Unit 7 Optics
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
(Energy does NOT play a part in this spectrum)
How does AM and FM show how wavelength correlates with travel distance?
It is a spectrum of electromagnetic radiation with the left having the shortest wavelengths and shorter travel distance under IDEAL CONDITIONS
-AM wavelengths are longer than the FM ones so it theory they should travel longer but they DON'T
--> This is due to AM waves having less energy so stuff interfere with it more IRL (trees, buildings).
--> FM waves (more energy) get less interference
What do these symbols mean?
di, do, hi, ho
--> What are the relationships between an object and a plane mirror (flat mirror)? and WHY?
di = image distance
do = object distance
hi = image size
ho = object sive
--> In a plane mirror, di=do and hi=ho due to the law of reflection and also lateral inversion (not vertical inversion)
What is the difference between vertical and horizontal inversion
Vertical inversion = flipping using the x-axis (person standing would look like their are coming from ceiling)
|
Horizontal inversion = lateral inversion = This is what a PLANE MIRROR uses!
(image is inverted using the y-axis like a plane mirror)
What are the 4 steps to drawing the image coming from a object to a plane/flat mirror?
1. Draw a horizontal line from the top of the object to mirror and label it do
2. Extend the line an equal distance behind mirror on virtual side and label it di
3. draw the object from equal dist marked in prev step with equal height to the image and label hi
4. Draw any angles based on Q (Law of reflection will apply)
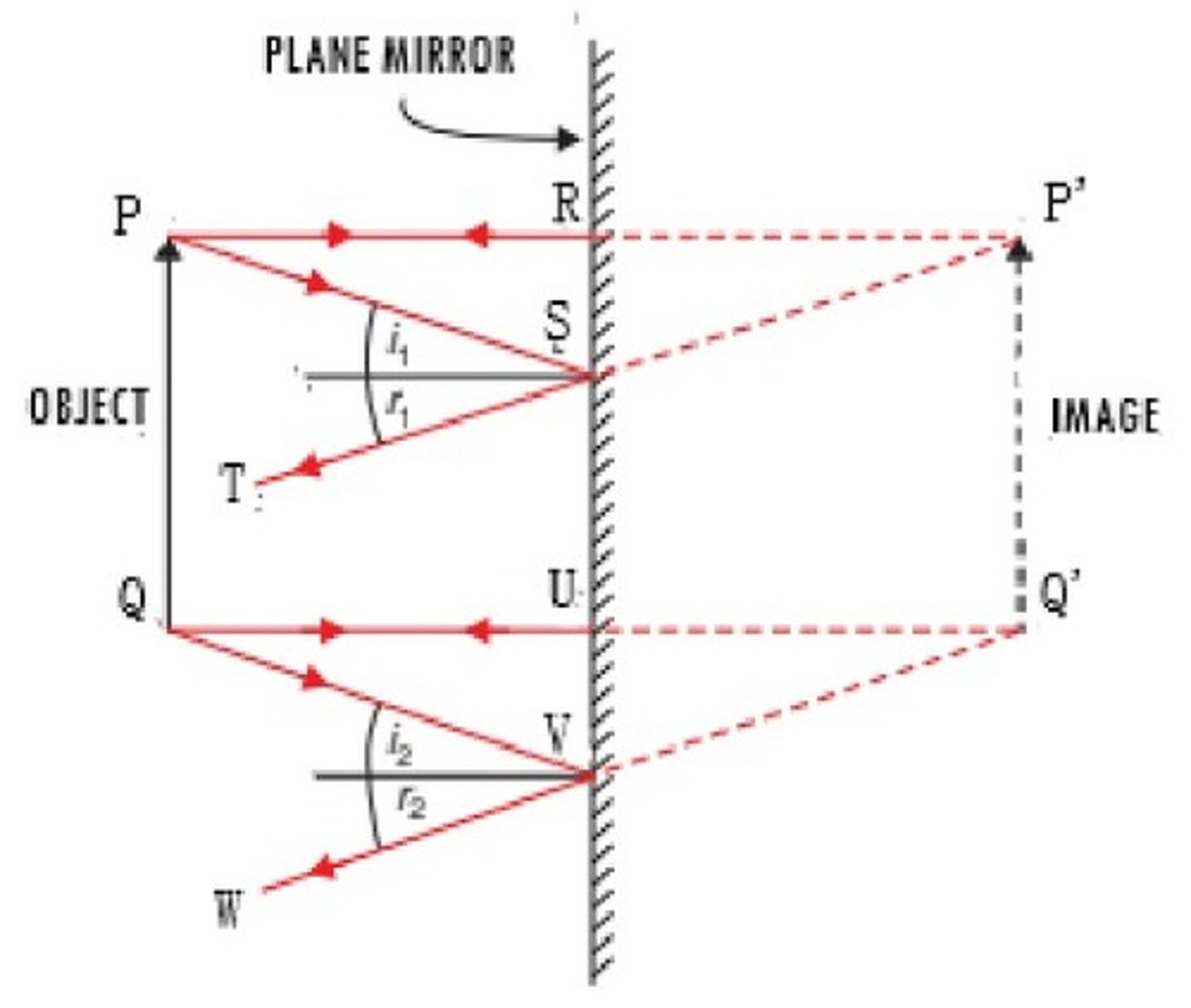
What are the 3 characteristics of an image in a plane/flat mirror?
