Wealth/Income Redistribution and Inequality.
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are some ways that the government can reduce income and wealth disparity?
Direct and indirect taxes
Tranfer payments
Minimum wages
State provision of essential goods and services
What is the diference between income and wealth?
Income refers to the flow of money.
Welath refers to a store of money or assets.
Having a high inflow doesnt mean you have a large store.
What is the difference between equality and equity?
Equality means everyone is treated the same. (Sameness)
Equity means everyone in the same situation is treated the same. (Fairness)
NOTE: Economists may sometimes call equal income distribution as an equitable income distribution
Why does the market not result in an equal income distribution?
In a market system, how much you own and how much of the factors of production you own determines your income. (Duh, the more wealth you have, the more you can generate income.)
Since some ppl have more stuff than others, then some ppl will have more income than others.
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical equity?
Horizontal equity means “equal treatment of equals'“ those in the same situation should get the same treatment (eg same income, same tax)
Vertical equity means if you have more, you should contribute more. (More income, more tax)
Two principles work hand-in-hand with each other
Give an example of a tradeoff between equity and efficiency
Methods to achieve alllocative efficiency (through taxes and subsidies) may affect certain groups more disproportionately than others.
A specific tax on cigarretes will affect the poor more than the rich (As the tax is not proportional to their income.
What are progressive taxes?
Progressive taxes are taxes where the marginal tax rate rises with income.
Those who earn more, pay more taxes
What are regressive taxes? Give an example.
Regressive taxes are taxes that will affect the poor more than the rich.
Specific indirect taxes are regressive.
What is the marginal tax rate?
The tax on additional income. It is the amount of additional tax paid divided by an change in income.
What are the pros and cons of specific taxes?
Pros: It is easy to implement
Cons: they are regressive (average tax rate rises as income drops)
What are the pros and cons of specific taxes?
Pros: can help reduce the income gap
Cons: decentivises people from high paying jobs, (as they are going to be taxed!)
Diferrences between proportional taxation, progressive taxation, and regressive taxation?
Proportional taxation: Same proportion of tax no matter the income. Rich and poor pay the same proportion (Not amount!). Marginal rate (tax on additional income) is constant.
Progressive taxation: Increasing proportion of tax as income increases. Marginal rate increases as income increases. Rich people pay a larger proportion than poorer people.
Regressive taxation: Tax burdens low income households more than higher income households. Marginal rate decreases as income increases.
what are transfer payments?
Government given benefits of goods, coupons, or money to poor households.
Pros and cons for minimum wage and price controls?
Pros: Minimum wage can protect workers and price controls can protect consumers.
Cons: Companies may layoff workers and unemployment can rise. Deadweight loss can occur with price controls.
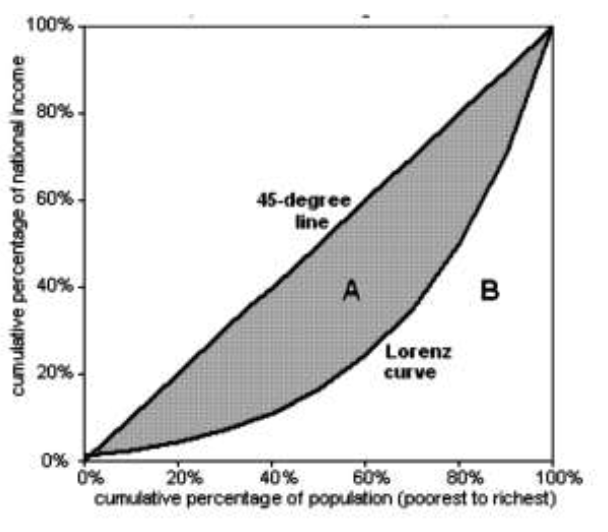
Decribe the graph with a lorenz curve. (Axis lables and 2 curves
Y axis is the cumulative percentage of national income, x axis is the cumulative percentage of population.
The straight line is the line of absolute equality, and the curve is the lorenz curve.
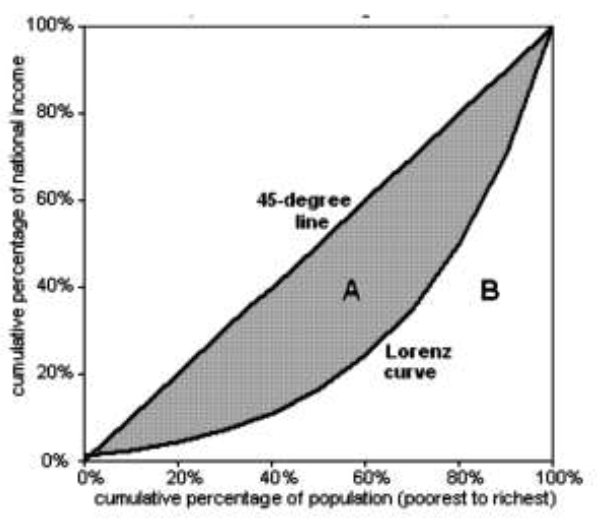
What is the gini coefficient? How to calculate it?
What does a gini coefficient = 1 mean?
What does a gini coefficient < 1 mean?
What does a gini coefficient = 0 mean?
It is a measure of equality in income distribution. It is namely A / A+B
Gini coefficient = 1 means absolute equality
Gini coefficient < 1 means there is some inequality.
Gini coefficient = 0 means 1 person owns 100% of the national income.
The closer to 1, the more equal income is distributed.
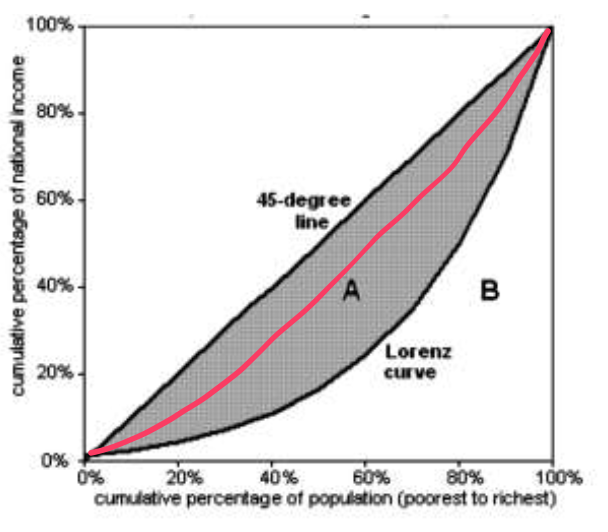
What happend to the lorenze curve if the gini coefficient gets closer to 1
It gets closer to the line of absolute equality
What are the causes of income and wealth inequality?
Labour market explanation
Different jobs are valued differently at different times, so people will get paid differently. Higher skilled workers will be paid more than lower skill ones.
Inheritance
Some people will get an advantage over others due to family wealth that is accumulated over generations. More wealth means a higher capacity to generate more income.
Demographic changes
If the demographic of the country ages, young people will have to work to support the pensions of the older generation. Taxes could then burden a portion of society more than another.