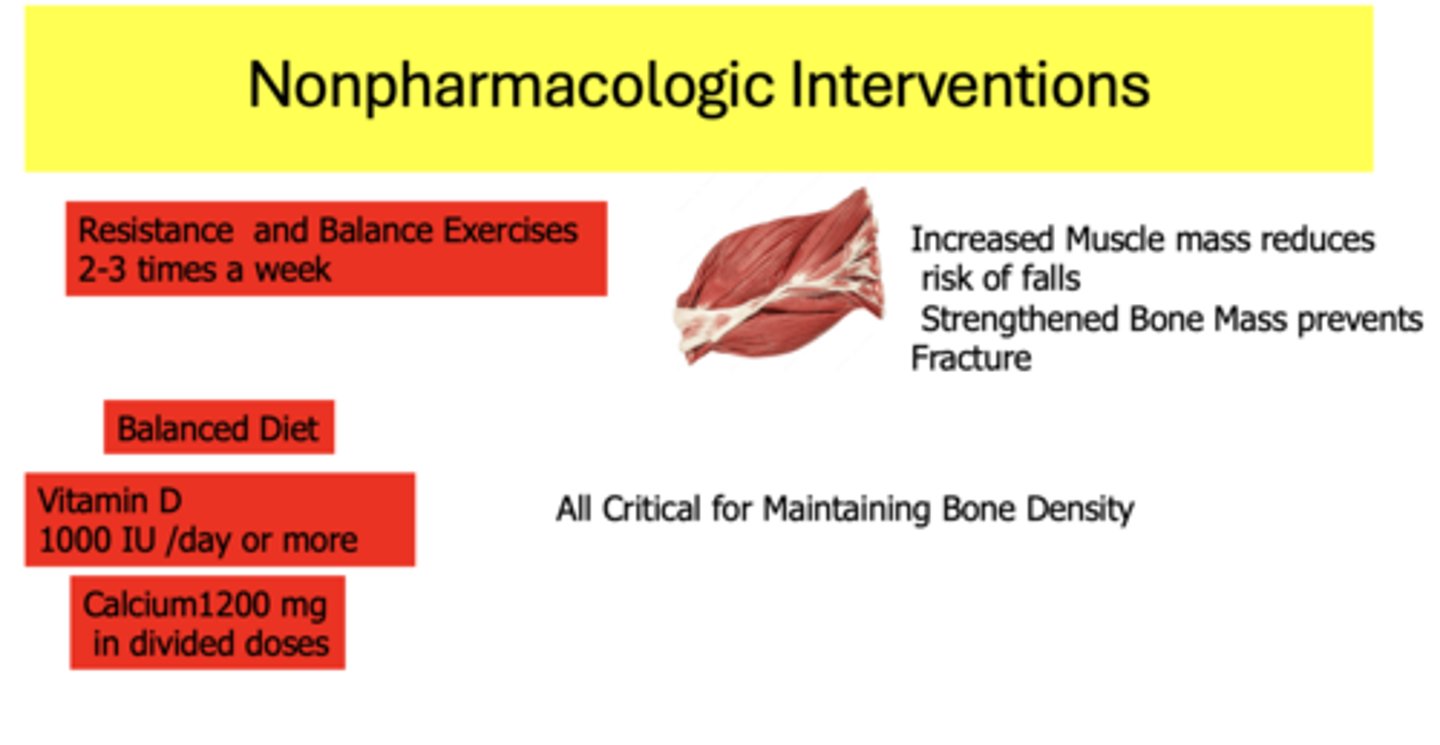
_________ muscle mass reduces risk of falls. _________ bone mass prevents fracture
Increased, Strengthened
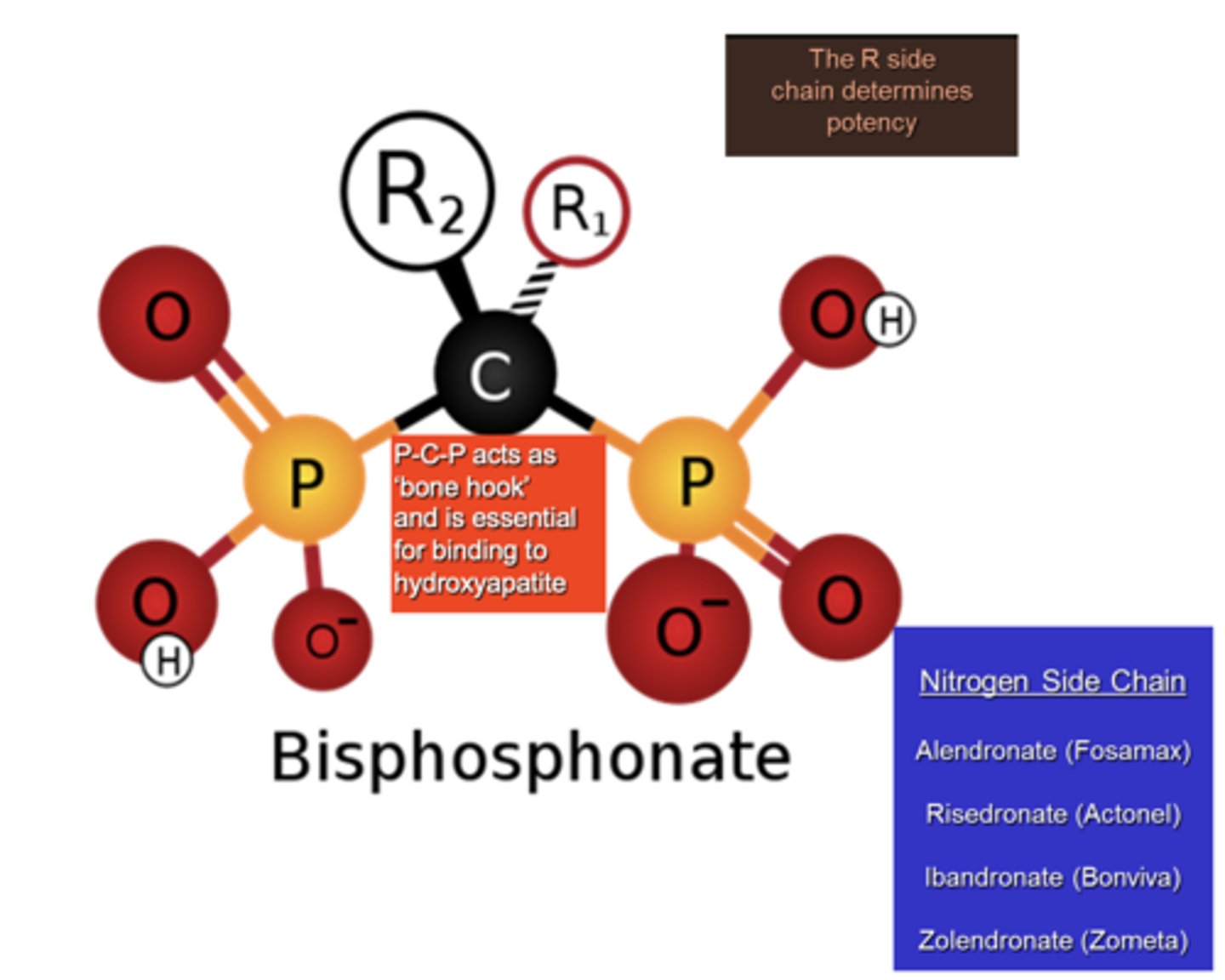
What has the following characteristics?
- Alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate
- May cause irritation to upper gastrointestinal mucosa
- - Should be taken before first food of the day and with 6-8 oz of water
- - Patient should remain upright for at least 30 min and until after eating
Bisphosphonates

What determines how toxic bisphosphonate can be to the bone?