1. Image is the same size as the object
2. Image is vertically erect/upright
3. The image is virtual
What is Light?
What are 2 facts about Light?
- Light is a form of radiant energy that the eye can detect.
We see objects because light is reflected or emitted from them.
⚠Light is a transverse wave AND a particle (Einstein)(Wave Model)⚠
What is the difference between Luminous and Non-Luminous Objects?
What is the difference between Reflection and Refraction?
Luminous object = (a light SOURCE) produces light, so are seen by their own light (candle, flames, sun, lightbulb)
|
Non-Luminous object = does not emit their own light but they REFLECT light from another object (Moon, Earth)
|
Reflection = light rebounding from a shiny surface (laser light in mirror and light can be seen in fog)
|
Refraction = light bends as it travels from one medium to another (straw in water or sunlight on hot pavement)
What is the Particle Model?
What is the Wave Model?
What is the Quantum Model (particle and wave theory)?
--> How does light travel in a Vacuum, in air, and how can we show its path?
Particle Model = Light is particles radiating from the source
Wave Model = Light is transverse waves radiating away from the source
Quantum Model = Light are photons with wave properties
--> Light travels in a straight line or uniformly in a vacuum and in a medium like air (cus we assume Vacuum and Air have the same index of reflection(N) )
we can show the path of light as a model in RAY DIAGRAMS
Define:
- Translucent
- Transparent
- Opaque
- Parallax
- Translucent = transmits light (lets light in but not image) (EX: frosted glass)
- Transparent = glass (see through) (EX: window)
- Opaque = does not let light pass (EX: wood)
- Parallax = Apparent motion of an object nearby with reference to a more distant object.
(put finger in front of you and then switch eyes)
|
GPT: (Parallax is the apparent shift in the position of an object when you look at it from different angles or positions.)
What is the value we will use for the speed of light in this Unit?
What are the 2 formulas?
Speed of light = 3 x 10^8 m/s
formula: C=fλ OR C = nv
What is the index of refraction?
What is Polarization?
What is the TRUE def of Polarization?
What is Spherical Aberration?
The index of refraction = the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a given material.
—> use the formula to get speed of light (C = fλ) and compare to 3 x 10^8 m/s)
|
Polarization = direction of an electric field’s oscillations (light from light bulbs or the Sun is unpolarized)
—> Some light is already polarized (LCD monitors or lasers)
|
Polarization is the process of stopping the electric field of light from vibrating all over the place perpendicular to the direction of travel (transverse), and forces it to vibrate on one plane
|
Spherical Aberration = failure of a mirror, refracting surface, or lens to produce an exact point-to-point correspondence between an object and an image. (fuzzy image) OR (failure to make an image from a object)
What is the formula for the Index of Refraction?
