8th Grade US History Comp - Flashcards
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Colonization
The establishment of settlements by European powers in North America.
Revolutionary Era
The period of the American Revolution leading to independence from British rule.
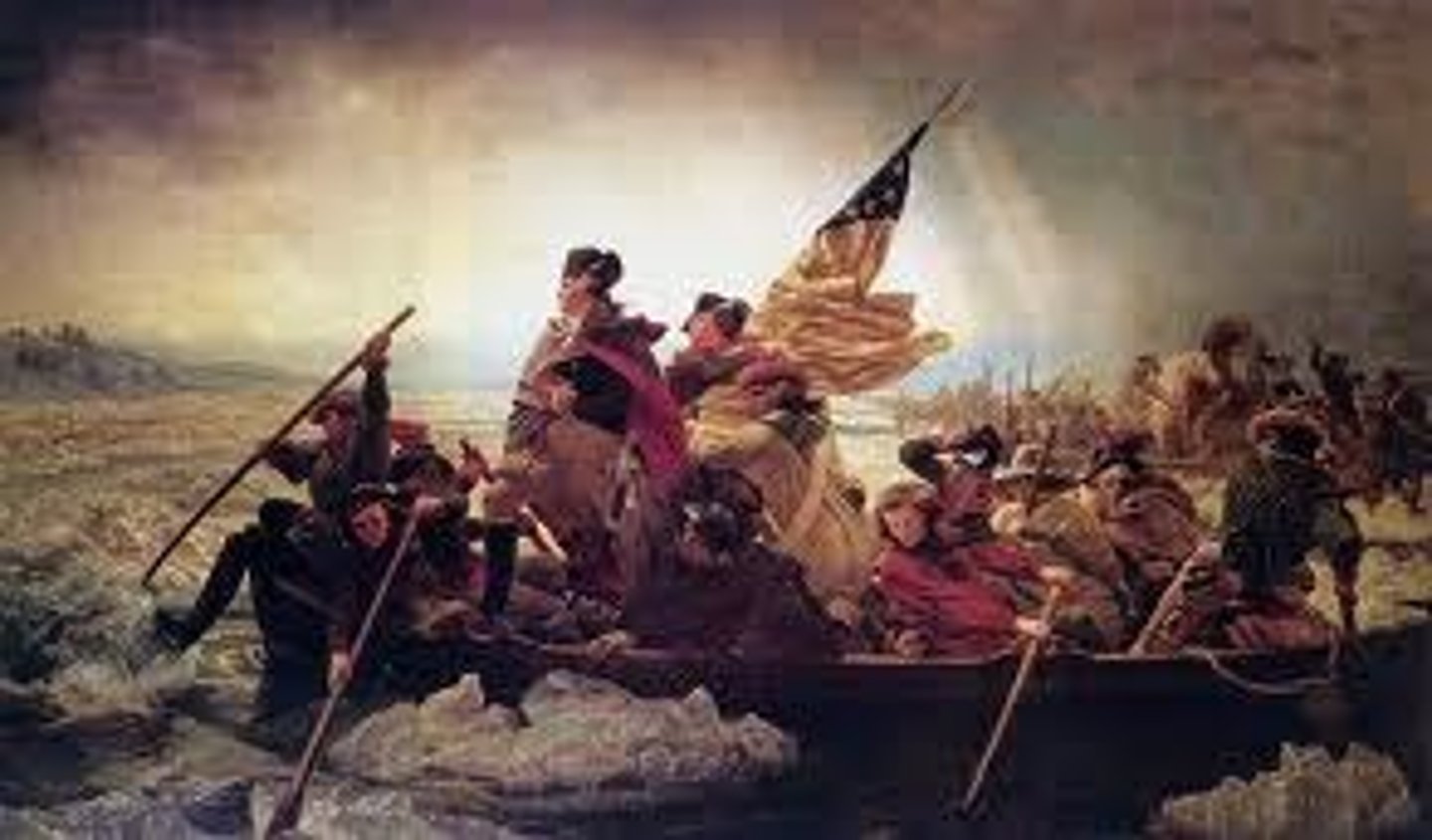

Creation and Ratification of the Constitution
The process of drafting and approving the U.S. Constitution in 1787.

Early Republic
The period in U.S. history following the ratification of the Constitution.

Age of Jackson
The era during the presidency of Andrew Jackson, characterized by increased democracy.