R side chains
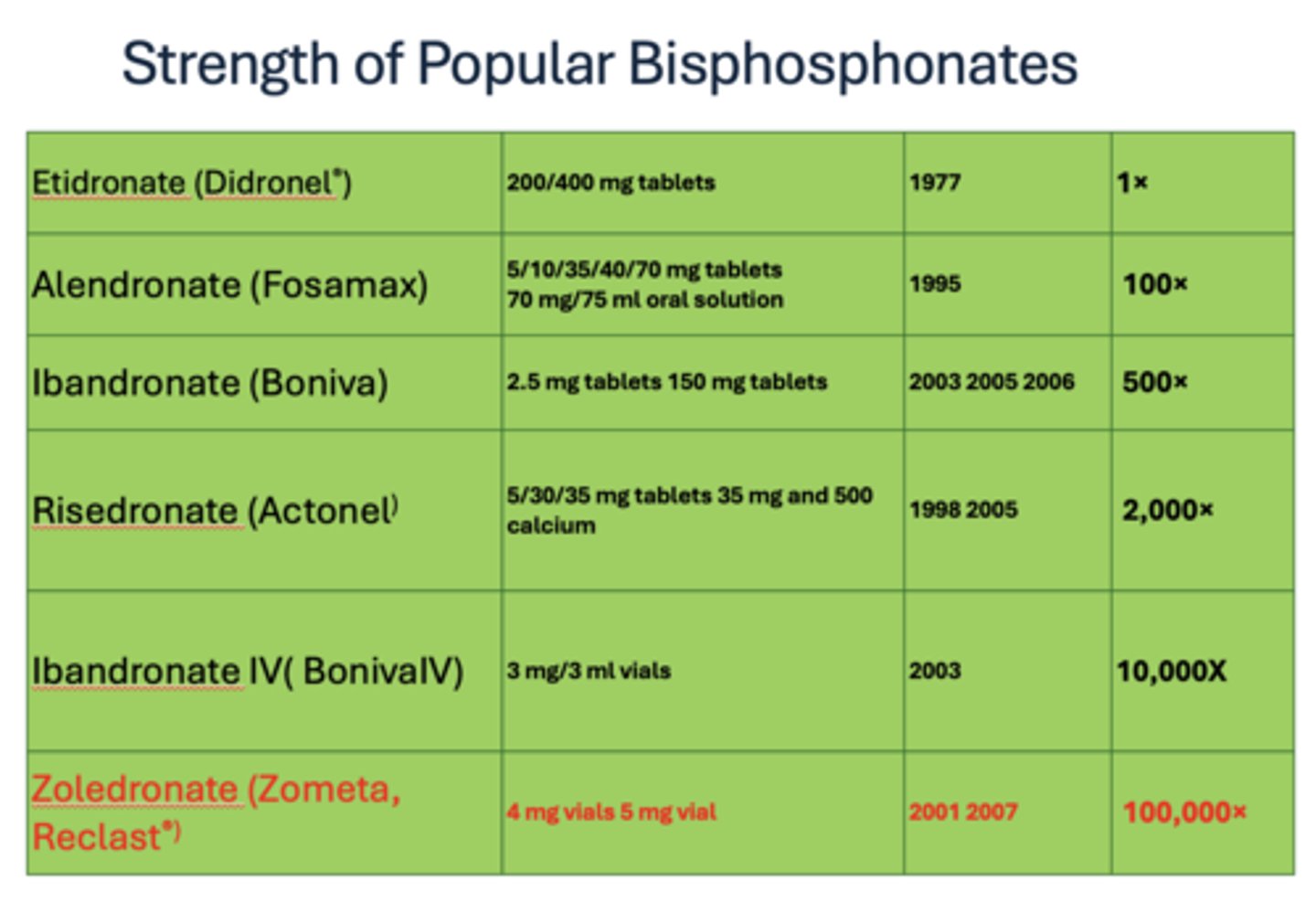
What has the greatest strength of popular bisphosphates (100,000x)?
Zoledronate (Zometa, Reclast®)
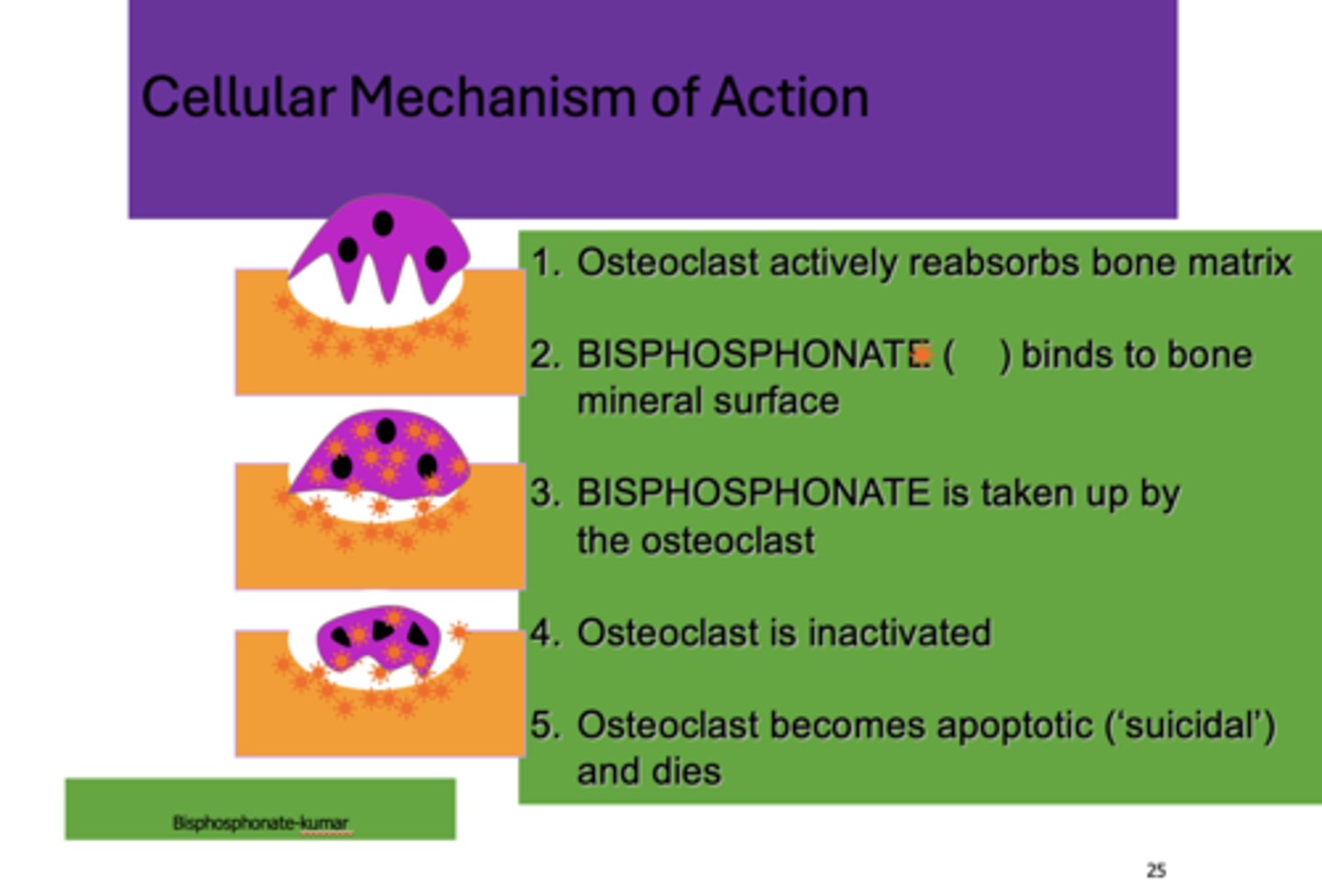
What are the five steps for the cellular mechanism of bisphosphonates?
1. Osteoclast actively reabsorbs bone matrix
2. Bisphosphonate binds to bone mineral surface
3. Bisphosphonate is taken up by the osteoclast
4. Osteoclast is inactivated
5. Osteoclast becomes apoptotic ('suicidal') and dies
What are the oral side effects of bisphosphates?
- Heartburn and GERD
- Nausea
- Pain in abdomen

What are the IV side effects of bisphosphates?
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches

What has the following characteristics?
- Rankl inhibitor
- Monoclonal antibody against Rankl Ligand (part of pathway that stimulates osteoclasts)
- Sub-cutaneaous every 6 months
Denosumab (Prolia)

What two drugs are analogs that bind to the PTH1 receptor?