n = c/v where,
n = index of refraction
c = 3x10^8 m/s (constant)
v = actual speed of light (C= Fλ)
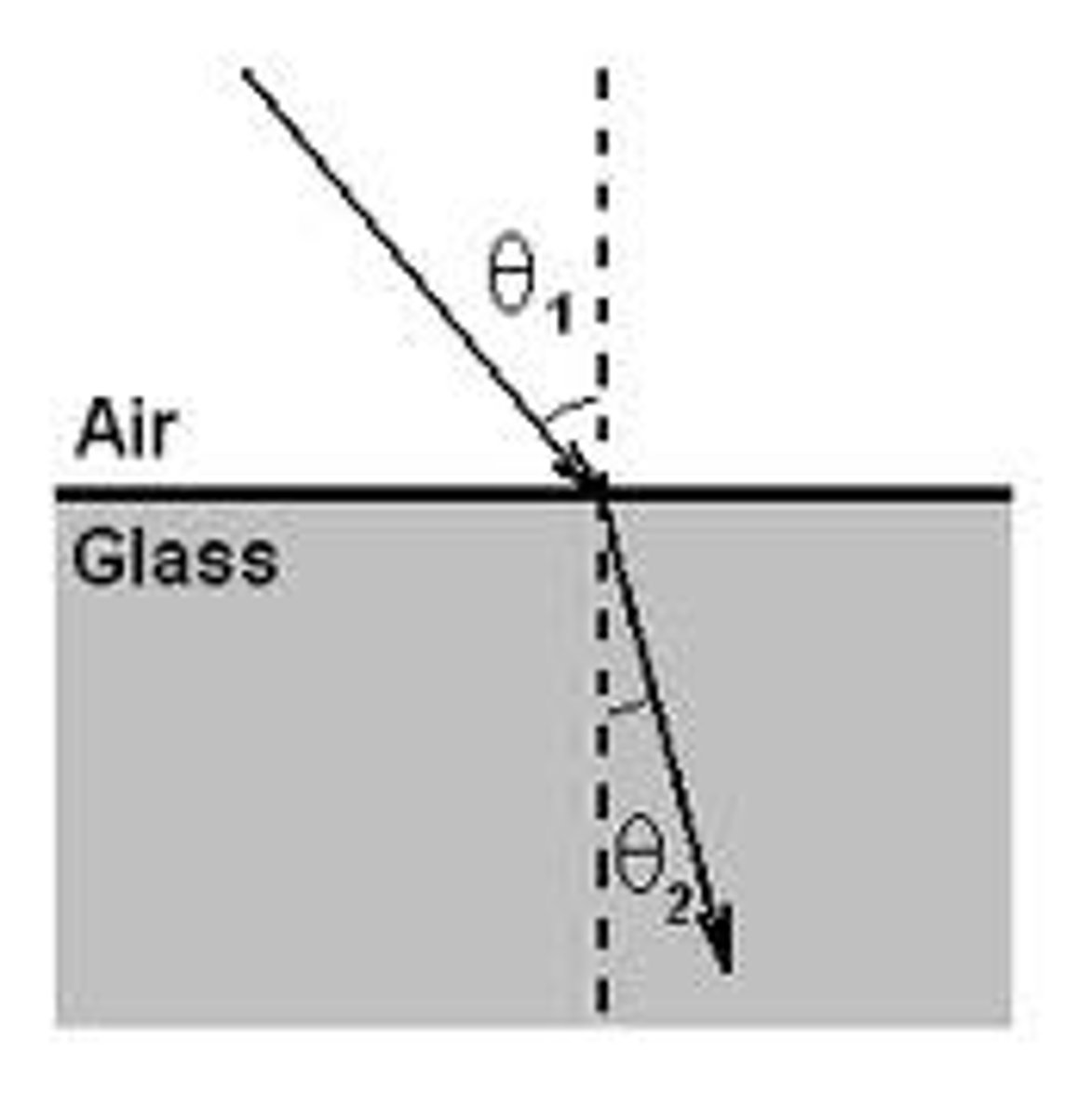
When looking at the normal line in refraction, what must we remember about light going from a less dense to a more dense medium?
If Light goes from a less dense to a more dense medium, it bends TOWARDS the normal line.
What are the 4 Characteristics you MUST say after drawing a Ray Diagram?
(SALT)
Size = image is same size/larger/smaller
Attitude = image is Inverted/Upright
Location = between C and F or etc...
