Rest of reproductive notes and next chapter notes
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Bulb of the penis connects what?
Corpus spongiosum to rest of penis
What connects the penis to the pelvis?
Crus of the penis (attached part of corpus cavernosum)
What is the term used for the ball sac?
Corpus spongiosum
What doe the corpus spongiosum (ball sac area) have inside it?
Bulbourethral glands
What is the opening of the penis?
External urethral orifice
What connects the external urethral orifice (opening of penis) and the bulbourethral gland within deep pouch?
Urethra
What is the muscle around the ball sac?
Bulbospongiosus
What is the muscle that surrounds the crus of the penis?
Ischiocavernosus
Integumentary system is referencing what?
Skin and accessory structures (glands, nails, hairs)
What is the largest organ system of the body (16% of body weight)?
integumentary system
What is the outer and inner layer of the skin (Cutaneous layer)?
Epidermis (4-5 layers, outer) and dermis (two layers, inner)
What is not part of the integumentary system?
Hypodermis. Below dermis, consist of blood vessels, areolar tissue, and adipocytes.
What are the structures of the Epidermis?
Deepest to superficial;
Stratum germinativum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin)
Stratum corneum
What does the stratum germinativum consist of?
melanocytes, keratinocytes, and tactile cells
What does Stratum Germinativum form?
epidermal ridges and fingerprints (create with dermal papillae)
What to remember about Stratum spinosum?
The spiny layer, eight to ten layers.
What are the eight-ten layers of Stratum Spinosum bounded by?
desmosomes
What is the Stratum Granulosum called?
grainy layer
What does the Stratum Granulosum consist of?
cells that produce a protein called keratin
What is stratum lucidum called?
the clear skin
where is the stratum lucidum found?
in thick skin
What does the stratum lucidum do?
covers stratum granulosum and deep to stratum corneum
What is the stratum corneum called?
horn layer
What does the stratum corneum consist of?
dehydrated squamous cells, used for protection.
The dermis consist of two layers, what are they?
Papillary layer (superficial layer) and Reticular layer (deeper layer)
Where is the Dermis located between?
epidermis and subcutaneous
What are the main components of the Papillary layer?
sebaceous glands and arrector pili muscles
What does the sebaceous glands do in the papillary layer?
lubricate the epidermis
What do Arrector pili muscles do in Papillary layers?
Attach to hair follicles, create goose bumps upon contraction, contraction generates heat.
Where is the reticular layer located?
Deep to papillary layer
The reticular layer consist of?
Two types of sweat glands: Apocrine and Meocrine
What do Ceruminous glands do and where are they located?
Produce Cerumen (ear wax) and located in external acoustic canal.
What do Sebaceous glands do?
produce sebum (causes acne)
Where are Sebaceous glands located?
Papillary layer of dermis, located everywhere except palms and soles.
Where are Apocrine sweat glands and Merocrine sweat glands located?
reticular layer of dermis
What do Apocrine sweat glands do?
Secrete products into hair follicles, produce oily and smelly sweat, produce pheromones (sexual attraction)
What does Merocrine Sweat Glands do?
Secrete products directly to skin surface, product sweat (watery) for cooling purpose
What are Cleavage lines in the Dermis?
Collagen fibers (bundled) in the dermis. They are patterns of wrinkles and creases on the skin following collagen fibers.
What do nails do?
Protect fingers and toes- continuous growth of the epidermis
What is the Lunula of the Nails?
pale crescents at the base of the nail
Sides of nails lay how?
lateral nail grooves
What is Hyponychium?
Skin beneath the distal free edge of the nail
What is Eponychium (cuticle)?
Visible nail emerges from here
What is the Vulva?