Westward Expansion
The movement of settlers into the western territories of the United States.
Reform & Culture Movements
Social movements aimed at improving society & culture during the 19th century.
Sectionalism
The division of the United States into different regions with distinct interests.
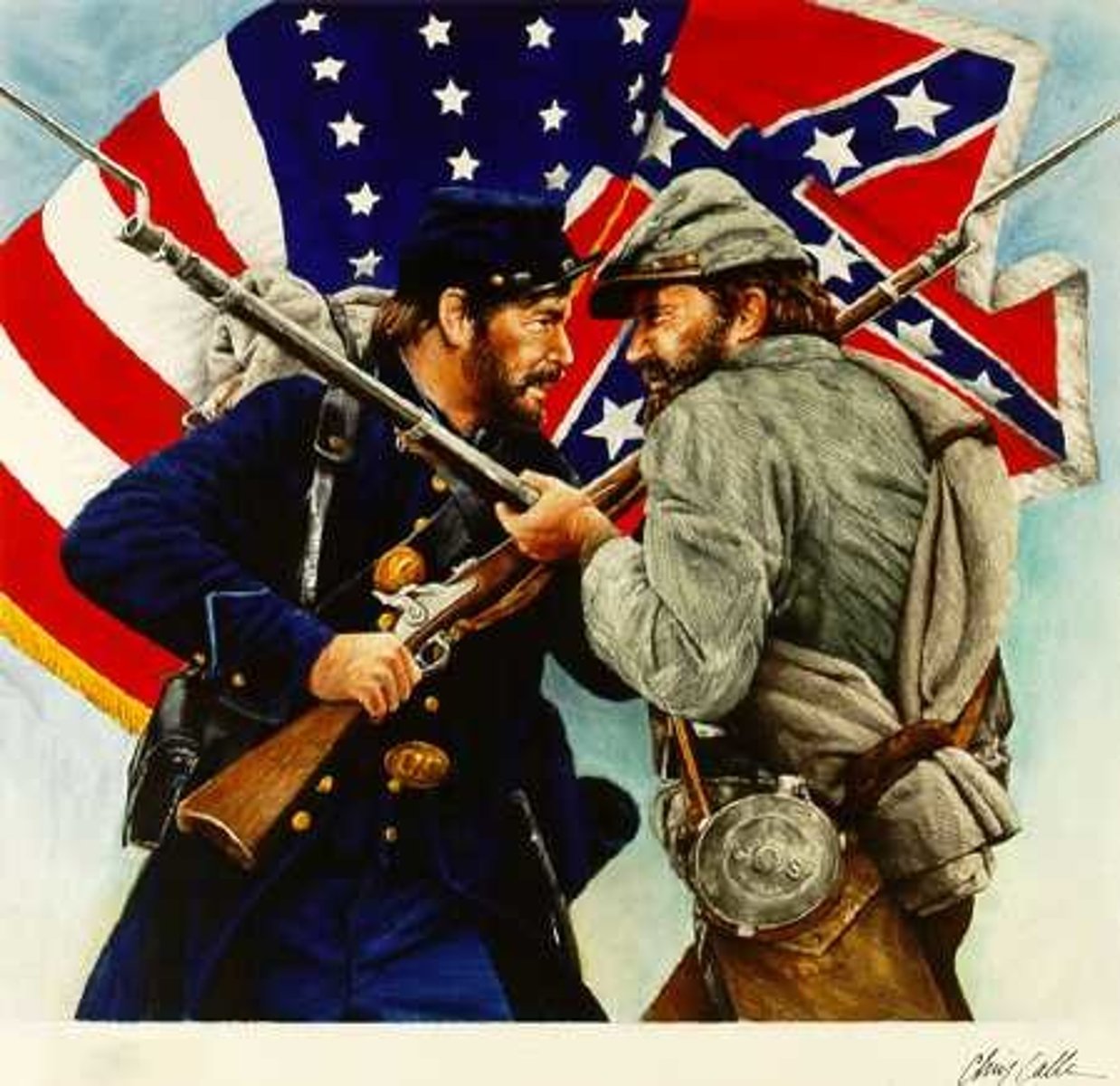
Civil War
The conflict between Northern and Southern states from 1861 to 1865.

Reconstruction
The period following the Civil War focused on rebuilding the South and integrating emancipated African Americans.
1607 - Jamestown
The first permanent English settlement in North America.
1620 - Mayflower Compact
The document was signed by the Pilgrims aboard the Mayflower ship who agreed to act as a single political body and follow laws made by the group. It is the first sign of self-governance in the New World.

1776 - Declaration of Independence
Adoption of the Declaration of Independence.

1787 - The U.S. Constitution
The document which replaced the Articles of Confederation & structured the 3 branches of the U.S. Political System.

