hello
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
excretory system
removes waste from body to maintain homeostasis
endocrine system
regulates body functions through hormones which are released by glands
glands which system
in the endocrine system
pituitary (growth
thyroid (metabolism
adrenal (stress response
pancreas (blood sugar
hemeostasis in endocrine and excretory system
endocrine - maintains balance eg- bloodsugar levels with insulin/glucagon
excretory- maintains blood pH, electrolyte balance and fluid levels
excretory system structures
kidneys -filter blood
ureters- transport urine.
bladder -stores urine
urethra-excretes urine
excretory organs
lungs - remoce CO2
skin - sweat
liver- removes toxins
types of neurons
sensory neuron (carry signals to the CNS
motor neuron- carry signals to muscles
interneurons - connect neurons
blood in circulatory system
red blood- carry oxygen
white blood - fight infectin
plasma- transport nutrients (by carrying
platelets - clotting (prevnt blood loss)
neurons
transmit chemical and electrical signals
structure of neuron
cell body(contain nucleus)
dendrite (recieve signals)
axon (transmit signals)
respiratory system
facilitates gas exchange supplying oxygen to thr body and removing carbondioxide
gas exchange
oxygen diffuses into blood and carbondioxide diffuses out alveoli
noble gas
unreactive
valence shell is full
making them not inclined to gain, lose, or share electrons with other atoms.
how are ions formed
when an atom gain or lose electrons
how are ionic bonds formed
when atoms transfer electrons, occurs because one atom has a strong attraction for electros and the other easily loses them.
the resulting positive and negatively charged are held together by electrostatic forces
cation
a cation is a positively charged ion, formed when an atom loses one or more electrons
anion
an anion is a negatively charged ion, formed when an atom gains one or more electrons
nonmetals
strong attraction for electrons
metals
easily loses electrons
summarize ionic bonding
when atoms transfer electrons
atoms become + and - ions
these ions now attract and become ionic bond
transcription
dna genetic code copied into messanger RNA for protein syrhesis
dna to dna
dna replication by which dna is copied before cell division so it passed to daughter cells
DNA VS RNA
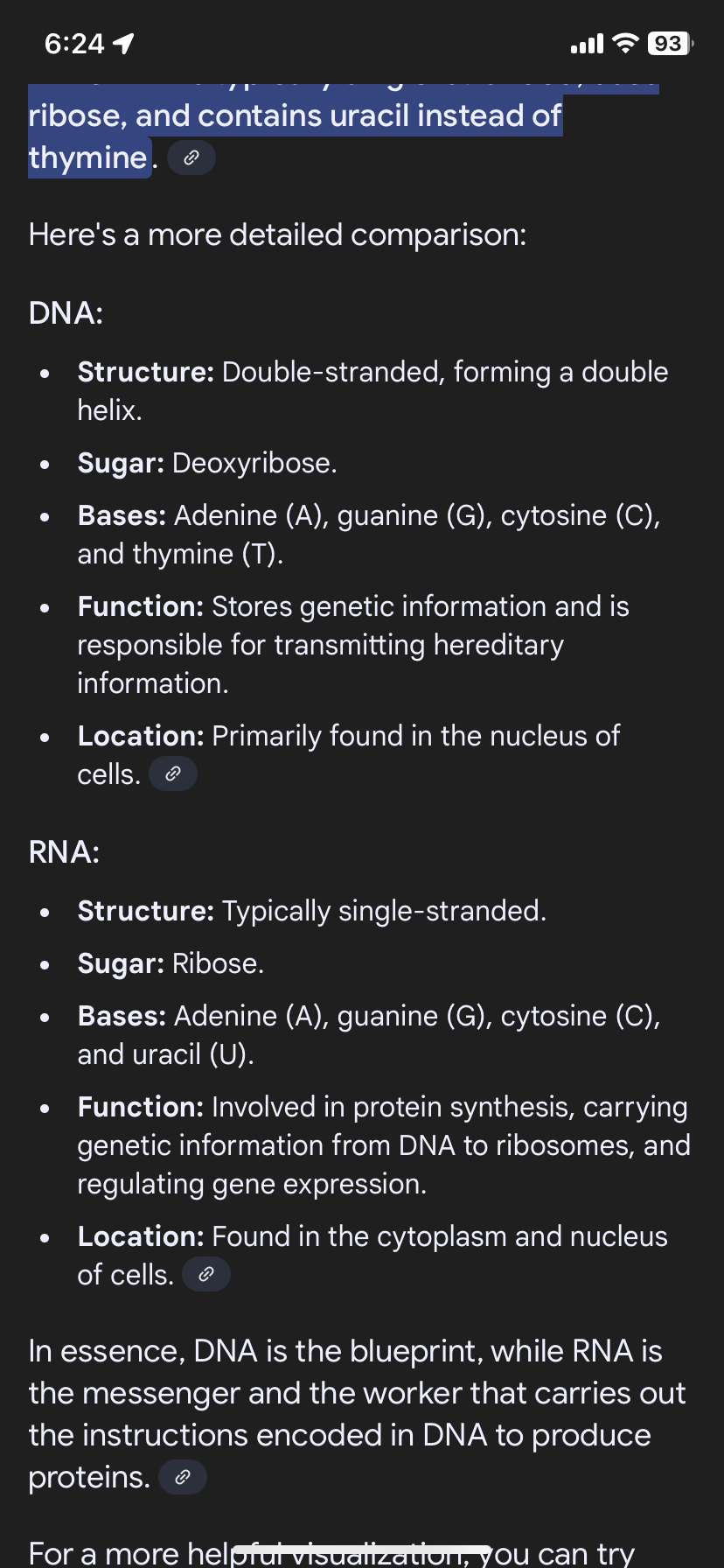
dna to rna
basically transcription
producing rna from dna
mrna leaves neucleus to direst protein synthesis in ribosome
translation
mRNA genetic code is read at ribosomes to synthesize proteins mRNA codes for proteins
translation process
mRNA cotains codons read in groups of 3 bases this encoded for specific amino acids by the tRNA
trRNA has anticodon matches with mrna codon
transfer RNA bring amino acid matching each condon
amino acids link to form a protein (polypptide chain)
AUG codes for
methionine
base pairing
DNA to DNA: A–T, T–A, C–G, G–C.
DNA to RNA: A–U, T–A, C–G, G–C.
DNA has T, RNA has U.
which has Uracil which has Thymine
DNA have Thymine RNA have Uracil
conduction
heat transfer through particle fron touch
usualy solids
touch → transfer
convection
heat transfer through movement of fluid
warm fluid rise cool fluid sinks
radiation
heat travels as waves
enzymes
speed up chemical reactions in cells allowing them to occur more effeciently
acceleration
how quickly speed is changing
change in speed divided by the time taken
a = final velocity - initial v / time
momentum
p= m x v
weight
force due to gravity acting on object
w= m x g
g= 9.8meter per sec on earth
effort load and fulcrum
effort input force
load output force
fulcrum fixed point