Chapter 18 Study Guide
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
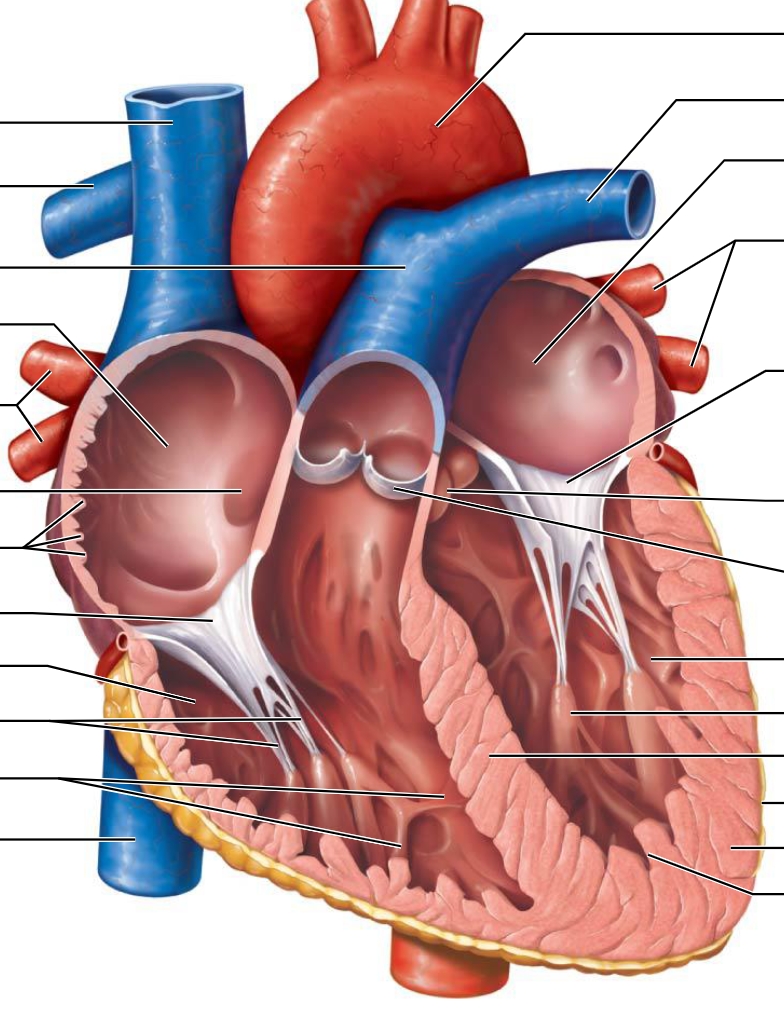
Pericardium - Double wall
Fibrous Pericardium - Protects, anchors the heart, and prevents overfilling
Serous Pericardium - Double sac
Parietal layer - internal surface
Visceral (epicardium) -
Serous Cavity - The fluid
Epicardium - external surface
Myocardium - Cardiac muscle that functions as the layer that contracts
Endocardium - sheet of squamous epithelium
Superior Vena Cava
Inferior Vena Cava
Coronary Sinus
Name the heart valves and describe their location, function, and mechanism of operation.
Atrioventricular Valves - Between the Atriums and Ventricles; keeps blood unidirectional; Opens when pressure builds in Atriums, but closes and balloons once Ventricular pressure increases.
(1)Tricuspid Valve - Between right Atria and right ventricle; deoxygenated
(3) Mitral Valve - Between left Atria and left ventricle; oxygenated
Semilunar Valves - Between Ventricles and the main arteries; keeps blood from back flowing into Ventricles after contraction; Pops open to release blood into Aortic SL and Pulmonary SL, but shuts once pressure in arteries build.
(2) Pulmonary Valve - Between right ventricle and Pulmonary artery; leaves to get deoxygenated
(4)Aortic Valve - Between left ventricle and Aorta; leaves to supply body
What is the function of the chordae tendineae?
