MRAD 4218 Module 3-6 Pathology Radiographic Appearances
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hepatobiliary, Endocrine, Reproductive, and Hematopoietic Pathologies
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
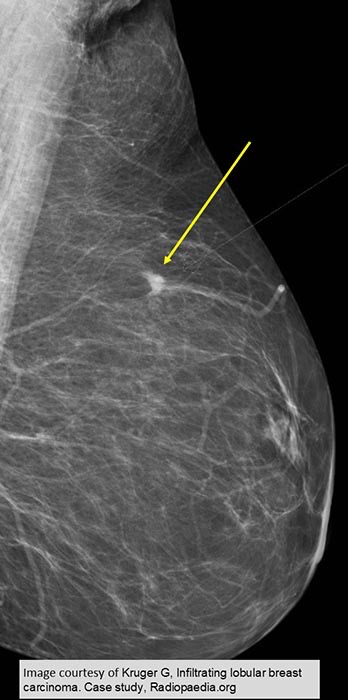
ILC
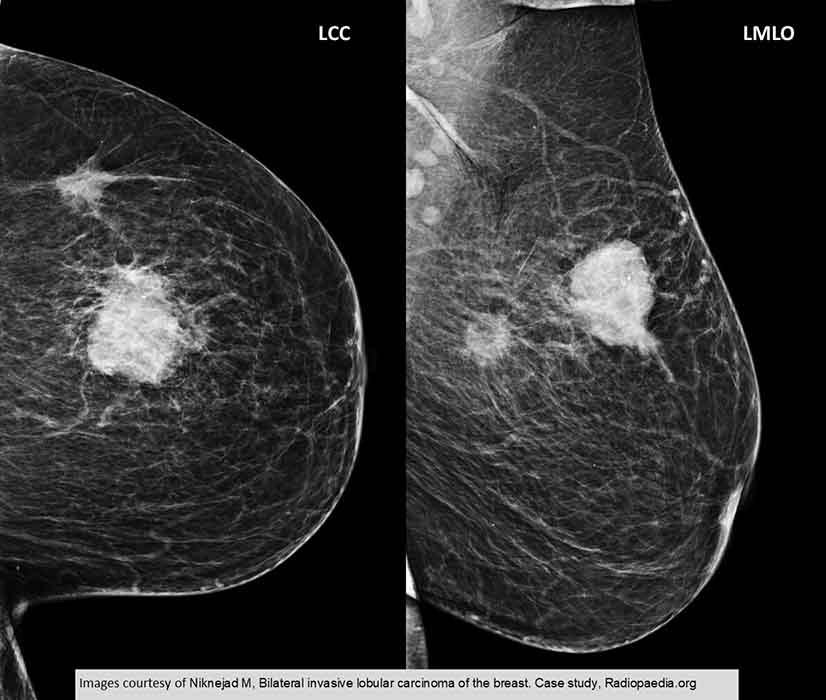
ILC
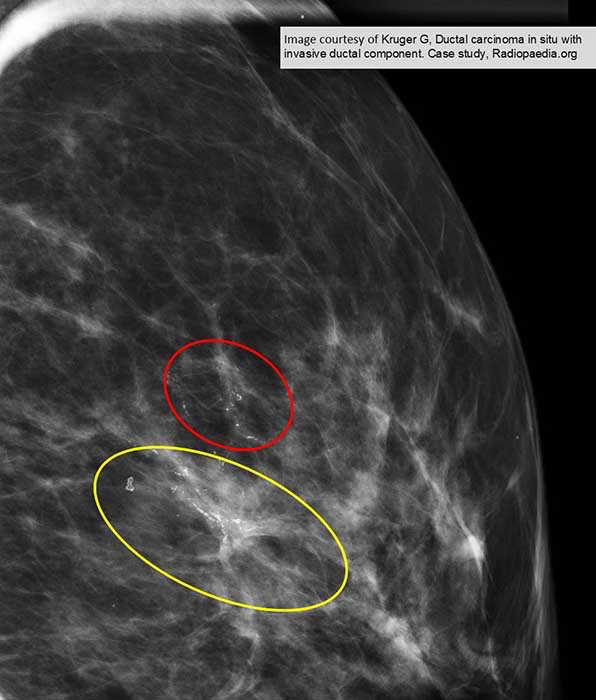
DCIS AND IDC
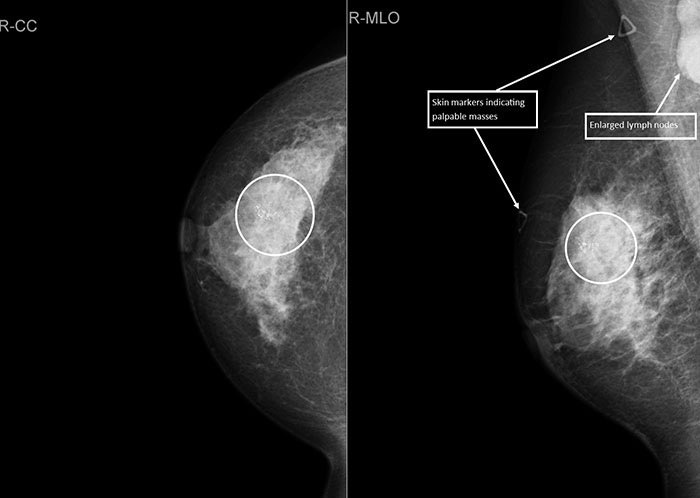
IDC: A lead marker has been put on the skin surface to indicate a palpable mass
There is an additional marker over a palpable lymph node that may be sus for mets
White circle indicates multiple calcification

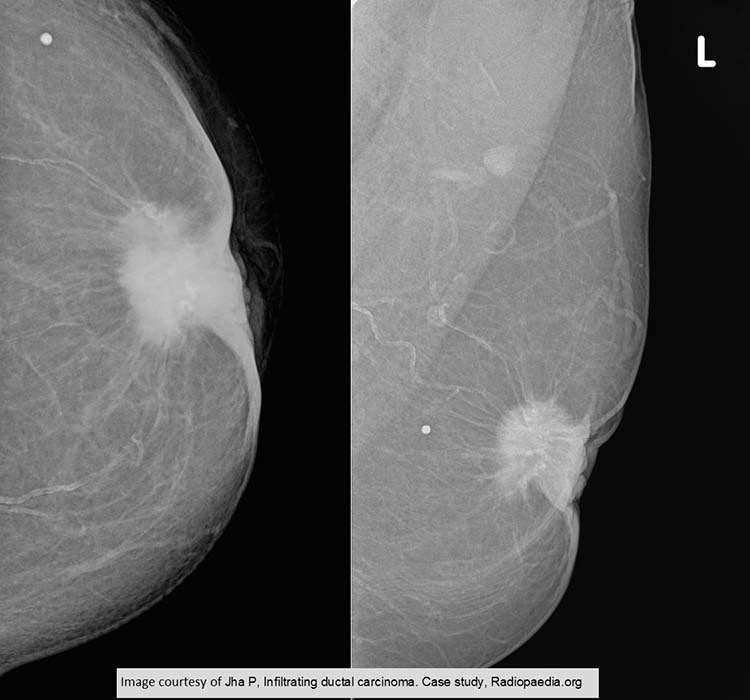
IDC: PT has undergone involution and her breast tissue is far less dense
Round BBs have put on both images to indicate a palpable mass
The calcifications within and the nipple retraction
The mass is spiculated w/ tentacles coming off its
surface

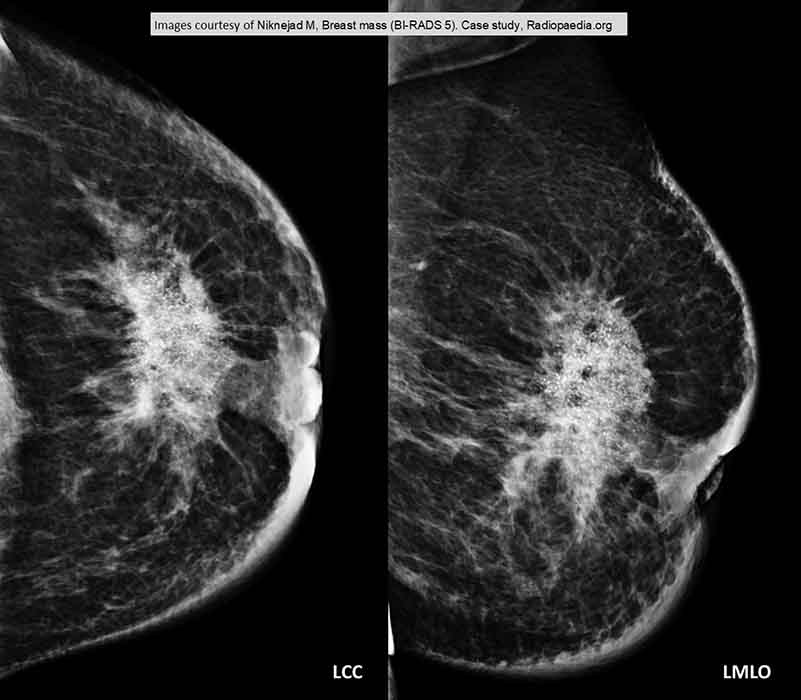
IDC: Great number of calcifications and some spicules present
Nipple retraction

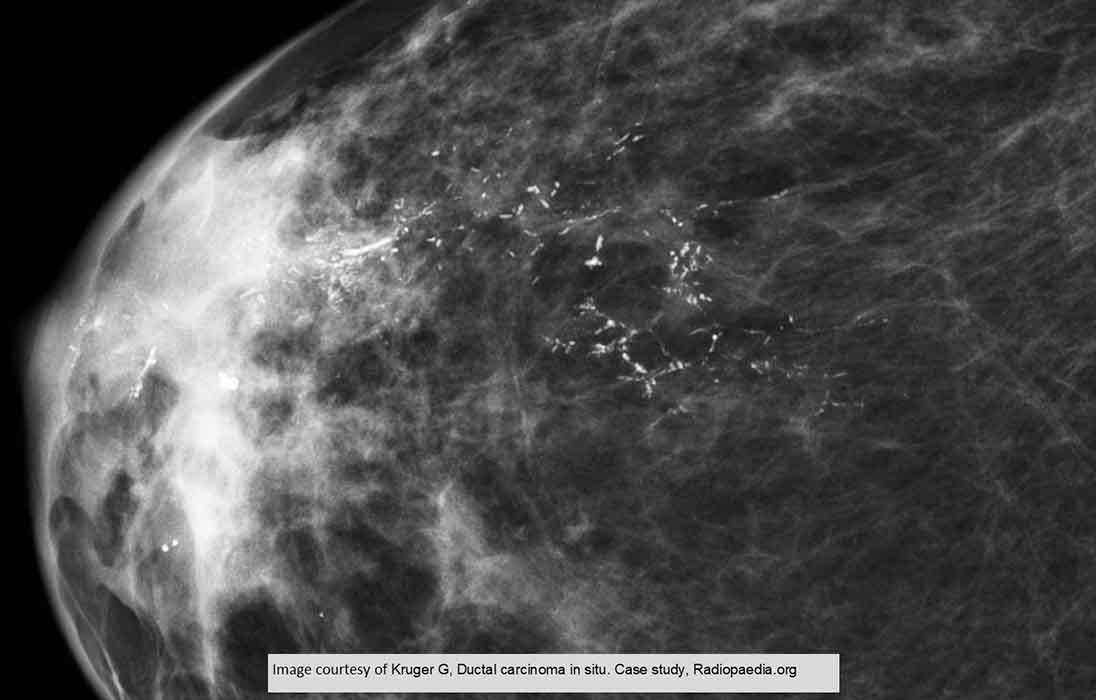
DCIS: Very noticeable linear calcified castings throughout the entire breast

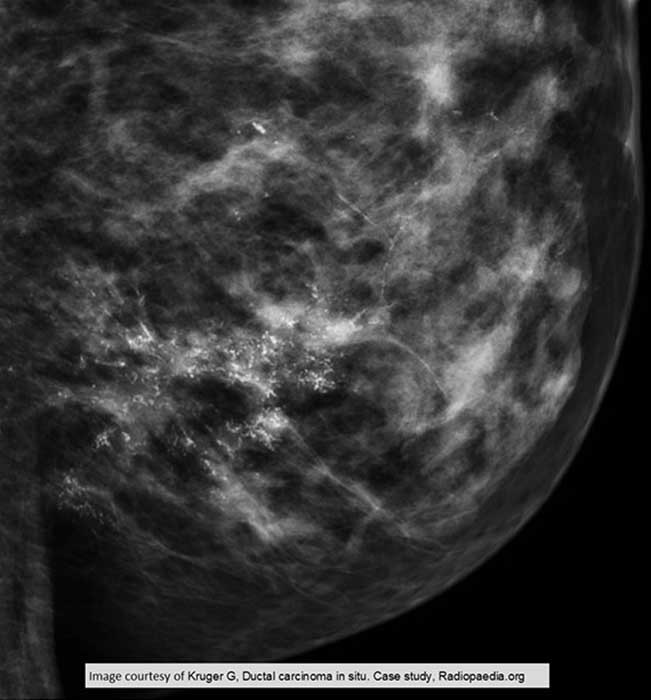
DCIS: More widespread calcified castings