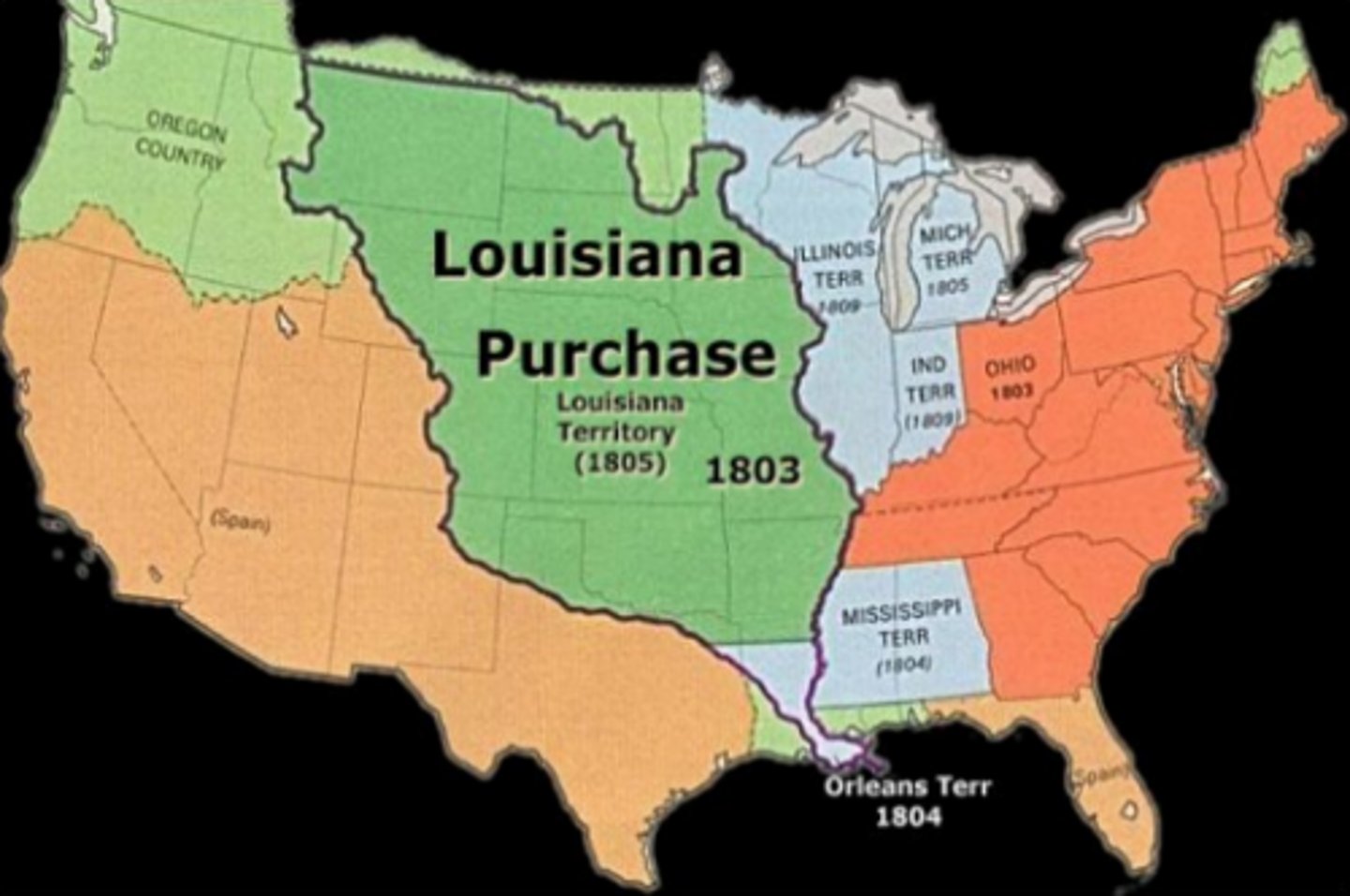
1803 - Louisiana Purchase
Purchasing this land from France doubled the size of the United States.
Reasons for Exploration
Political, economic, religious, and social motivations for European exploration.
congress
a meeting of delegates to discuss or vote on matters of concern.
1638 - Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
considered the first written constitution in America, establishing a framework for government.

Virginia House of Burgesses
The first legislative assembly in the American colonies, established in Virginia.

Causes of the American Revolution
Factors leading to the American Revolution, including the Proclamation of 1763, the Stamp Act, & the Townshend Acts (1766 - 1767).
American Revolution key figures
Key figures such as Abigail Adams, Thomas Jefferson, and George Washington who influenced the revolution.
Events of the American Revolution
The battles of Lexington and Concord, and the signing of the Treaty of Paris of 1783.

1787 - Constitutional Convention
Meeting to address issues with the Articles of Confederation, leading to the creation of the Constitution.
Major domestic problems of the new republic
Maintaining national security, creating a stable economic system, and setting up the court system.
1783 - Fugitive Slave Act
The law threatened the safety of all African Americans, slave and free, and forced many Northerners to become more defiant in their support of fugitives during the late 18th century.
The Jacksonian Era
Which era dealt with issues regarding protective tariffs (the tariff of abominations), taxation, and the banking system?
free enterprise system
a system in which privately owned businesses operate with minimal government regulation.