- Triparatide
- FORTEO
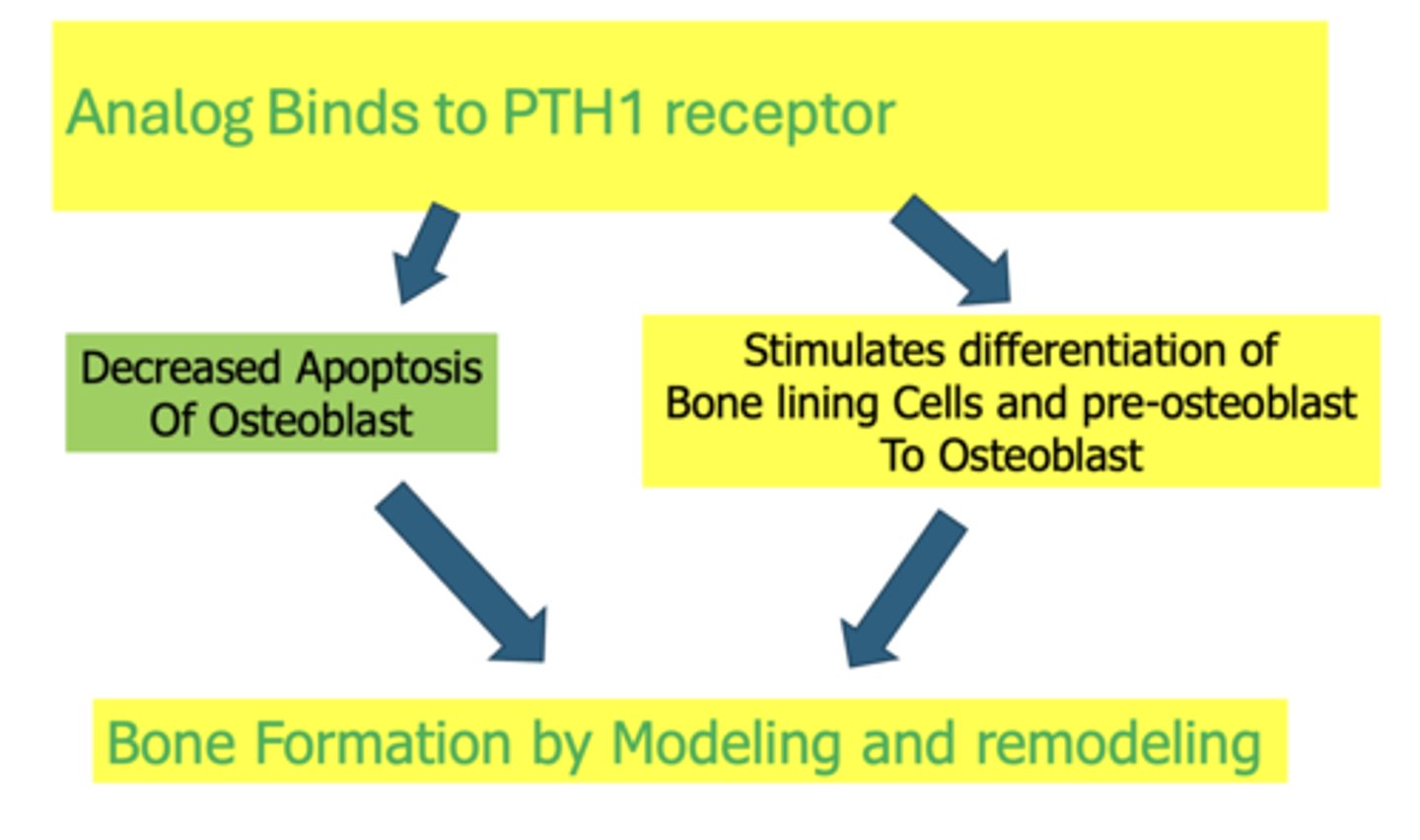
Triparatide and FORTEO decrease apoptosis of osteoblast and stimulates differentiation of bone lining cells and pre-osteoblast to Osteoblast, leading to what?
Bone formation by modeling and remodeling
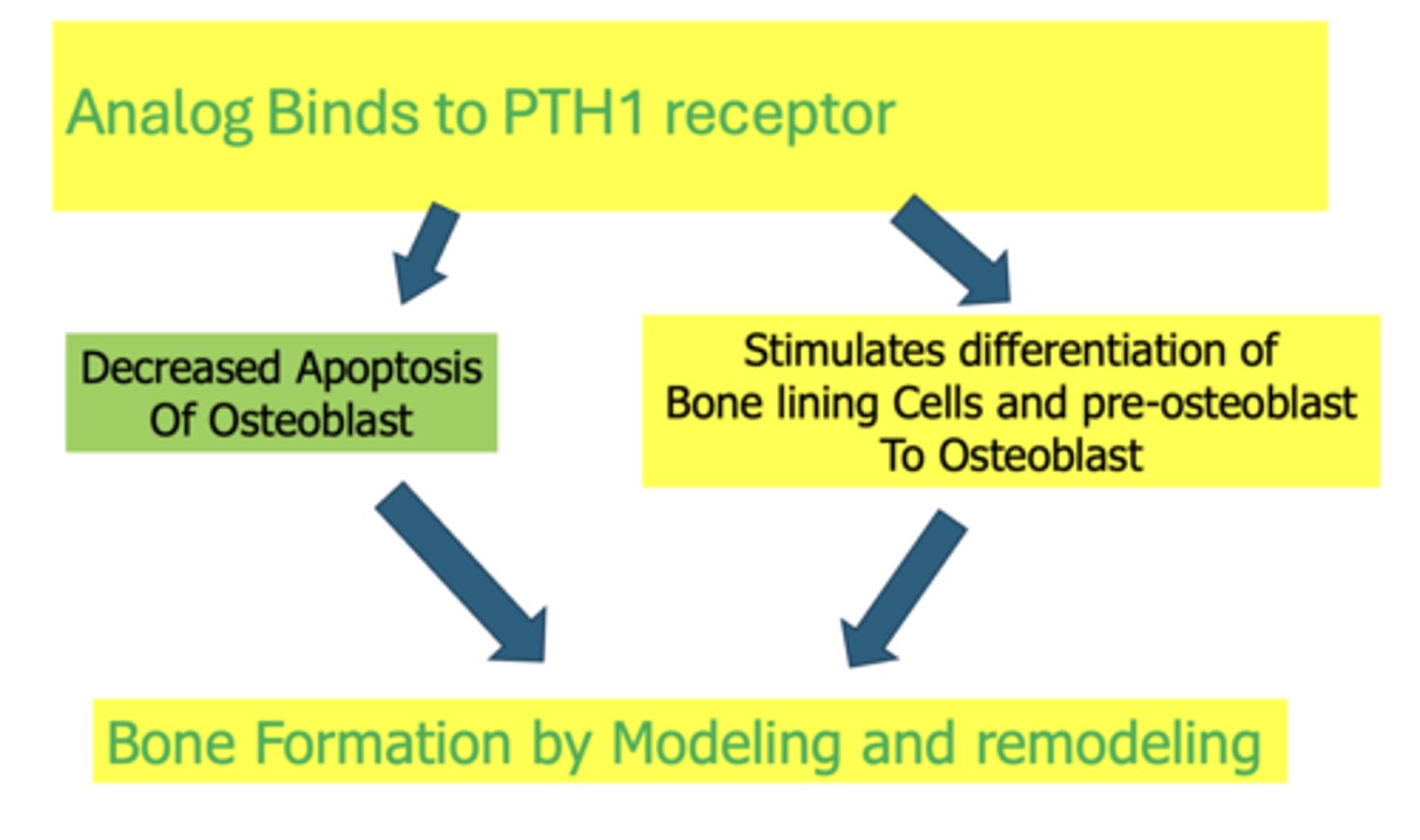
What two drugs result in the following:
- Increase In Bone Volume And Connectivity
- Increase In Skeletal Mass And Bone Strength
- Triparatide
- FORTEO
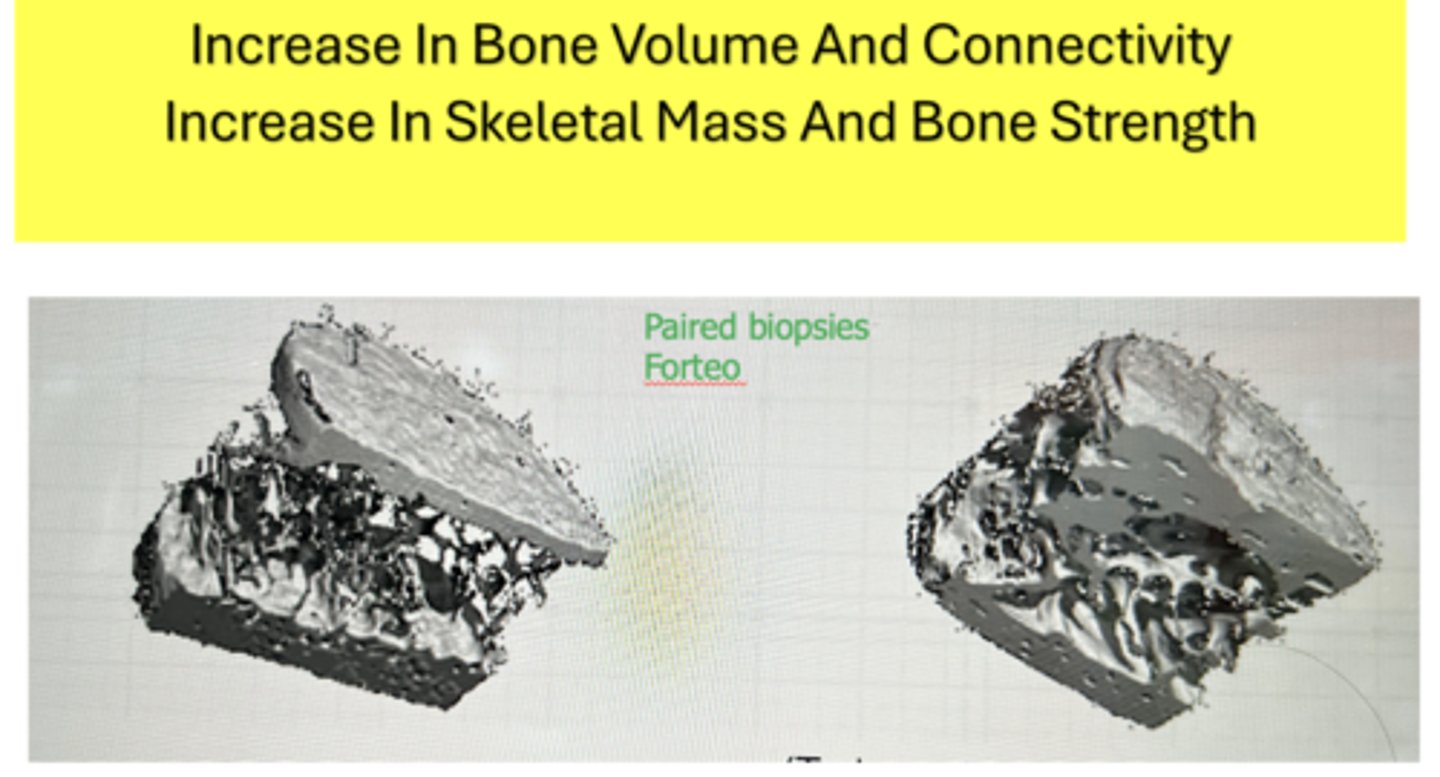
What has the following characteristics?