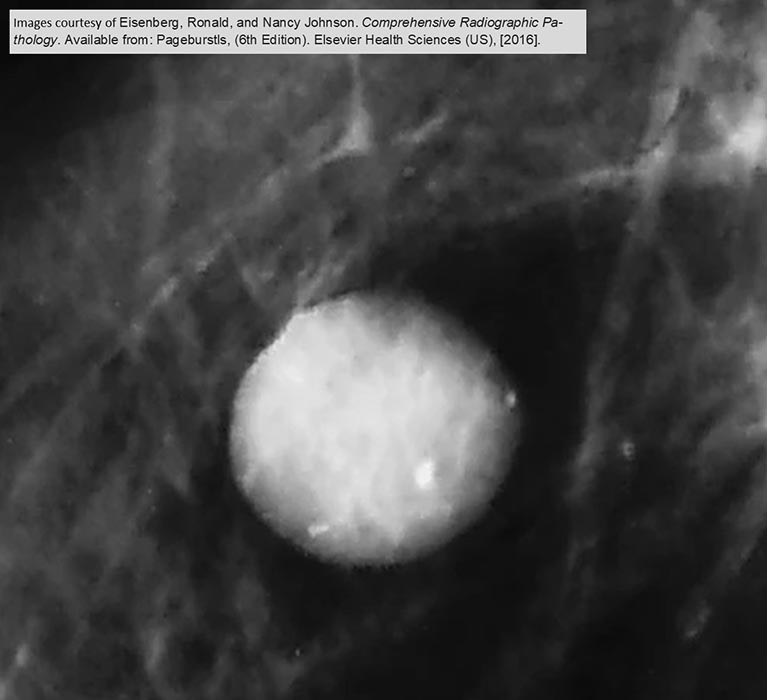
Fibroadenoma: Magnified image of a fibroadenoma demonstrates it's smooth and rounded appearance
Has normal calcification present

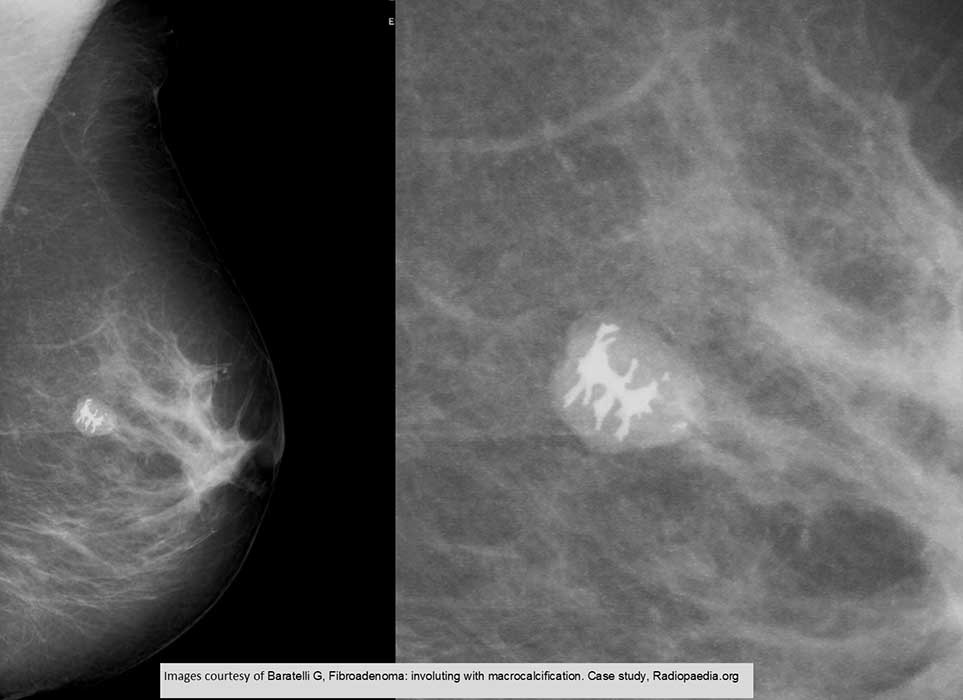
Fibroadenoma
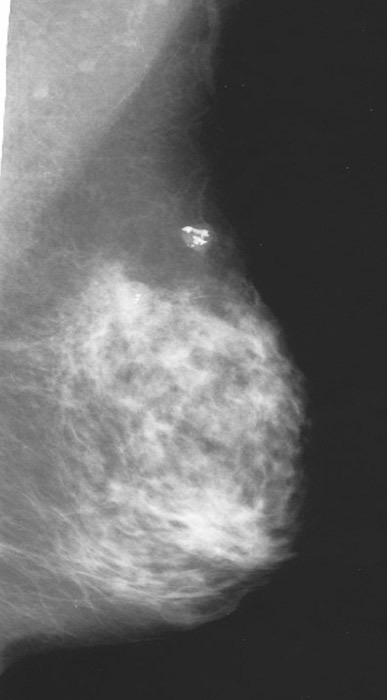
Fibroadenoma is well demonstrated
Notice the denseness of the breast tissue

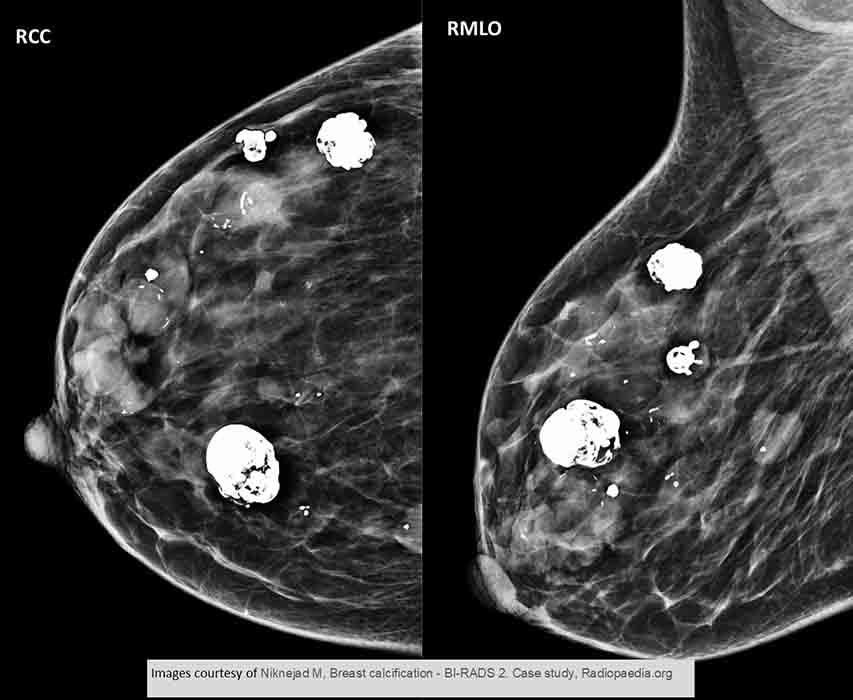
An unusual case w/ multiple fibroadenomas seen in 2 views. Only 10-15% of patients present w/ multiple fibroadenomas

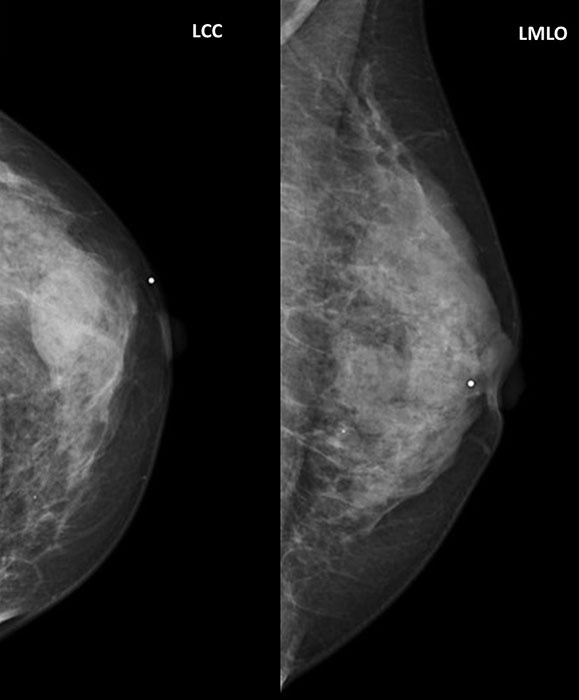
Fibrocystic
Fibrocystic
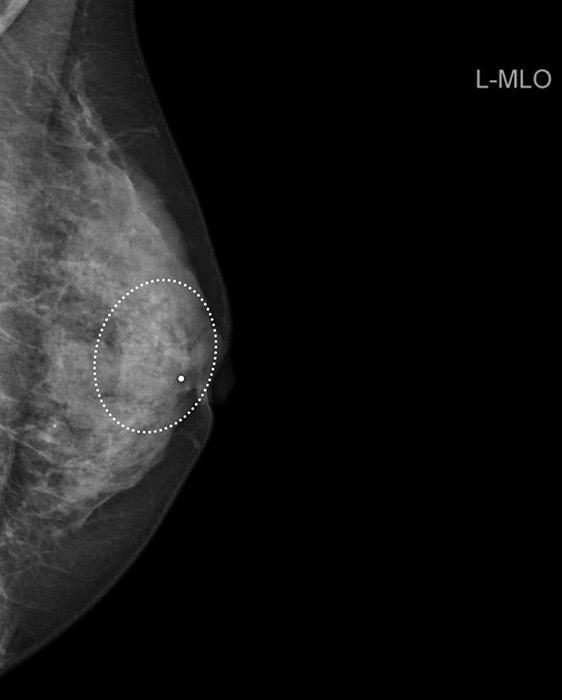
Fibrocystic
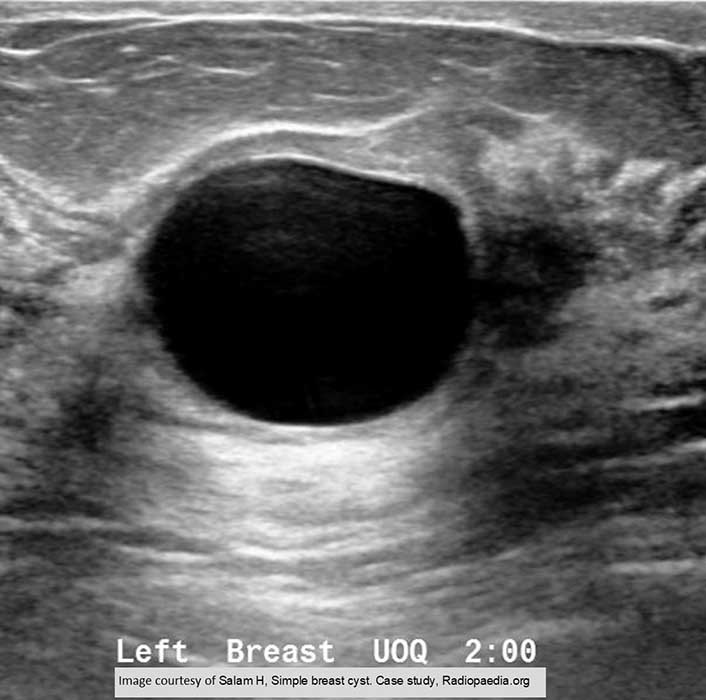
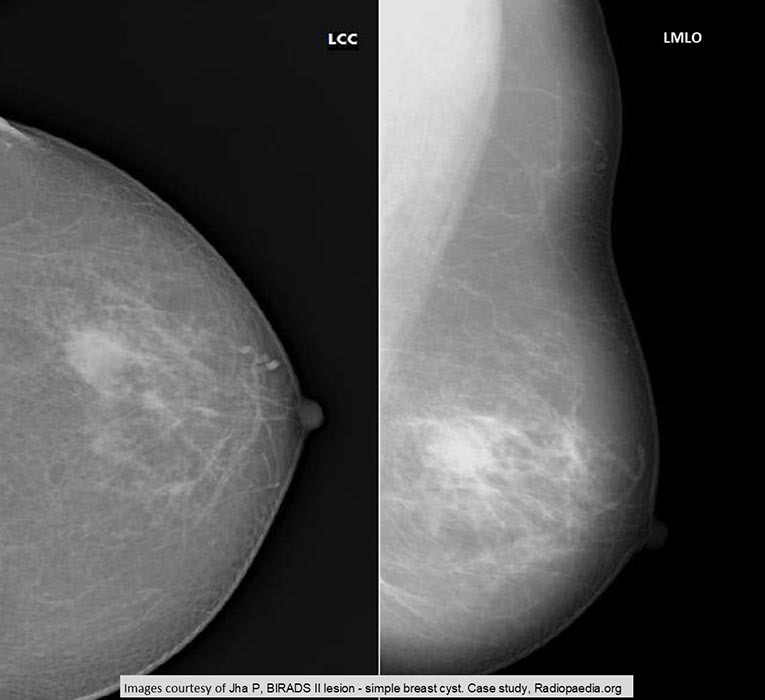
Fibrocystic
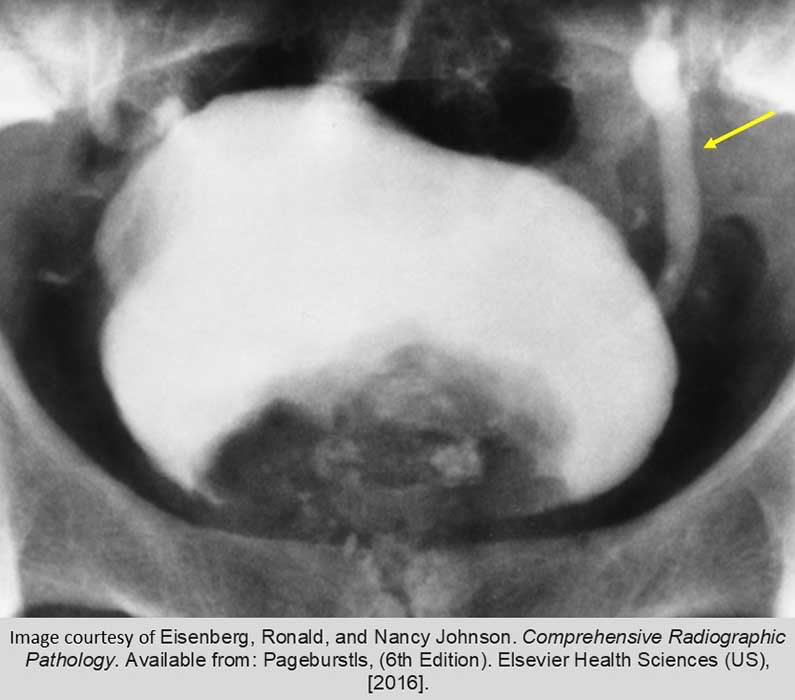
Prostate Ca: Shows the irregularity of the impression that Prostate Ca on the bladder
Yellow arrow indicated a dilated left ureter, indicative of obstruction by the tumor

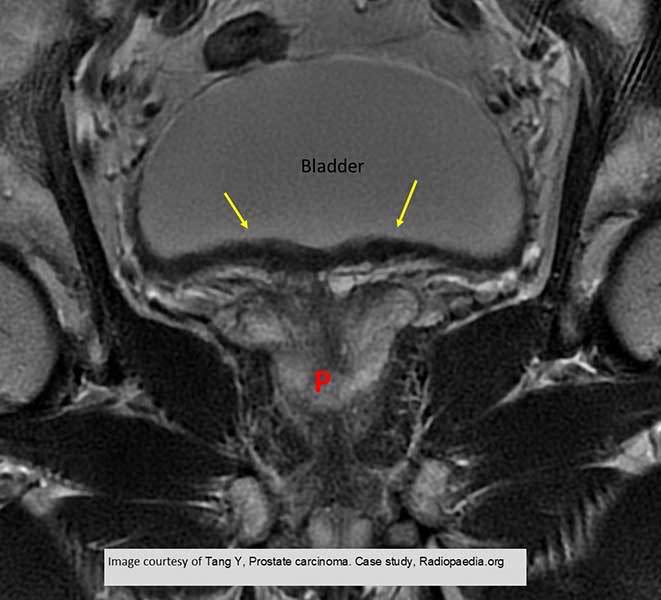
Prostate Ca
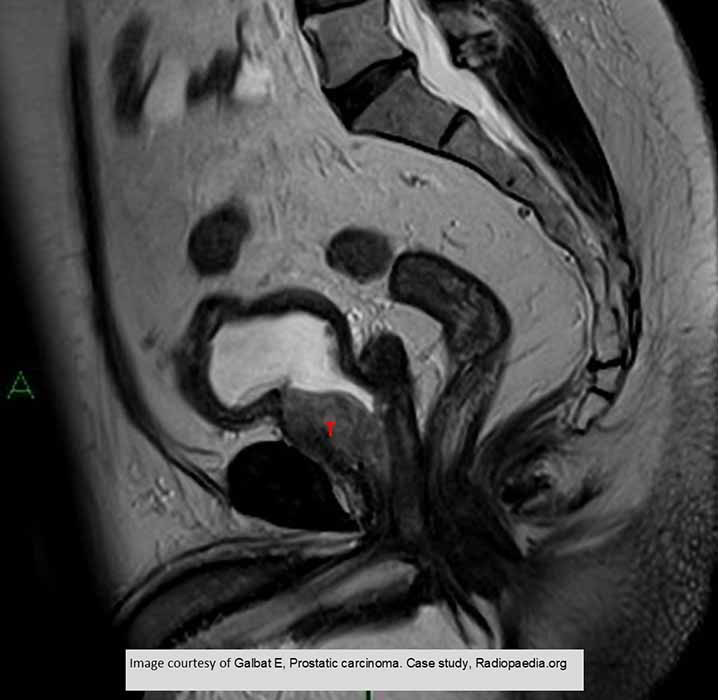
Prostate Ca
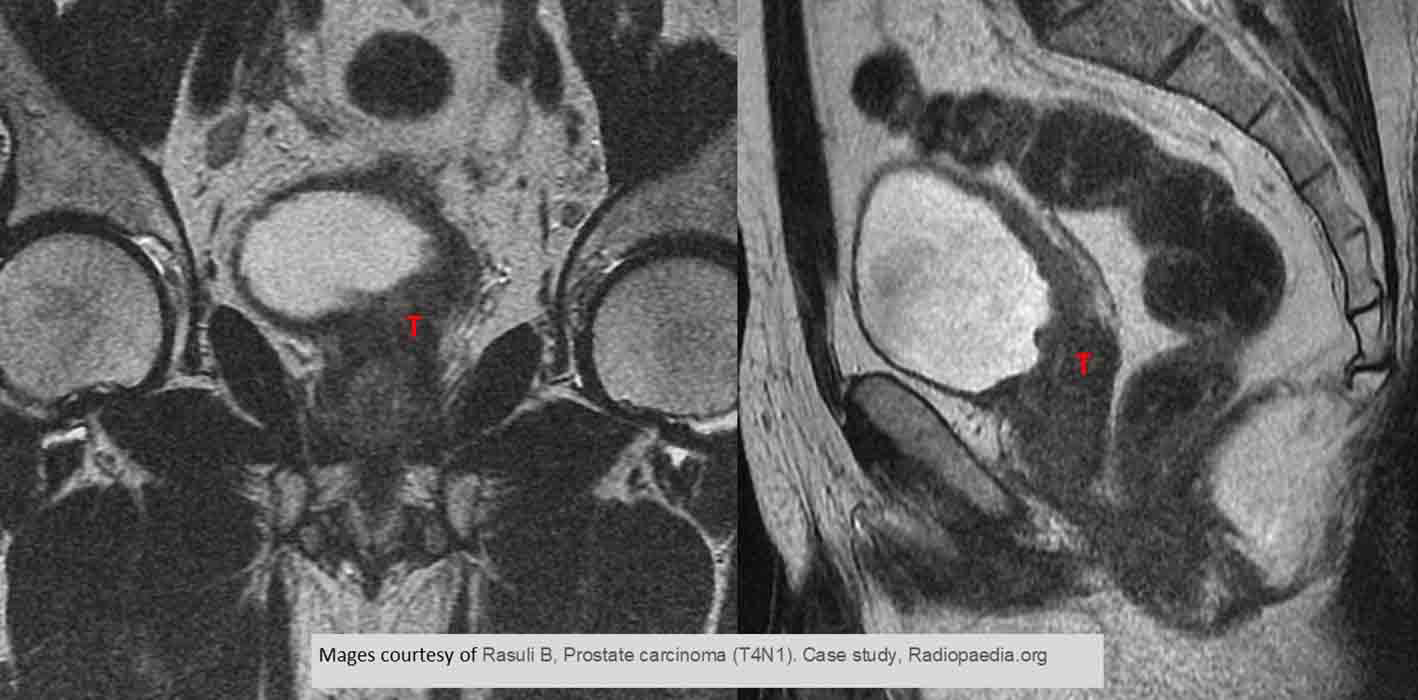
Prostate Ca
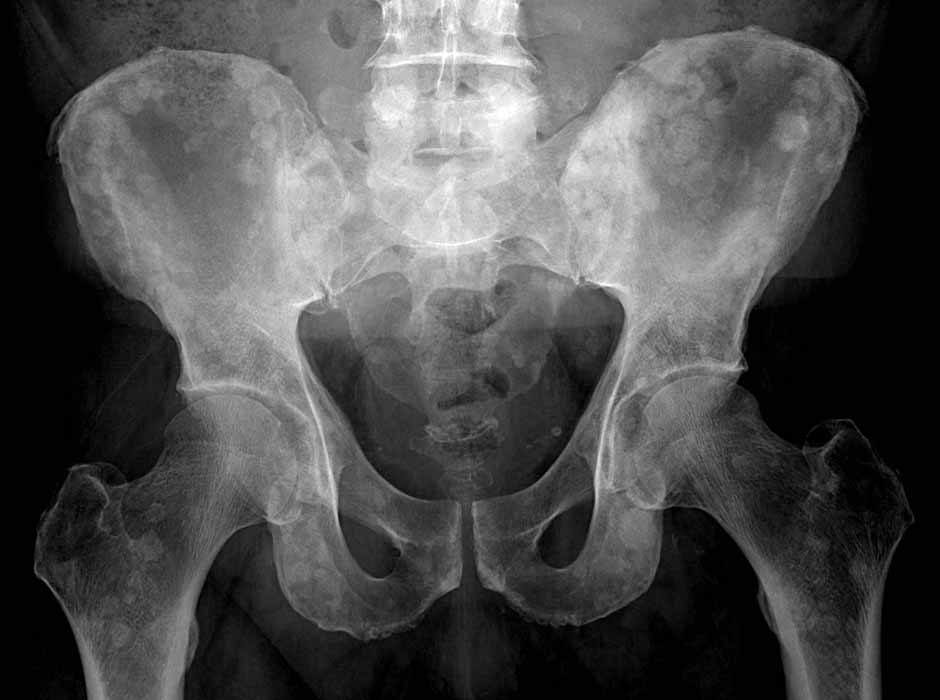
Prostate Ca mets throughout the pelvis and upper femora
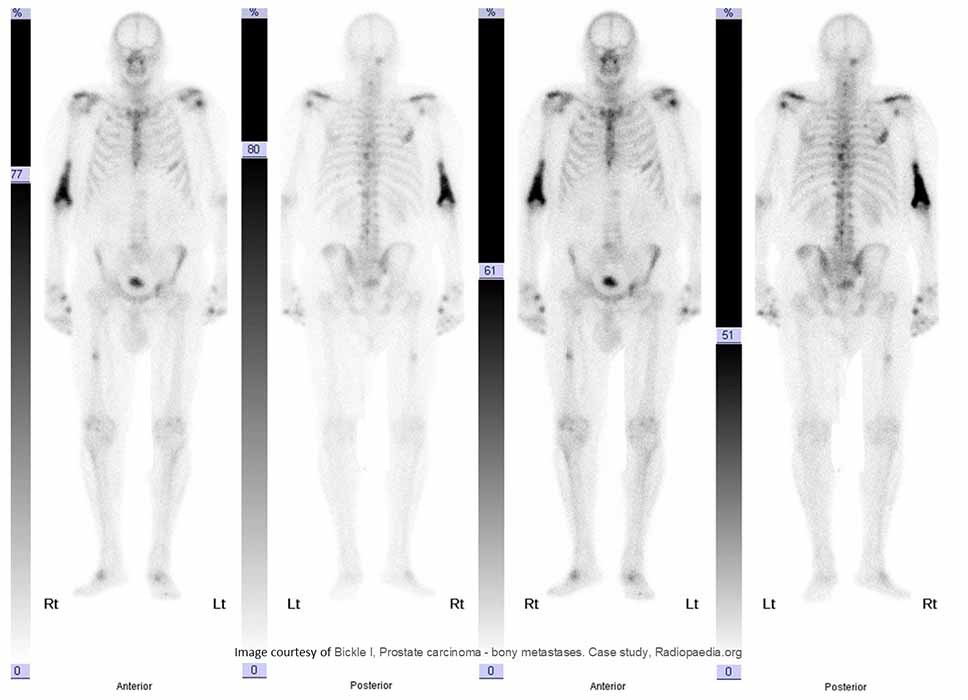
Bone scan demonstrates met spread throughout
