The Cenozoic Era: Evolution and Climate Changes
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
222 Terms
What does the term 'Cenozoic Era' translate to?
New life.
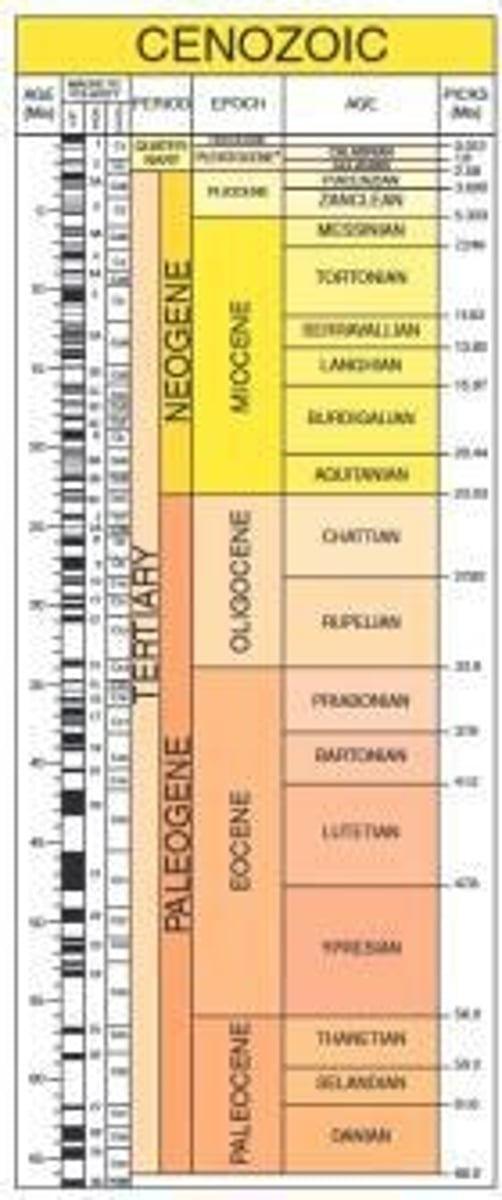
When did the Cenozoic Era begin and end?
It extends from about 65 million years ago (Ma) to the present.
What significant event marks the beginning of the Cenozoic Era?
It begins after the mass extinction that took out the dinosaurs.

Which group of animals dominated during the Cenozoic Era?
Mammals.

What are the three periods into which the Cenozoic Era is divided?
Paleogene, Neogene, and Quaternary.
What major tectonic change occurred during the Cenozoic Era?
Continents took on near modern shapes and locations.
What geographical feature formed as India collided with Asia during the Cenozoic Era?
The Himalayan Mountains.

What was the climate like during the Paleocene epoch?
It was mainly a recovery time with lush vegetation coverage due to a warm climate.
What was the average global temperature at the end of the Paleocene epoch?
Roughly 75 °F (24 °C).
Which species became dominant land species during the Paleocene?
Mammals and birds.
What major climate event is associated with the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM)?
Up to 4.5 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean.
What were some causes of the PETM?
Large volcanic episodes, meteorite impacts, peat burning from wildfires, and methane release from submarine gas hydrates.
What was the state of oceanic life during the Cenozoic Era?
Oceans were void of large Mesozoic reptiles, and sharks became the dominant oceanic predators.

What percentage of fish species went extinct during the K-Pg extinction?
Only about 12%.
How did placental mammals evolve during the Paleocene?
They continued to diversify and develop, with emerging species being approximately 9% larger.
What significant change occurred in bird species during the Paleocene?
Birds diversified and certain species reached giant sizes.
What was the impact of the lack of large reptiles on mammal diversification?
Birds and mammals rapidly diversified without the threat of large reptiles.
What geological feature continued to rise during the Cenozoic Era?
The Rocky Mountains due to the Laramide Orogeny.
How did the Americas change during the Cenozoic Era?
They migrated closer together but were not yet connected.
What was the role of oceanic predators during the Cenozoic Era?
Sharks became the dominant oceanic predators.