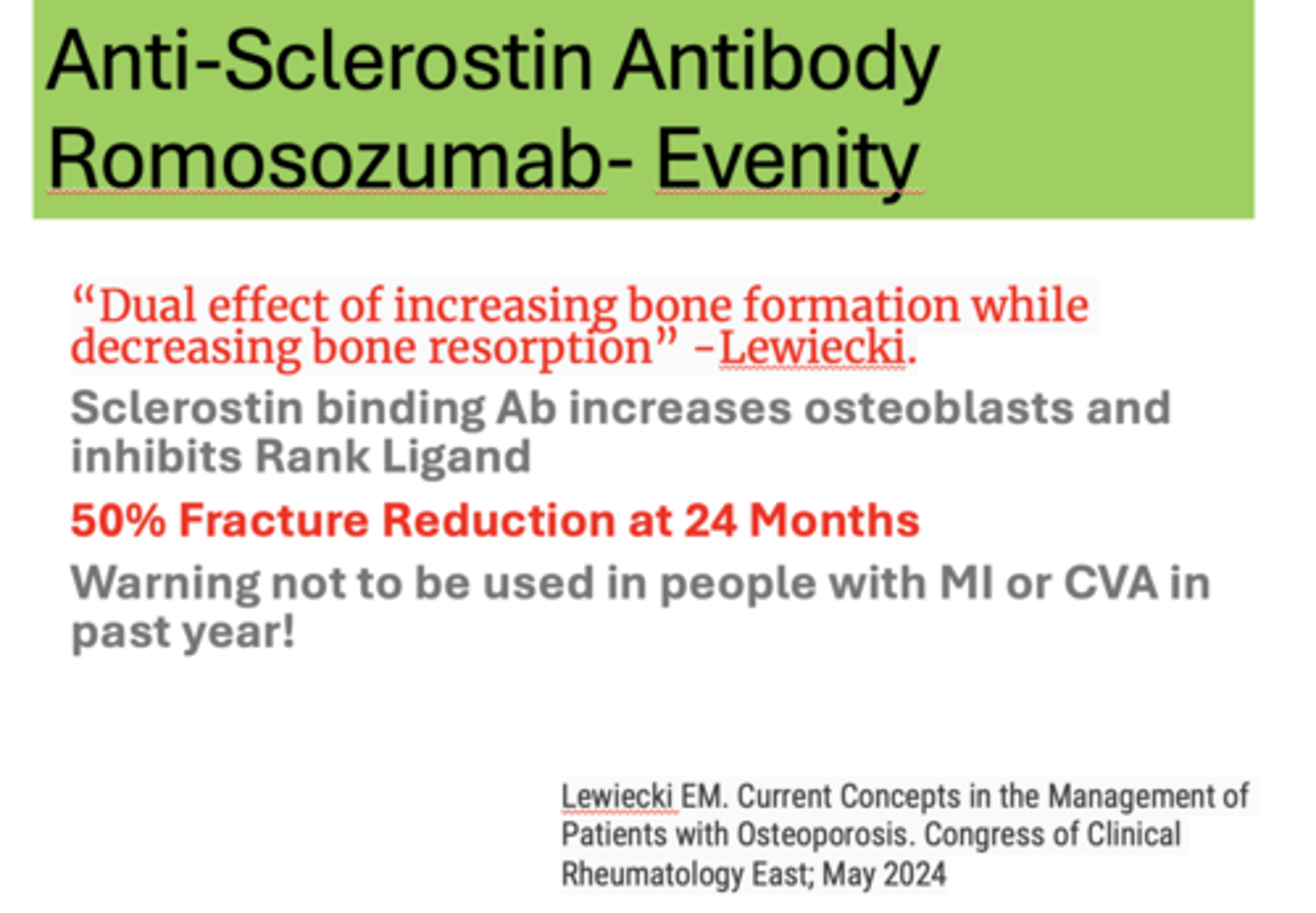
Increases bone formation and decreases bone resorption by inhibiting Sclerostin-should not be taken if Cardiac or Stroke Risk exists
Evenity
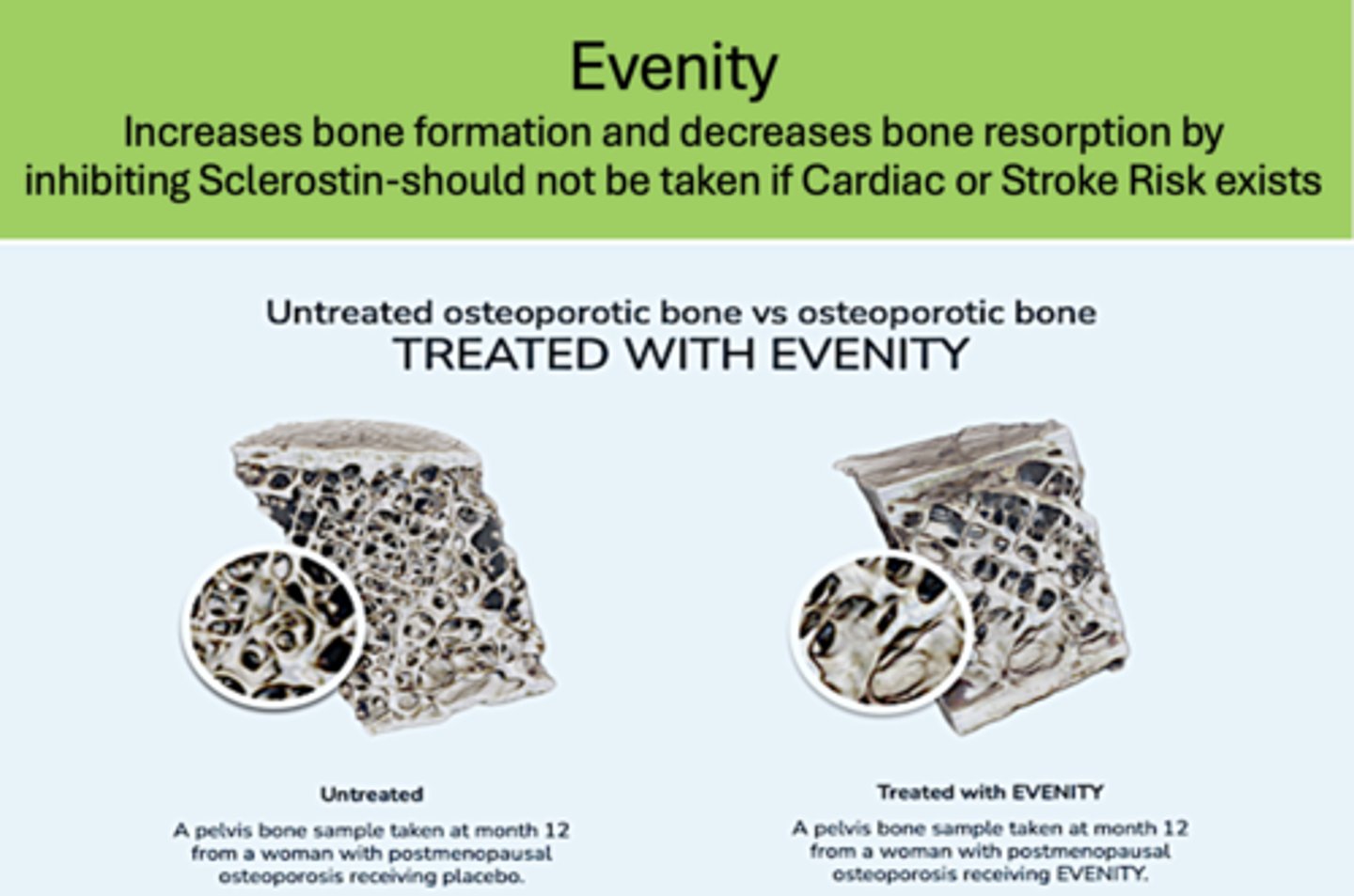
What has a "Dual effect of increasing bone formation while decreasing bone resorption?"