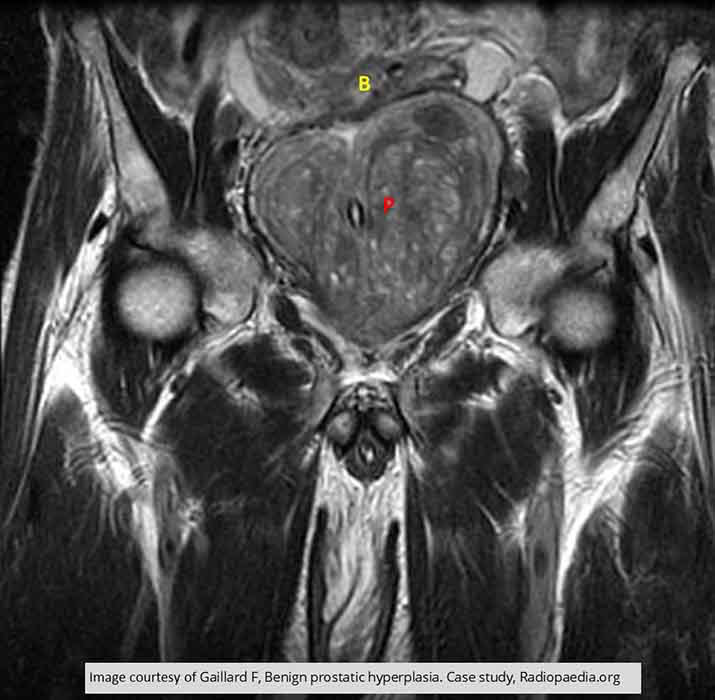
BPH: demonstrates the affects of the enlarged prostate has on the bladder
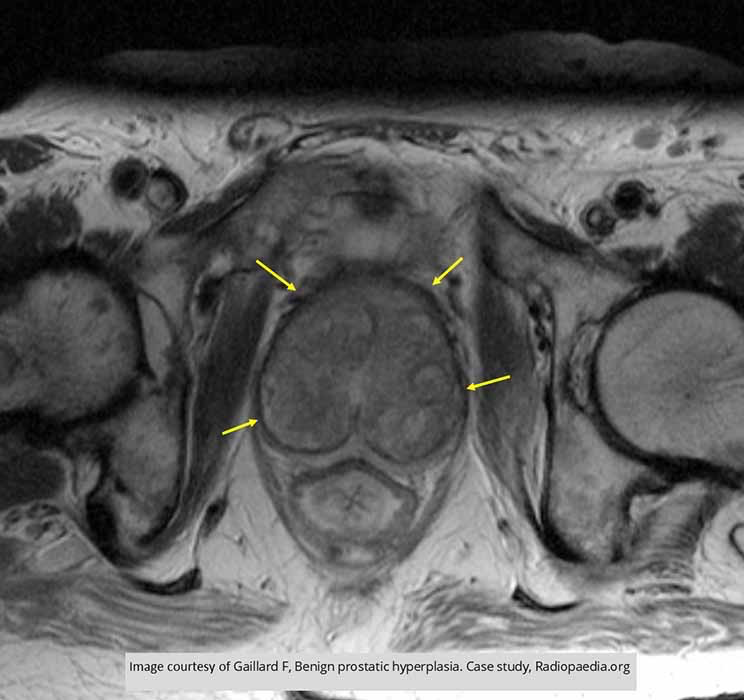
BPH: pseudocapsule
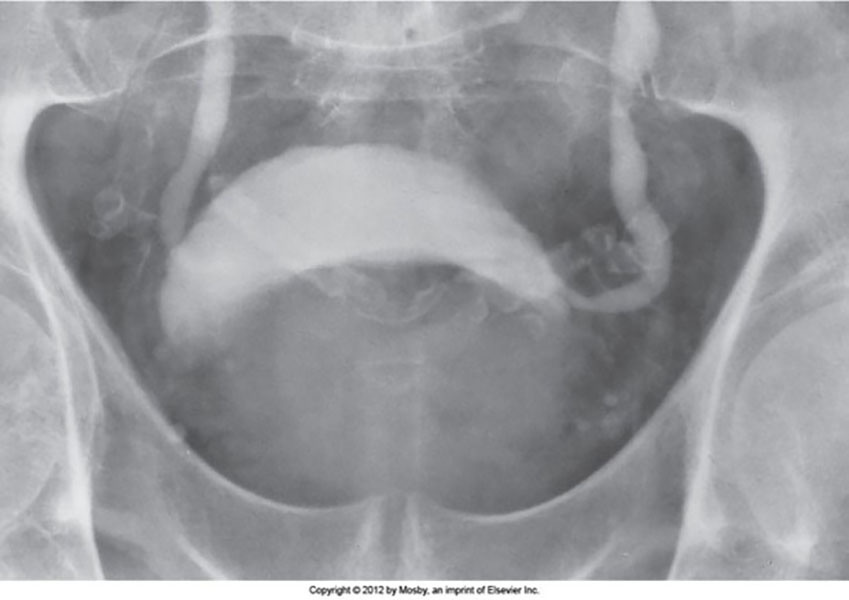
BPH: Urinary Exam
The impression that the enlarged prostate has made on the floor of the bladder
The left ureter is "J" shaped as the trigone area of the bladder has been elevated

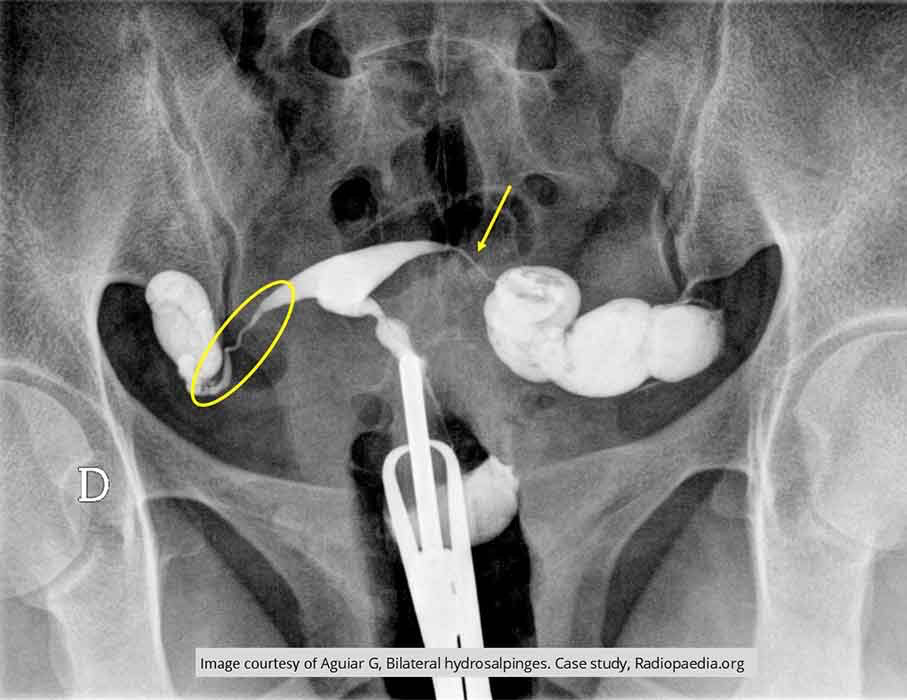
Female Infertility: Both fallopian tubes show spillage into the peritoneum
Right side shows a very tortuous tube and left fallopian tube appears narrowed
These two factors could be contributing to infertility

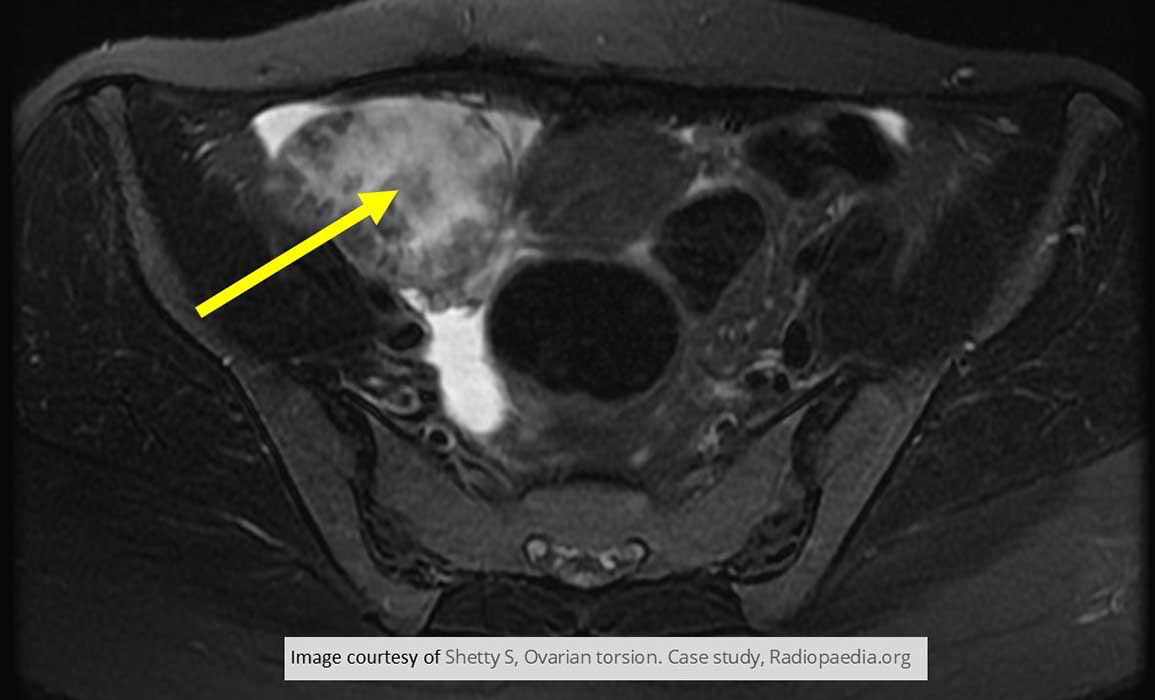
Female Infertility: Polycystic Ovary Disease
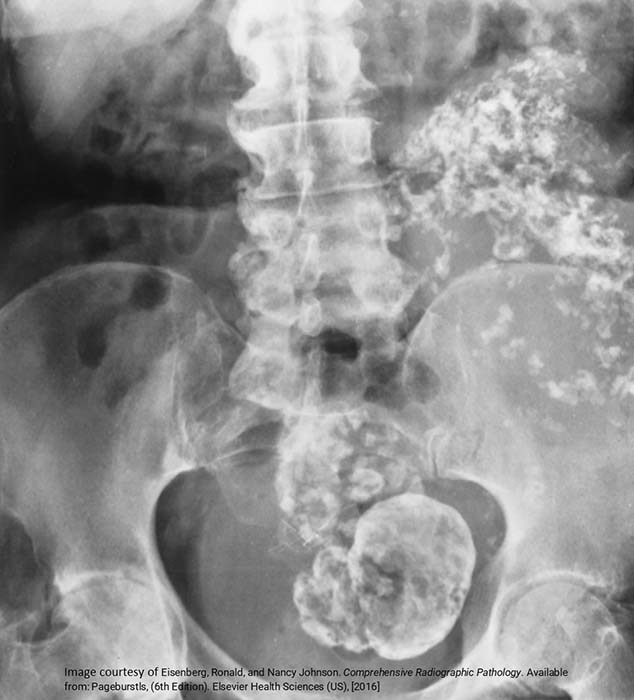
Calcified Fibroid
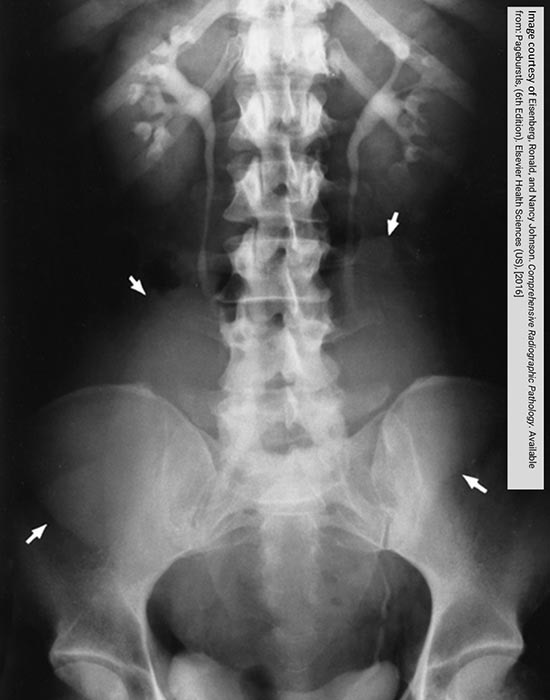
IVP exam shows the resulting impact of a very large fibroid
Arrows indicate the fibroid, compressing the ureters, causing some back up into the kidneys
Note the impression of the fibroid into the contrast filled bladder

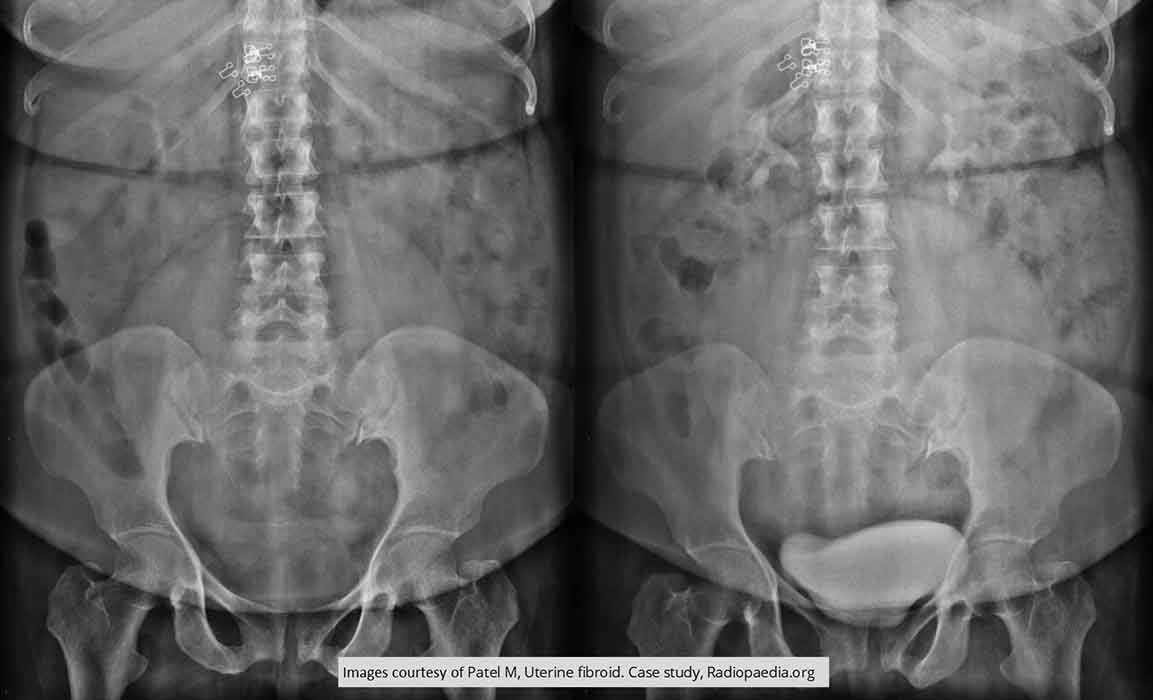
IVP exam
Pre and post IV contrast injection
Large ovoid mass in the center of the lower abdomen/pelvis
Fibroid leaving an impression on the lower bladder