Anchors the AV valves to prevent them from collapsing
Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. (Flip to see correct pathway)
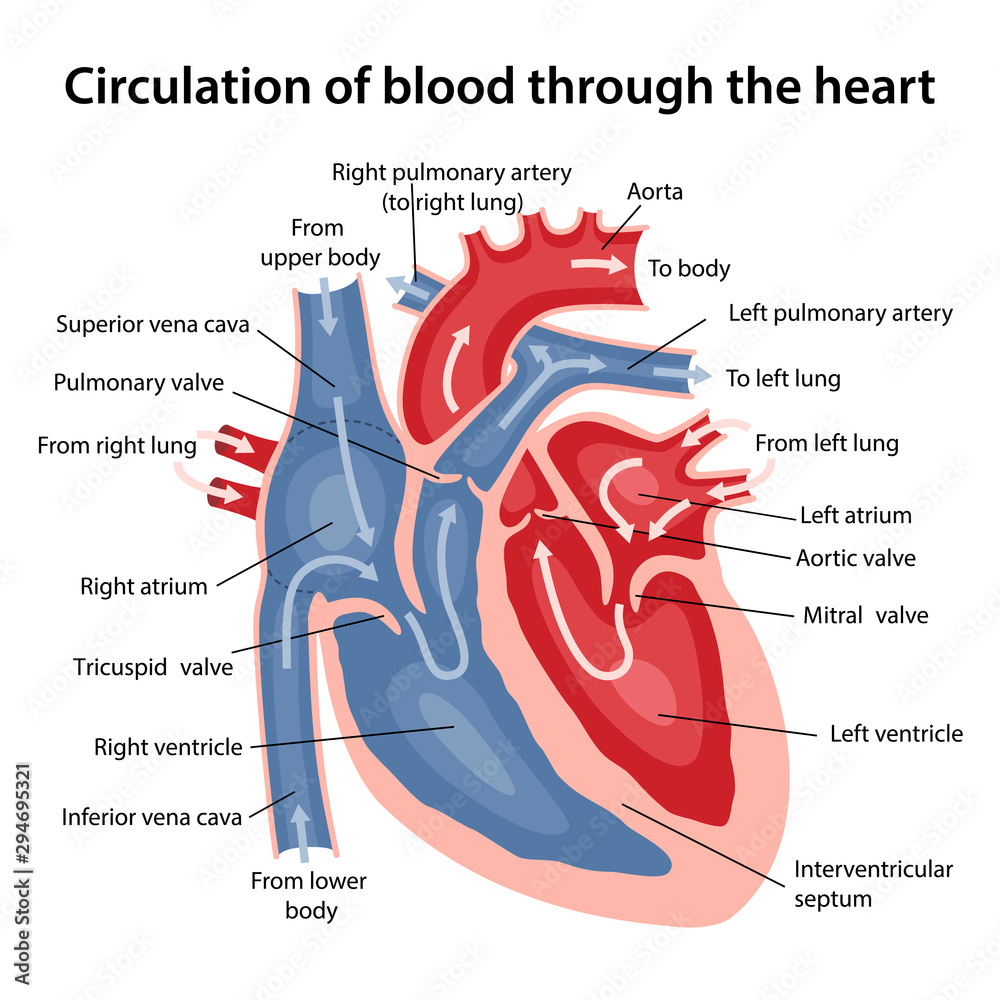
True or False? Veins always carry oxygen-poor blood, and arteries oxygen-rich blood.
False
Name the major branches and describe the distribution of the coronary arteries. What is their function?
Left coronary artery
Anterior interventricular artery - supplies interventricular
sulcus, interventricular septum and anterior walls of both
ventricles
Circumflex artery - supplies the left atrium and the posterior
walls of the left ventricle
Right coronary artery
Right marginal artery - supplies the myocardium of the
lateral right side of the heart
Posterior interventricular artery - supplies the posterior ventricular walls
What is the result of coronary artery blockade?
Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
What is the coronary sinus?
Vein
How does the structure and function of cardiac muscle cells differ from skeletal muscle fibers?
Cardiac muscles has less, but thicker t-tubules and their SR is less convoluted. Because it can contract without neural stimulation, has many more mitochondria.
What structures can you find in the intercalated discs of cardiac cells? What is their function?
Desmosomes - Gap junctions
Allow electrical signals to go throughout the cells
What is a functional syncytium? Which structures of the intercalated discs allow the myocardium to function as a functional syncytium?
Functional Syncytium means the entire heart works together