Term used to encompass all the external genitalia in women
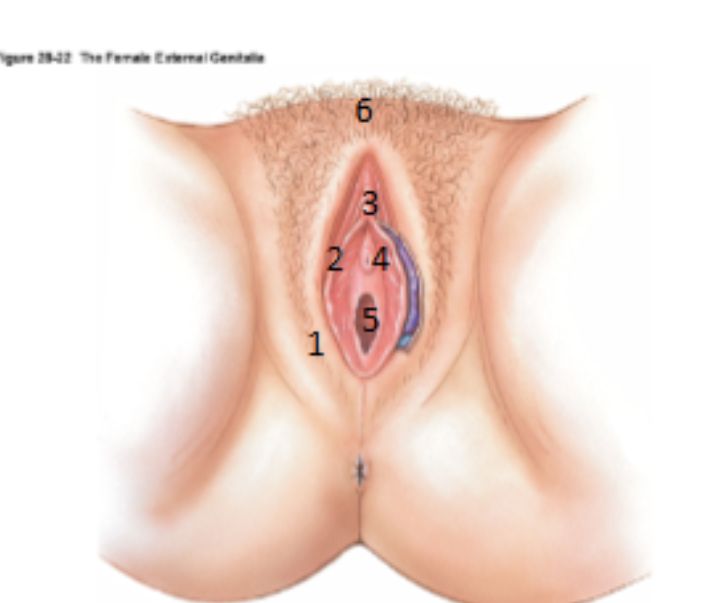
What is 1?
Labia majora
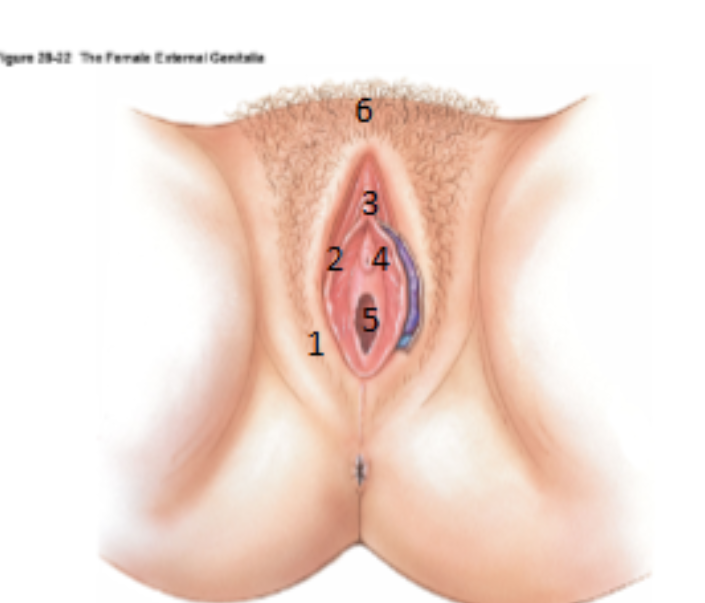
What is 2?
Labia minora
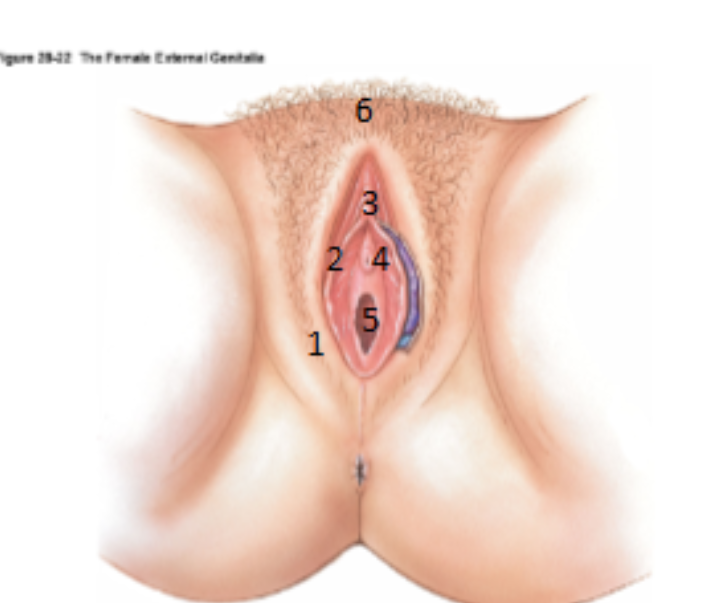
What is 3?
