Disorders Cardiac Conduction/Rhythm
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
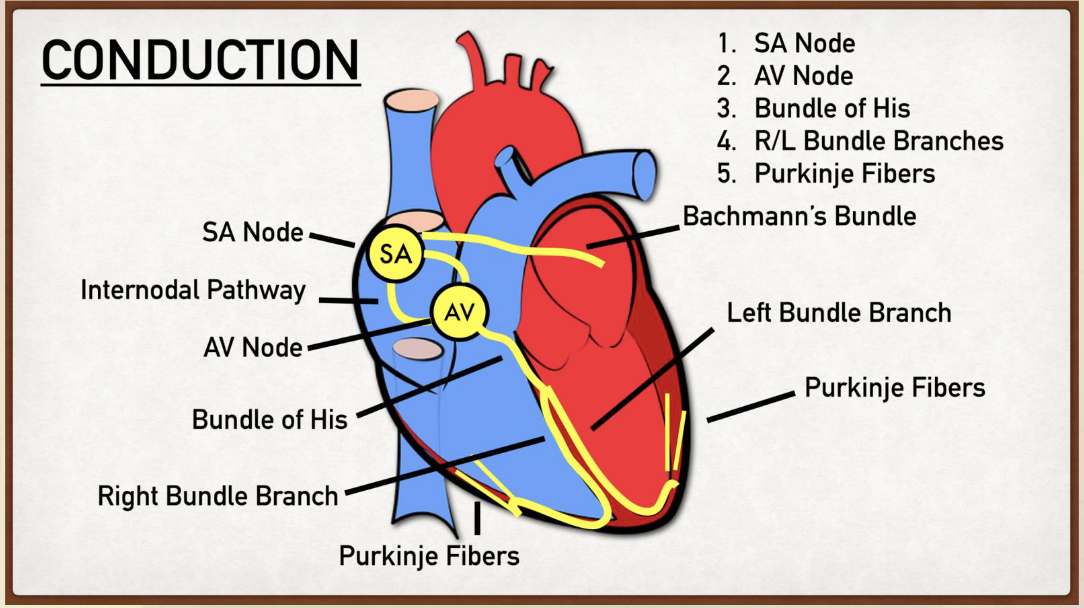
electrical system of the heart in order
Sa Node
AV Node
Bundle of His
R/L Bundle Branches
Purkinje Fibers
Electrocardiogram- EKG
a graphic recording of the electrical activity of the heart
documents both disturbances in rhythm (dysrhythmia/arrythmia) and disturbances in conduction (heart block)
EKG order when looking at the waves
PQRST
depolarization
contracting (lub)…systole
repolarization
filling (dub)…diastole
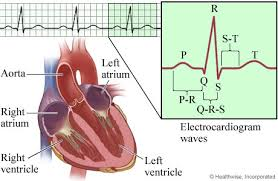
P Wave
Represents atrial depolarization on an ECG.
PR interval
time from firing of SA node to the beginning of depolarization of ventricles
QRS Complex
Represents ventricular depolarization on an ECG.
T Wave
Represents ventricular repolarization on an ECG.
cardiac dysrhythmias
Abnormal electrical conduction or automaticity
what causes cardiac dysrhythmias
Acid-base imbalance, hypoxia, drugs, electrolyte imbalance, stress, MI, caffeine, nicotine, congenital disorders, medications
automaticity
the ability of specialized cardiac cells to spontaneously initiate an electrical impulse
conductivity
ability to conduct impulses
SA node conductivity
60-100 bpm
AV node conductivity
40-60 bpm
Purkinje fibers
15-40 bpm
what are the 2 types of atrial disturbances
atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation
atrial flutter
rapid regular contractions of the atria but its not normal looking; 250-350 bpm
atrial fibrillation
extremely irregular and chaotic looking; irregular, uncoordinated contractions of the atria
Predisposes patient to clot formation!
Sinus Node Dysrhythmias
Due to disturbances in automaticity and conductivity, slow or fast
not life threatening
bradycardia (<60 bpm); tachycardia (>100 bpm)
ventricular dysrhythmias
Interfere with the pumping action of the heart
can be life threatening
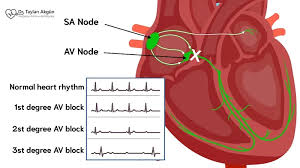
heart blocks
Occur when conduction between the atria and ventricles is interrupted
diagnostic tools used with the cardiovascular system (3)
EKG, Holter monitor (wear for 7-14 days), exercise stress test
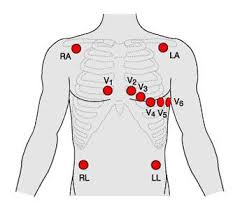
12 lead EKG
a painless test that measures the electrical activity of your heart, providing a detailed view of its rhythm and function, often used to detect heart problems or assess how well certain treatments are working.
electrophysiology ablation
a procedure that treats certain types of arrhythmia by destroying problematic heart tissue