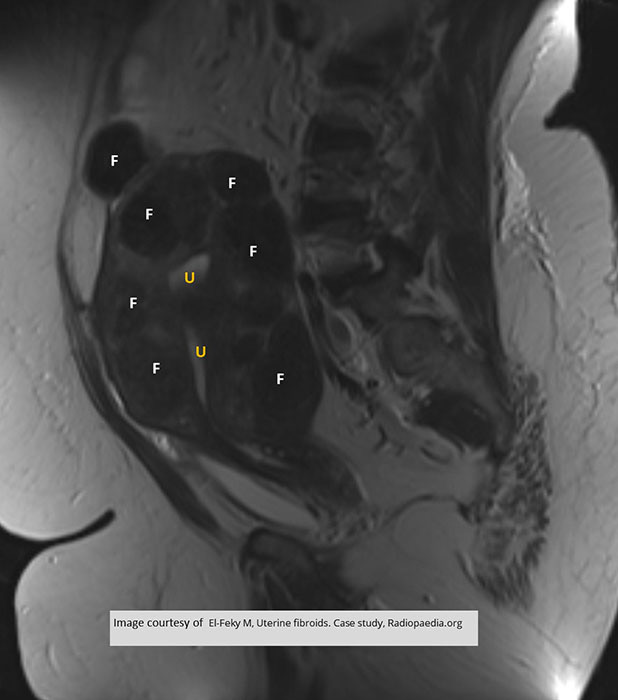
MRI Fibroid
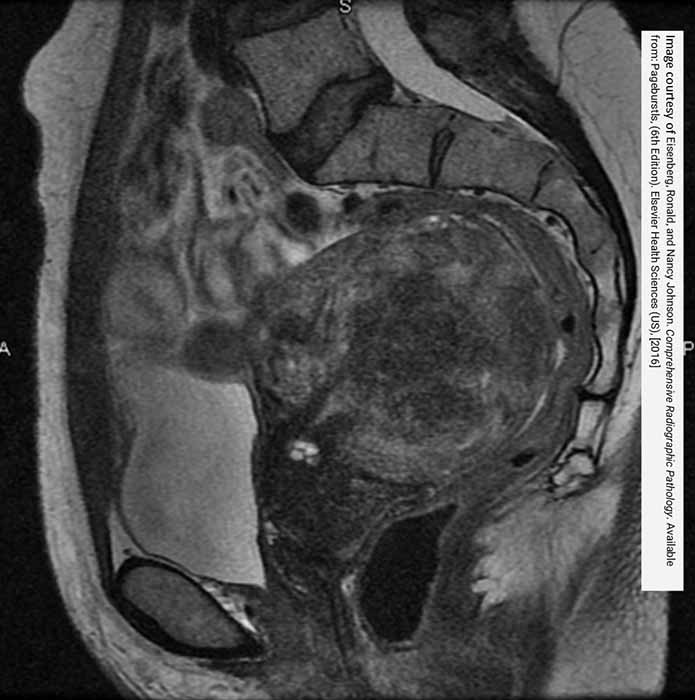
Extremely large fibroid seen in sagittal MRI
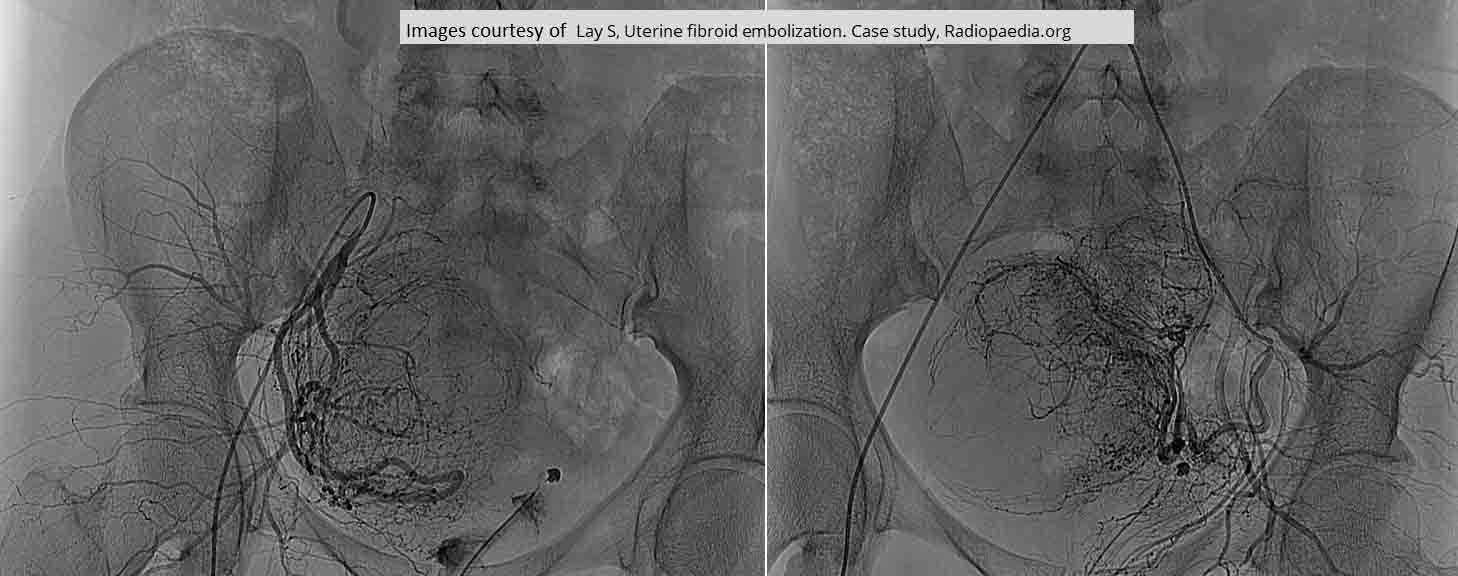
Embolization of Fibroids
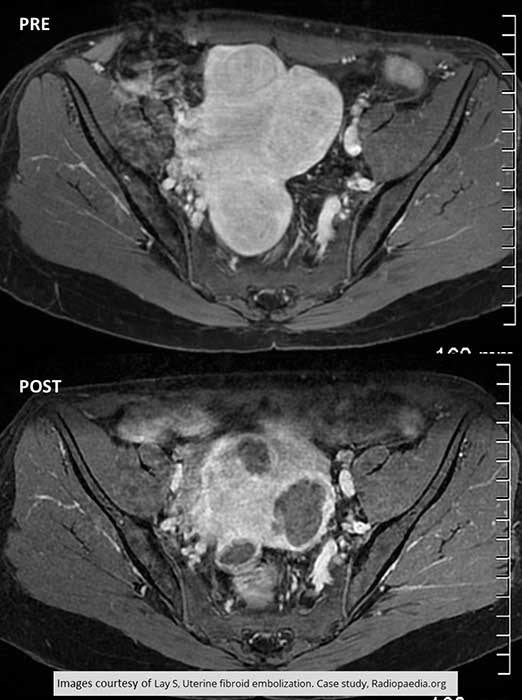
Pre and Post Treatment for Fibroid
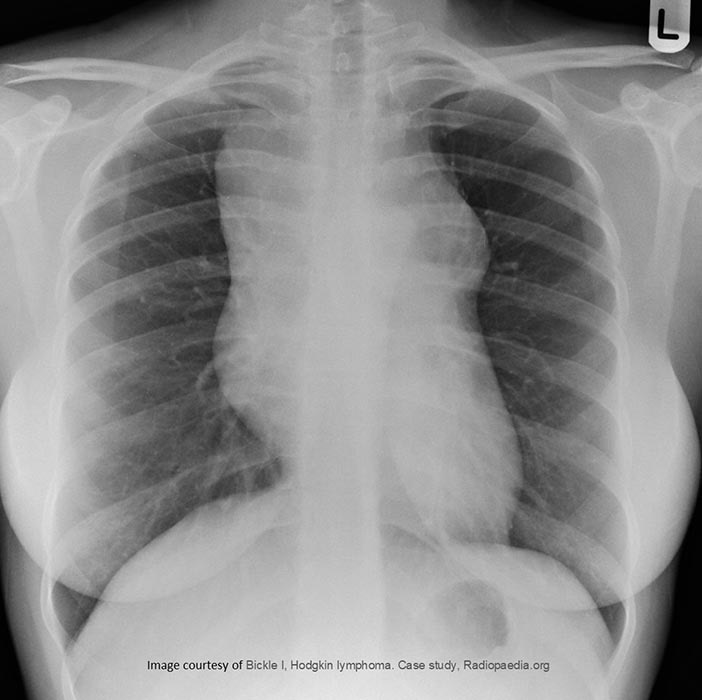
HL
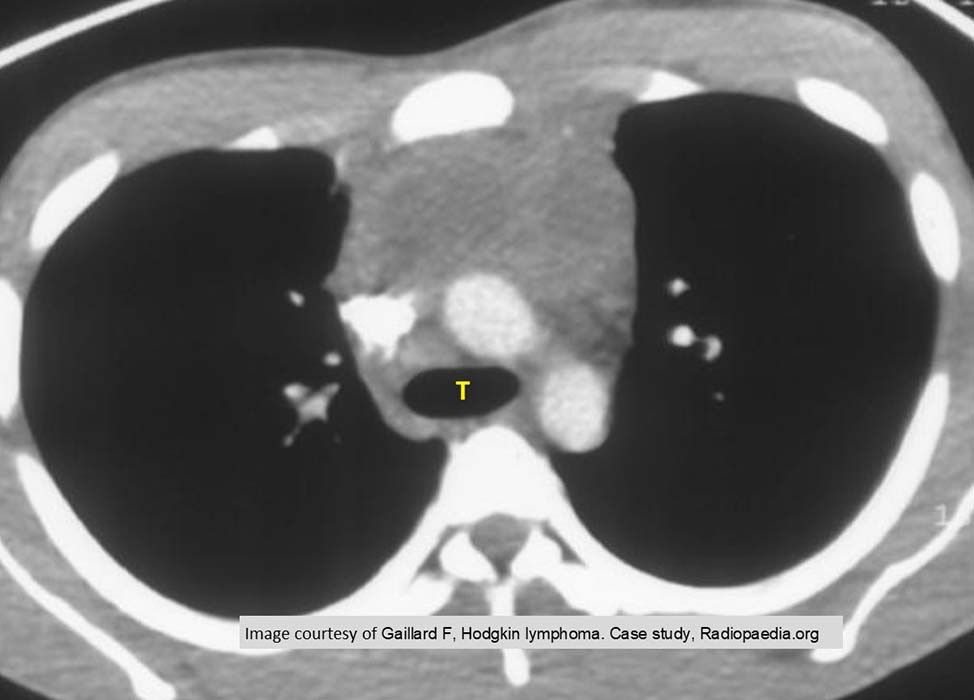
HL
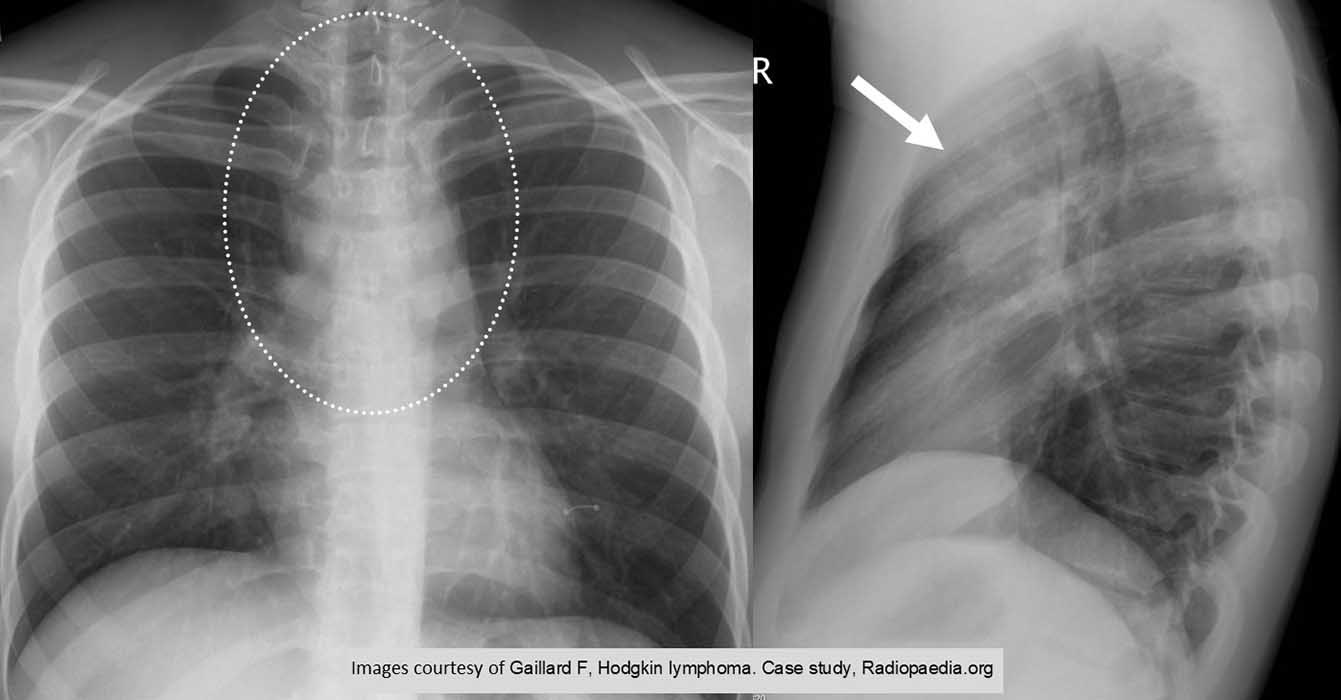
HL
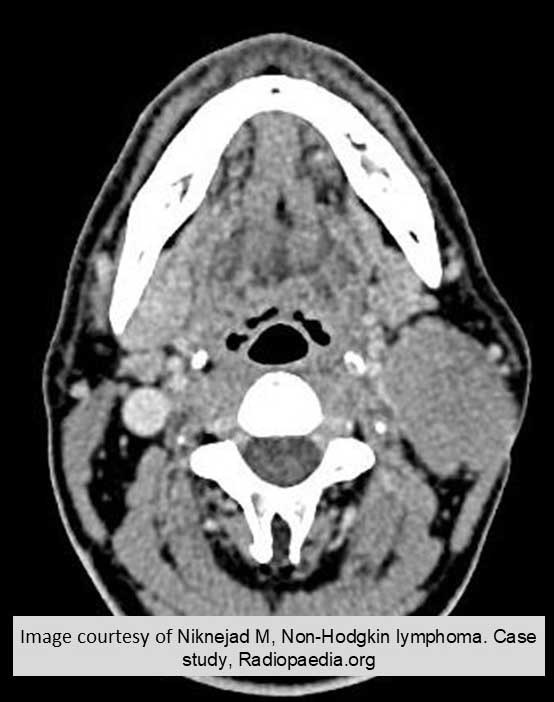
HL
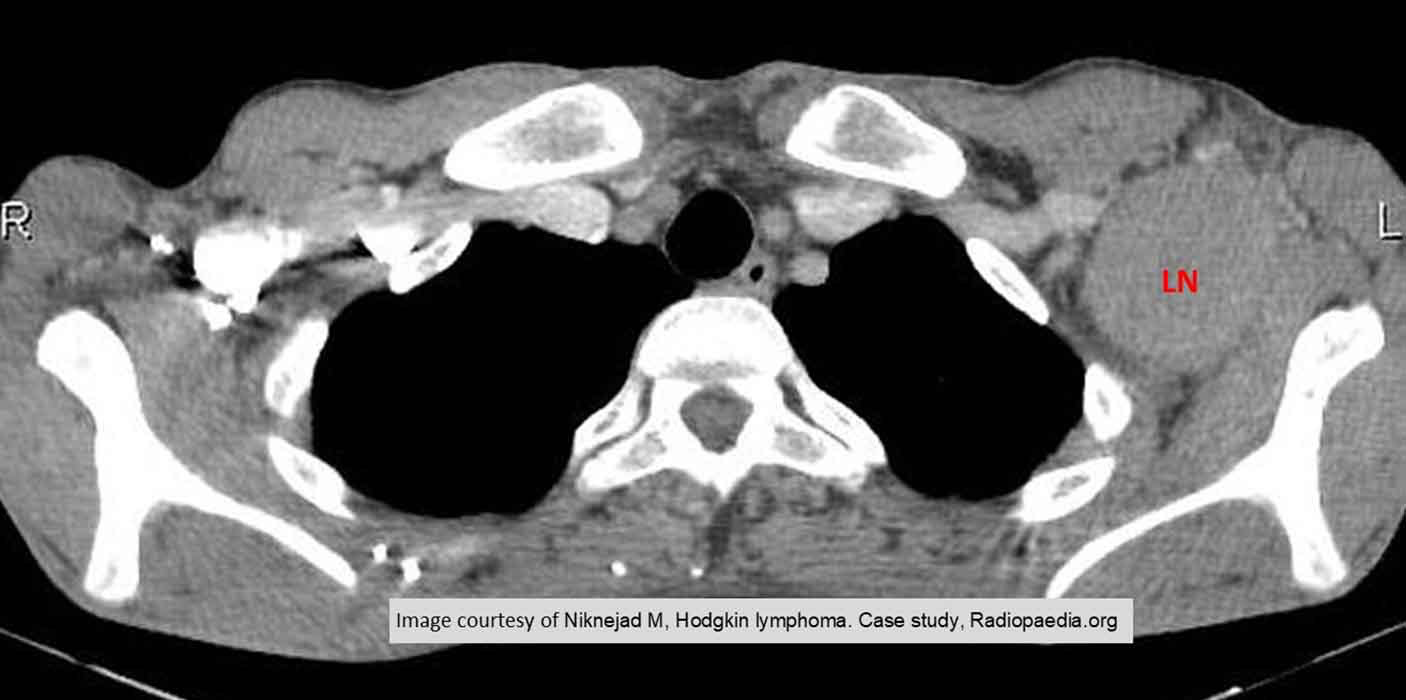
HL
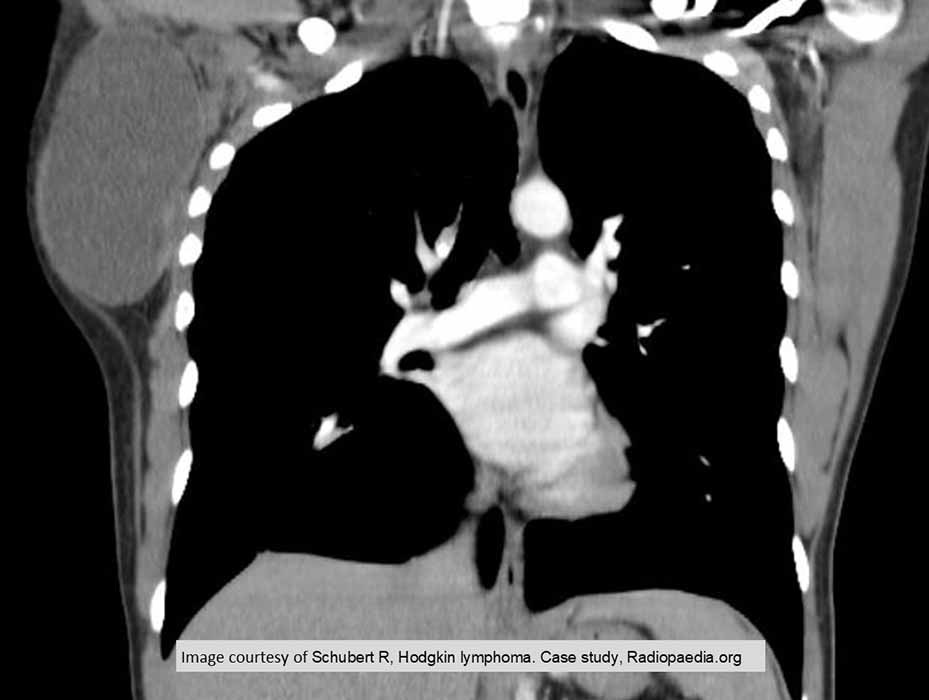
HL
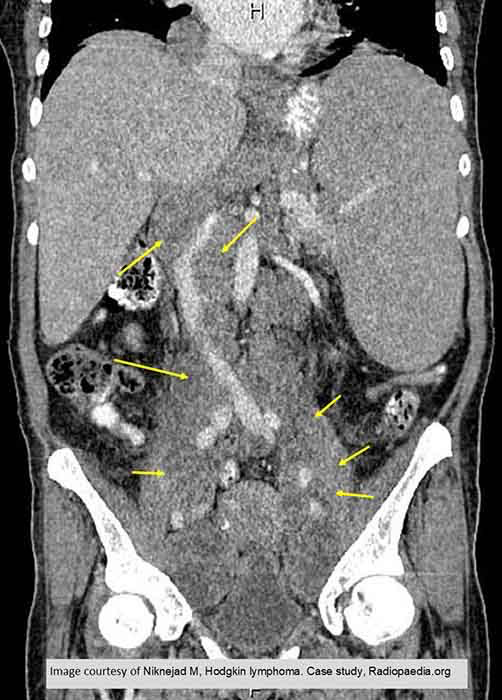
NHL: demonstrates multiple enlarged abdominal lymph nodes
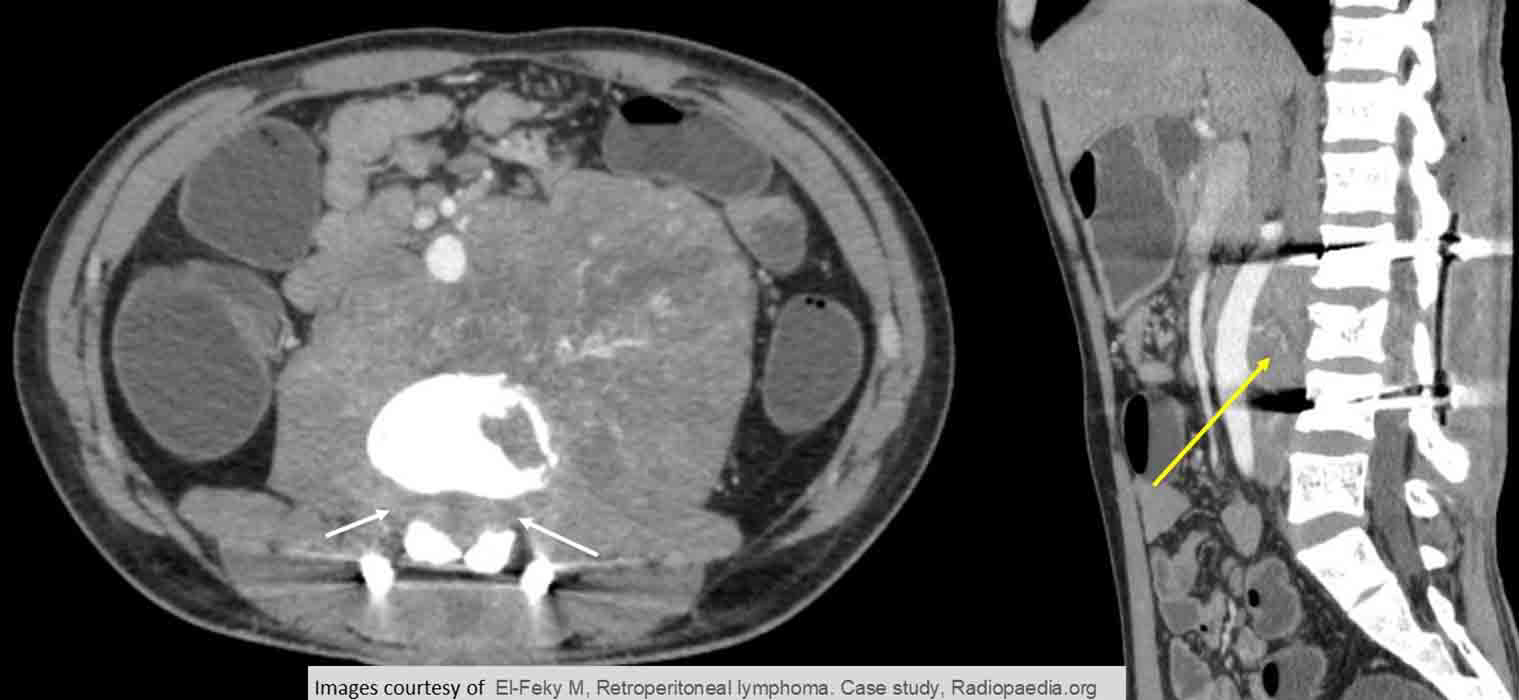
NHL: shows a retroperitoneal mass
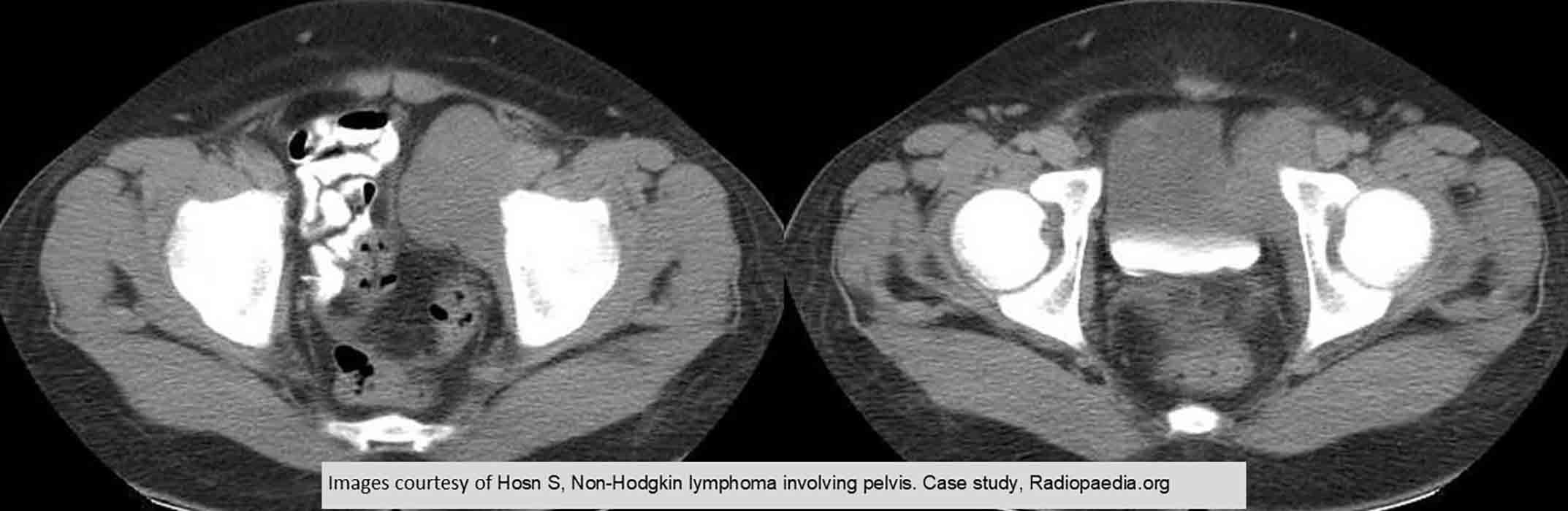
NHL
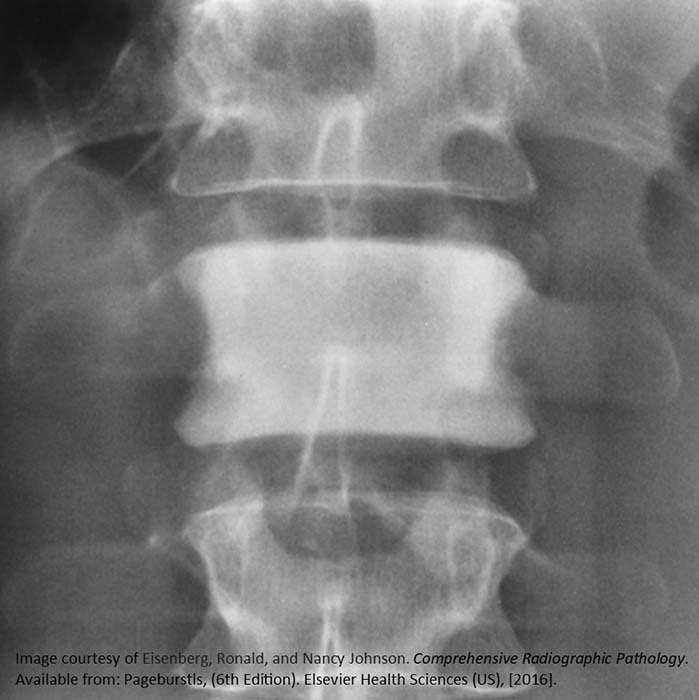
HL
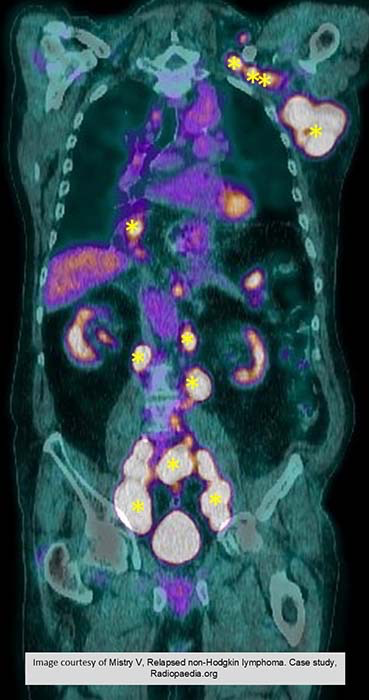
NHL
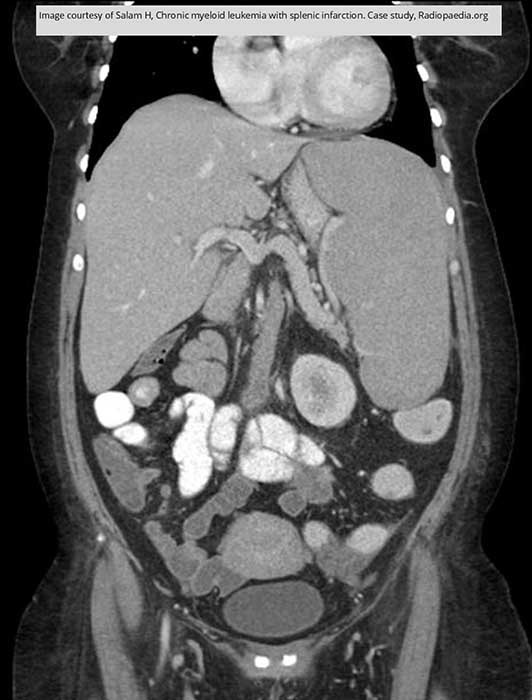
Leukemia: Hepatosplenomegaly
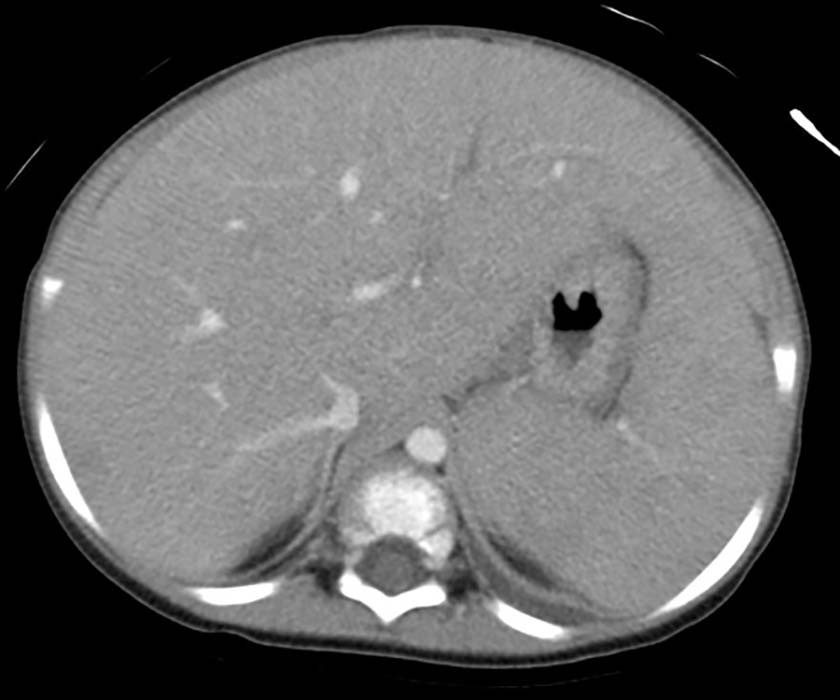
Hepatosplenomegaly
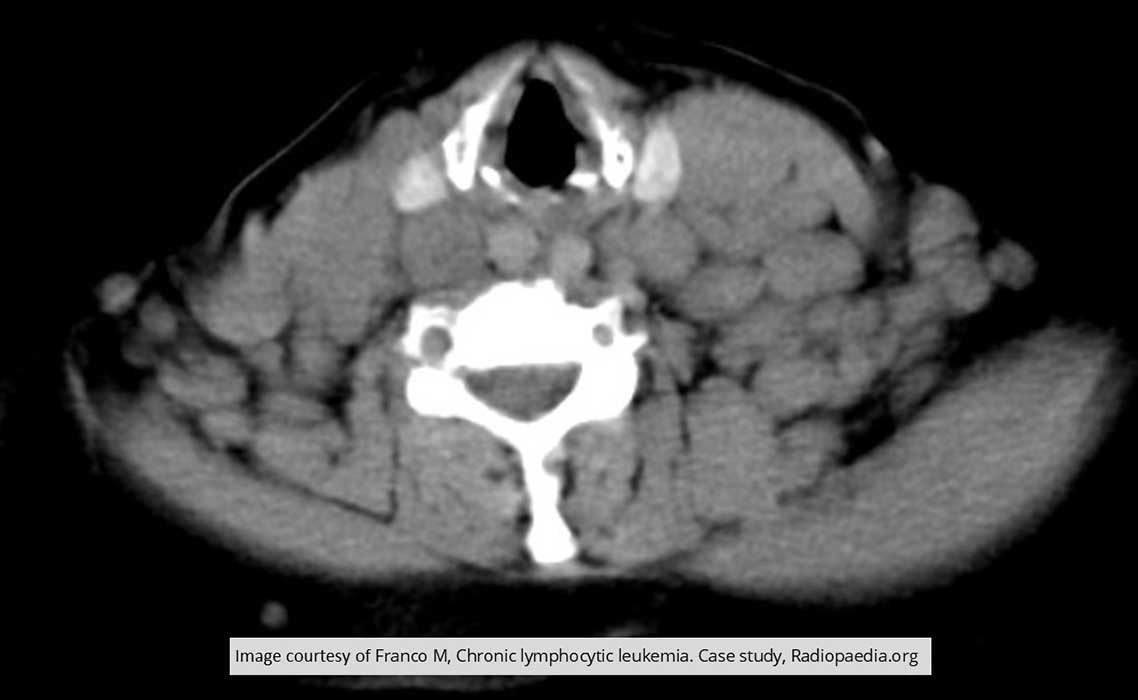
ALL
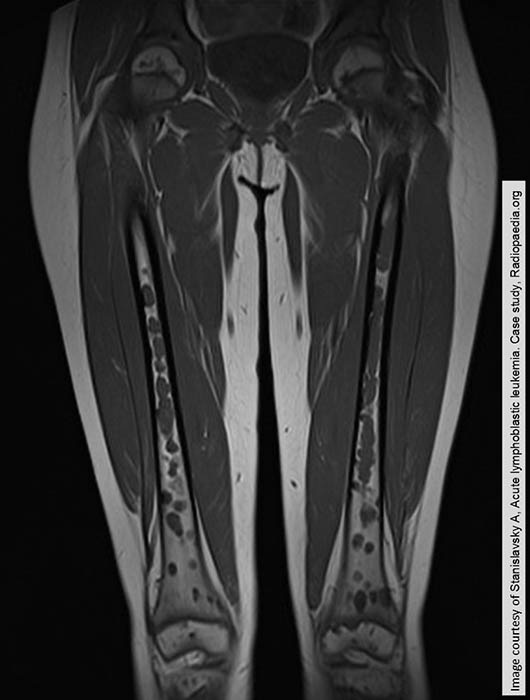
ALL: multiple osteolytic lesions
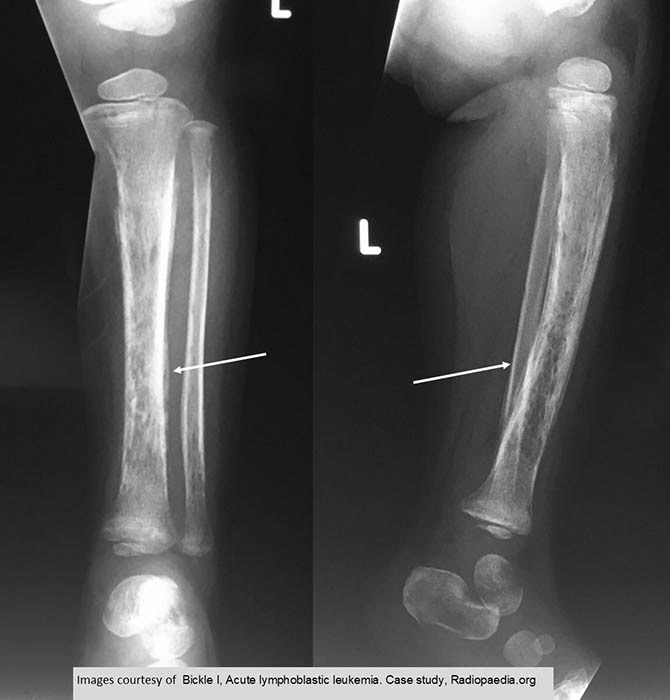
ALL: subperiosteal new bone formation
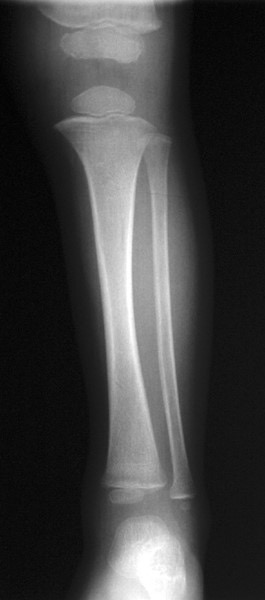