Clitoris
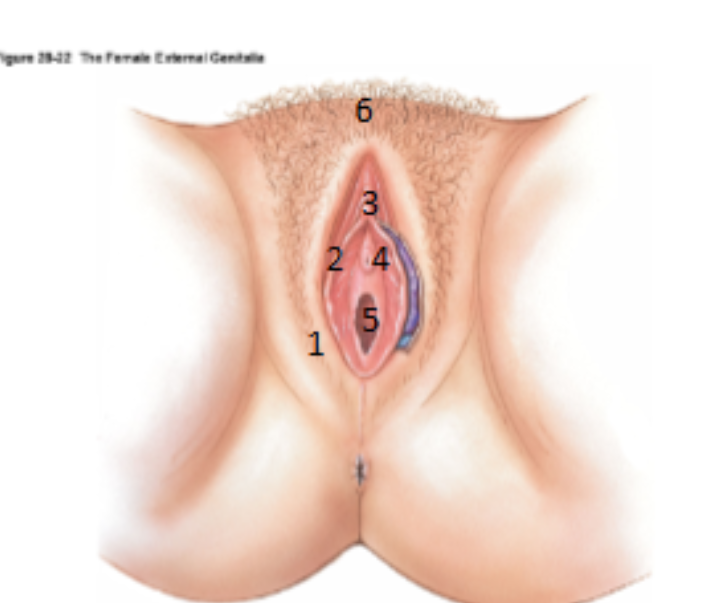
What is 4?
urethral opening
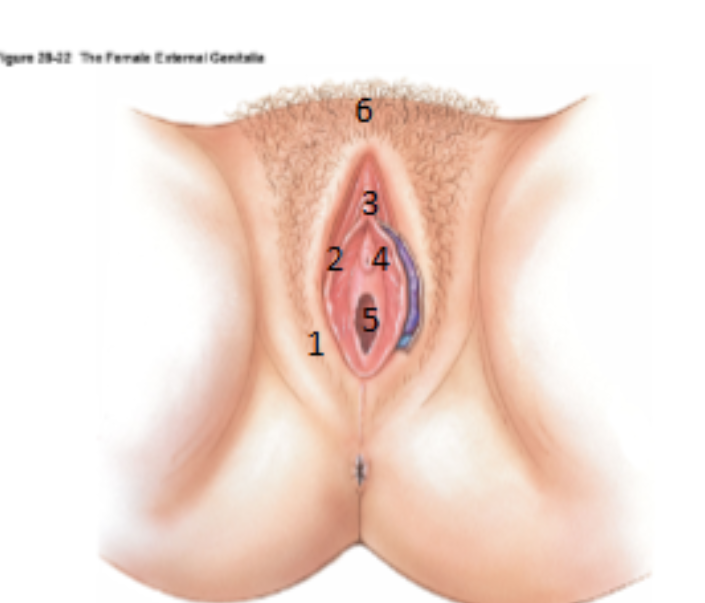
What is 5?
Vagina (hymen)
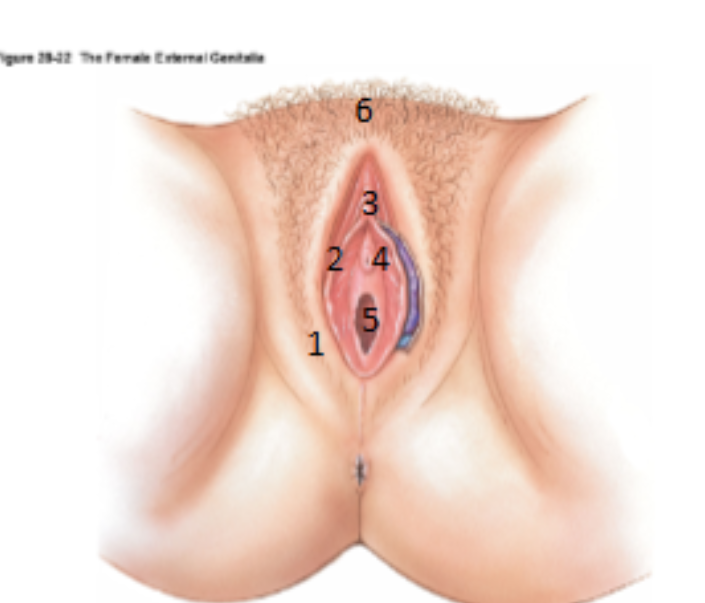
What is 6?
