Supply Chain - Exam 3
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
A computer system that integrates application programs in accounting, sales, manufacturing, and the other functions in a firm.
Material requirements planning (MRP)
The logic for determining the number of parts, components, and materials needed to produce a product.
Data sources needed for an MRP Program
Master production schedule
Bill-of-materials file
Inventory records file
Master production schedule (MPS)
A time-phased plan specifying how many end items the firm plans to build, and when.
Available to promise
A feature of MRP systems that identifies the difference between the number of units currently included in the master schedule and the actual (firm) customer orders.
Bill-of-materials (BOM)
The complete product description, listing the materials, parts, and components, and also the sequence in which the product is created.
Inventory status record
A document or record that provides a real-time snapshot of a company's stock, including details like quantity, location, availability, and allocation to specific orders or transfers.
Net change systems
An MRP system that calculates the impact of a change in the MRP data (the inventory status, BOM, or master schedule) immediately.
Time fence
Period of time during which a customer has a specified level of opportunity to make changes.
Scheduled receipts
Orders that have already been placed and scheduled to arrive in the future (in this time period). Add to inventory.
Gross requirements
Total amount required for an item. Aka the demand. This is the only category that pulls from inventory.
Net requirements
This is the amount needed after considering what we currently have in inventory and what we expect to arrive in the future. If it's greater than 0, you need to take care of the shortage.
Lead time
The planned-order receipt and planned-order release are offset by this amount of time.
Lot sizes
The part quantities issued in the planned-order release section of an MRP report. (The quantity of an item manufactured in a single production run).
Lot-sizing techniques
Lot-for-lot (L4L)
Economic order quantity (EOQ)
Least total cost (LTC)
Least unit cost (LUC)
Lot-for-lot ordering
The term for ordering exactly what is needed each period without regard to economic considerations.
Economic order quantity (EOQ)
The ideal quantity of units a company should purchase to meet demand while minimizing inventory costs such as holding, shortage, and order costs.
Not designed for a system with discrete time periods such as MRP. The lot sizes generated by this don't always cover the entire number of periods.
Least total cost (LTC)
A dynamic lot-sizing technique to calculate order quantity that compares carrying cost and the setup costs for various lot sizes.
Least unit cost (LUC)
A dynamic lot-sizing technique that adds ordering and inventory carrying cost for each
trial lot size and divides by the number of units in each lot size.
Capacity
None of the techniques for determining order quantity consider this important noneconomic factor that could make the order quantity infeasible.
Projected available balance
Units expected in inventory at the end of a period (end of the week).
Planned order receipts
Quantity that is planned to be released and will arrive in this time period. End of a production run, add to inventory.
Safety stock (aka buffer stock)
Extra inventory held to prevent stockouts caused by unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply, acting as a protective cushion against disruptions.
Planned order release
The process in which the order is planned. Start of a production run.
Total quality management (TQM)
A management system for a customer-focused organization that involves all employees in continual improvement, so that the entire organization excels on all dimensions of products and services that are important to the customer.
Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award
An award established by the U.S. Department of Commerce given annually to companies that excel in quality.
Design quality
The inherent value of the product in the marketplace.
Conformance quality
The degree to which the product or service design specifications are met.
Quality at the source
Making the person who does the work responsible for ensuring that specifications are met.
Dimensions of quality
Criteria by which quality is measured.
Cost of quality (COQ)
Expenditures related to achieving product or service quality, such as the costs of prevention, appraisal, internal failure, and external failure.
Appraisal costs
Costs of the inspection, testing, and other tasks to ensure that the product or process is acceptable.
Prevention costs
Sum of all the costs to prevent defects.
Internal failure costs
Costs for defects incurred within the system: scrap, rework, repair.
External failure costs
Costs for defects that reach the customer.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
Series of standards agreed upon by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
ISO Certification has three different forms:
1st Party - a firm audits itself against ISO standards.
2nd Party - a customer audits its supplier.
3rd Party - a certifying agency serves as auditor.