ALL: radiolucent banding seen in the distal and proximal metaphyseal
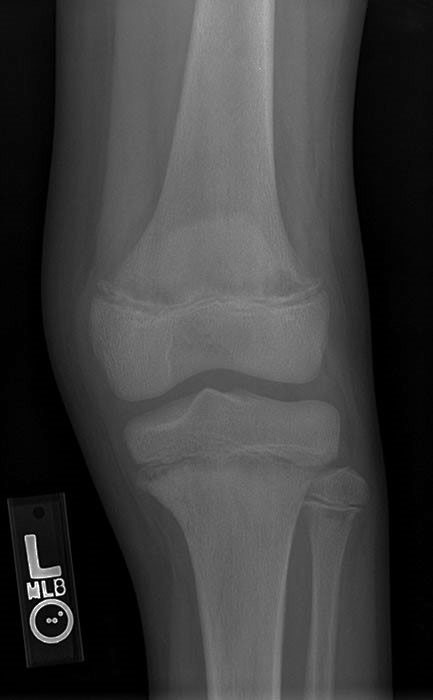
ALL: radiolucent metaphyseal banding
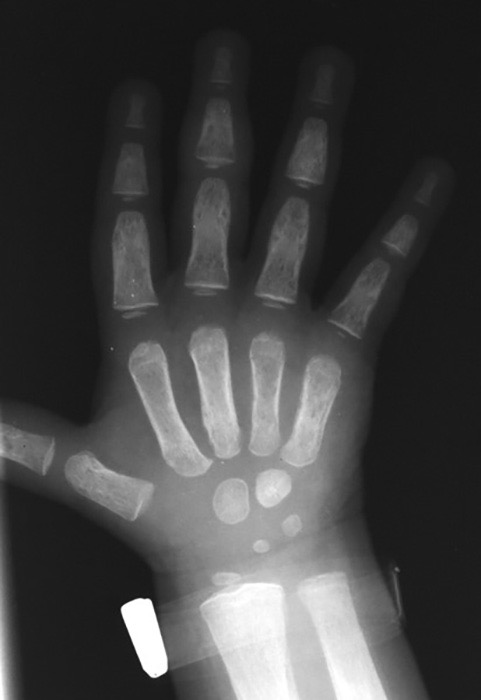
ALL: Osteolytic lesions and radiolucent metaphyseal banding
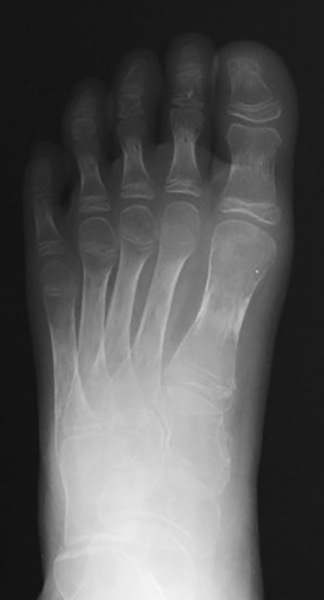
ALL: Osteolytic lesions through the proximal phalanges. Subperiosteal new bone formation happening MT #1 and proximal phalange #1
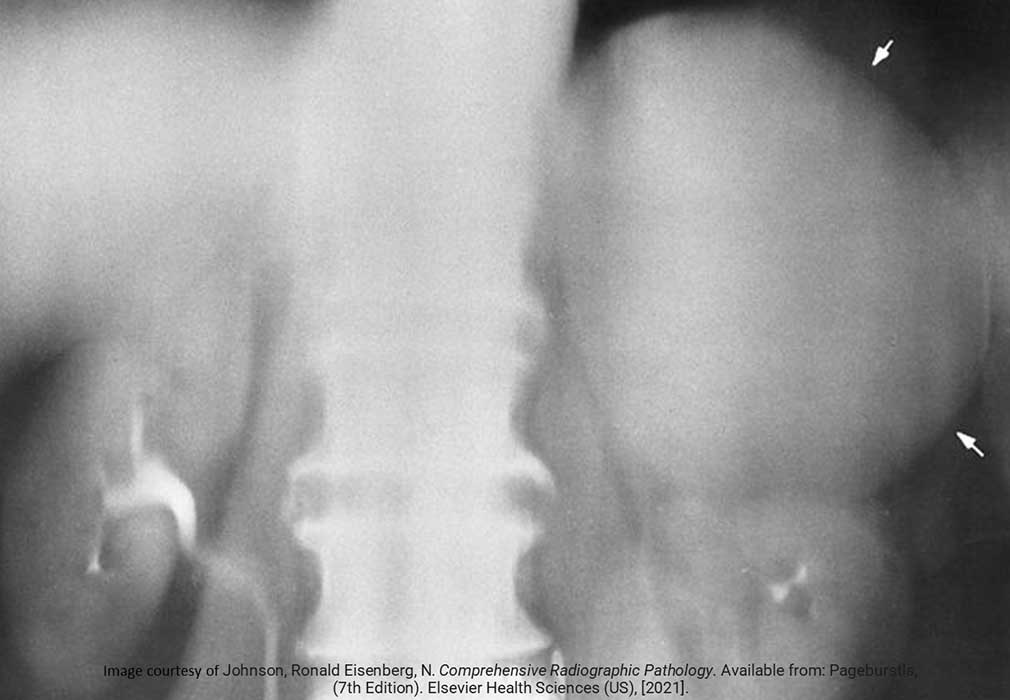
Massive Adrenal tumor: Cushing’s Disease
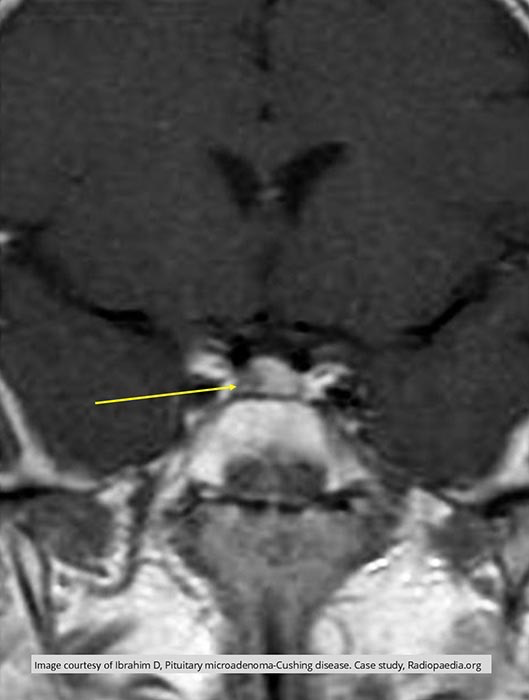
Coronal MRI image of pituitary tumor: Cushing’s Disease
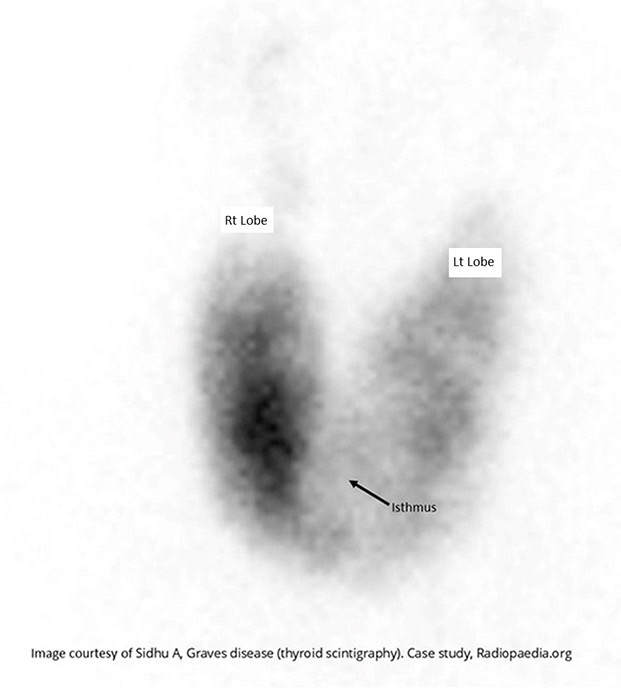
Hyperthyroidism
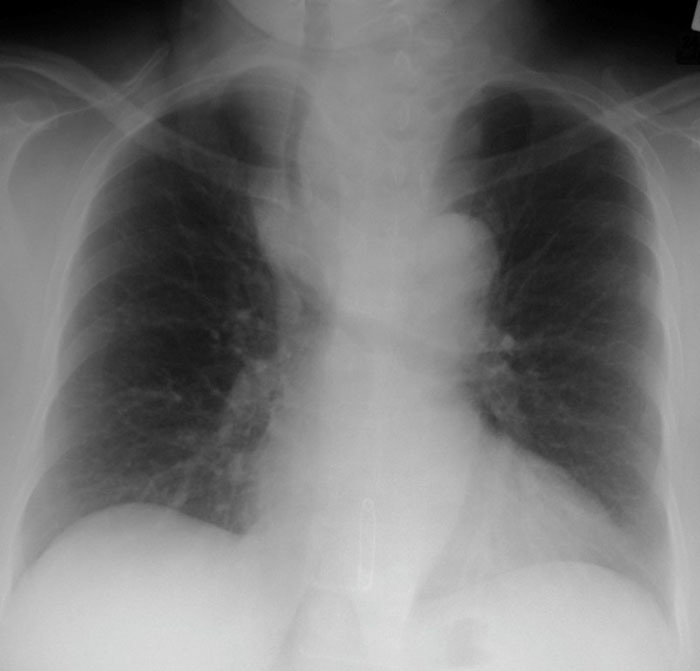
Hyperthyroidism: enlarged thyroid. Increased ST midline above clavicles as well as the tracheal shift to the right
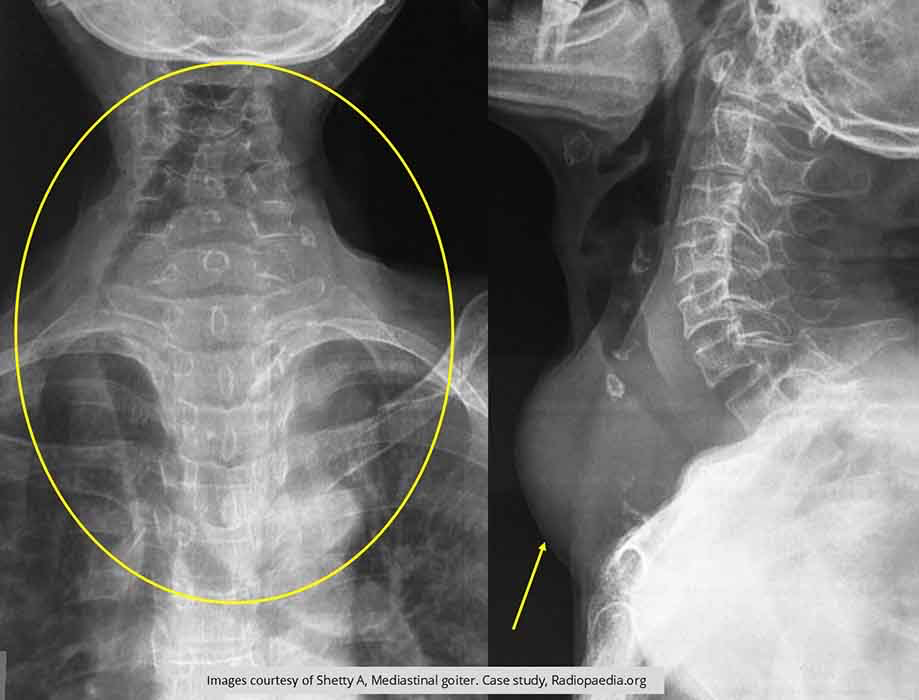
Hyperthyroidism
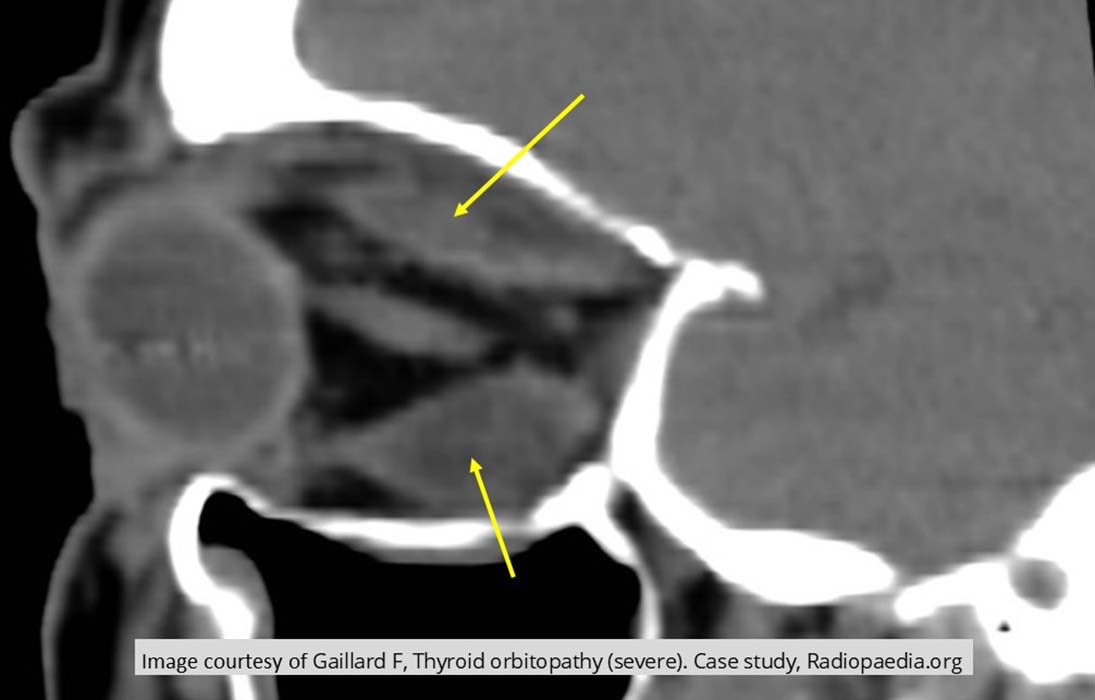
MRI: expohtalmos - hyperthyroidism
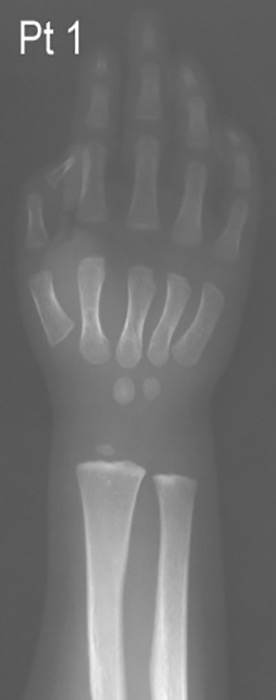
Hypothyroidism
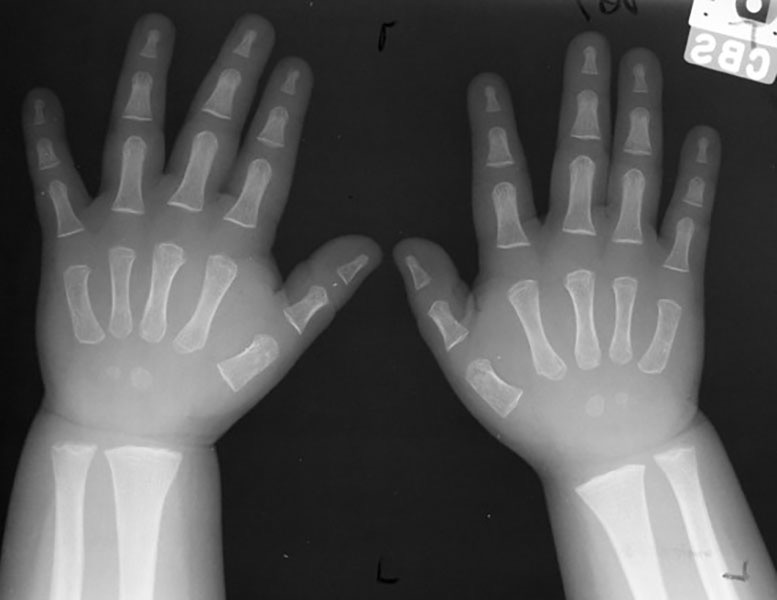
Hypothyroidism
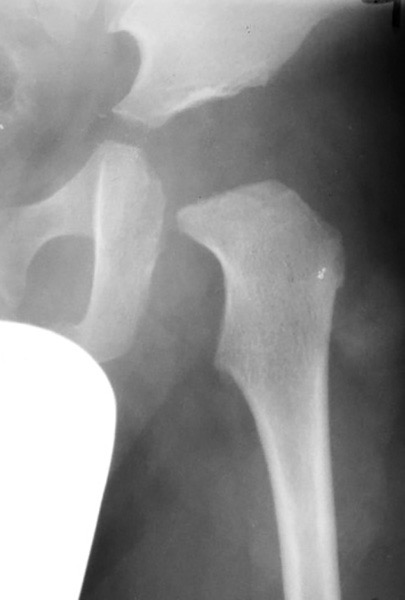
Hypothyroidism
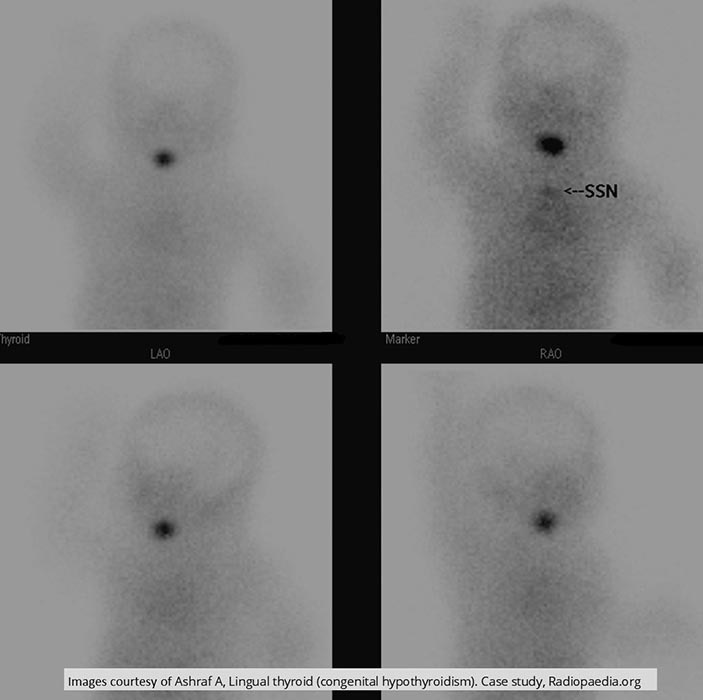
Hypothyroidism: SNN shows infant w/ an ectopic thyroid
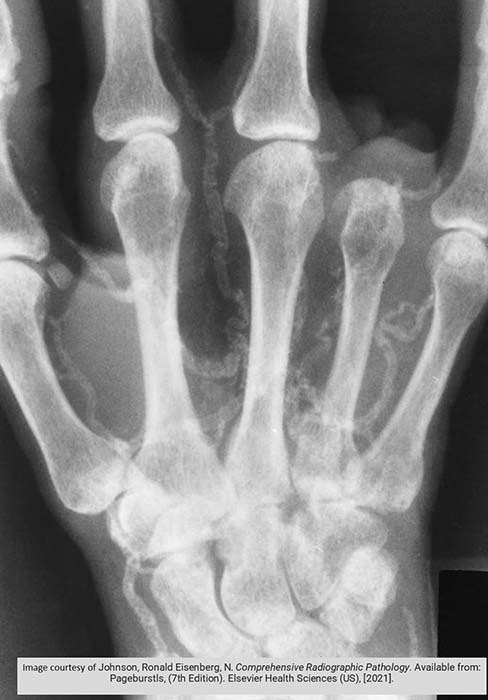
Diabetes: Osteomyelitis