Mons pubis
What is the cavity between the labia minora?
Vestibule
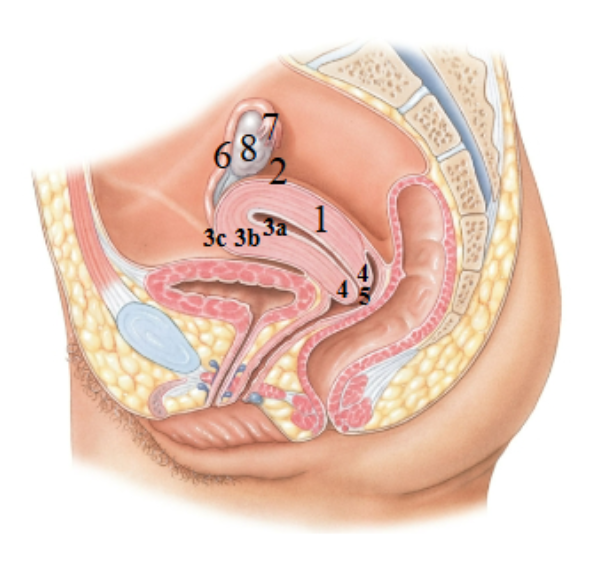
What is 1 pointing at?
Uterus
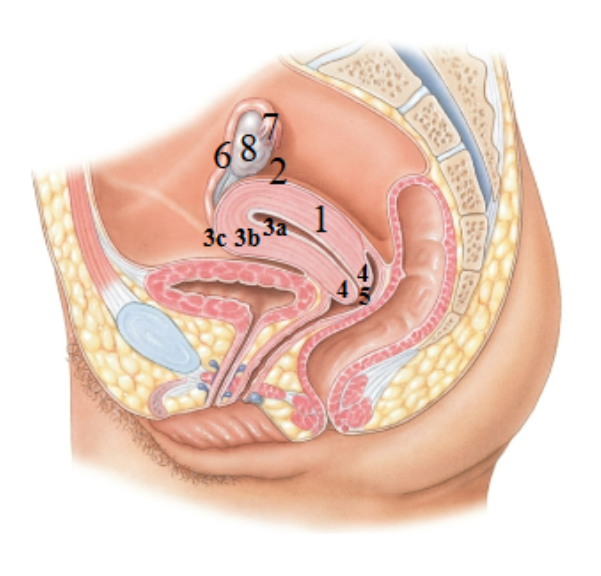
What is 2 pointing at?
fundus of the uterus
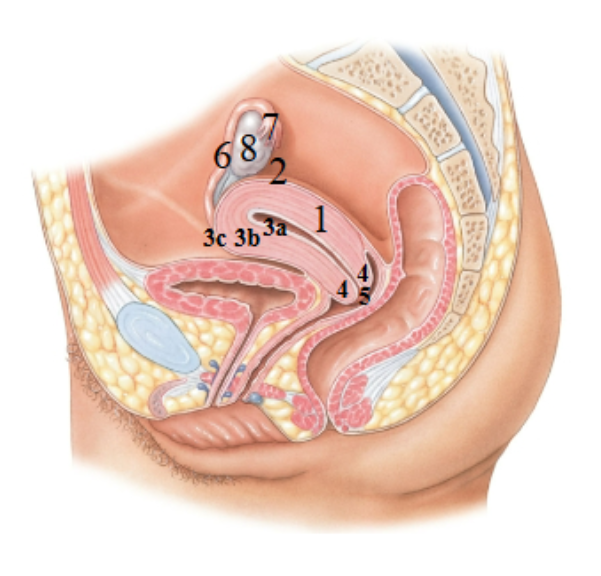
What is 3a pointing at?