What was the significance of the Isthmus of Panama during the Cenozoic Era?
It eventually connected the Americas.
What was the state of plant diversity during the Late Paleocene?
Fossils suggest limited forest plant diversity until the Late Paleocene.
What was the climate condition at the poles during the PETM?
There was no glaciation at the poles.
What is G Altiatlasius known for?
It is the oldest primate-like mammal genus and the first true primate, with only a few teeth and a jaw fragment discovered from Morocco.
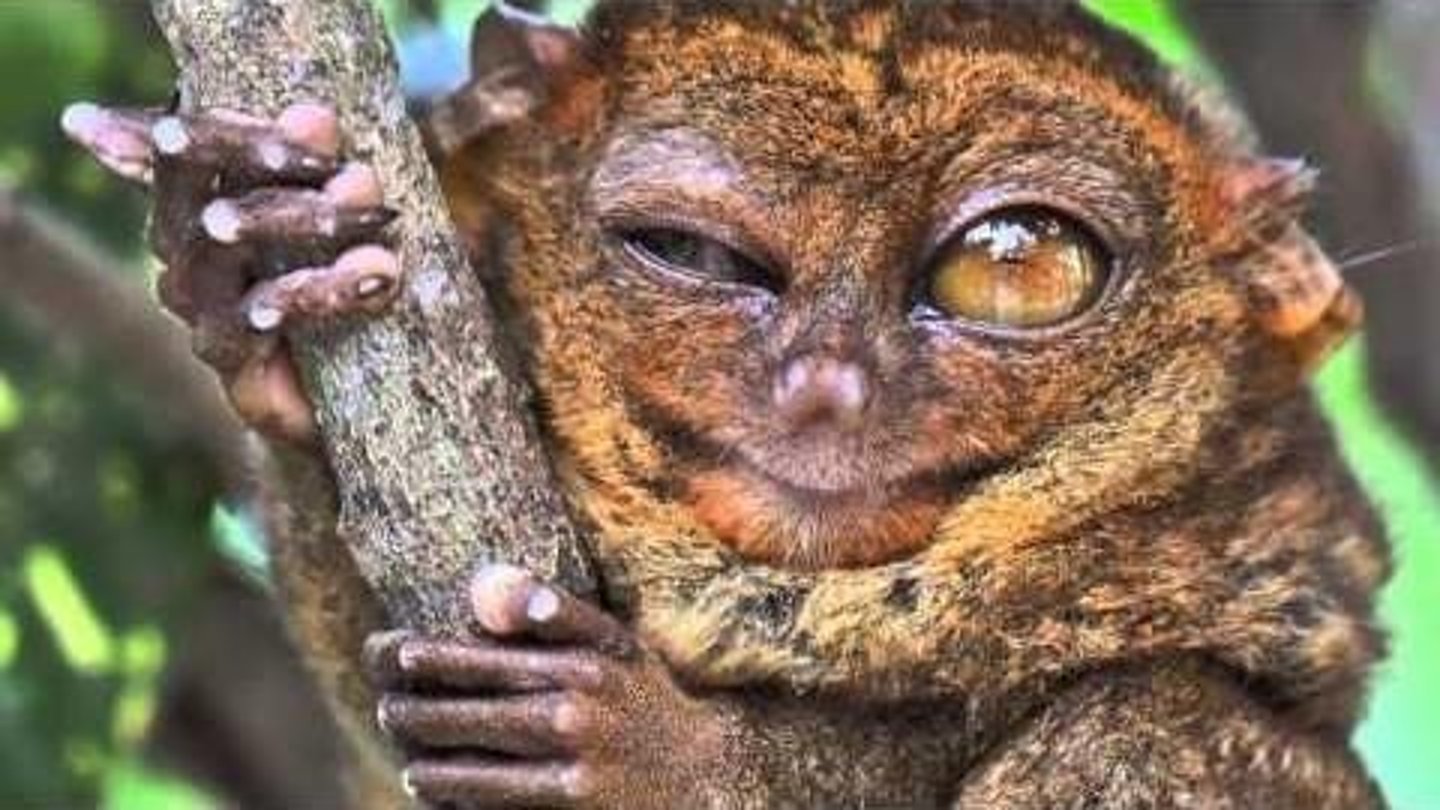

What characteristics suggest that G Altiatlasius was tree dwelling?