Type = image is real/virtual
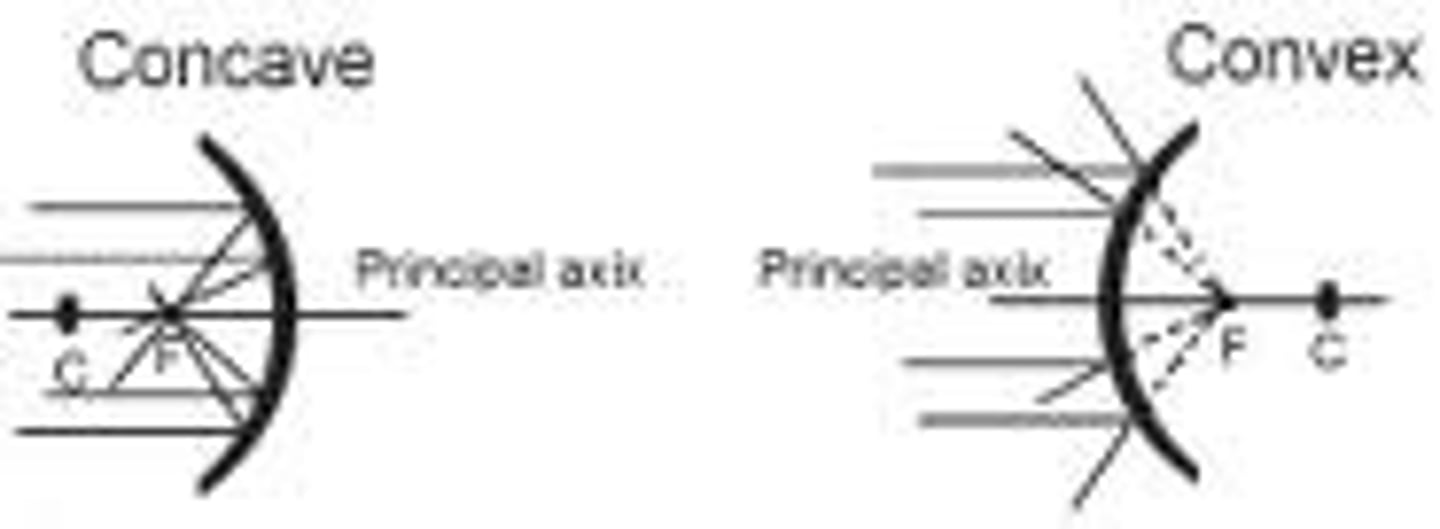
What are the general pattern light rays follow for CONCAVE and CONVEX mirrors
—> what does it mean you have to do for Convex mirror ray diagrams?
Concave mirrors will keep light rays on the real side
Convex mirrors will put light on virtual side (this means you will use DOTTED LINES‼️)
What is:
- The Principal Axis (PA)?
- Centre of Curvature (C)?
- Focal Point/ Focus (F)?
- Vertex?
Principal Axis = Horizontal line drawn right in the middle of the curved mirror
Centre of Curvature = If a Convex/Concave mirror was drawn out as a full circle, C would be the centre point of it and Vertex marks the radius
Focus = focal length of the mirror (length from centre marked as vertex to the farthest curved point of the mirror which are the top and bottom)
Vertex = one the Principal Axis line and marks the true centre of the mirror in both X and Y axes
What are the 3 Steps you MUST follow when drawing the light rays for a Concave/ Convex mirror
1. Draw a parallel line to the PA from the top of the object to the top of the mirror and then down through the focus
2. Line from top of object through the focus, hit the bottom of the mirror, then parallel to the PA
3. Top of object through C to the bottom of the mirror
What’s a cool way to remember if the image will be bigger/smaller/same for a Concave Mirror?
What are the 5 cases for Concave Mirrors and what is the SALT of the image?
For CONCAVE, think of C as the centre point.
If object is behind, image will be SMALLER
if object is in front, image will be BIGGER
If object is on C then SAME size
|
1. Object to the left of C = smaller, inverted, between F and C, and real
|
2. Object on C = same size, inverted, closer to C but between F and C, real
|
3. Object between C and F = bigger, inverted, behind C, real
|
4. Object on F = NO IMAGE
|
5. Object to right of F (will be on virtual side)—> you will need to do step 2 differently (through F, touch top of object, touch top of mirror and perpendicular to left BUT extend to virtual)
= Bigger, upright, past the mirror and to the right of Vertex, VIRTUAL
What are the 3 special cases in Concave mirror Ray Diagrams?
When object is directly on F, NO image can be made
When object is to the right of F, for step 2, draw a line going through F, the top of object, and then the top of mirror, then go left perpendicular, and extend ALL LINES to the virtual side
Image will be INVERTED if object is DIRECTLY on C or to the left of C or between C and F (this image will also be behind object and is the hardest to get all 3 lines to come to a point)
Test Q: Why would you use a Concave mirror for camping?
you use a Concave mirror for camping cus it actually focuses light to converge at one point which allows the sun to produce enough heat to burn something like paper that can be used to start a fire
What are the 2 cases for Convex Mirrors and what is the SALT of the image?
—> What do you need to remember abt one of the STEPS?
1. Object is upright —> smaller, upright, between V and F, virtual AND (for step 2, do a parallel line AND one that goes through focus)
|
2. Object is inverted —> smaller, inverted (shows that image follows orientation of OG object), between V and F, virtual (same thing for step 2, draw parallel AND one going through focus)
What is the Thin Lens Equation?
What is the Magnification of Lenses Equation?
(What MUST you remember about the units of these and for this UNIT?)
The units will ALWAYS be in CM for this Eq and also for everything else in this UNIT

In the Thin Lens Equation, what should you remember about f and how it relates to C?