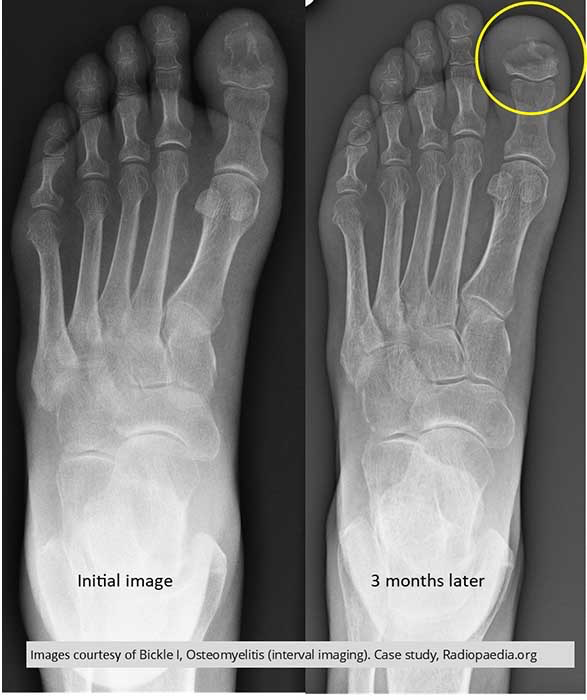
Diabetes: Osteomyelitis
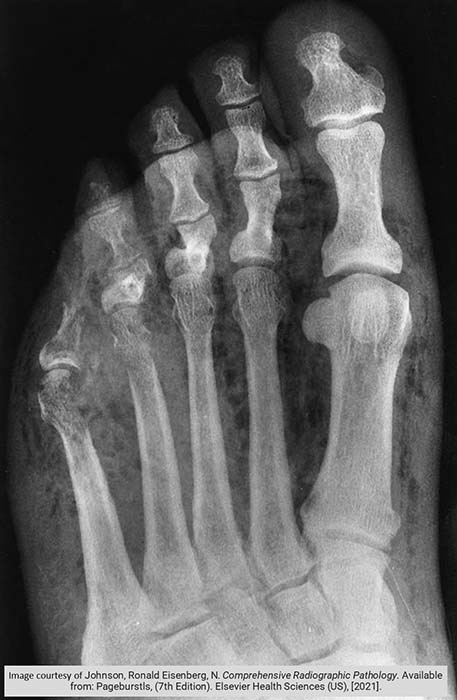
Diabetes: Osteomyelitis
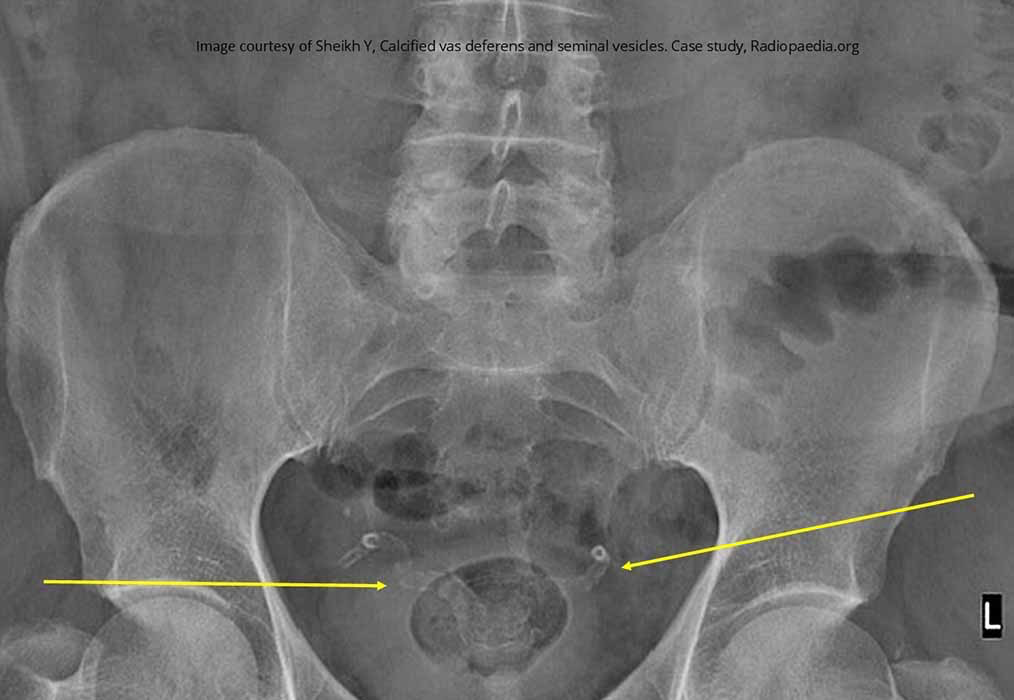
Diabetes: gas gangrene
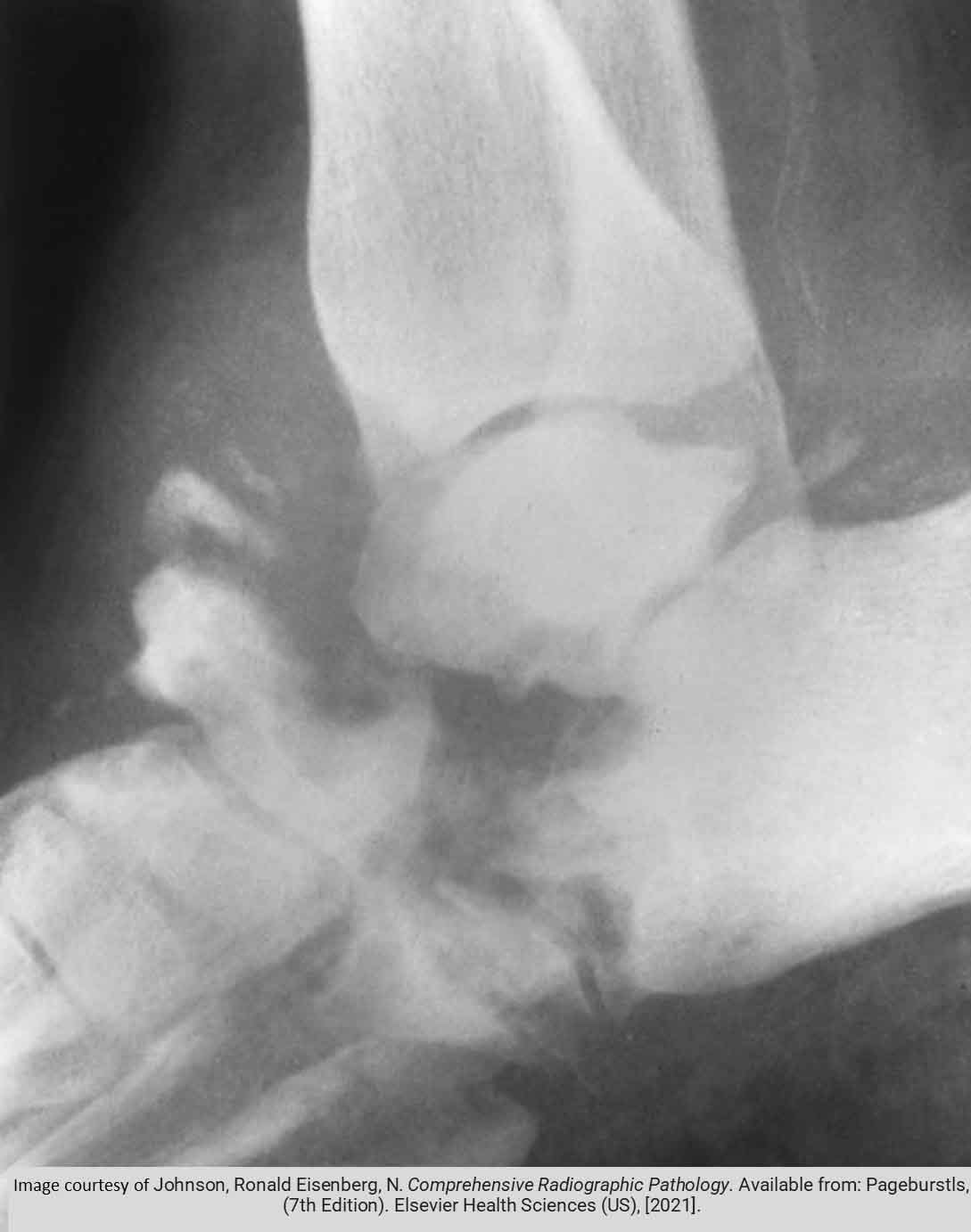
Diabetes
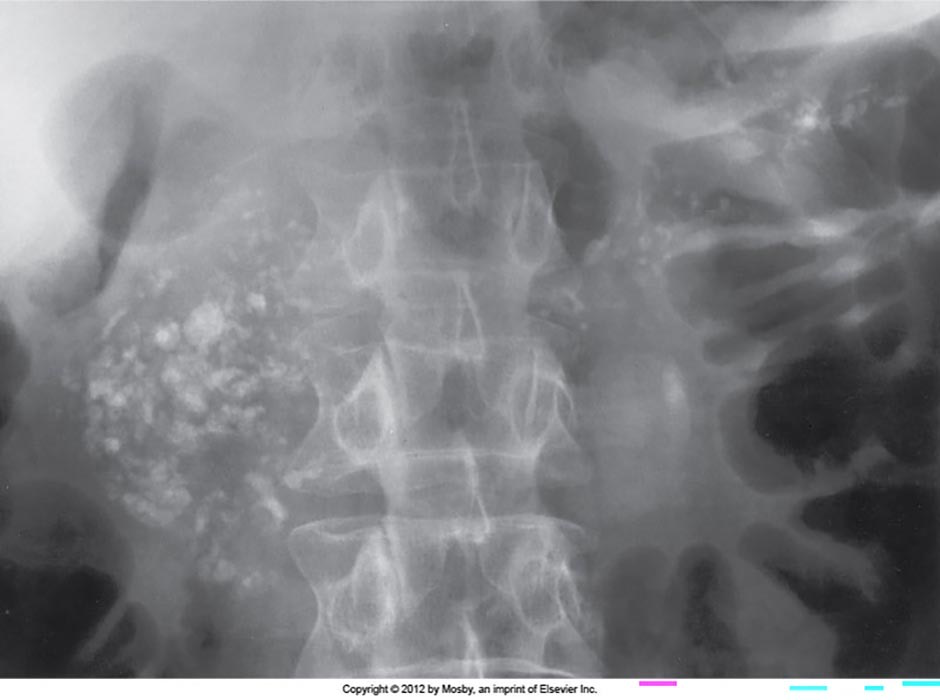
Chronic Pancreatitis: Calcification in the head of pancreas
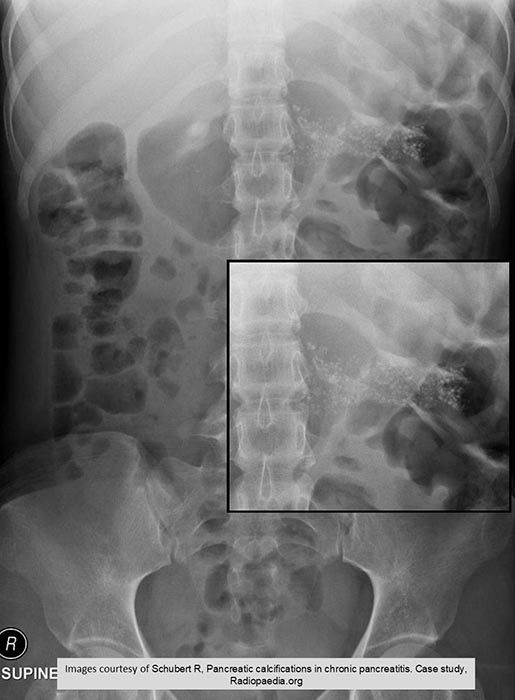
Chronic Pancreatitis: Calcification throughout entire pancreas
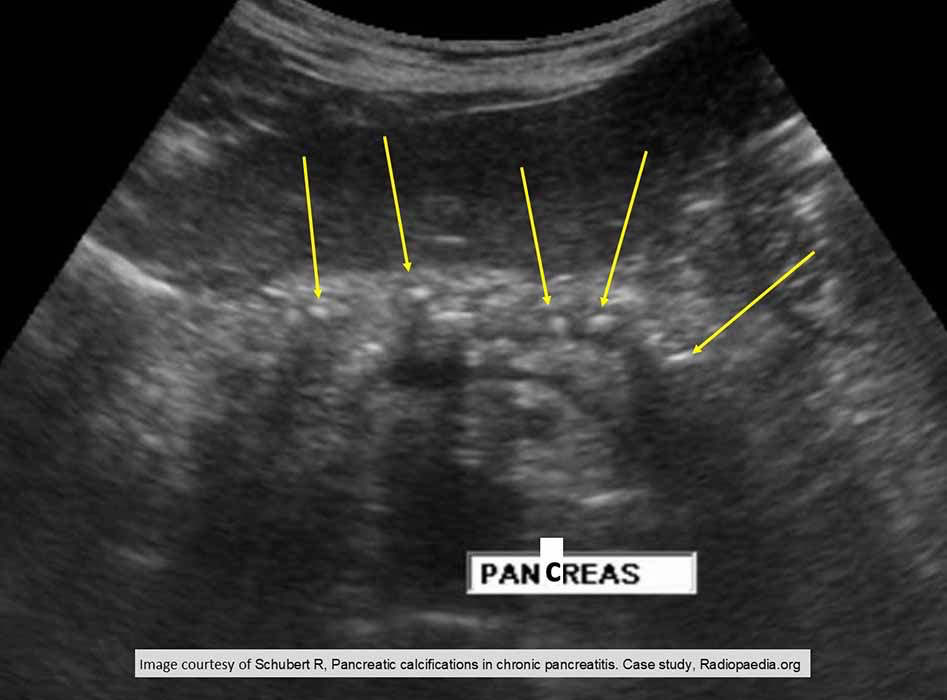
Chronic Pancreatitis: U/S demonstrating calcification
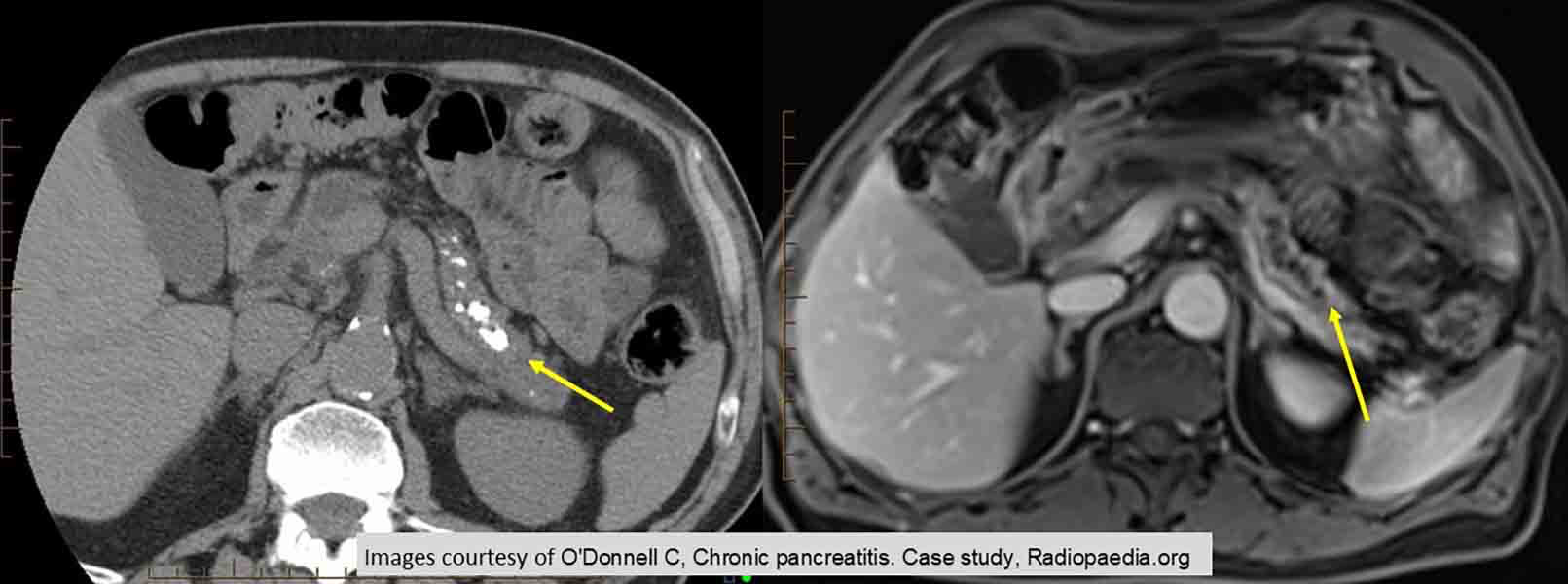
Chronic Pancreatitis: demonstrating calcifications
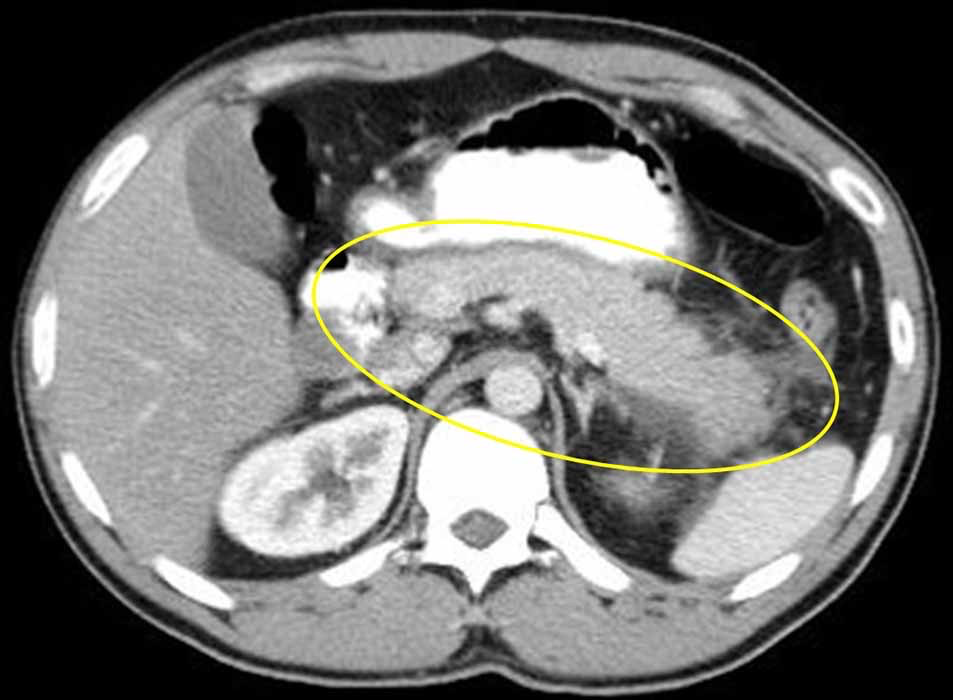
Acute Pancreatitis: enlargement of the pancreas. Margins appear hard to distinguish due to the inflammation and edema
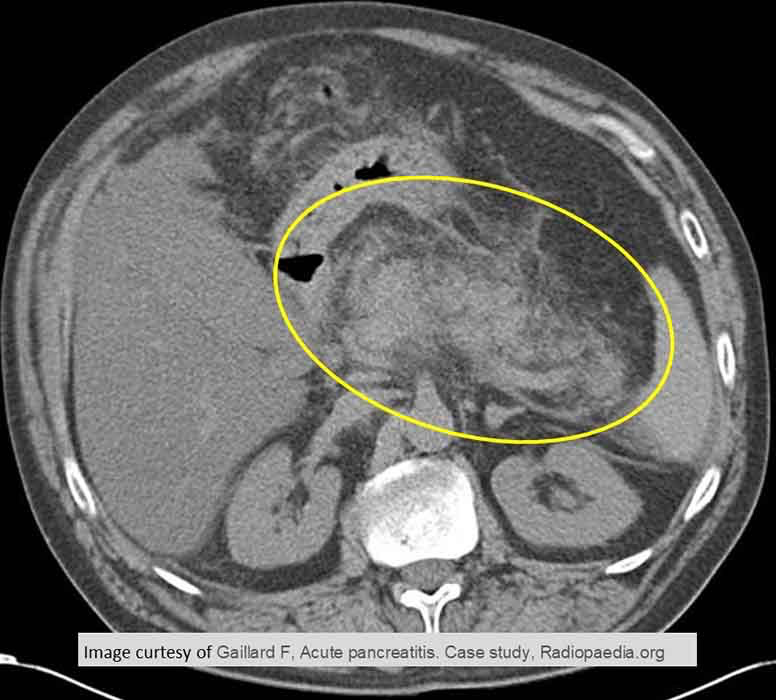
Acute Pancreatitis: very enlarged pancreas w/ indistinct borders
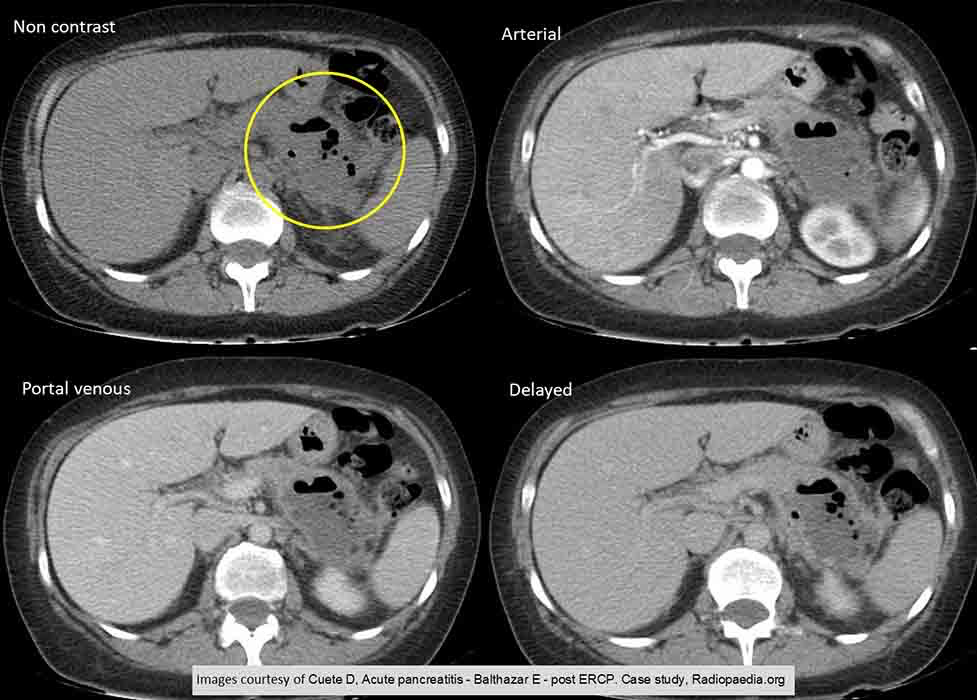
Acute Pancreatitis: due to a nosocomial infection. Air in the tissue from the infection seen in the tail of the pancreas
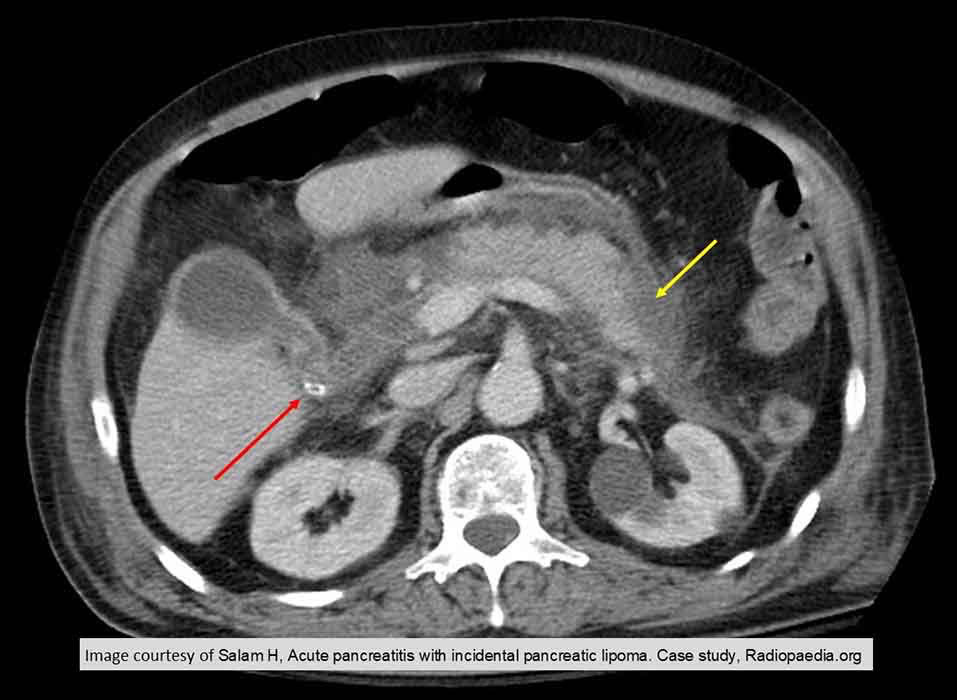
Acute Pancreatitis: stone seen in the common bile duct
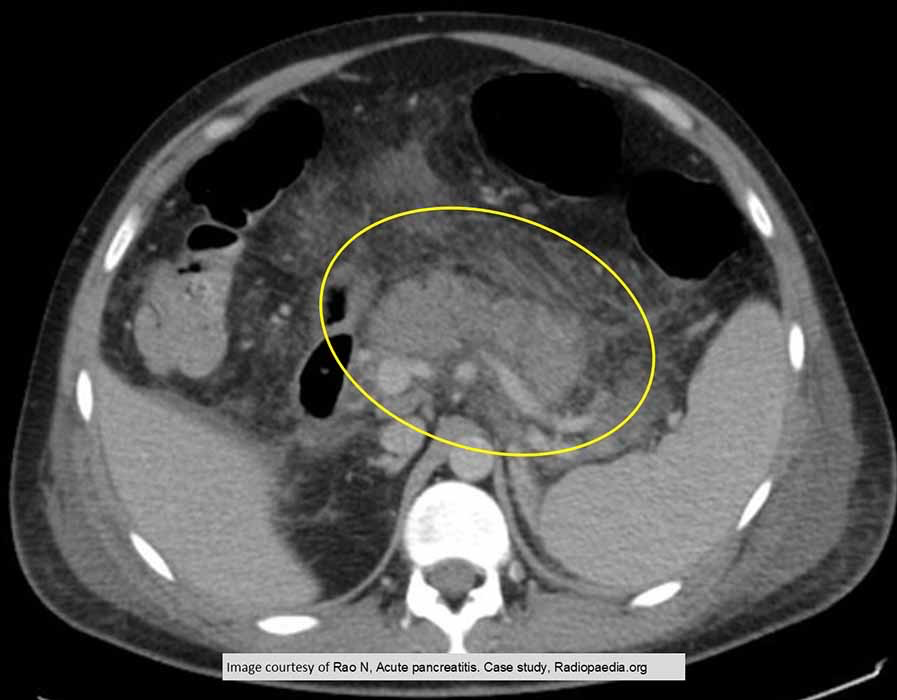
Acute Pancreatitis: gallstone inducted. Exam 5 days post cholecystectomy