endometrial (uterus lining)
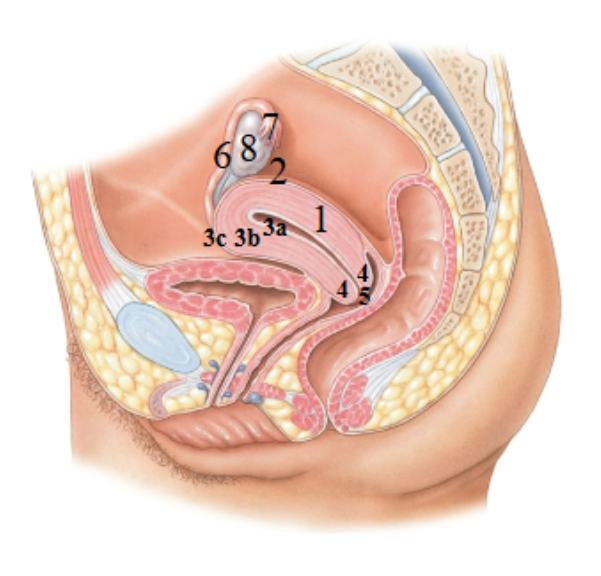
What is 3b?
Myometrium
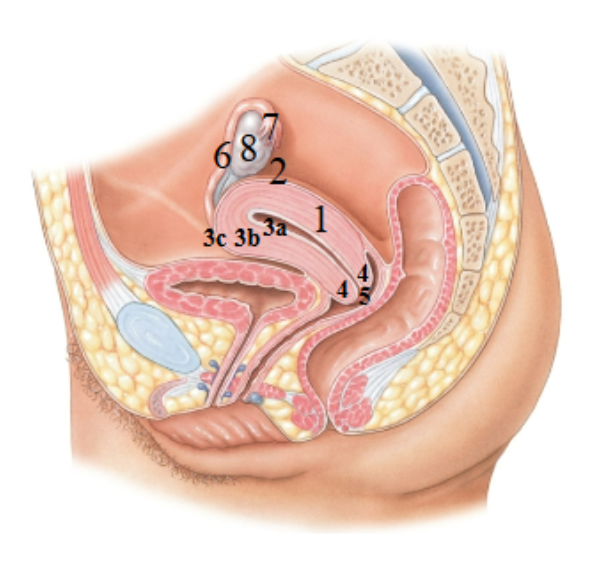
What is 3c?
Perimetrium
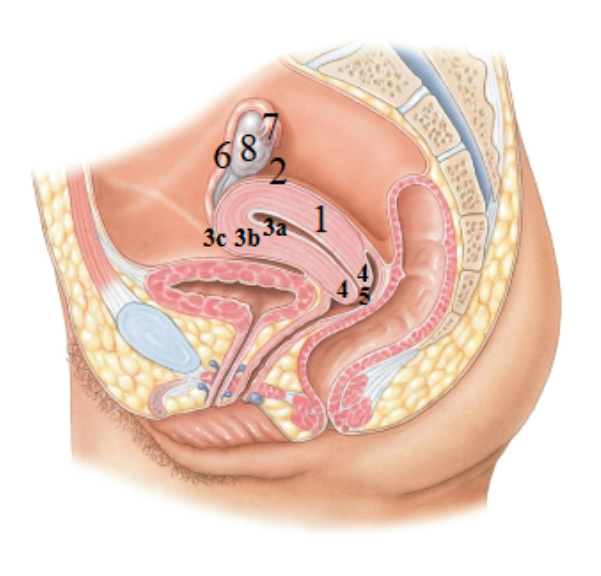
What is 4?