It had short strong limbs, long claws, and a long bushy tail.
What is the estimated weight of G Altiatlasius?
About 4.5 lbs (2.2 kg).
What are the two main hypotheses regarding G Altiatlasius's relation to modern primates?
Some researchers believe it might be an ancient forefather of monkeys and apes, while others think it is similar to a group of primitive tarsier-like primates.
What does the term 'Creodonta' translate to?
It translates to 'flesh tooth'.
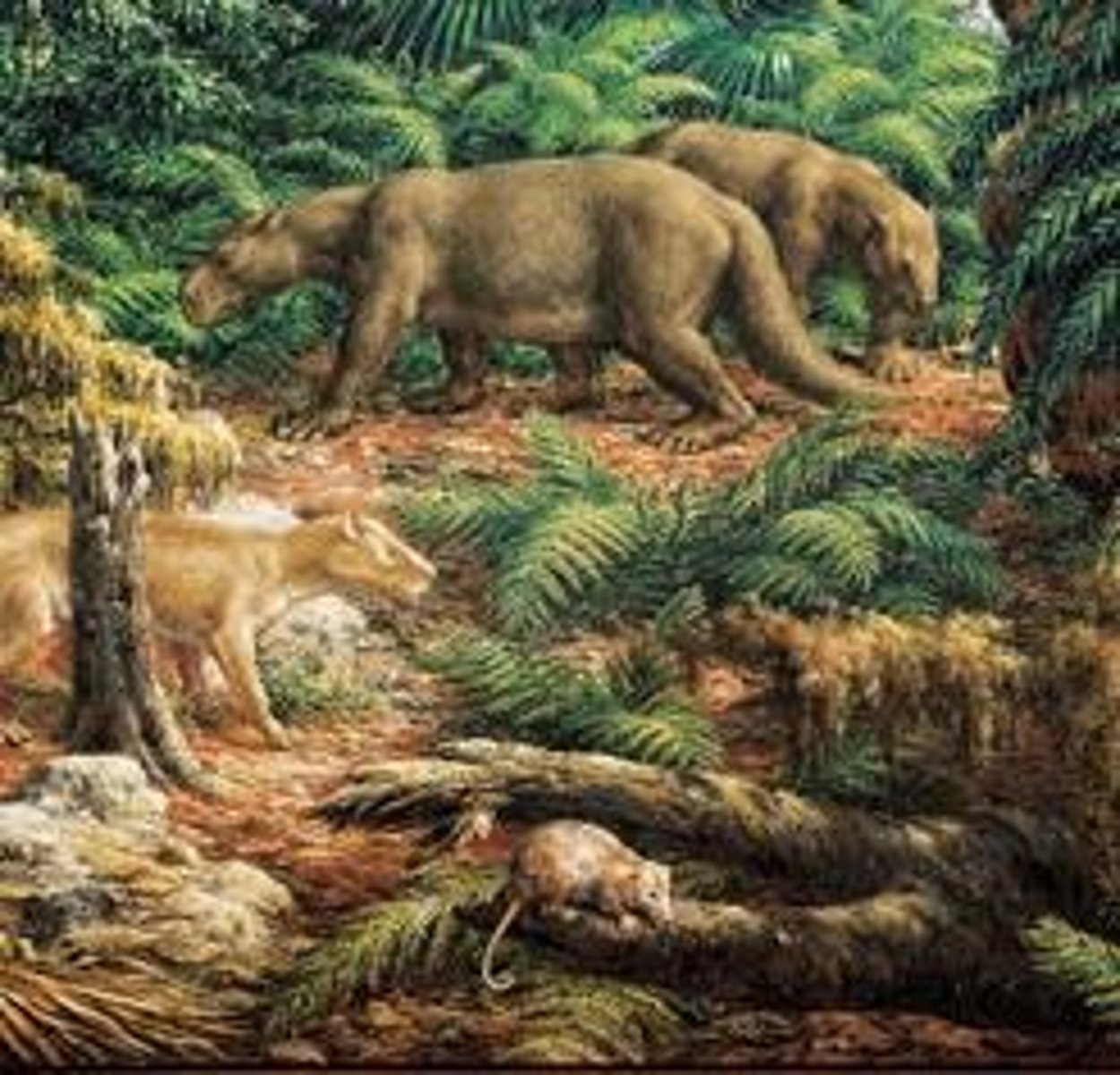
What distinguishes the earliest creodonts?