Includes:
ISO 9000
ISO 14000
ISO 26000
ISO 9000 (quality)
Directs you to "document what you do and then do as you documented".
ISO 14000 (environmental management)
More than 350 standards for monitoring the quality of air, water, and soil.
ISO 26000 (social responsibility)
Discuss issues and possible actions with relevant stakeholders.
External Benchmarking
Looking outside the company to examine what excellent performers inside and outside the company's industry are doing in the way of quality.
Six Sigma Quality
A customer focused philosophy and set of methods companies use to eliminate defects in
their products and processes. It seeks to reduce variation in the processes that lead to product defects
Six Sigma
A statistical term to describe the quality goal of no more than 3.4 defects out of every million units. Also refers to a quality improvement philosophy and program.
Defects per million opportunities (DPMO)
A metric used to describe the variability of a process.
Requires 3 pieces of data:
1) Unit - the item produced or being services
2) Defect - any item or event that doesn't meet the customer's requirements
3) Opportunity - a chance for a defect to occur
DMAIC
An acronym for the Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control improvement methodology followed by companies engaging in Six Sigma programs.
Define the goals of the improvement activity
Measure the existing process
Analyze the process
Improve the process
Control the new process
Statistical quality control (SQC)
A number of different techniques designed to evaluate quality from a conformance view.
Assignable variation
Deviation in the output of a process that can be clearly identified and managed.
Common variation
Deviation in the output of a process that is random and inherent in the process itself.
Upper and lower specification limits
The range of values in a measure associated with a process when a product or service is designed, that is allowable given the intended use of the product or service.
Capability index (Cpk)
The ratio of the range of values allowed by the design specifications divided by the range of values produced by a process.
Statistical process control (SPC)
Testing a random sample from a process to determine whether the process is producing items within the control range.
Attributes
Quality characteristics that are classified as either conforming or not conforming to specifications.
Variables
Quality characteristics that are measured in actual weight, volume, inches, centimeters, or other measure units.
Fitness for use