Cervix
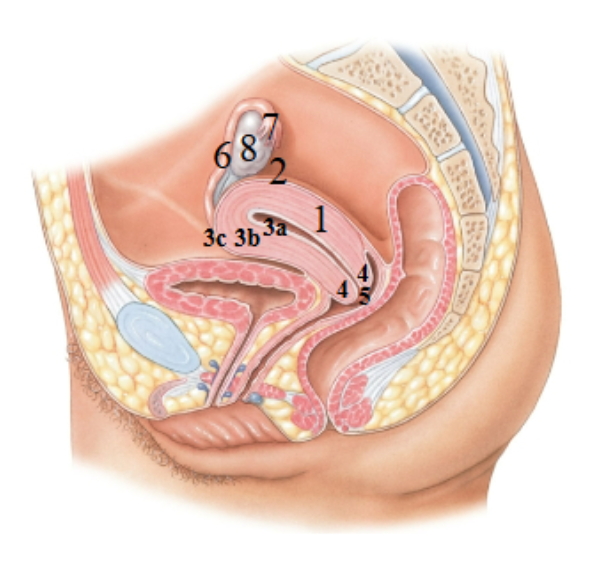
What is 5?
External os?
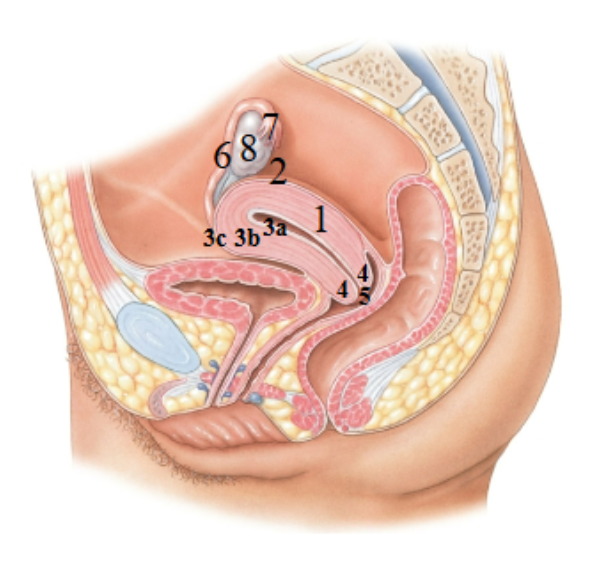
What is 6?
Uterine tube
What is 7?
Fimbriae
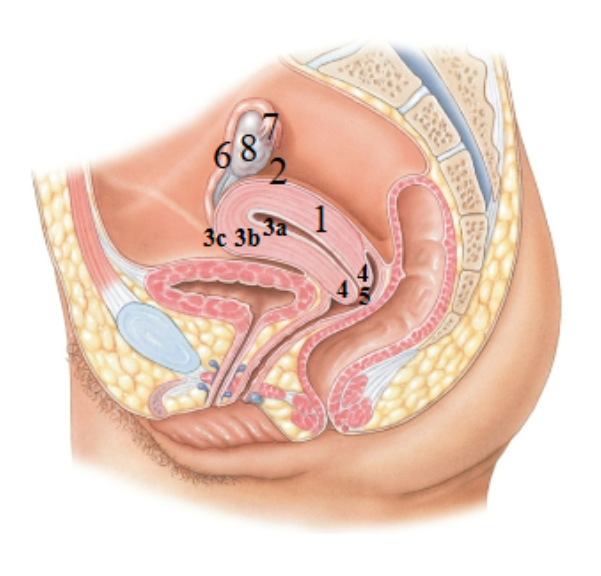
What is 8?
Ovary
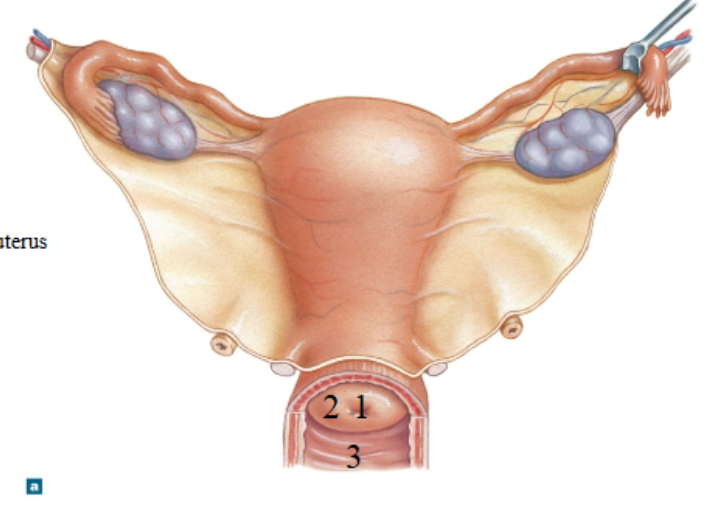
What is 1?