They were the first large-sized obviously carnivorous mammals, but are technically not in Order Carnivora due to their teeth structure.
What are Phorusrhacidae commonly known as?
Terror Birds.
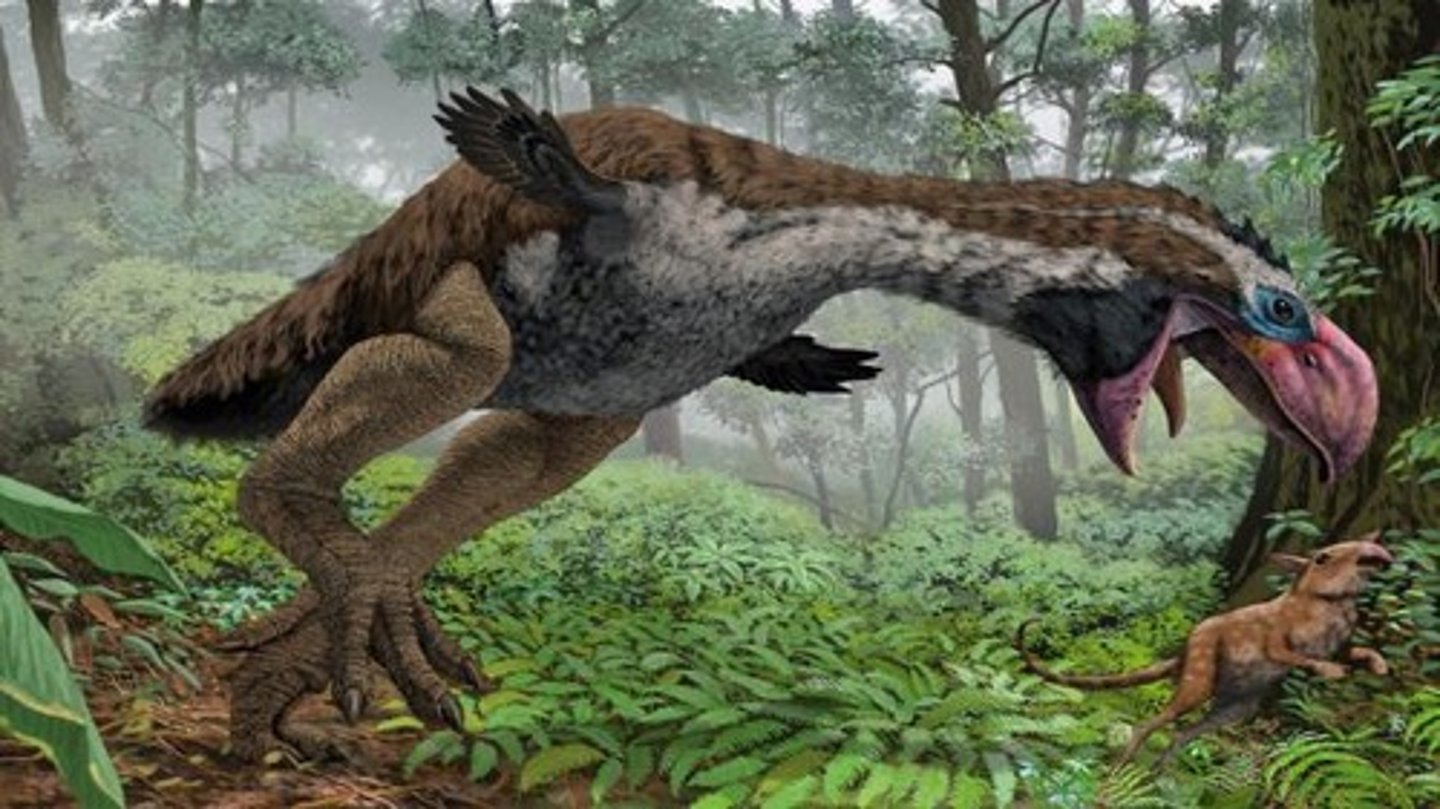

What are the size and weight range of Phorusrhacidae?