Remember that C is the Center of Curvature = radius of mirror
*C = 2f* —> This means radius of mirror is 2 times the focal length of the mirror
using this, you only need one to find the other
What are the 5 Sign conventions for Mirrors that you should memorize? VERY IMPORTANT TO KNOW
Focal length sign is the opposite of what you’d normally expect (cus real side is + and on left and virtual is - and on right side)
do will always be positive as it is on the real side
di changes with which side image is on
hi and ho follow wether image is upright (+) or inverted (-)
Magnification follows wether both images are upright (+) or opposite of each other (-)

What are the 4 sign conventions for Lens? VERY IMPORTANT TO KNOW
Focal Length: f is pos for a CONVEX lens, and neg for a CONCAVE lens (opposite of what it is for mirrors)
|
Magnification: m is pos for a upright image and neg for a inverted image relative to the object (if both object and image are inverted then m is pos for both mirrors and lenses)
|
Image distance: di is POS for an image on the OPPOSITE side to the object (real side), and NEG for an image on the SAME side as the object (virtual)
—> (this is because anything on the virtual side is negative which also includes the object now cus real and virtual sides are flipped for Lenses)
|
Object Distance: do ALWAYS POSITIVE for all LENSES
What must you remember to do before the test?
RE READ ALL OF THE NOTES
--> Note the index of refraction values
--> Look at drawn diagrams
What does Mrs. Smith want us to know about Roemer and Huygens?
Roemer and Huygens calculated that light took 22 minutes to cross Earth’s orbit (diameter which they considered as 3 × 1011 m)
The actual time (what we use today) is 16 minutes or 960 seconds
What may Smith want us to know:
What was Roemer famous for?
What was Huygens famous for?
Roemer was famous for being the FIRST person to estimate/create the speed of light value.
He did this by observing the eclipses on Jupiter’s moon Io
|
Huygens was famous for being the one who created the wave theory of light (“Light is transverse waves radiating away from the source“)
What are Concave Mirrors Called?
What are Convex Mirrors Called?
|
What are Concave Lenses Called?
What are Convex Lenses Called?
Concave = Converging
Convex = Diverging
|
Concave = Diverging