External os of the uterus
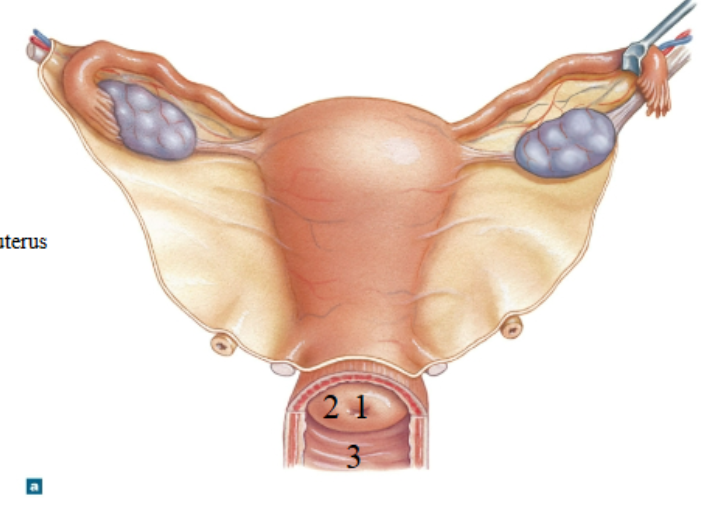
What is 2?
Cervix
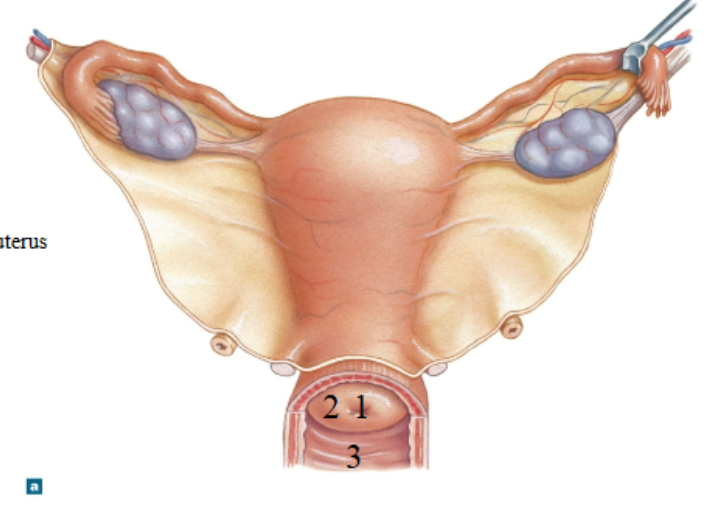
What is 3?
Vagina
What is the process of fertilization of an egg?
Ovulation: ovary ovulates an egg
fimbriae will draw the ovulated egg into the uterine tube
sperm cells are deposited at the entrance of the external os
sperm enters uterus, then the uterine tube then 2/3 way down the uterine tubes
ovulated egg is fertilized by sperm
Implantation of the Zygote?
Zygotes (fertilized egg) travels through the uterine tube, reaches the cavity of the uterus, implants in the endometrial lining and then the placenta forms.
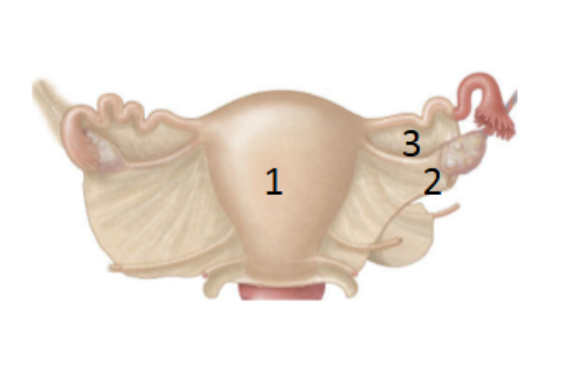
What is 1?
