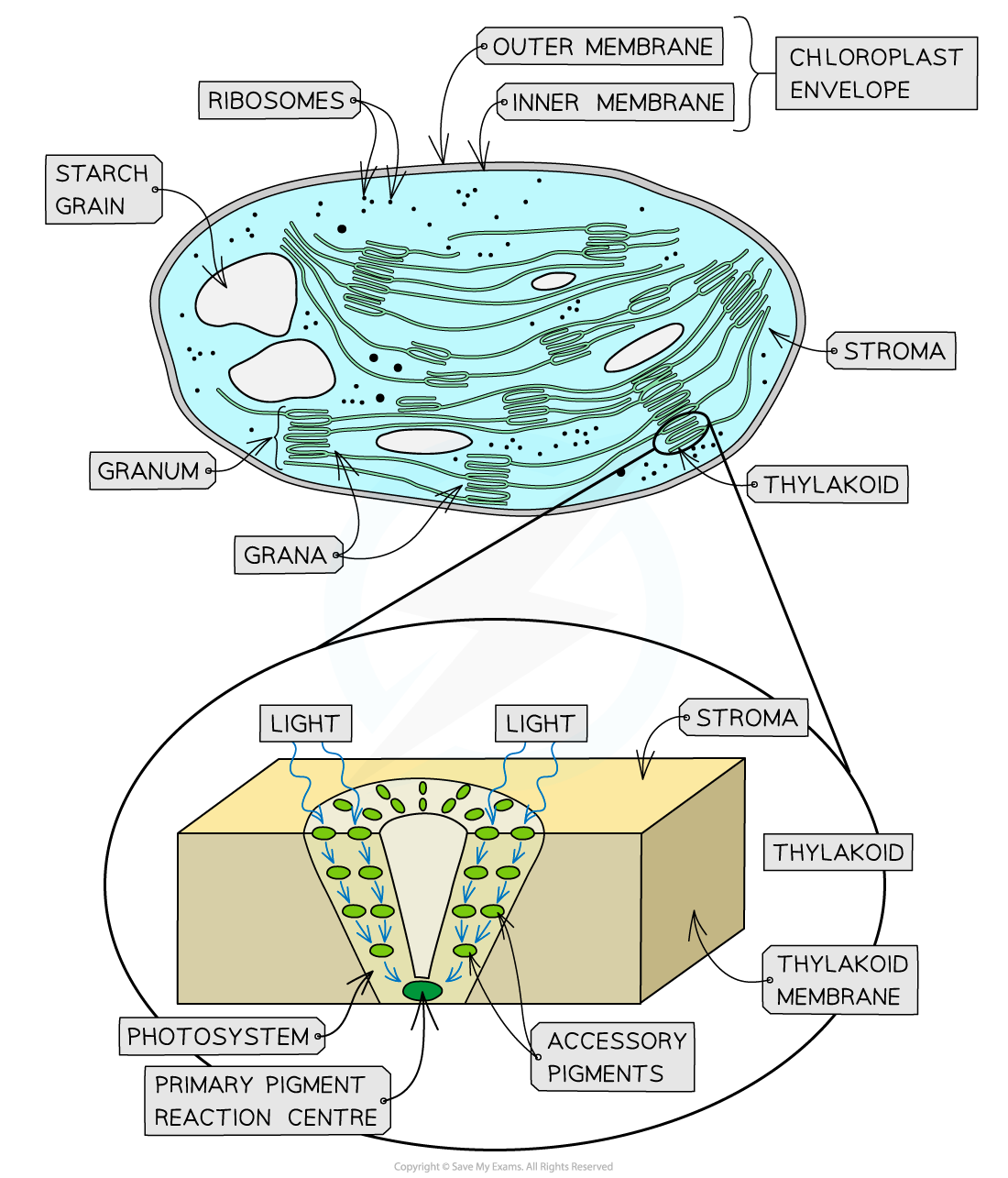
(b) the structure of a chloroplast and the sites of the two main stages of photosynthesis
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
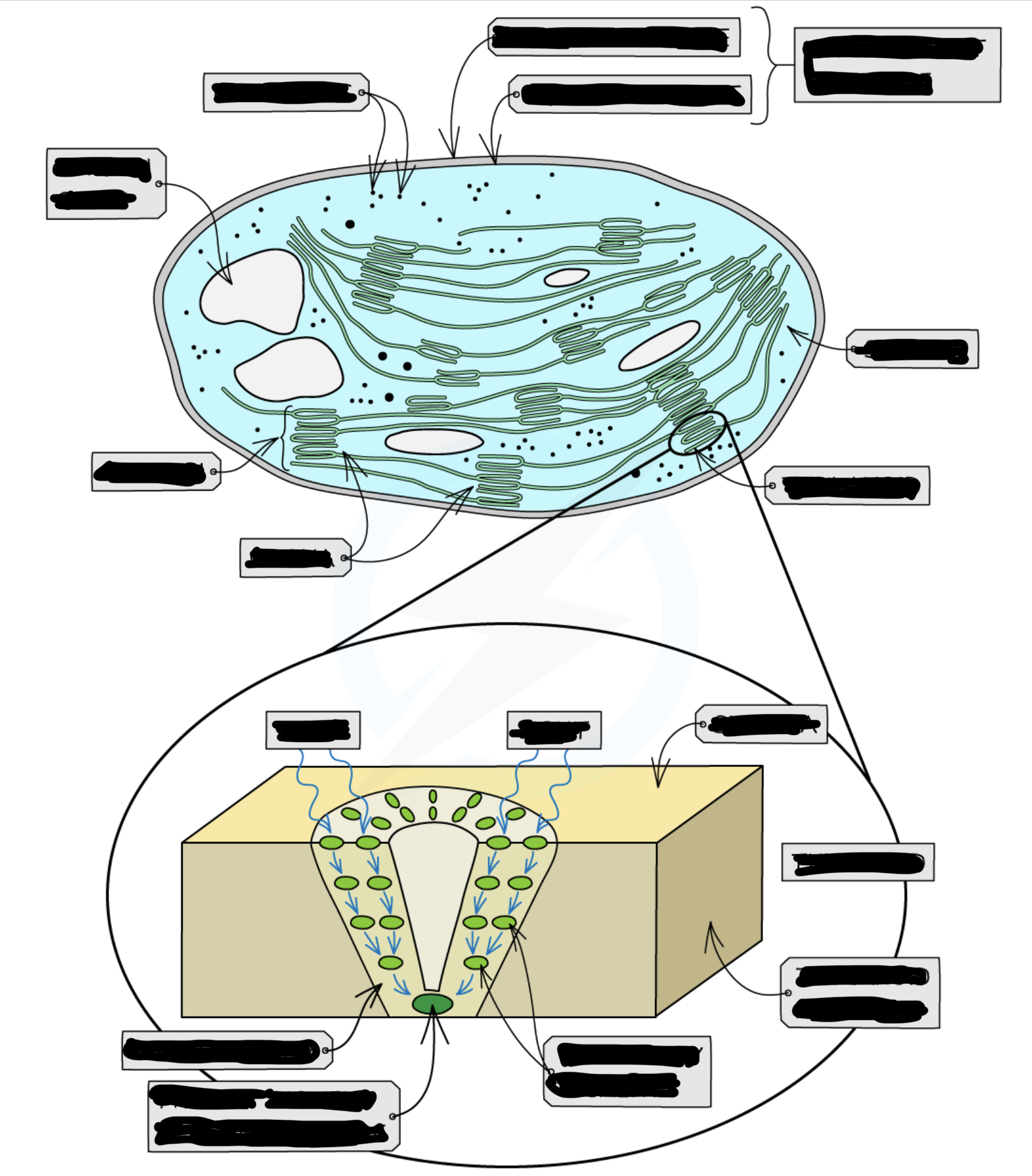
The components of a chloroplast including outer membrane, lamellae, grana, thylakoid, stroma and DNA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Chloroplasts
are the organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs
These organelles are roughly 2 - 10 μm in diameter (they are larger than mitochondria)
Each chloroplast is surrounded by a double-membrane envelope called chloroplast envelope
are filled with a cytosol-like fluid - stroma
CO2, sugars, enzymes and other molecules are dissolved in the stroma
the double membrane envelope
Each of the envelope membranes is a phospholipid bilayer
The outer membrane is permeable to a range of ions and small molecules
The inner membrane contains transport proteins that only allow certain molecules or ions to enter or leave the chloroplast
membrane system of stroma
consists of a series of flattened fluid-filled sacs known as thylakoids
thylakoid membranes contain pigments, enzymes and electron carriers
they stack up to form structures known as grana (singular – granum)
membrane system provides a large number of pigment molecules that ensure as much light as necessary is absorbed
grana
are connected by membranous channels called stroma lamellae, which ensure the grana are connected but distanced from each other
The membranes of the grana create a large surface area
Pigment molecules
are arranged in light-harvesting clusters known as photosystems
In a photosystem, the different pigment molecules are arranged in funnel-like structures in the thylakoid membrane (each pigment molecule passes energy down to the next pigment molecule in the cluster until it reaches the primary pigment reaction centre)