Convex = Converging
What are the 6 N values you should know?
Vacuum = Air = 1
Water = 1.33
Ethanol = 1.36
Quartz = 1.46
Crown glass = 1.52
Diamond = 2.42 (Nothing will be greater than diamond’s index of refraction)
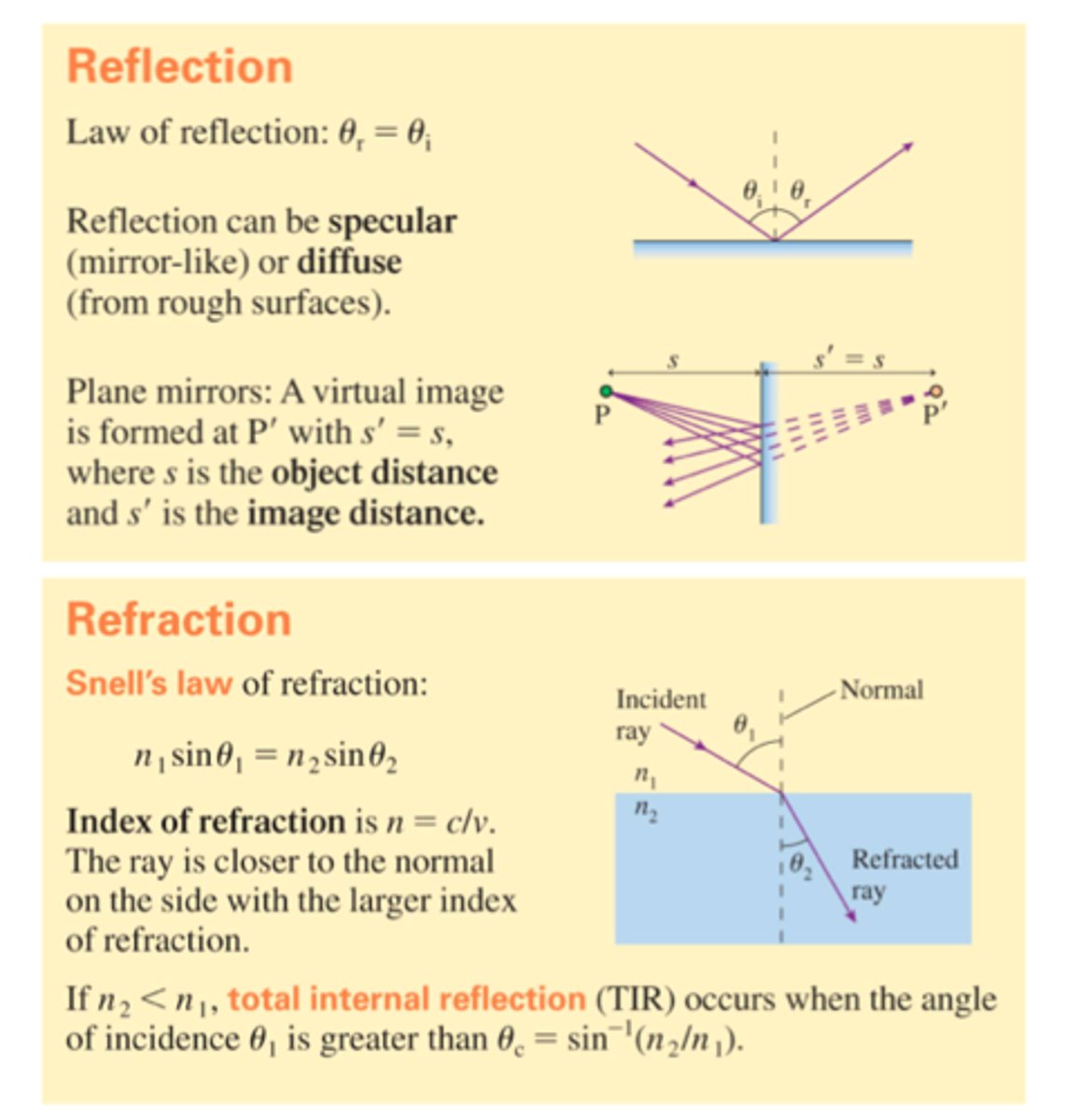
What should you ALWAYS remember with the Law of Reflection?
—> How does this relate to refraction from less dense to more dense?
The angle is found with reference to the NORMAL
This means if the normal is the Y-axis, find angle from the y-axis
This also means you should never have to do 90- angle given, and the angle given usually will be the angle
—> This relates as when a light ray goes from a
less dense to a more dense medium, the ray slows down and bends TOWARDS the normal.
more dense to less dense medium, the ray speeds up and bends AWAY from the normal.
What does Wave Speed depend on?
What is the definition for Refraction?
What is another name for the Index of Refraction (n)?
Wave speed depends on the medium
Refraction = A change in direction of light as it passes at an angle from one medium to another
Another name for the index of refraction (n) is Optical Density
What is Snell’s Law?
What is the formula?
What is the formula if using speed of light in a medium?
What does each θ mean?
Snell Law = how light (or other waves) bends when it passes from one medium to another
|
Formula: n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
|
Alt formula: v1sinθ1 = v2sinθ2
θ1 = θi = angle of incidence
θ2 = θR = angle of refraction
What is Total Internal Reflection (TIR)?
What is a Critical Angle and what will it be in TIR?
Why is θ2 = 90°
What does TIR basically mean?
TIR = when θ2 = Critical Angle (θc = θ1)
—> This means θ1 or incident angle is the critical angle
|
The critical angle is the angle of a light ray FROM THE NORMAL.
The critical angle = angle of incidence = θ1
|
θ2 = 90° because no light rays go into the second medium, so θ2 (angle of refraction) is drawn with a 90-degree angle to the normal line and x-axis
|
—> basically this means the Law of Reflection (cus θ2 = θ1)
The light ray DOES NOT enter the second medium (gets reflected in 1st medium and Law of reflection applies)
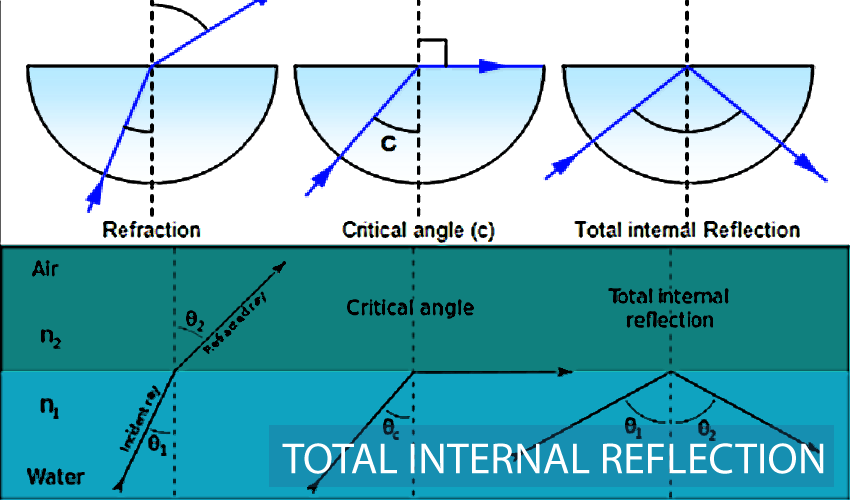
When a question asks for the critical angle of a medium, what 2 things does it tell you?