They were extremely large flightless birds, 3-10 ft (1-3 m) tall, weighing up to 223 lbs (101 kg).

What was the ecological role of Phorusrhacidae during the Cenozoic?
They were the largest predators in South America.
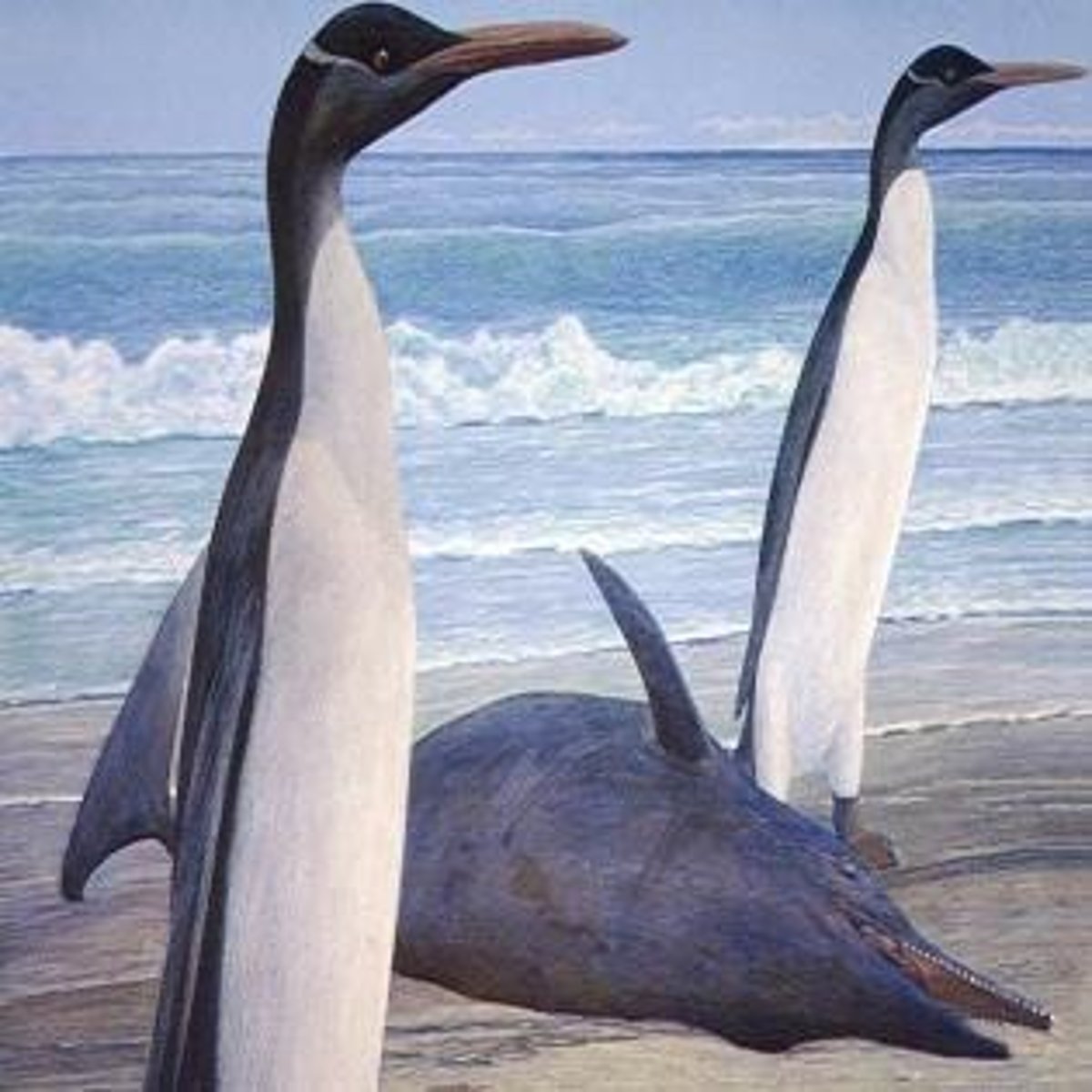
What significant discovery was made about Kumimanu?