Evenity
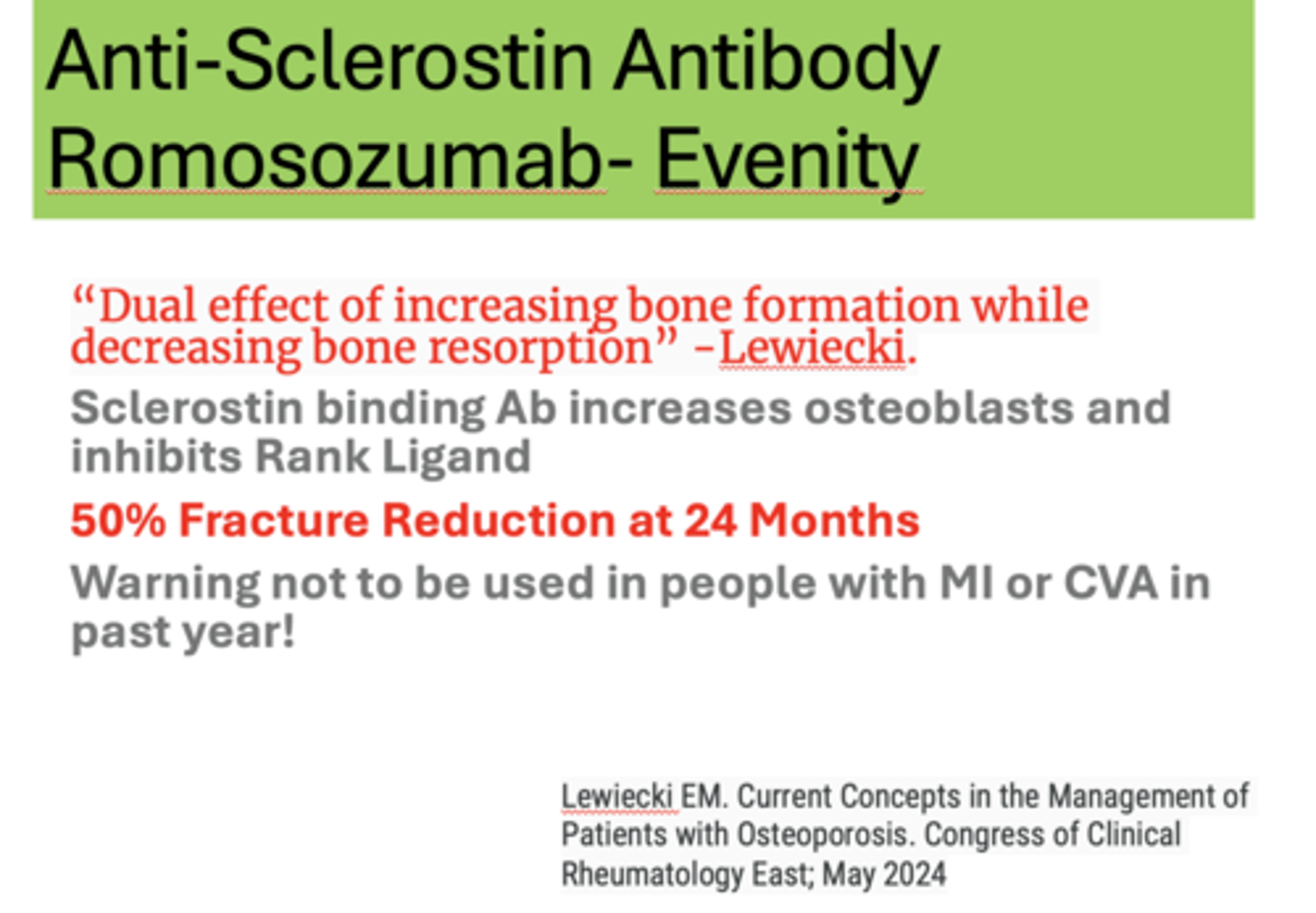
Anti-Sclerostin Antibody, such as Romosozumab - Evenity, result in what percent of fracture reduction at 24 months?
50%
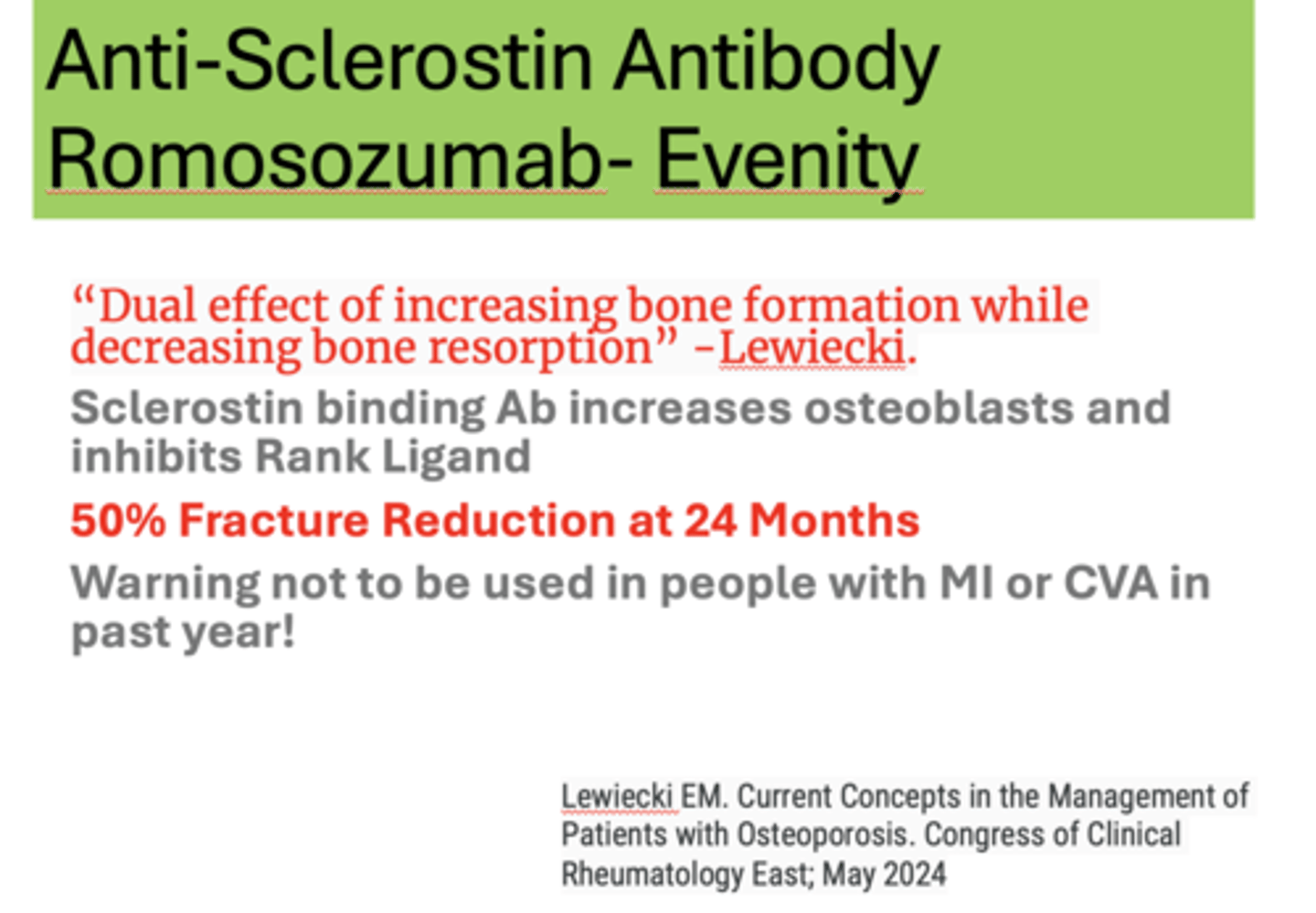
T/F: Evenity should not be used in people with MI or CVA in past year!
True
What is the ideal treatment of Anti-Sclerostin Antibody, such as Romosozumab- Evenity?