Relates to how well a product or service meets design specifications.
Process capability
The ability of a process to consistently produce a good or deliver a service with a low probability of generating defect.
Specification limits
Range of variation that is considered acceptable by the designer or customer. (Example: The part must be between 1.9 inches and 2.1 inches long).
Process control limits
Range of variation that a process can maintain with a high degree of certainty. (Example: 99.7% of the parts are between 1.95 inches and 2.05 inches long).
Control Chart Evidence for Investigation - One point beyond control limit
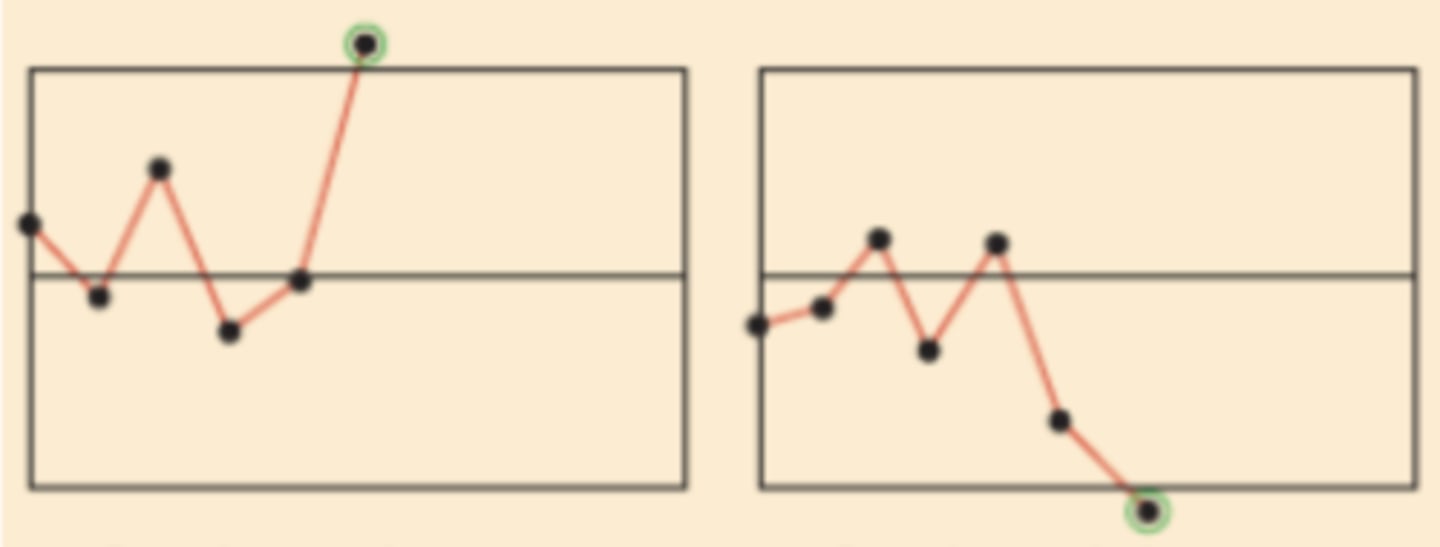
Control Chart Evidence for Investigation - Two points near control limit
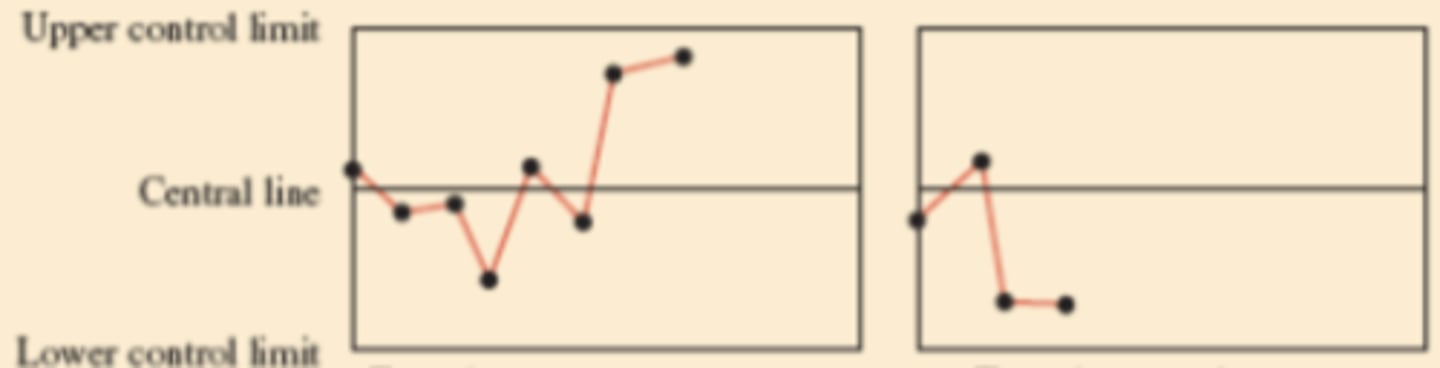
Control Chart Evidence for Investigation - Run of 5 above or below central line
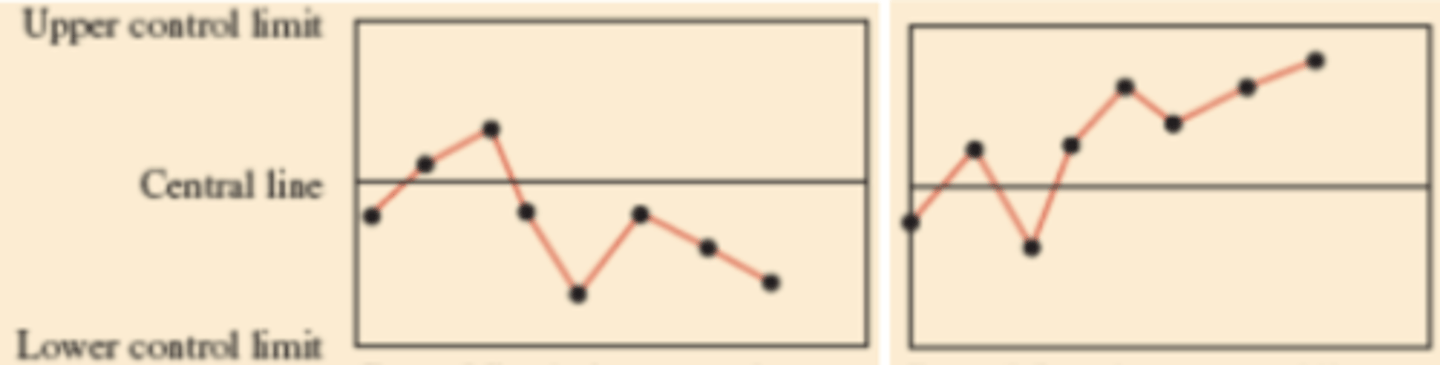
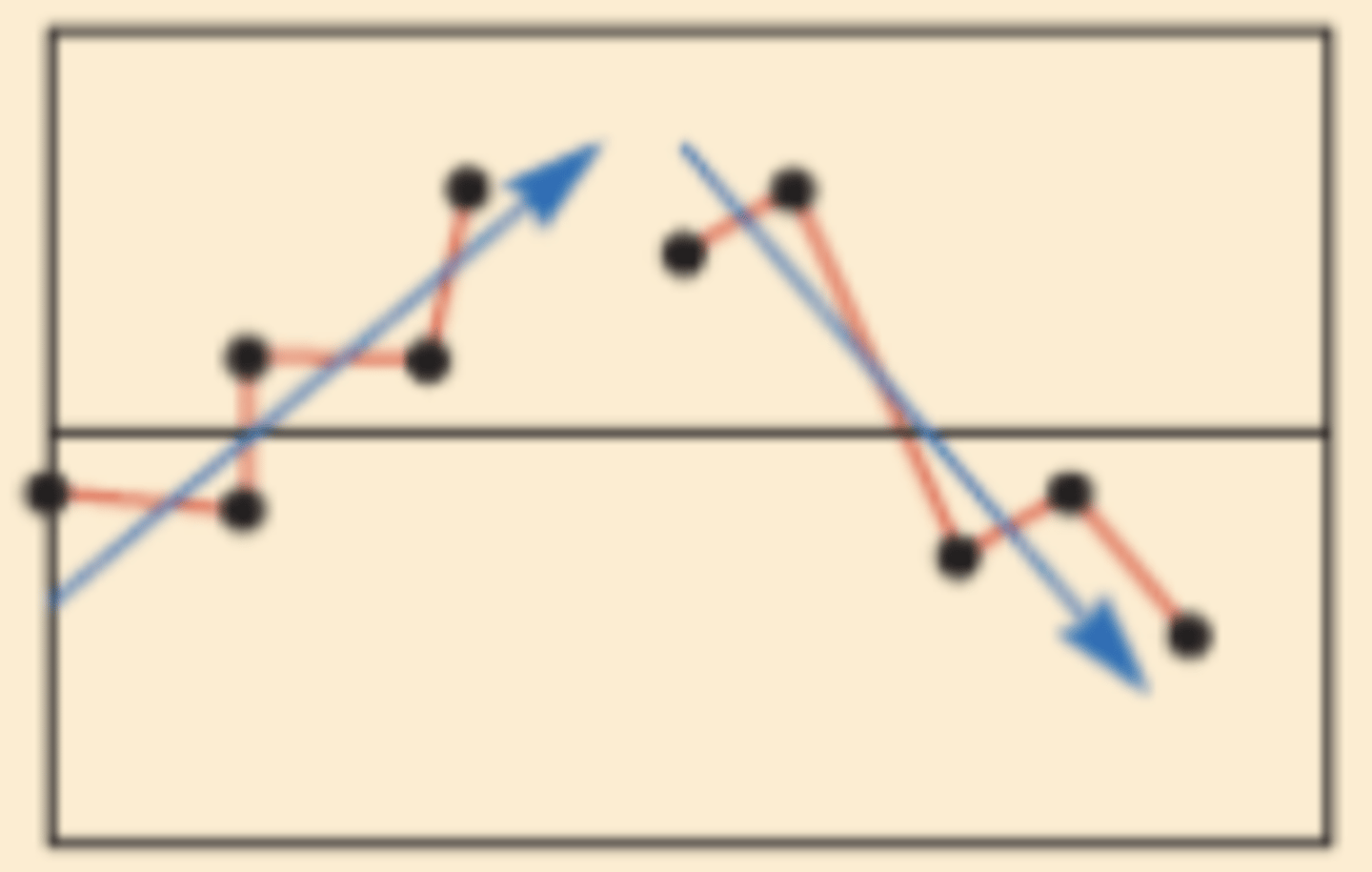
Control Chart Evidence for Investigation - Upward or downward trend
Control Chart Evidence for Investigation - Erratic behavior
Control Chart Evidence for Investigation - Sudden change in level (moving average)
Control Chart Evidence for Investigation - Normal behavior
Inventory
The stock of any item or resource used in an organization.