It was discovered in New Zealand in 2017 and is a giant and distant relative of penguins.
What was the average global temperature by the end of the Paleocene?
The average global temperature was approximately 57 °F (14 °C).
Which of the following was NOT a possible cause for the Paleocene Eocene Thermal Maximum?
Human induced Carbon emissions.
What were the first large-sized obviously carnivorous mammals during the Eocene?
Creodonts.
What characterized the Eocene transition in terms of climate?
It transitioned from the warmest Cenozoic epoch to a cooling stage.
What was the global temperature during the Eocene?
Roughly 86 °F (30 °C) with little temperature change from pole to pole.
What significant plant appeared during the Late Eocene?
The first primitive cacti.
How did forestation change during the Eocene?
It started with warm temperatures and oceans conducive to plant growth, leading to the spread of forests from pole to pole.
What happened to deciduous forests by the end of the Eocene?
Deciduous forests covered large areas of northern continents.
What was the impact of cooling on rainforests during the Eocene?
Rainforests became dense and common, spreading to higher latitudes.
What climatic trend began midway through the Eocene?
Cooling started, favoring deciduous trees and converting forests to tundra.
What are Plesiadapids?
Early primitive primates, whales, and horses.
What are Creodonts?
An extinct group of carnivorous mammals that thrived during the Cenozoic.

What significant climatic event occurred during the Eocene epoch?
The transition from the warmest Cenozoic epoch to a cooling stage.
What major plant development occurred during the Late Eocene?
The first primitive cacti appeared according to molecular studies.

How did the Eocene affect forestation?
It started with warm temperatures conducive to plant growth, leading to extensive rainforestation.
What type of forests were common during the Eocene?
Dense rainforests were common, restricted to equatorial regions.
What happened to deciduous forests by the end of the Eocene?
They covered large areas of northern continents.
How did the climate change affect tree species during the Eocene?
Cooling favored deciduous trees and led to the conversion of forests to tundra.
What evidence suggests the early diversification of mammals?
Most modern mammal orders appeared within the early Eocene.
What is the significance of grass-like structures found in Cretaceous coprolites?
They suggest that grass existed around 66 million years ago, earlier than previously thought.
What impact did the Eocene-Oligocene extinction have?
It mostly affected marine or aquatic organisms.
What were the causes of the Eocene-Oligocene extinction?
Global cooling phase, extensive volcanism, and large meteorite impacts.
What types of mammals evolved during the Eocene?
Early primates, whales, horses, and many other early mammal forms.
What was the effect of grass expansion during the Eocene?
It fostered the evolution of numerous grazing mammals.
What characterized the forest creatures during the Eocene?
Dense forest species were unable to evolve into larger sizes, with no species present over 22 lbs (10 kg).
What climatic conditions did the Eocene start with?
Warm temperatures and oceans conducive to plant growth.
What happened to the rainforests by the end of the Eocene?
They spread to higher latitudes, with tropical and subtropical plants found as far north as Greenland and Alaska.
What was the impact of Antarctic glaciation during the Eocene?
It contributed to the cooling phase and affected global climate.
What is the significance of the PETM in relation to the Eocene?
It marks the warmest epoch of the Cenozoic before transitioning into a cooling stage.
What role did extensive volcanism play during the Eocene?
It contributed to the global cooling and extinction events.