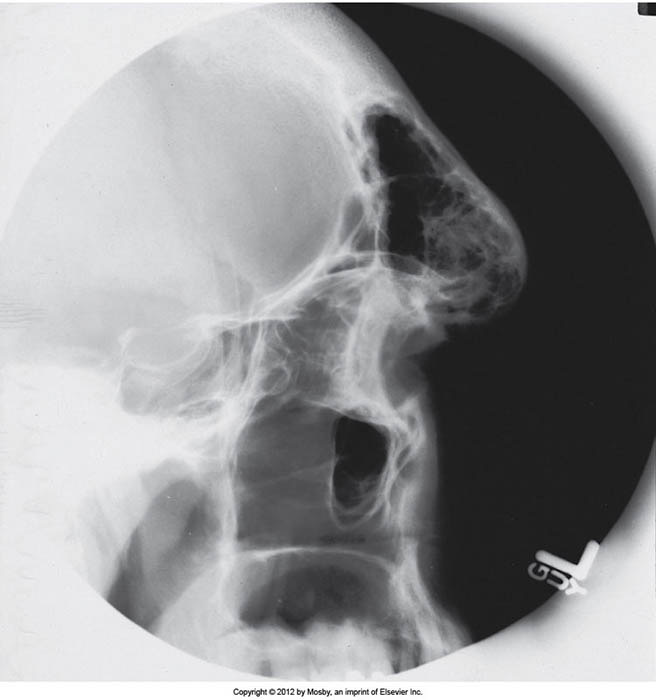
Acromegaly: frontal bossing
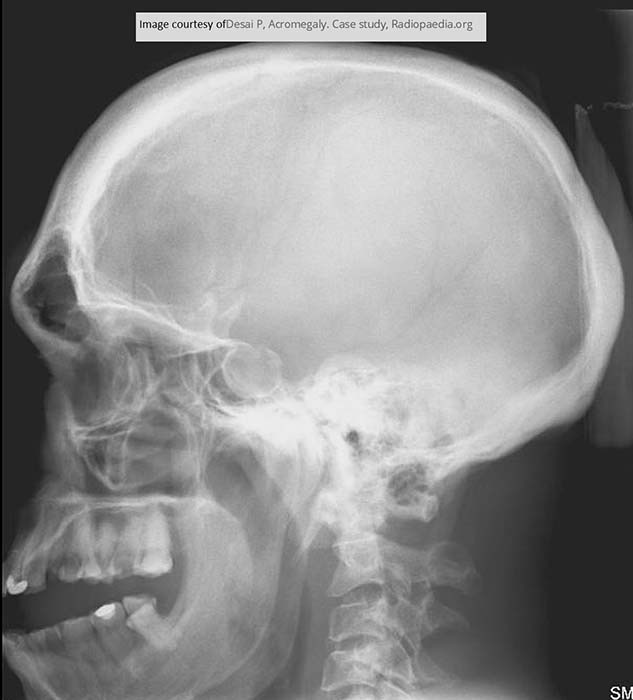
Acromegaly: frontal bossing. Thickening of the skull in the frontal and occipital regions. Enlarged mandible
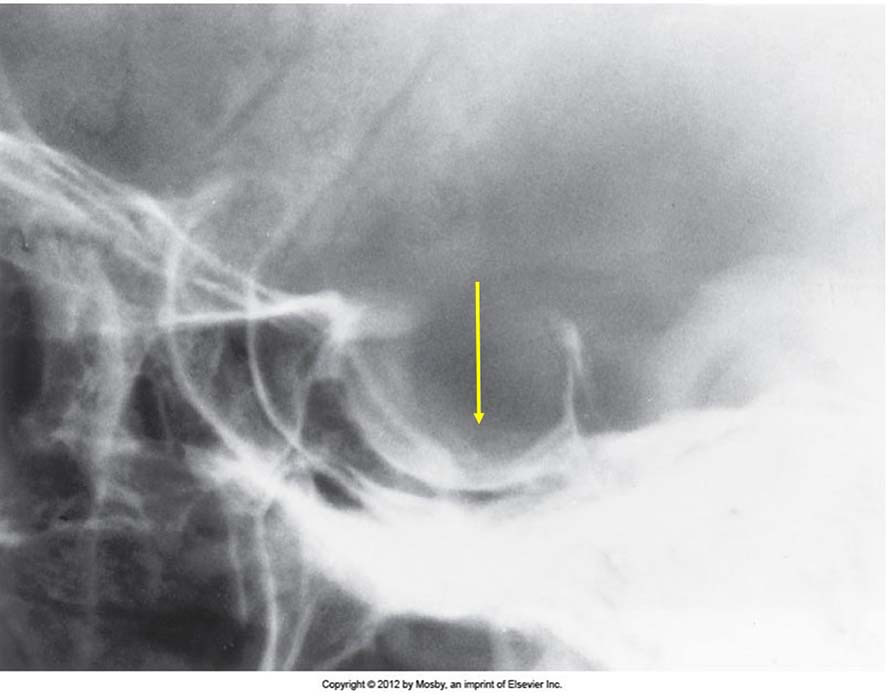
Acromegaly: Sella Turcica Enlargement - pituitary tumor is eroding the floor of the sella
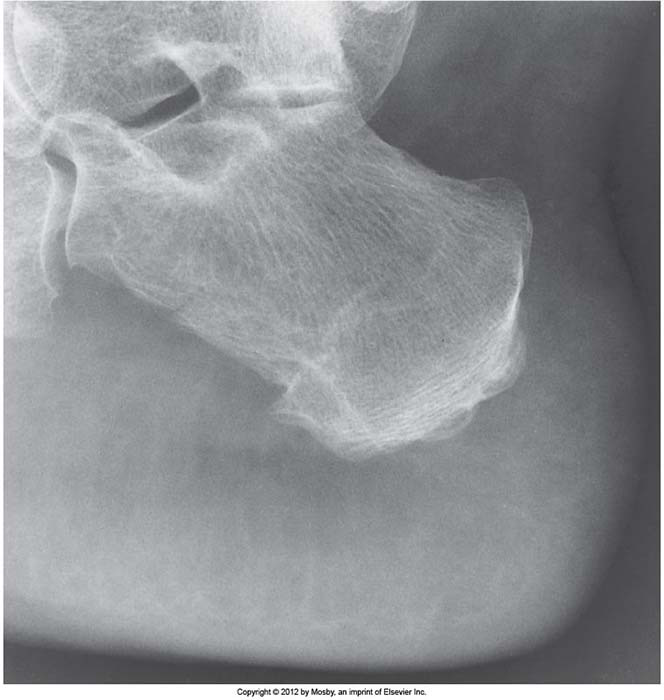
Acromegaly: Excessive ST and thickened heel pad
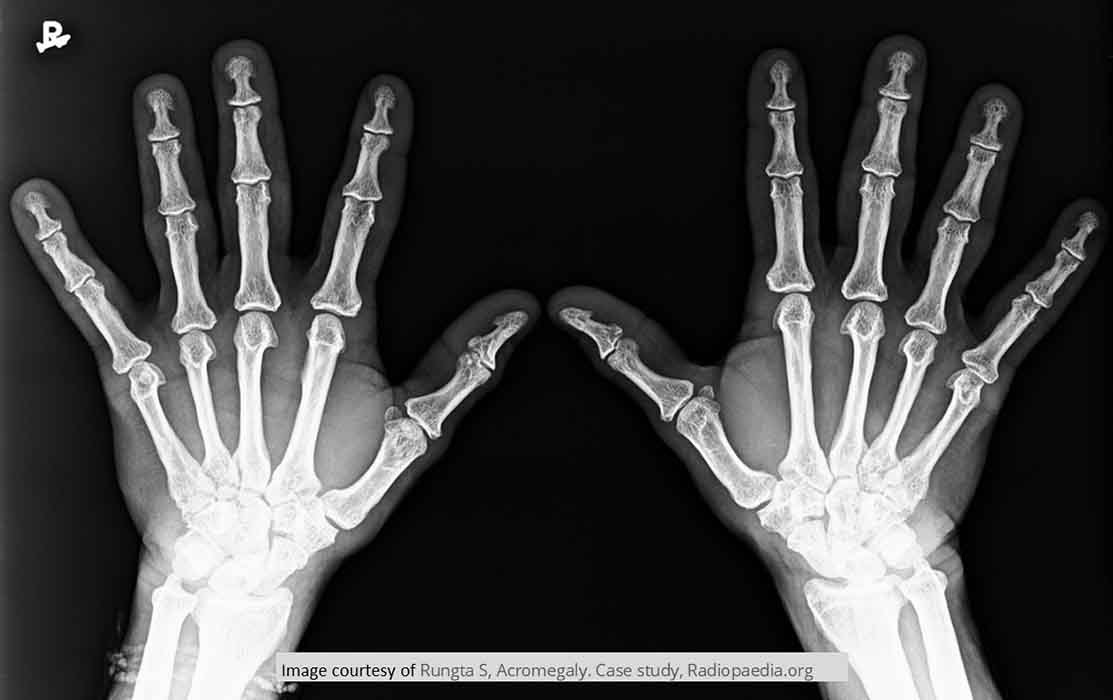
Acromegaly: some tufts display the distinct spade shape
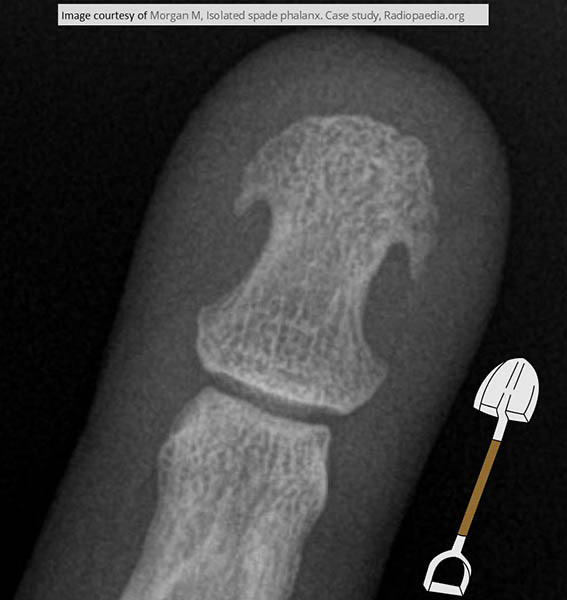
Acromegaly: spade shape
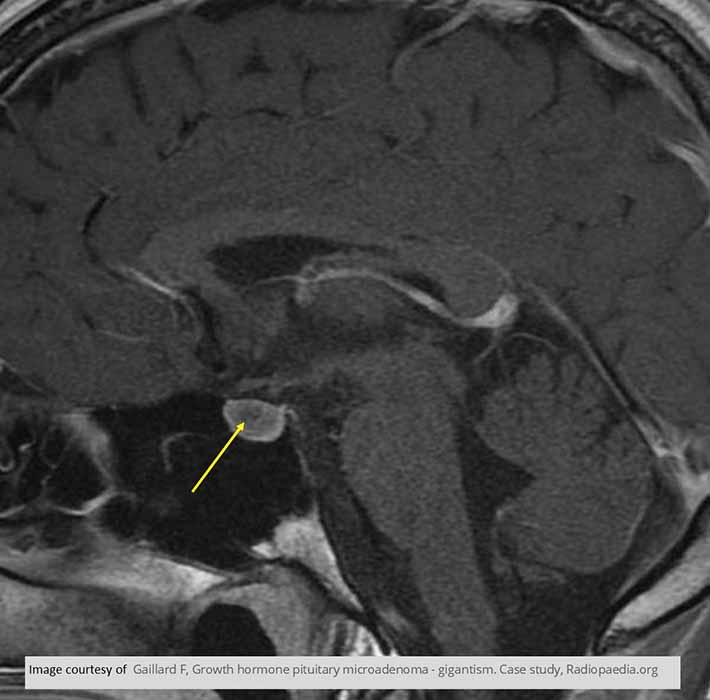
Acromegaly: MRI T1 sagittal image show the low intensity signal of the pituitary tumor
Acromegaly: MRI T1 demonstrates a low intensity signal from a pituitary tuor
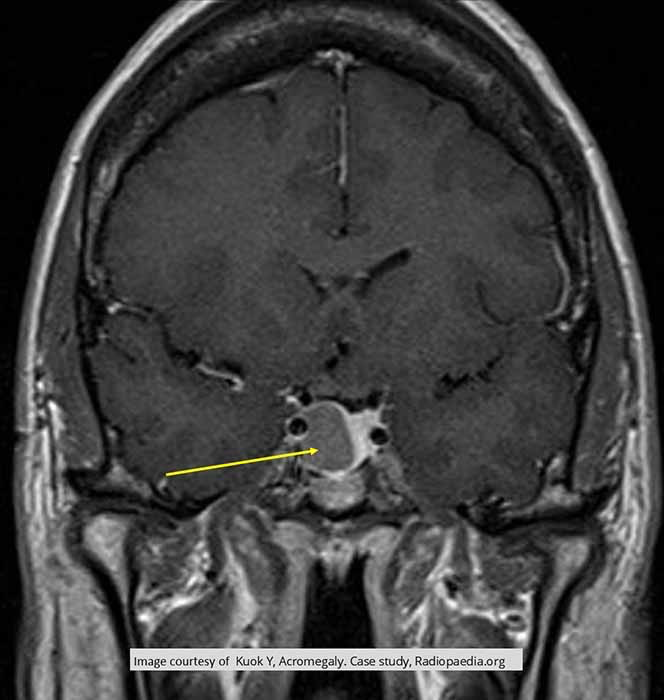
Acromegaly: MRI shows enlargement of sella turcica
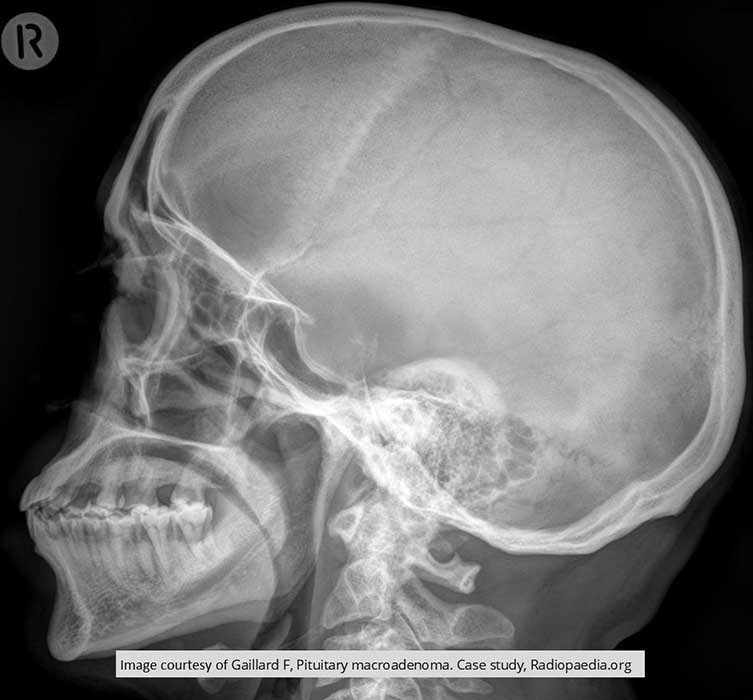
Pituitary Macroadenoma: enlarged sella turcica
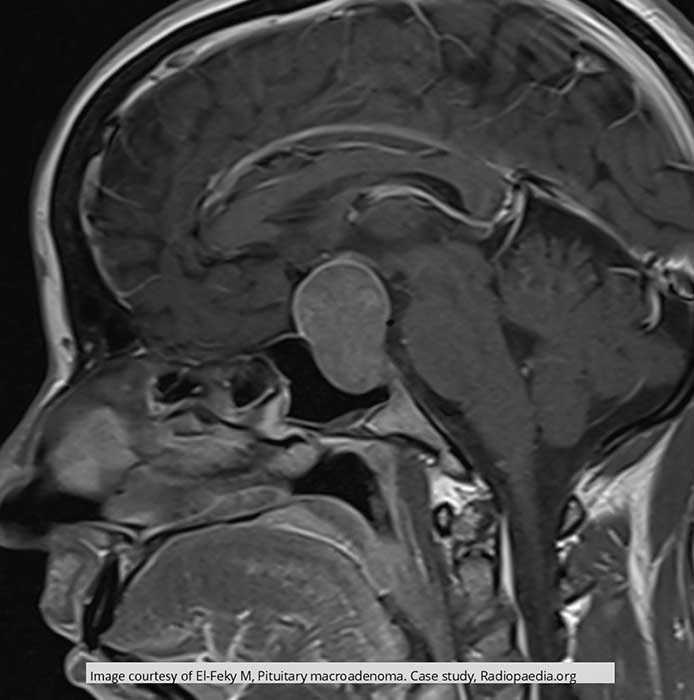
Pituitary Macroadenoma: large pituitary compressing brain tissue above the sella turcica
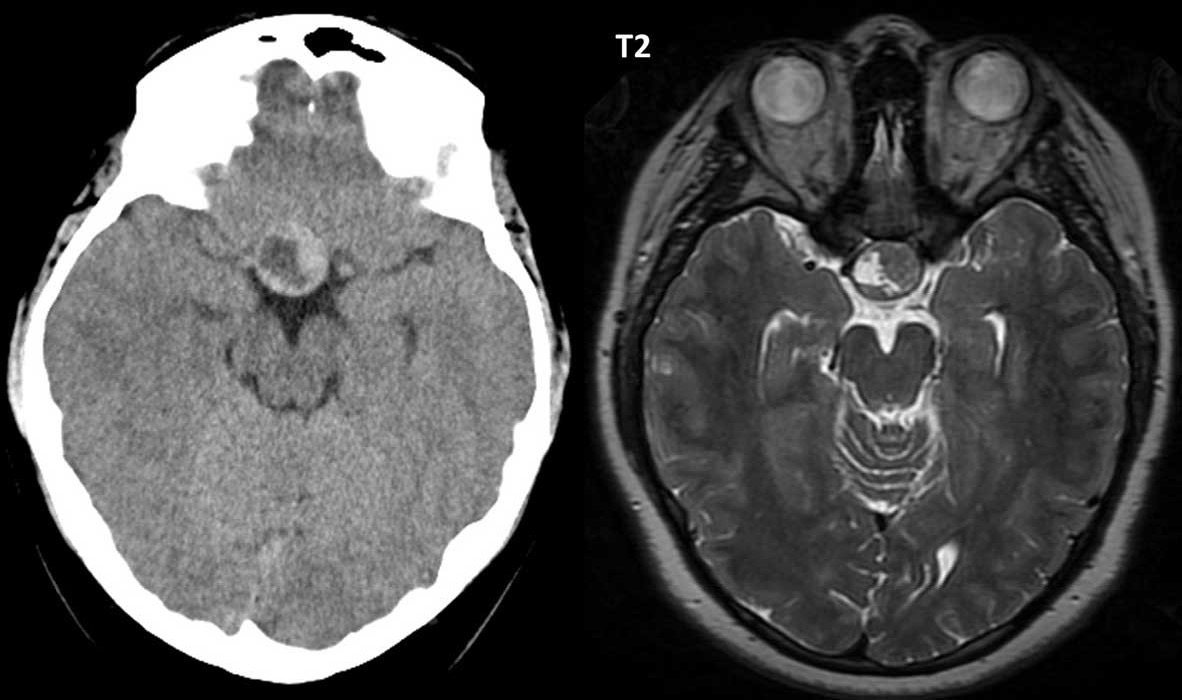
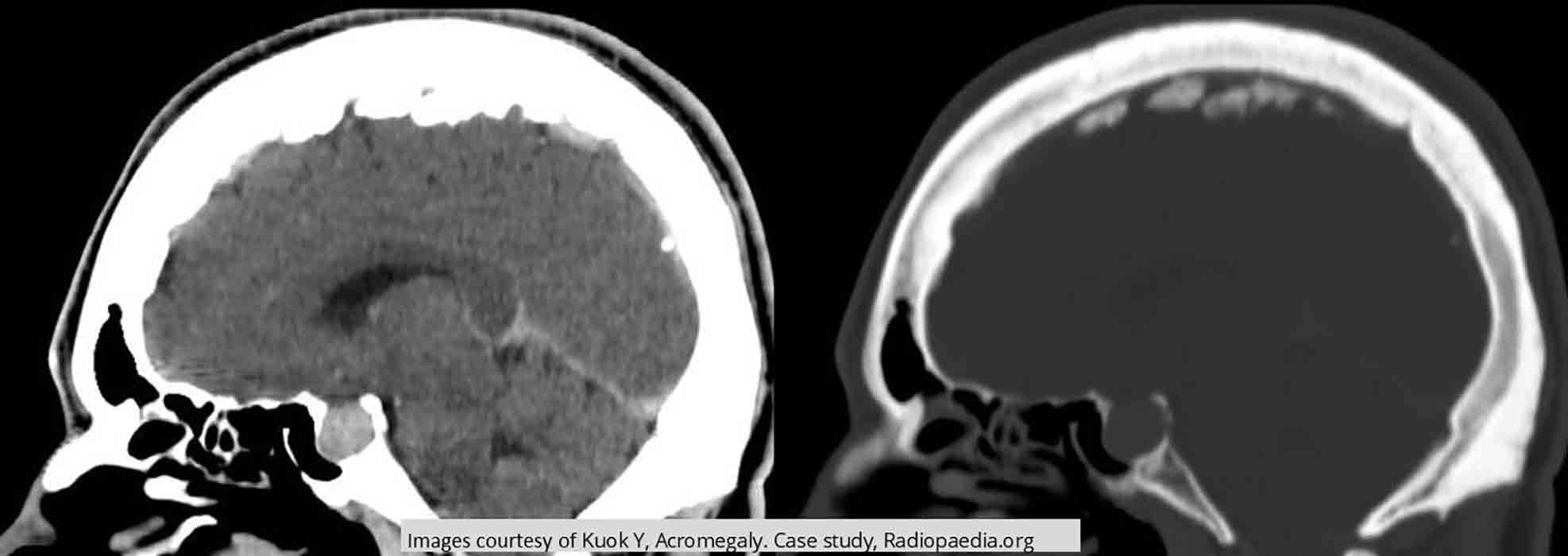