Stroma
contains small (70S) ribosomes, a loop of DNA and starch grains:
The loop of DNA codes for some of the chloroplast proteins (other chloroplast proteins are coded for by the DNA in the plant cell nucleus)
The proteins coded for by this loop of chloroplast DNA are produced at the 70S ribosomes
Sugars formed during photosynthesis are stored as starch inside starch grains in the stroma
Location of stages photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis is made up of two stages, the light-dependent stage and the light-independent stage
These stages take place in specific locations within the chloroplast
The first stage, the light-dependent stage takes place on the thylakoid membranes of the grana
Light becomes trapped within the reaction centres of the grana
The light-independent stage takes place in the stroma
Adaptations of chloroplasts to photosynthesis
Stroma: The gel-like fluid contains enzymes that catalyse the reactions of the light-independent stage. The stroma surrounds the grana and membranes, making the transport of products from the light-dependent stage into the stroma rapid
Grana: The granal stacks create a large surface area for the presence of many photosystems which allows for the maximum absorption of light. It also provides more membrane space for electron carriers and ATP synthase enzymes
DNA: The chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) contains genes that code for some of the proteins and enzymes used in photosynthesis
Ribosomes: The presence of ribosomes allows for the translation of proteins coded by cpDNA
Inner membrane of chloroplast envelope: The selective transport proteins present in the inner membrane control the flow of molecules between the stroma and cytosol (the cytoplasm of the plant cell)