What are some examples of early mammals mentioned in the notes?
Pakicetus, Necrolemur, and Mesohippus.
What significant event may have contributed to Antarctic glaciation during the Eocene?
The Azolla Event, which involved large blooms of aquatic ferns that consumed CO2.
What was the effect of the Azolla blooms on atmospheric CO2 levels?
They caused a significant decrease in atmospheric CO2.
How did the Antarctic Circumpolar Current relate to the Azolla Event?
It may have been triggered by the Azolla Event, isolating cold waters and reducing incoming warm current heat transport.
What was the estimated weight range of Andrewsarchus, the largest carnivorous mammal of the Eocene?
1500-2200 lbs (700-1000 kg).
What was the migration rate of India toward Asia before the Eocene?
3.5-6 inches per year (9-16 cm/yr).
What was the reduced migration rate of India during the Eocene?
1.5-3.5 inches per year (4-6 cm/yr).
Which animal is regarded as the first (basal) whale?
Pakicetus.

What characteristics did Pakicetus demonstrate that link it to whales?
It had inner ear features found only in the whale family (Cetaceans) and a skull resembling that of toothed whales.
What is the size range of the early whale genus Rodhocetus?
3-6.5 feet (1-2 m).

What was Mesohippus, and how did it compare to modern horses?
A distant horse relative, taller than previous relatives but much smaller than modern horses, with no hooves and two small side toes.
What is the significance of Necrolemur in relation to modern animals?
It is related to Tarsiers and had a relatively large brain for its size.
What was the highest average global temperature during the Eocene?
86 °F (30 °C).
Which plant bloom is linked to Eocene cooling?
Azolla.
Which statement about Eocene tetrapods is FALSE?
Eocene horse relatives were no taller than 2 ft (0.6 m) is false; they were taller.
What was the appearance of the animal that exhibited a rhinoceros-like appearance but was more closely related to horses?
Brontothere.
What was a notable feature of the brontothere's horns?
They were made of bone, not keratin like modern rhinos.
What was the significance of the Antarctic glaciation during the Eocene?
It marked a significant cooling period in Earth's climate.
What geological event is associated with the Himalayas during the Eocene?
The Himalayan Orogeny.
What role did Azolla play in the Eocene climate?
It consumed large amounts of CO2, contributing to cooling.
What is the relationship between Azolla and the Arctic Ocean during the Eocene?
High CO2 levels possibly caused Azolla blooms across the Arctic Ocean.
What type of currents did Azolla create in the ocean?
Large circulating currents (gyres) that upwelled colder deep waters.
What is the significance of the fossil record of the Eocene?
It provides insights into the evolution of mammals and climate changes during that period.
What type of animal is Moeritherium considered to be?
An early proboscidian and the earliest ancestor to modern elephants.
What significant event marks the start of recovery in early mammals?
Recovery from an extinction event.
What is the Grande Coupure?
A sudden change in animal life in western Europe, where many new animal groups from Asia immigrated and replaced earlier Eocene animal groups.
Which animal is considered a stem ancestor for Old World monkeys?
Aegyptopithecus.
What are the two main lineages of early canine relatives?
Foxes, coyotes, wolves, and dogs.
What are the two main lineages of early feline relatives?
Wildcats, big cats, and domestic cats.
What is the significance of the Paleogene epoch in relation to mammal evolution?
It marks the final epoch during which significant evolutionary changes occurred.
What are the characteristics of New World monkeys?
They have widely spaced circular nostrils, non-padded buttocks, and sometimes prehensile tails.
What are the characteristics of Old World monkeys?
They have narrow downward pointing nostrils, more padded buttocks, non-prehensile tails, and are typically larger in size.
What is the approximate size of Aegyptopithecus?
1.8 - 3 ft (0.5-0.9 m).
What are the two possible ways that monkeys could have migrated to South America?
Rafting and a land bridge.
What is the significance of the Eocene in relation to monkey evolution?
The earliest monkeys may have appeared during the Eocene, just before Aegyptopithecus.
What is Basilosaurus known for?
