Cardio test 5
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What does the blockade of the hERG channel lead to?
Prolonged QT risk
If there is a long QT interval what medication should be administered to prevent Torsades
Non-dihydropyridine CCBs
What is Torsades
polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
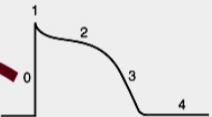
What is 0
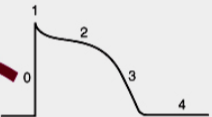
What is 1
Opening of Na+ current
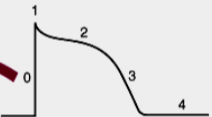
what is 2
Opening of Ca2+ channels
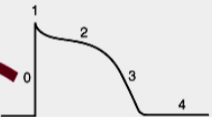
what is 3
opening of K+ channels
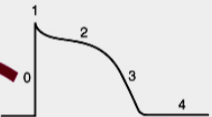
what is 4
Membrane at resting potential
Why is it important to weight the risk and benefits of AAD
AAD can exacerbate existing arrhythmias and cause new ones
What is the main goal of AAD
blunt or prevent abnormal impulses formation and/or abnormal conduction
What is the major MOA of class 1 AAD
Na+ channel inhibition
What is the major MOA of class 2 AAD
Beta blockers
What is the major MOA of class 3 AAD
K+ channel blockers
What is the major MOA of class 4 AAD
Ca 2+ channel blockers
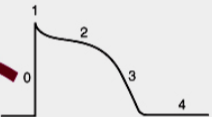
Where do the AAD work at in the graph
Effective refractory period
Rate of depolarization/repolarization (slope)
Resting potential (4)
Quinidine drug class
Class 1A sodium channel blocker
Procainamide drug class
Class 1A sodium channel blocker
Disopyramide drug class
Class 1A sodium channel blocker
Lidocaine drug class
Class 1B sodium channel blocker
Phenytoin drug class
Class 1B sodium channel blocker
Mexiletine drug class
Class 1B sodium channel blocker
Flecainide drug class
Class 1C sodium channel blocker
Propafenone drug class
Class 1C sodium channel blocker
What are the class 2 AAD
Beta blockers
What are the class 3 AAD
K+ channel blockers
Amiodarone Drug class
K+ channel blockers
Dofetilide Drug class
k+ channel blockers
Ibutilide drug class
k+ channel blockers
Sotalol drug class
k+ channel blockers
Diltiazem drug class
CCB
Verapamil drug class
CCB
Class 1A sodium channel MOA
Open >inactivated = slow dissociation
decrease Vmax in phase 0
Decrease in conduction velocity
increase duration of AP and ERP
Class 1B sodium channel MOA
Inactivated > open = rapid dissociation
Increase ERP due to depolarization cells due to slowed recovery of Na+ channels from inactivation
Class 1C sodium channel MOA
Open > inactivated = very slow dissociation
decreased Vmax and conduction velocity in AV node
Increased duration of ERP
Quinidine Therapeutic Uses
Supraventricular and ventricular dysrhythmias
Procainamide Therapeutic Uses
Atrial, Supraventricular, and VT dysrhythmia
Disopyramide Therapeutic Uses
VT dysthymia
What medication is preferred for short-term VT dysrhythmia
Amiodarone
Lidocaine Therapeutic Uses
Short-term VT dysrhythmia
Phenytoin Therapeutic Uses
Acute and chronic VT dysrhythmia
Mexilitene Therapeutic Uses
VT dysrhythmia
Flecainide Therapeutic Uses
SPVT and VT dysrhythmia
Propafenone Therapeutic Uses
SPVT and VT dysrhythmia
What cells get effected most by Class 1 AAD
Depolarized cells
Does lidocaine block sodium channels in normal cells
Nah
What is only class 1 AAD that does decrease refractory period
Lidocaine
Why would cells be depolarized
Ischemia, metabolic/electrolyte imbalance
What two sodium channel blockers AAD that act on the calcium channels
Disopyramide and Propafenone
What sodium channel blocker AAD act on K+ current
class 1A sodium channel blockers
How do all sodium channel AAD prolong ERP
slowing recovery of Na+ channels from inactivation and thus delaying new AP
Major site of metabolism of Quinidine and DDI
CYP2D6
Quinidine AEs
Cardiotoxic at higher doses due to anti-cholinergic effect
increasing SA automaticity, AV conduction
Quinidine DDI
Macrolide antibiotics
Amiodarone
digoxin
Procainamide metabolism
hepatic acetylation to NAPA- which can block K+ channels
Procainamide AEs
Lupus like syndrome
Procainamide DDI
Macrolide antibiotics
Amiodarone
Disopyramide AEs
Stong negative inotropic effect
cardiotoxicity at high doses
Disopyramide DDI
CYP2D6 macrolide antibiotics
Why is lidocaine preferred IV/IM and not oral
rapid hepatic metabolism orally and only 3% shows up in plasma
Lidocaine AEs
Direct CNS effects at high doses
Seizures
Drowsiness
confusion
Mexiletine administration
Orally
Low first pass effect
Mexiletine DDIs
Anti-depressants
Theophylline
What are the most are the most pro-arrhythmics of the sodium channel blockers
Class 1C
What drugs can you not use with in pts with MI
flecainide and propafenone
Of the class 3 AAD what medication really increase refractory period
Amiodarone and Dronedarone
what are amiodarone and dronedarone effect on QT interval
Very mush increase
What is the most commonly prescribed medication for post-operate arrhythmia
Amiodarone
Where are Amiodarone and Dronedarone metabolisms
CYP3A4
What is interesting about the amiodarone and dronedarone half lives
The half life is weeks
Amiodarone DDI
Increase serum lvls of Digoxin, warfarin, and statins
Amiodarone AEs
Bradycardia or heart block
pulmonary fibrosis
corneal deposits
hypothyroidism
Dronedarone AEs
exacerbation of severe HF
Amiodarone MOA
mixture of all 4 drug classes
Adenosine MoA
Blocks Ca2+ channels
Slows AV nodal conduction
Does the opposite effect of group 3 AAD
Does Esmolol act on Na+ channels?
Yes, acts on depolarized cells
Does Diltiazem act on the sympatholytic system
No
Sotalol MOA
Dual acting class 2 and 3
How does Mg2+ effect arrhythmics
Interacts with Na/K ATPase, weakly blocks Ca2+ channels
Increases AV conduction
Useful for long QT
How does K+ effect arrhythmias
Slows AV conduction
What is the P-wave
Atrial depolarization
Conduction
What is the QRS complex
Ventricular Depolarization
What is the T wave
Ventricular repolarization
What is the average QT interval
< 440 msec
What increases the atrial stretch
HTN
Ischemic heart disease
Valvular disorders
HF
Pulmonary disease
Obesity
What increase Sympathetic system
Hyperthyroidism
Alcohol intake
Sepsis/infection
Surgery
What are the symptoms of Arterial Fibrillation?
Palpitations
Dizziness
Fatigue
Dyspnea
Weakness
Decreased exercise tolerance
What are the ways to see Arterial Flutter in EKG
Absence of P waves
What are the goals of therapy for AF
Ventricular rate control
Preventing clots
Restore sinus rhythm
For acute AFib, what are the severe symptoms
low BP
Syncope
Altered mental status
Severe chest pain
What are the ways to treat severe symptoms in acute AFib
DCCV or electroshock
What are the minimal symptoms an Acute AFib
rapid ventricular rate
>120-140
What are the ways to treat minimal symptoms for acute AFib
BB, CCB and digoxin
What is the drug of choice for acute Ventricular Rate control in AFib
Beta blockers