ARCC BU REVIEWER PART 5 (Acoustics)
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From recorded lecture video (2024)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
CHB Wall
This is the most economical material to insulate sound inside a room/reflect sound around a room
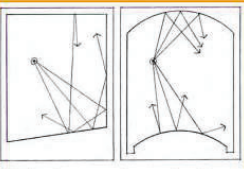
Reflection
An acoustic phenomenon where resultant sound energy returned from a surface that is not absorbed or otherwise dissipated upon contact with the surface (leads to echoes)
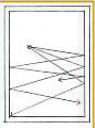
Refraction
An acoustic phenomenon where there is a change in the direction (along with speed and/or wavelength) of waves as they pass from one medium to another.
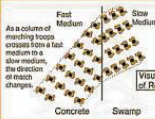
Diffraction
An acoustic phenomenon where there is bending of the travel of sound caused by an obstacle in its path; being of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves beyond small opening
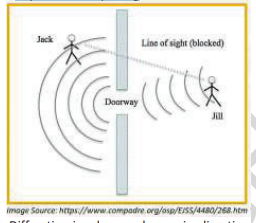
Diffusion
An acoustic phenomenon where sound reflects off a convex or uneven surface that spreads/disperses it so that it is less direct
Absorption
An acoustic phenomenon where sound is absorbed by soft materials
hard, smooth, and plain
Sound reflects off _______ surfaces (e.g. reinforced concrete, granite stone)
The back wall of the room/wall facing to the speaker
In a classroom/auditorium setting, the surface of this object should be soft—so that sound doesn’t reflect back from here to the speaker in front
Reflective materials
Classrooms, auditoriums, boardrooms, and courtrooms all need spaces with this type of acoustic materials.
Low ceilings
This feature in auditoriums are the reason why back rows can still receive reflected soundwaves despite their distance from the front
Soft surfaces
Cinemas are equipped with these types of surfaces (e.g. cloth, fabric) that absorb intense sound coming from its sound systems.
Absorptive Materials
Cinemas, open offices, home theaters, conference rooms, and recording studios all commonly need spaces with this type of acoustic materials.
Diffusive materials
These are hard materials with convex/concave, uneven, or rough surfaces, typically used in performance centers, operas, and home theaters.