Pituitary Adenoma: CT vs. MRI. MRI T2 demonstrates the sharpness of the tumor area compared to CT
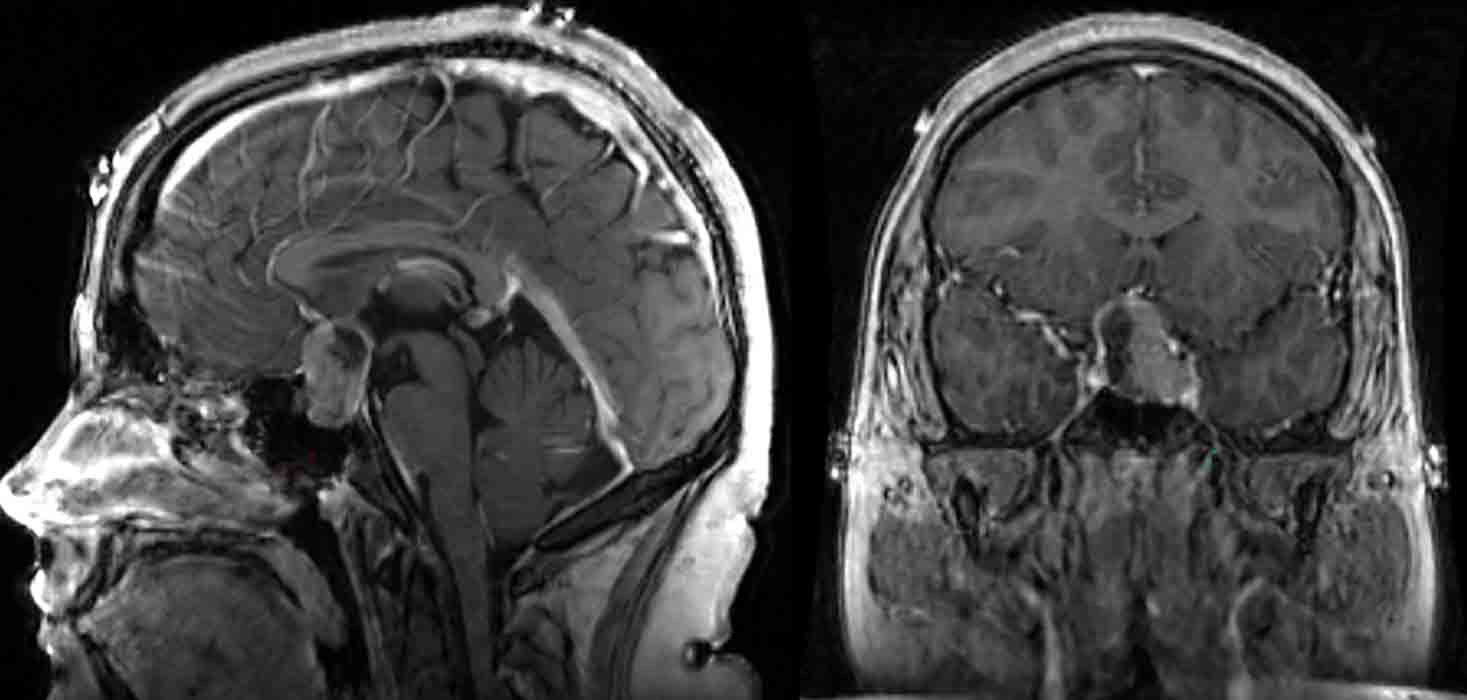
Pituitary Macroadenoma
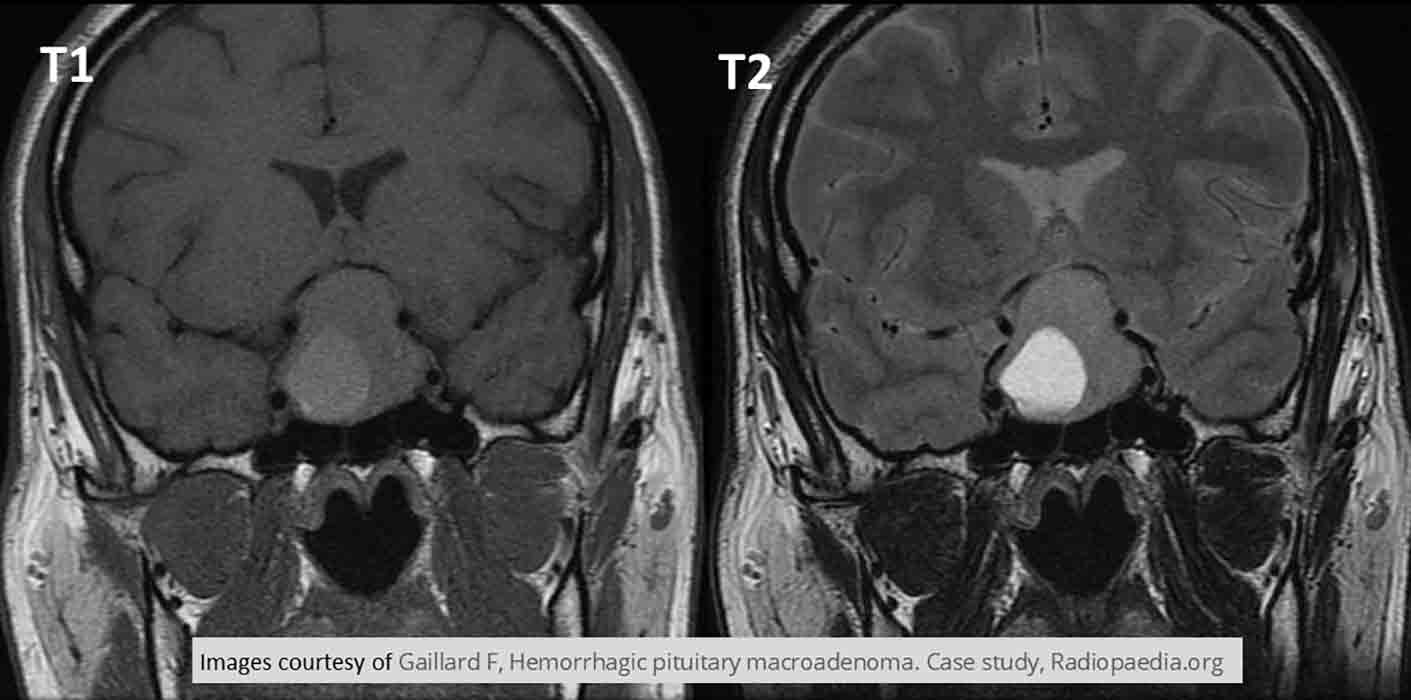
Pituitary Macroadenoma: T1 - tumor is hypodense. T2 - tumor is hyperdense
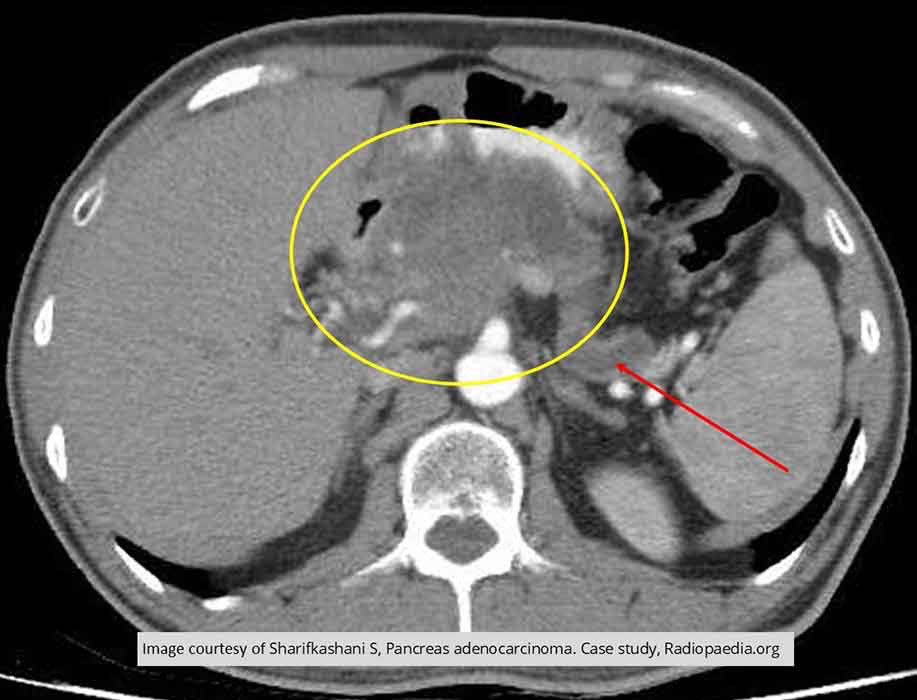
Pancreatic Ca: Demonstrates a mass of the head of the pancreas and dilation of the pancreatic duct
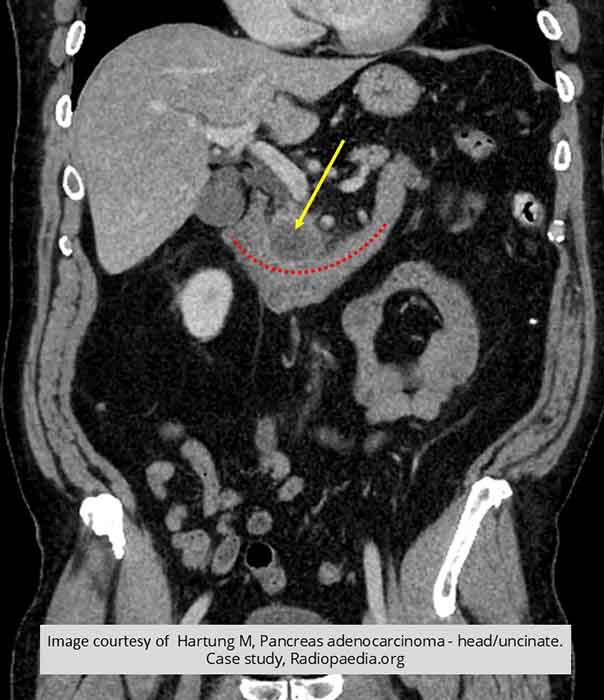
Pancreatic Ca: coronal view showing the mass
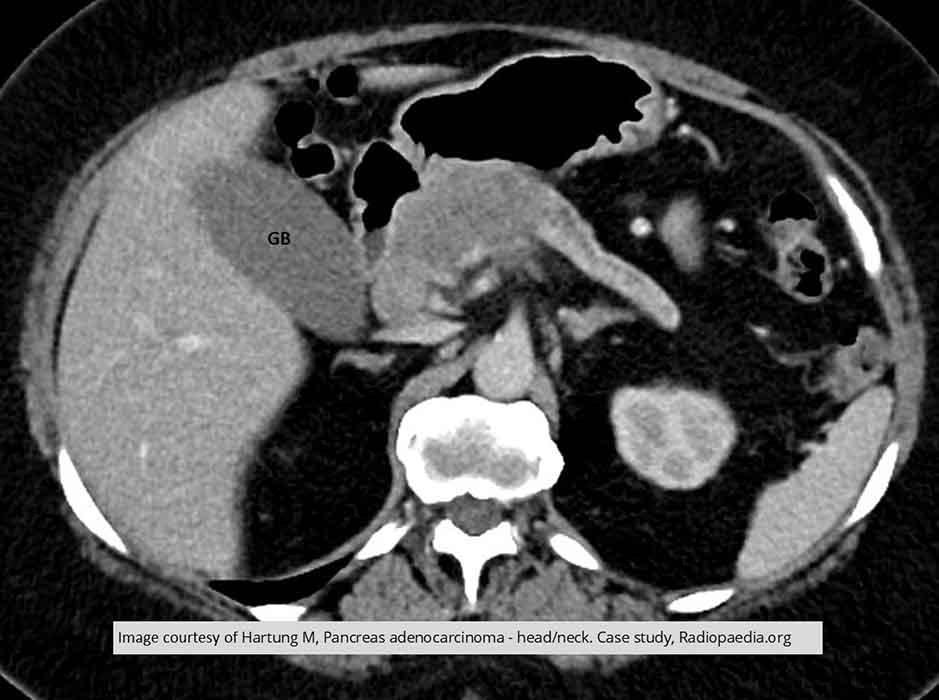
Pancreatic Ca: a mass in the head/body region w/ dilated pancreatic duct
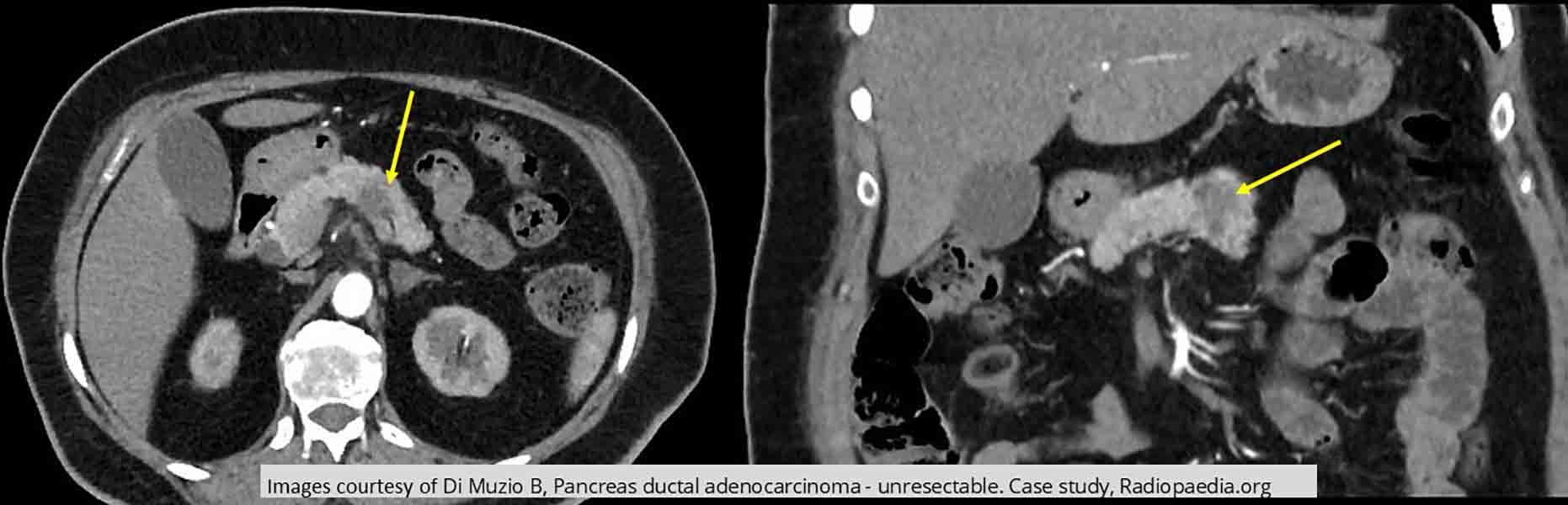
Pancreatic Ca: unresectable tumor in the body of the pancreas demonstrated in the axial and coronal slice
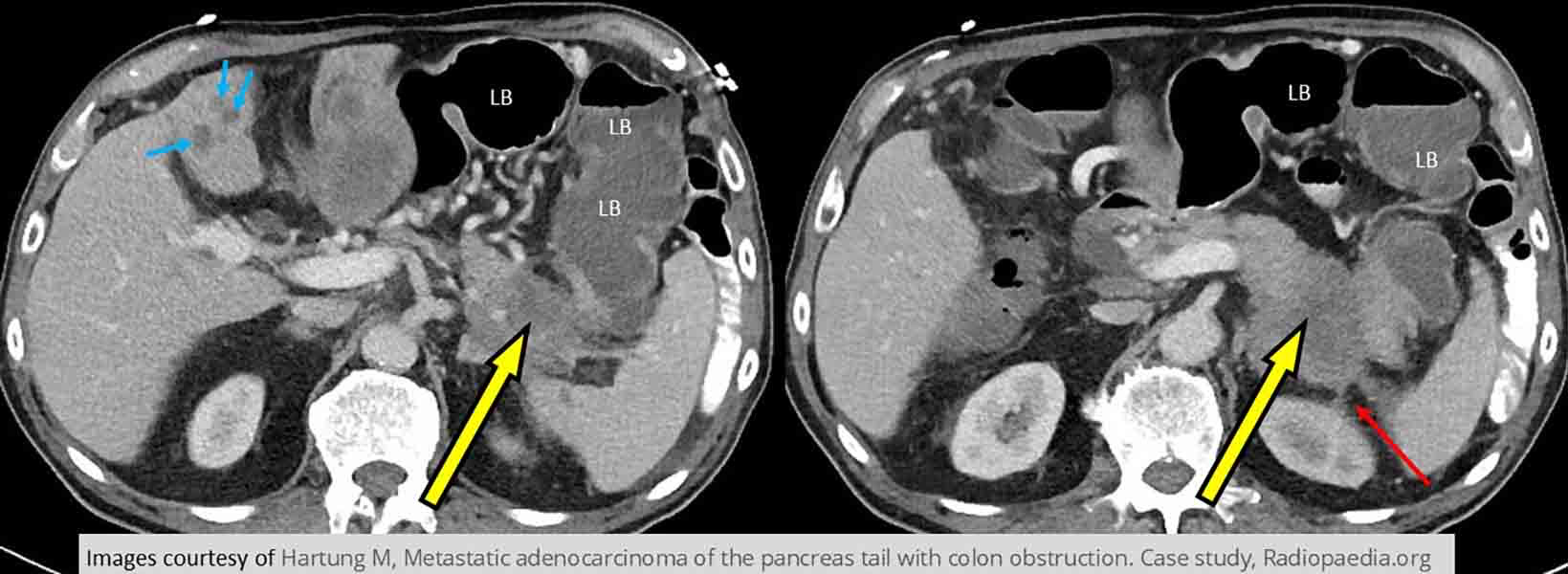
Pancreatic Ca: Tumor seen in tail of pancreas. Mets to the liver and into the left kidney. Dilated loops of large bowel indicative of a bowel obstruction
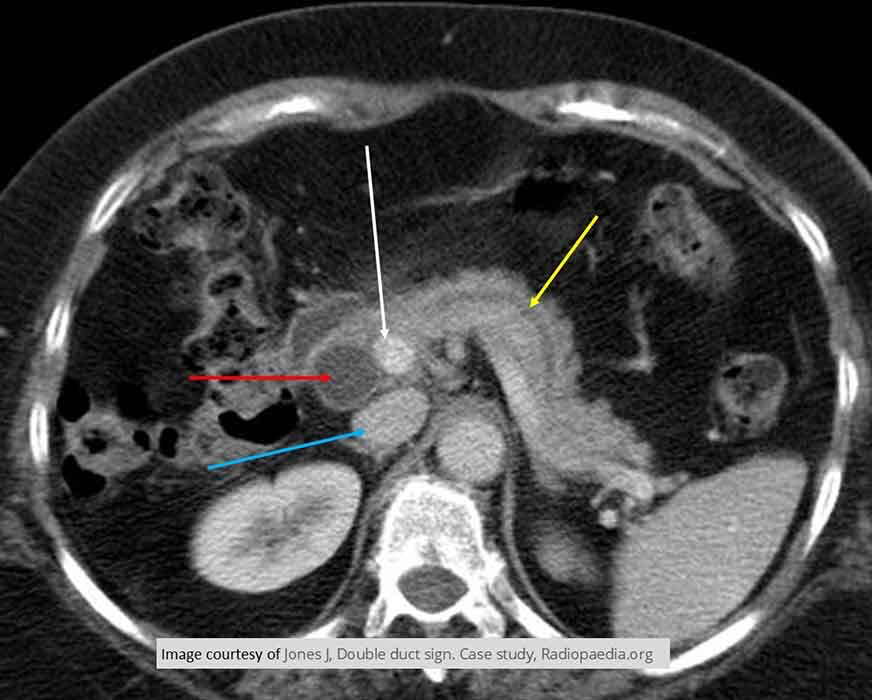
Pancreatic Ca: Double Duct Sign
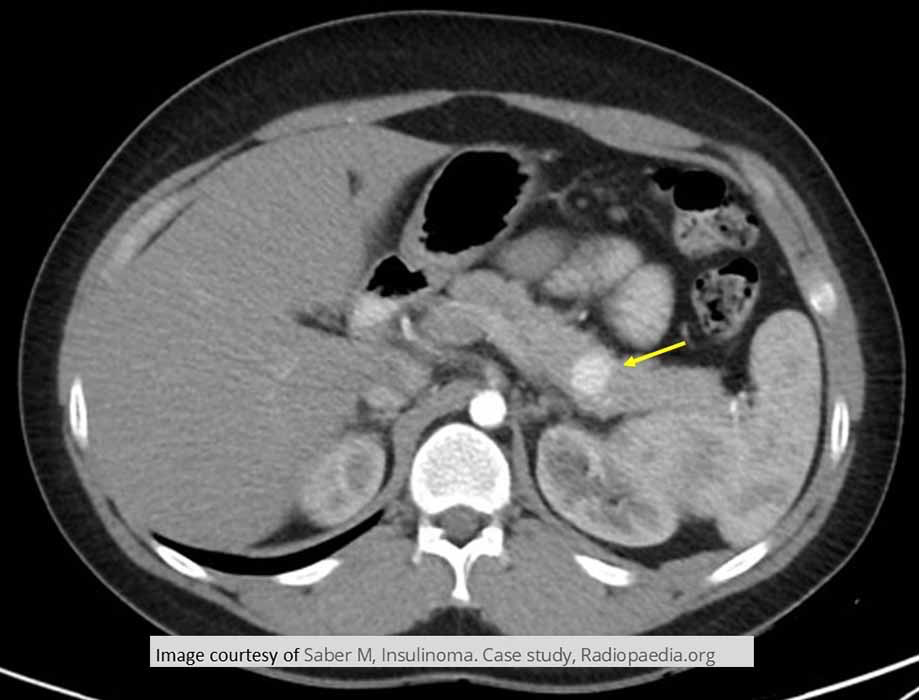
Hypoglycemia due to Insulinoma: Demonstrates an insulinoma in lower body to tail portion of the pancreas
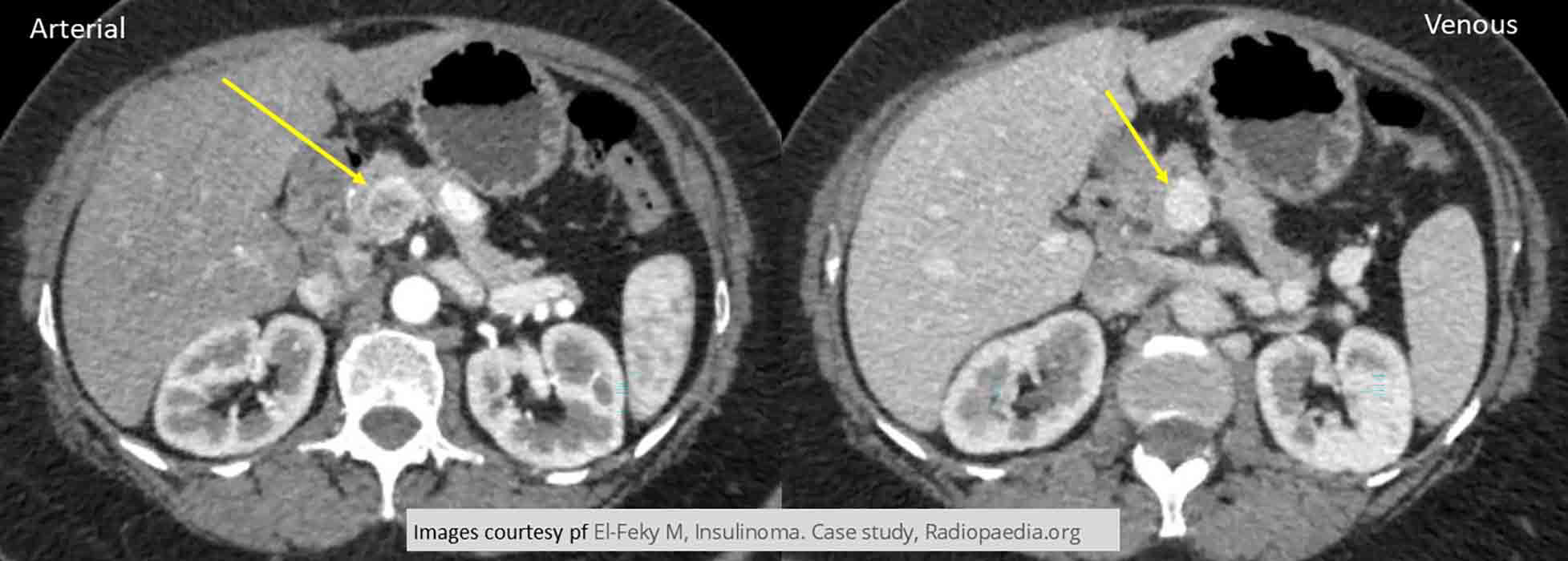
Hypoglycemia due to Insulinoma: Tumor starting to enhance in early arterial phase