The ideal one-two punch for someone with osteoporosis is to begin therapy with an anabolic agent and follow it up with an antiresorptive agent

Anabolic therapies can be less effective when administered after _________ agents have been used
Antiresorptive

It is important to treat with anti-resorptive immediately after __________
Anabolic

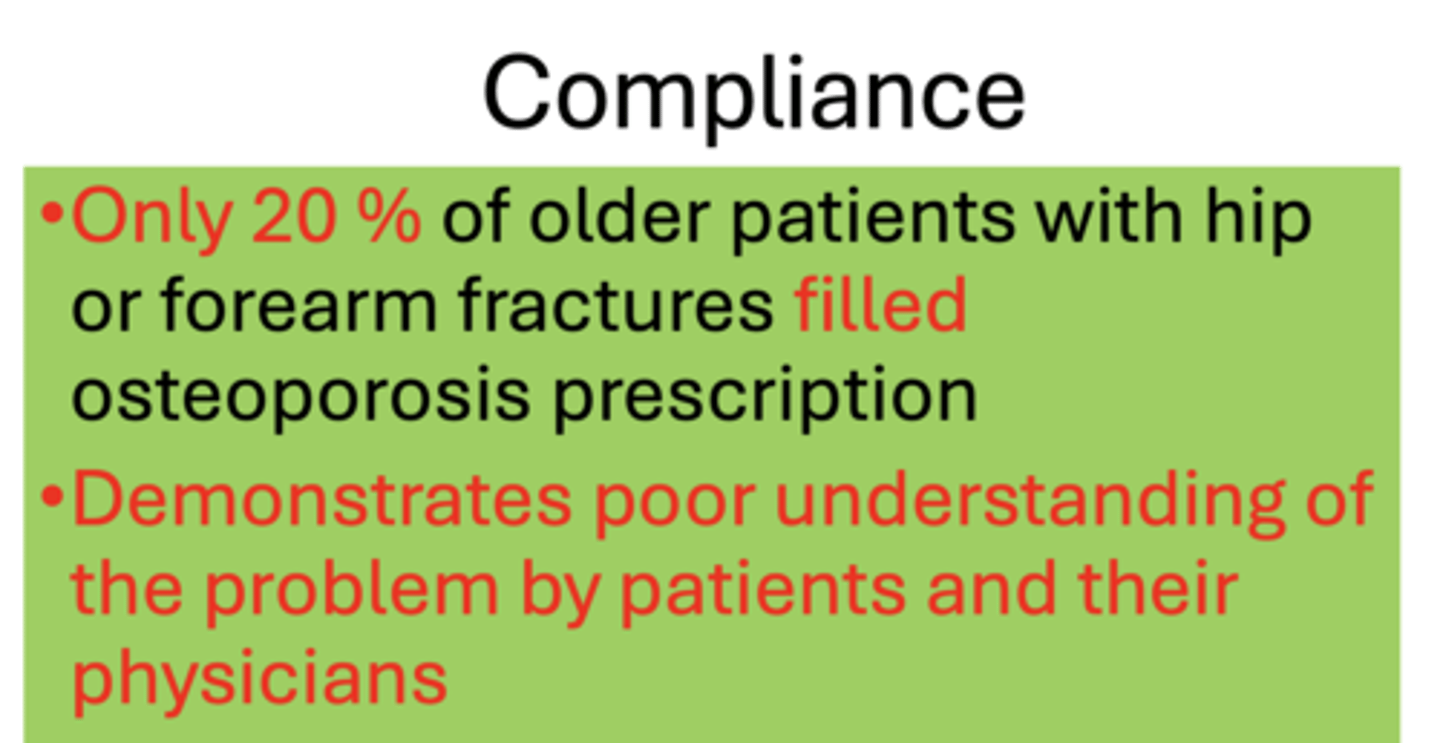
Only _____% of older patients with hip or forearm fractures filled osteoporosis prescription
20%
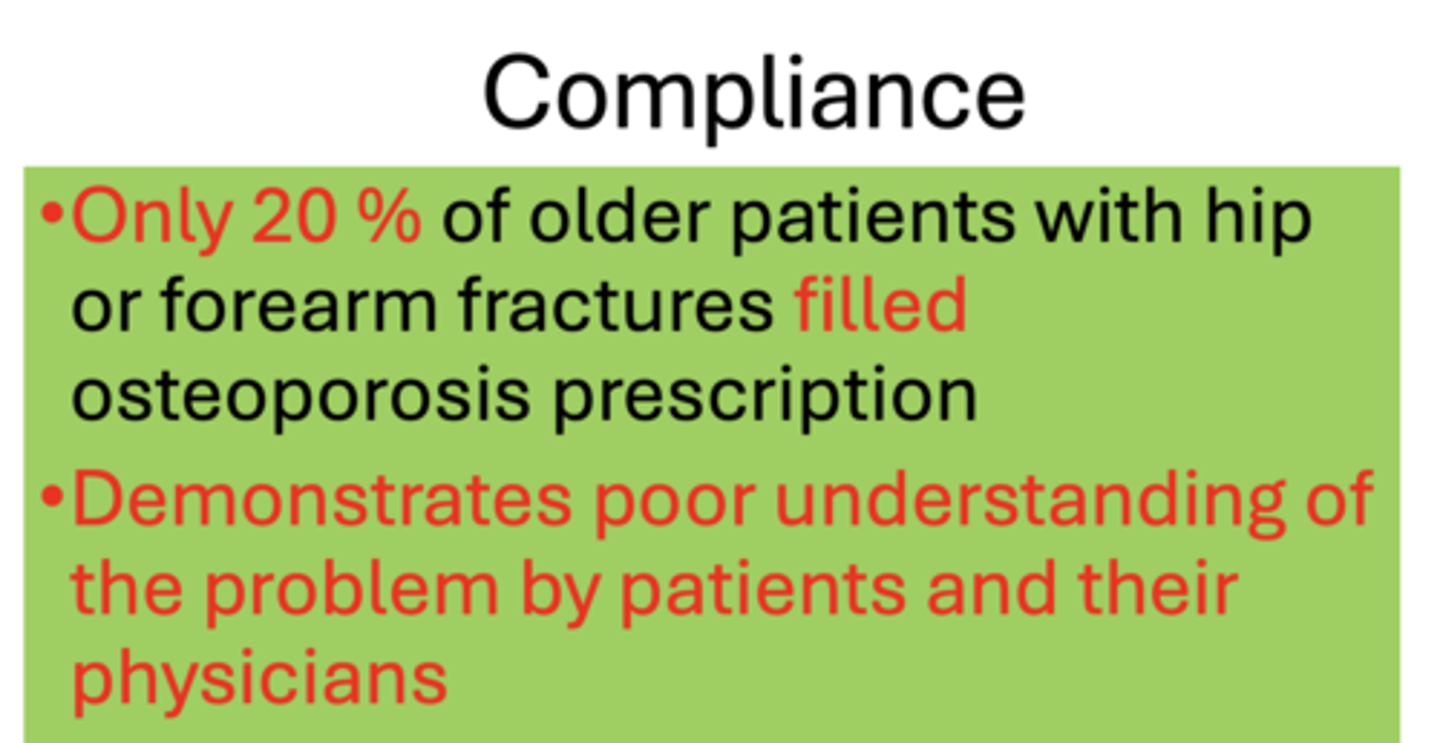
What does poor compliance of pharmacology demonstrate with patients and physicians?
Demonstrates poor understanding of the problem by patients and their physicians
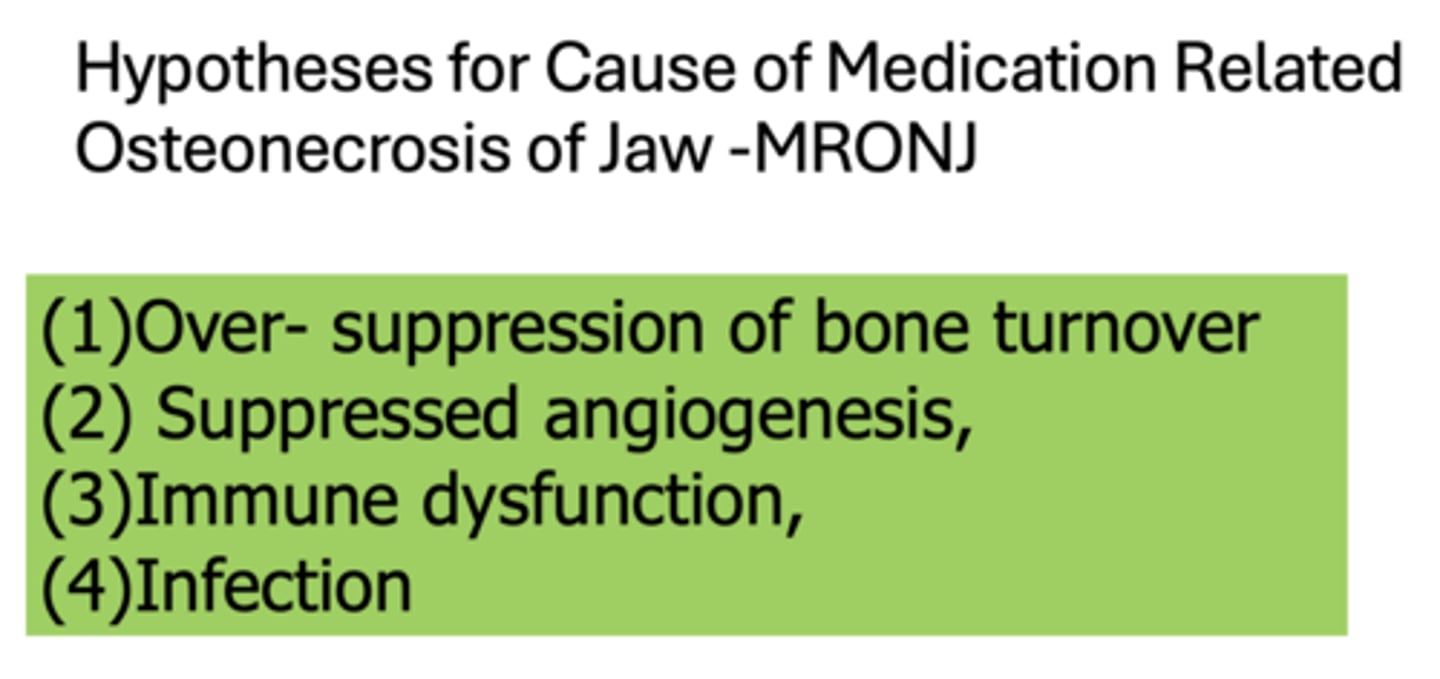
What are the four hypotheses for cause of medication related osteonecrosis of jaw?