immediately set θ2 =90 in the formula
This means that medium of the critical angle is the FIRST medium (incident) passing into a second medium
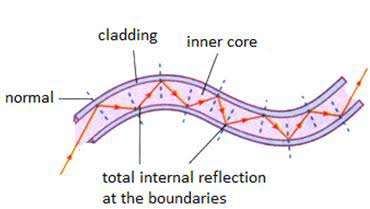
What are 2 applications of TIR that may be asked on the test?
Light pipe = this is known as Fibre Optics, and a laser emitters bounces laser rays so TIR happens each time it hits the edge of the light pipe
Endoscope = Also uses Fibre Optics in the form of 2 Fibre Optic tubes, so it follows the same process as a Light Pipe
What are the 5 things to remember that are different with Lens Ray Diagrams compared to mirrors?
Virtual Side is now on LEFT and Real on RIGHT (real left, and virtual right for mirrors)
ALWAYS draw the dotted line down the middle of the lens
The centre of curvature is now called the OPTICAL CENTER because the center has no curve anymore
f’ (f prime) and 2f’ are on the virtual side for CONVEX, and f’ and 2f’ are on real side for CONCAVE (sides where images are not formed)
Another way to memorize that f’ and 2f’ on on real/virtual is that for both lenses, the prime focal lengths will be on the side where the image is NOT formed
What are the 3 steps you must do for Lens Ray Diagrams?
Top of the object, parallel to the PA until it hits the Optical Center, THEN go diagonal through the PRIMARY focus
Top of the object through the OPTICAL CENTER of the lens and continue.
Top of the object, through the SECONDARY focus then hit the Optical Center and make the ray parallel to PA (only for convex)
—> for concave, go right through O until you hit f’ and keep going (won’t bend line to make parallel to PA cus you hit O before you hit f’)
What will the 4 REQUIRED steps be for a Ray Diagram of a Lens on the TEST?
Label f and 2f (primary), as well as f’ and 2f’ (prime = secondary)
label real/virtual sides
Do the 3 steps
Do SALT
What are the General Trends for the Object position and the resulting image size/attitude for BOTH Mirrors and Lenses?
For only Concave mirrors, C controls size of the image
—> if object behind C, image will be smaller, if on C then same size, and if past or to the right of C, then bigger image
|
For CONVEX lenses, F and 2F control image size
—> if object behind F, image will be bigger and inverted, if on F, NO image, if in front of f, then bigger image behind object
|
—> if object behind 2F, image will be smaller and inverted on real side, if on 2F, same size image inverted on real side (think equal lengths opp, sides), and if in front of 2F, image will be Bigger, inverted and on real side
What is the ONLY POSSIBLE Case for a Concave Lens? (only 1 case)
The object CAN change postions on the virtual side BUT
image will ALWAYS be between f (primary) and the lens
image will ALWAYS be virtual, upright, and smaller than the object height
Which Mirror is Diverging/Converging and what does it mean?
Which Lens if Diverging/Converging and what does it mean?
Mirrors
Diverging = Convex = - f
Converging = Concave = + f
|
Lenses
Diverging = Concave = - f
Converging = Convex = + f
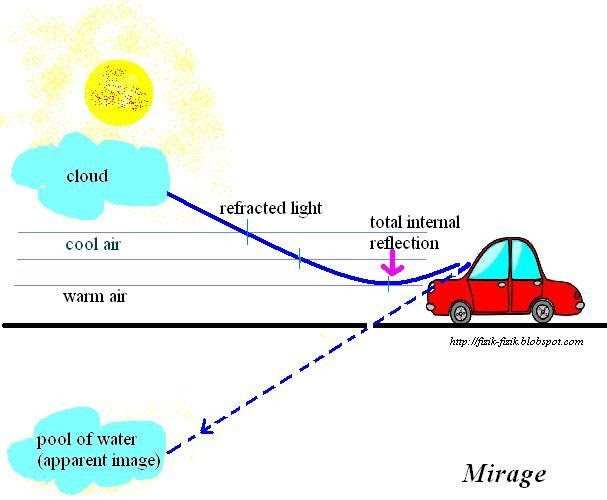
How do mirages work?