Mesomerism: largest portion extends from apical end of the uterus to inferior end of ovary
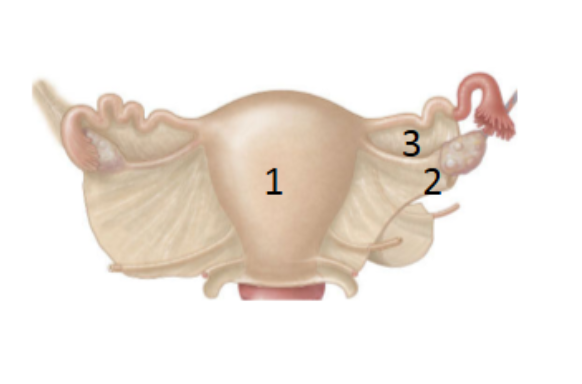
What is 2?
Mesovarium: portion that covers the ovary
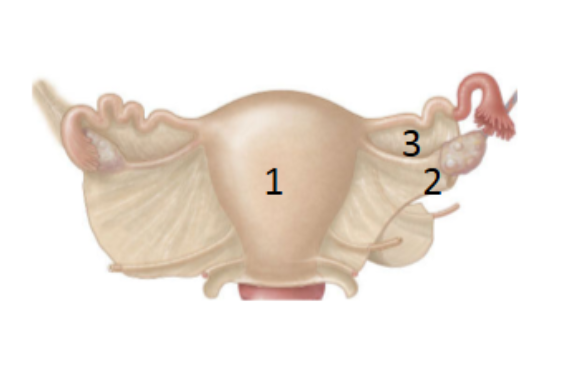
What is 3?
mesosalpinx: superior aspect of the ovary to the uterine tube and covers it
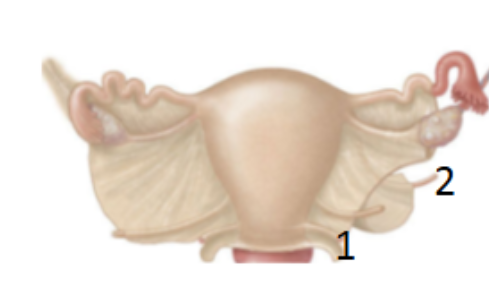
What is 1?
uterosacral ligament: attaches the uterus to the anterior face of the sacrum
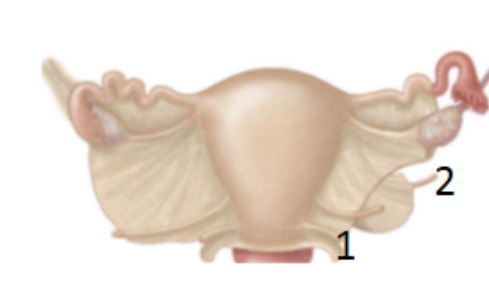
What is 2?
Round ligament: inferior to the uterine tube and connects to the labia majora and mons pubis area

What is 1?
Suspensory ligament: connects ovary to the pelvic wall
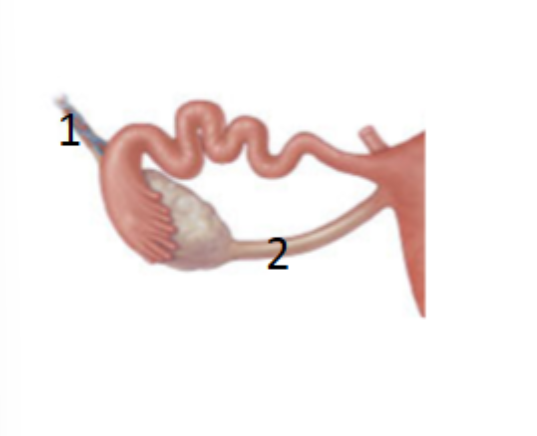
What is 2?
Ovarian ligament: connects medial portion of the ovary to the uterus
What does the cardinal ligament do?
Attaches lower portion of uterus to ischial spines of os coxa