(1) Over- suppression of bone turnover
(2) Suppressed angiogenesis
(3) Immune dysfunction
(4) Infection
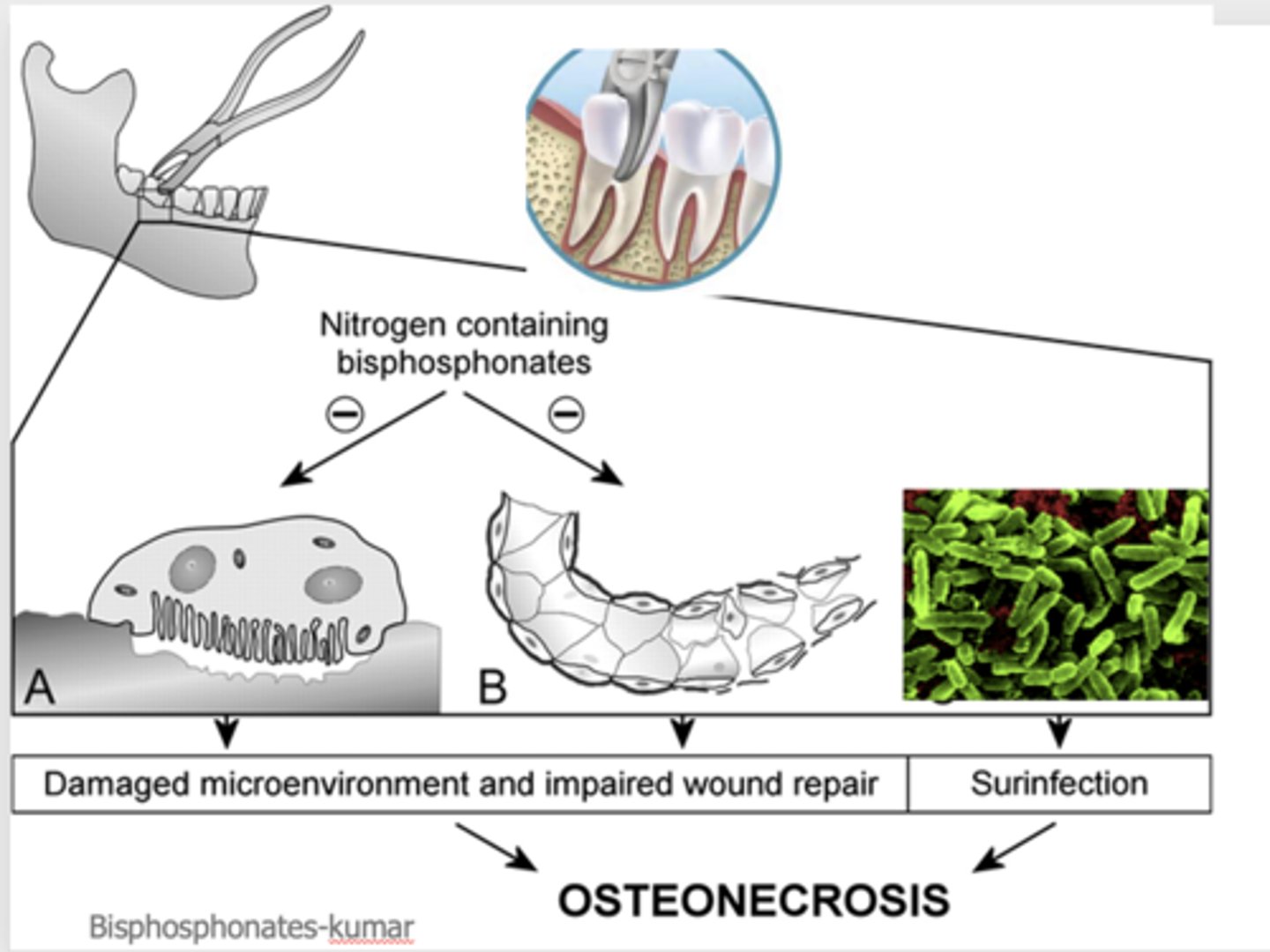
What can result when pulling a tooth in a damaged microenvironment and impaired wound repair or surinfection?
Osteonecrosis
All of the following are risk factors for developing what?
- Cancer-Multiple Myeloma, breast, prostate, lung
- Chronic Oral Glucocorticoid Use
- Prolonged Use of Bisphosphonates (more than 2yrs)
- Smoking
- Antiangiogenic agents;
- Diabetes
- Older Age (greater than 65 years)
- Periodontitis/Dentures/ Poor Oral Care
Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ)

Which of the following patients had the highest percentage of MRONJ?
A. Breast cancer
B. Multiple Myeloma
C. Other
B. Multiple Myeloma
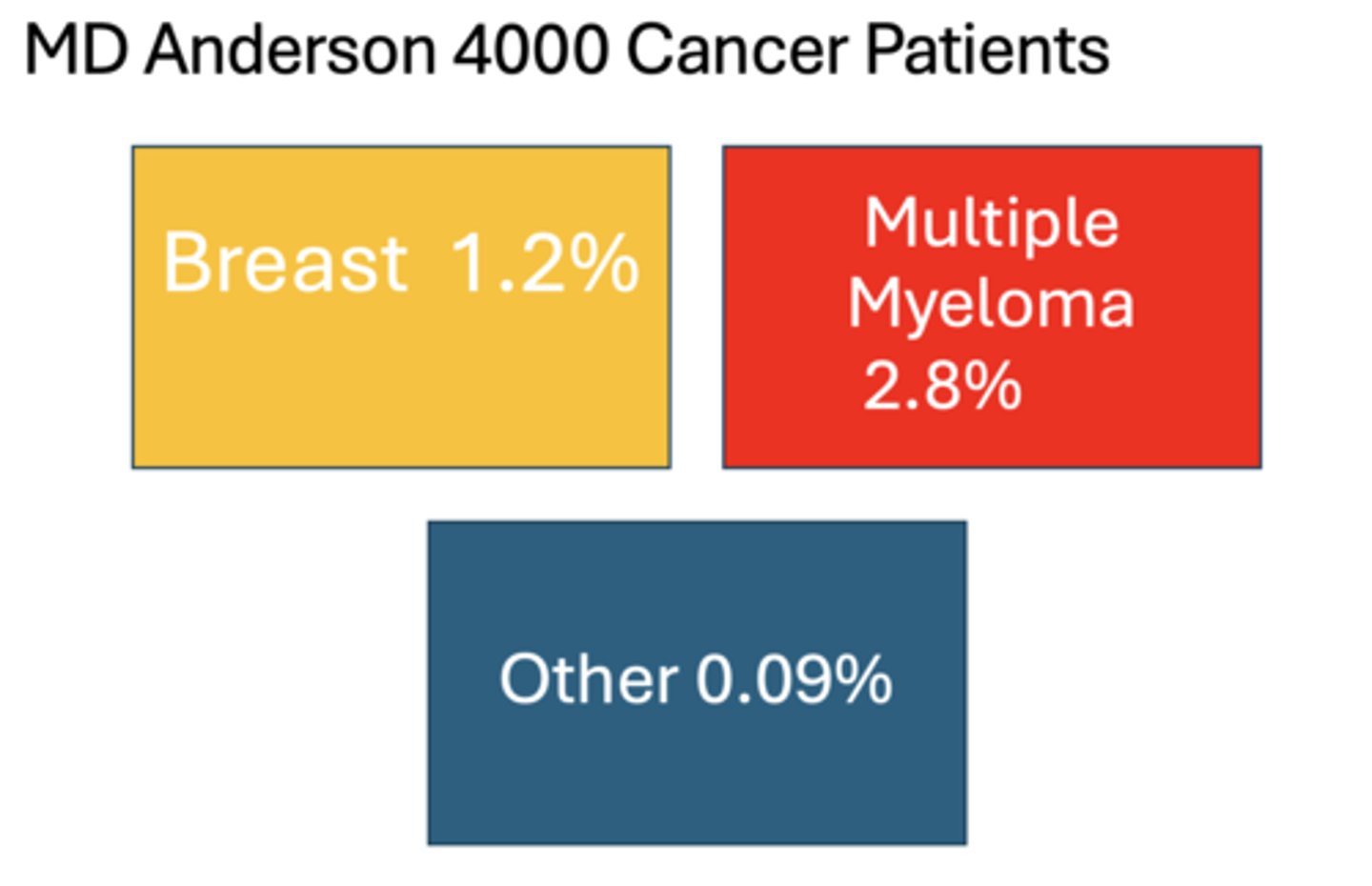
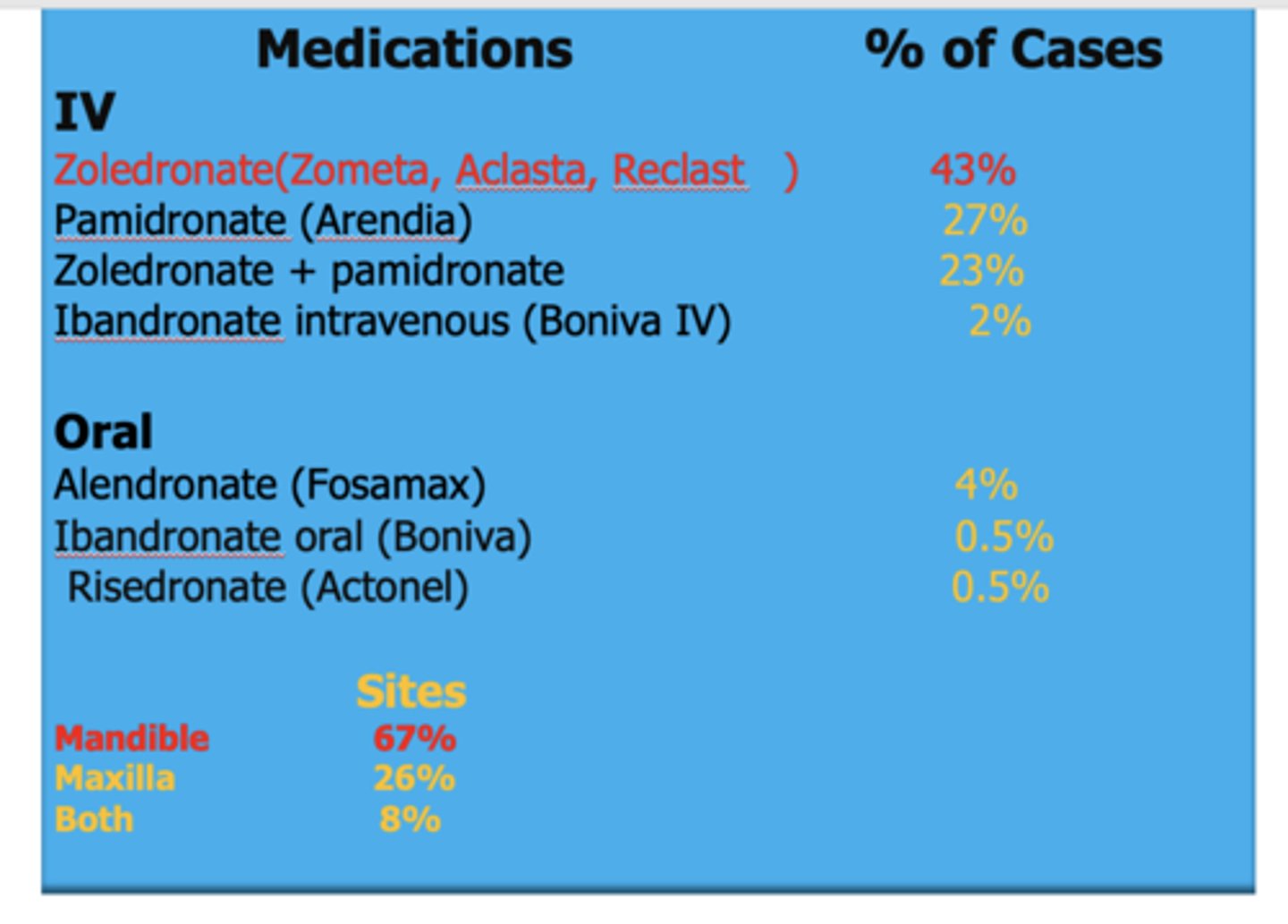
Which medication results in the most percent of cases of necrosis?
Zoledronate(Zometa, Aclasta, Reclast)
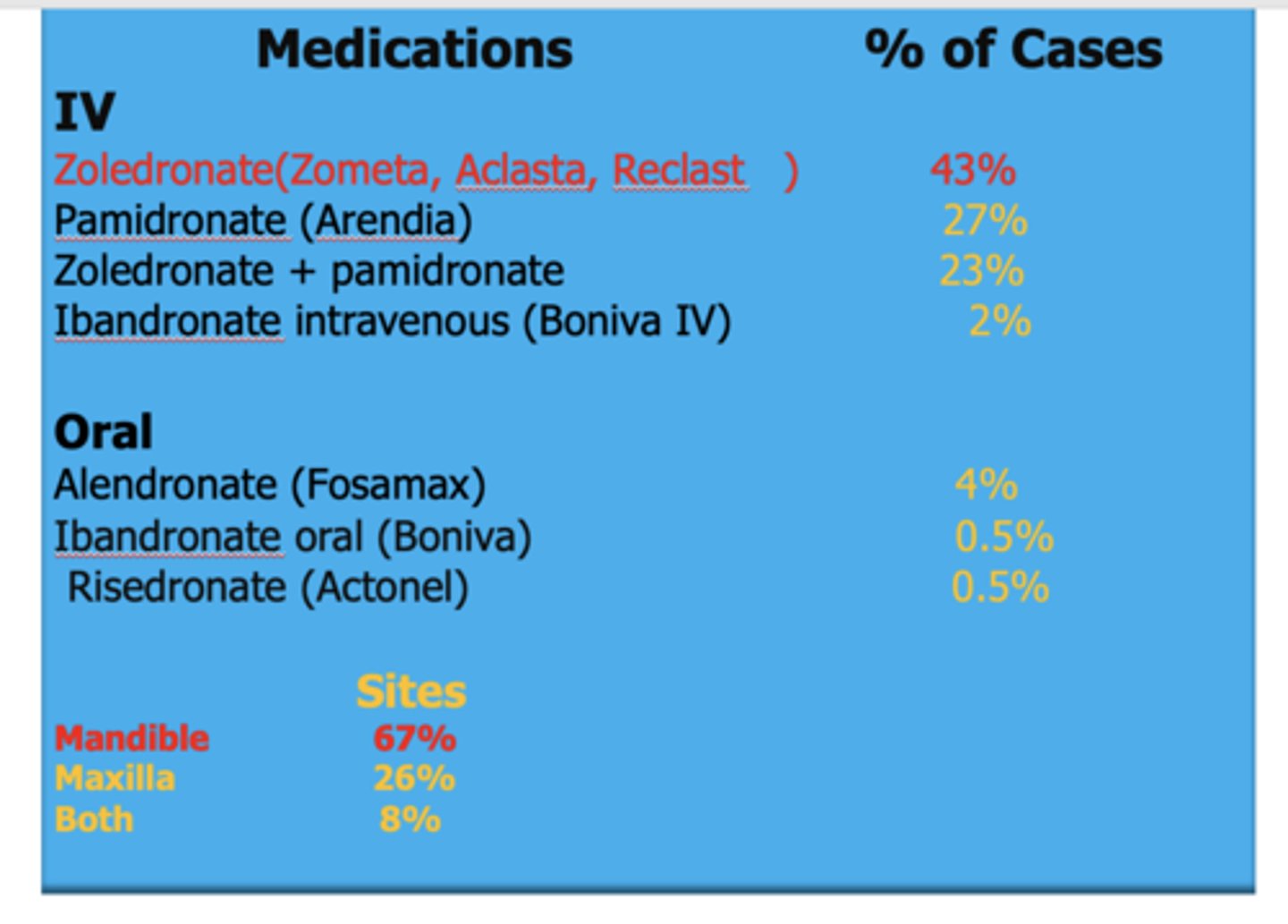
Which site has the high percentage of necrosis from MRONJ?
Mandible
What are signs to look for with MRONJ?
- Gingival infections and trauma that heal very slowly or do not heal at all for 6-8 weeks after a procedure and exposed bone.
- Some patients report a feeling of "roughness" on the gum tissue.
- BRONJ can be painless in the beginning.
- Patients feel pain after the exposed bone becomes infected. If this infection persists, there may even be numbness, especially in the lower jaw.

What are five treatments for MRONJ stage 2?
- Antibiotics (Broad Spectrum)
- Antimicrobial rinse
- Pain control
- Minimal debridement
- Daily Brushing by Patient
The FDA warning - taking bisphosphonates for longer than ______ years may put women at an increased risk of femur fractures and other problems.
5

What are ADA Panel Recommendations to patients taking bisphosphates?
- Routine Dental Care should not be withheld for patients on oral bisphosphonates
- Encourage frequent prophylaxis and routine care, and improved homecare routine.
- Inform patients of very low risks before they undergo invasive procedures