mirages form as hot air rises off the ground past the cold air, and eventually on top of the colder air
As hot air passes by cold air, since hot is less dense, the image will refract towards the normal
As the cold air passes by the hot air, the image will refract away from the normal
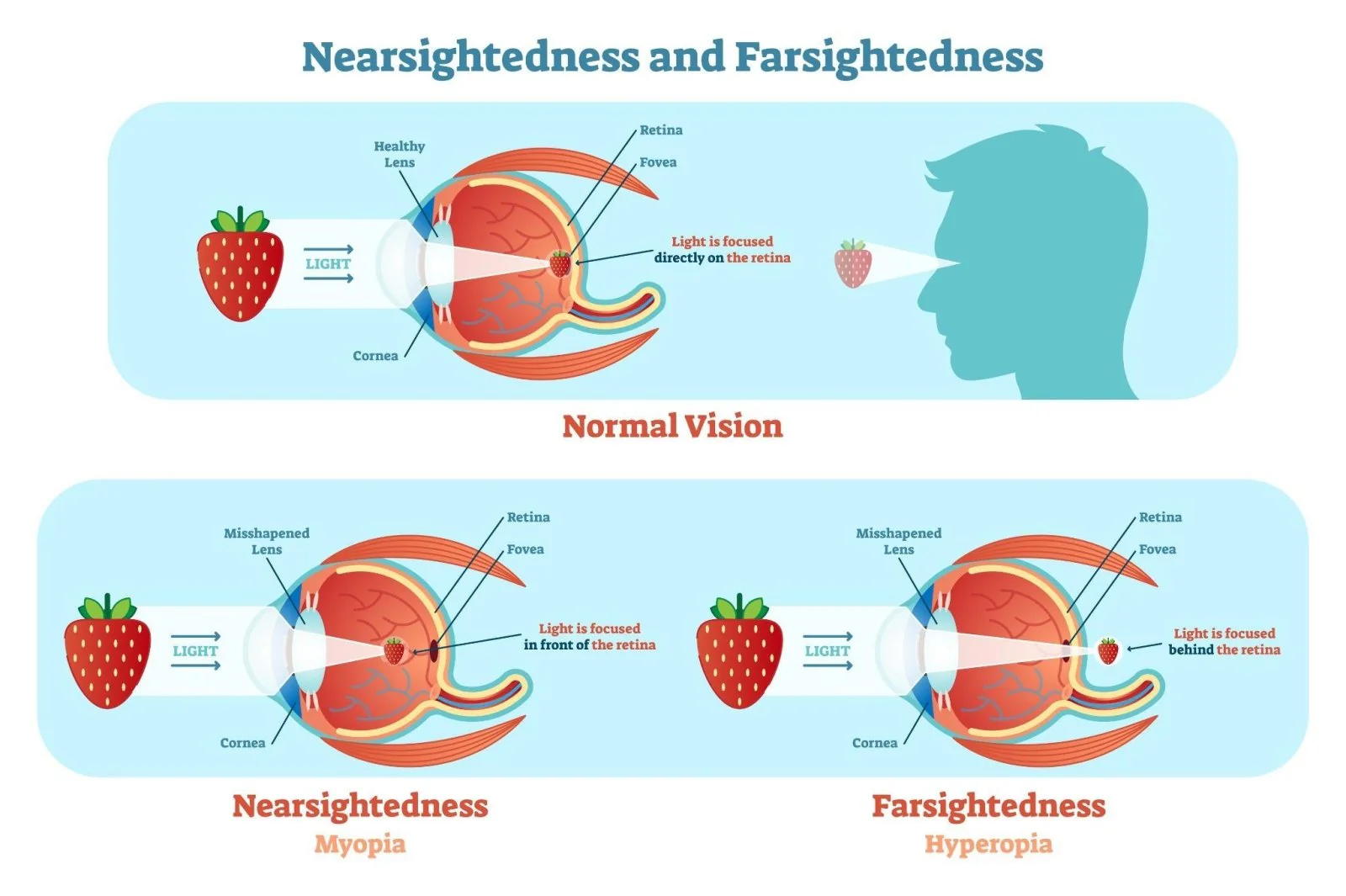
What is the difference between Myopia and Hyperopia?
Myopia = nearsightedness = Can’t see FAR objects because the image will form BEFORE retina
corrected with CONCAVE lenses
Hyperopia = farsightedness = Can’t see CLOSE objects because the image will form BEHIND retina
corrected with CONVEX lenses