Being one of the first fully aquatic whale relatives.
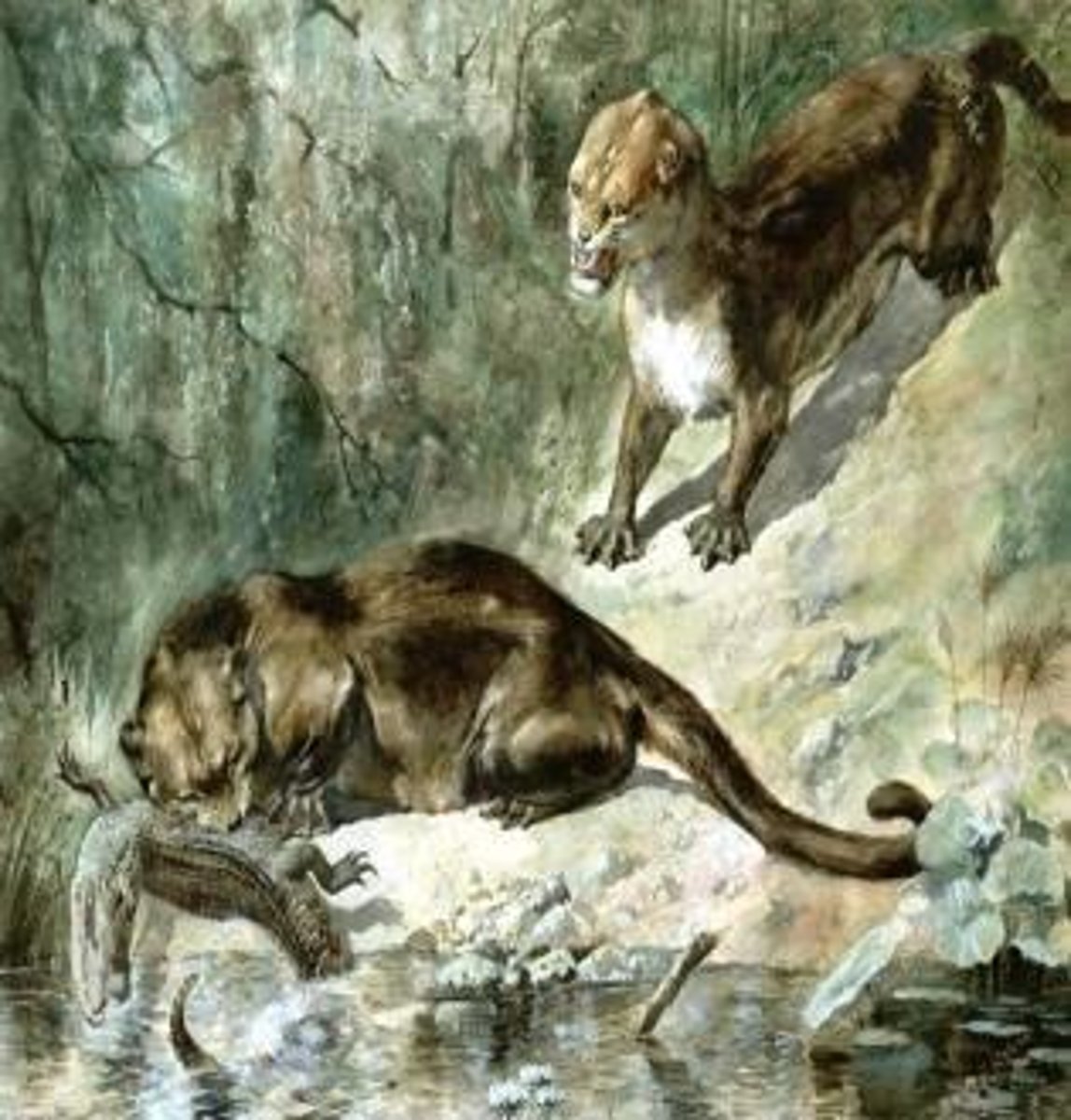

What size did Gigantophis reach?
Up to 35 ft (~10.5 m).