Includes: raw materials, finished products, component parts, work-in-process (WIP), and Maintenance, Repair and Operating supplies.
Independent demand
The demands for various items are unrelated to each other.
Dependent demand
The need for any one item is a direct result of the need for some other item, usually an item of which it is a part
Single-period problem
Answers the question of how much to order when an item is purchased only one time and it is expected that it will be used and then not reordered.
Fixed-order quantity model (Basic EOQ-model)
An inventory control model where the amount requisitioned is fixed and the actual ordering is triggered by inventory dropping to a specified level of inventory.
Price break model.
Fixed-order quantity
An inventory system where the inventory level for an item is constantly monitored and when the reorder point is reached, an order is released.
For critical and high-value items.
Fixed-time period model (P-model)
An inventory control model that specifies inventory is ordered at the end of a predetermined time period. The interval of time between orders is fixed and the order quantity varies.
Single-period model.
Fixed-time period
An inventory system where the inventory level for an item is checked at regular intervals and restocked to some predetermined level.
For less critical and low value items.
Inventory position
The amount on-hand plus on-order minus backordered quantities. In the case where inventory has been allocated for special purposes, the inventory position is reduced by these allocated amounts.
Optimal order quantity (Qopt)
This order size minimizes total annual inventory related costs
Reorder point
An order is placed when the inventory position drops this level.
Safety stock
The amount of inventory carried in addition to the expected demand.
Inventory turn
A measure of the expected number of times that inventory is replaced over a year.
Price-break model
This model is useful for finding the order quantity of an item when the price of the item varies with the order size.
ABC inventory classification
Divides inventory into dollar volume categories that map into strategies appropriate for the category.
Cycle counting
A physical inventory-taking technique in which inventory is counted on a frequent basis rather than once or twice a year.
Holding (or carrying) costs
Costs for storage, handling, insurance, pilferage, breakage, obsolescence, depreciation, taxes, and the opportunity cost of capital.
Setup (or production change) costs
Costs for obtaining the necessary materials, arranging specific equipment setups, filling out the required papers and so on.
Ordering costs
Costs of placing an order.
Shortage costs
Costs of stock-out.
Sustainability
The ability to meet current resource needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
Triple bottom line
Evaluating the firm against social, economic, and environmental criteria.
Operations and supply chain strategy
The setting of broad policies and plans that will guide the use of the resources needed by the firm to implement its corporate strategy.
Operations effectiveness
Performing activities in a manner that best implements strategic priorities at minimum cost.
Straddling
When a firm seeks to match what a competitor is doing by adding new features, services, or technologies to existing activities. This often creates problems if certain trade-offs need to be made.
Order winners
One or more specific marketing-oriented dimensions that clearly differentiate a product from competing products.
Order qualifiers
Dimensions used to screen a product or service as a candidate for purchase.
Activity-system maps
Diagrams that show how a company's strategy is delivered through a set of supporting activities.
Supply chain risk
The likelihood of a disruption that would impact the ability of a company to continuously supply products or services.
Productivity
A measure of how well resources are used.