War of 1812
Explain the causes, important events, and effects of the War of 1812.

Foreign policies of presidents Washington through Monroe
Identify the foreign policies of presidents Washington through Monroe and explain the impact of Washington's Farewell Address and the Monroe Doctrine.
Election of Andrew Jackson
Explain the impact of the election of Andrew Jackson, including expanded suffrage.
Removal and resettlement of Cherokee Indians
Analyze the reasons for the removal and resettlement of Cherokee Indians during the Jacksonian era, including the Indian Removal Act, Worcester v. Georgia, and the Trail of Tears.
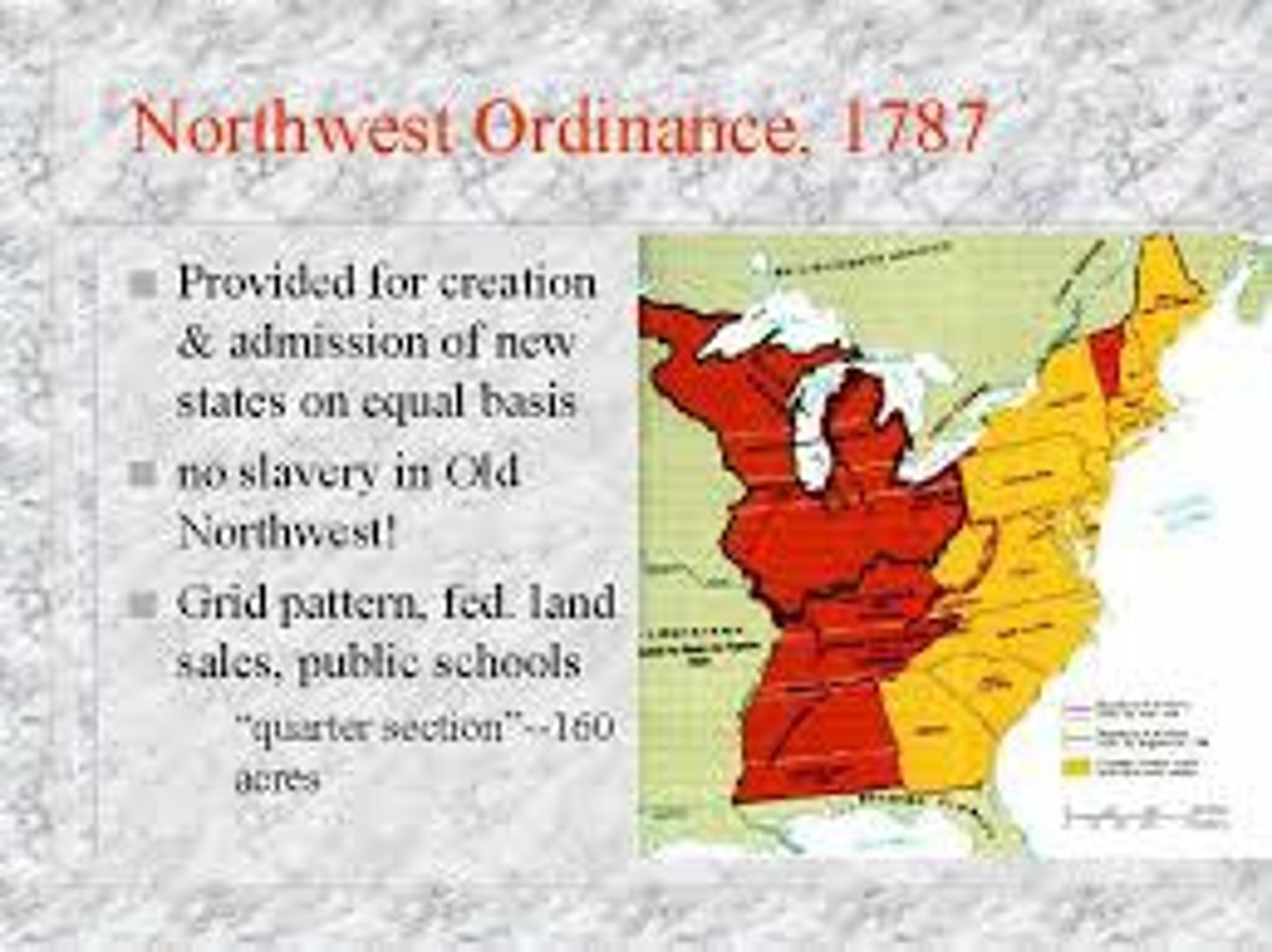
Northwest Ordinance
Explain how the Northwest Ordinance established principles and procedures for orderly expansion of the United States.
Westward growth of the nation
Analyze the westward growth of the nation, including the Louisiana Purchase and Manifest Destiny.
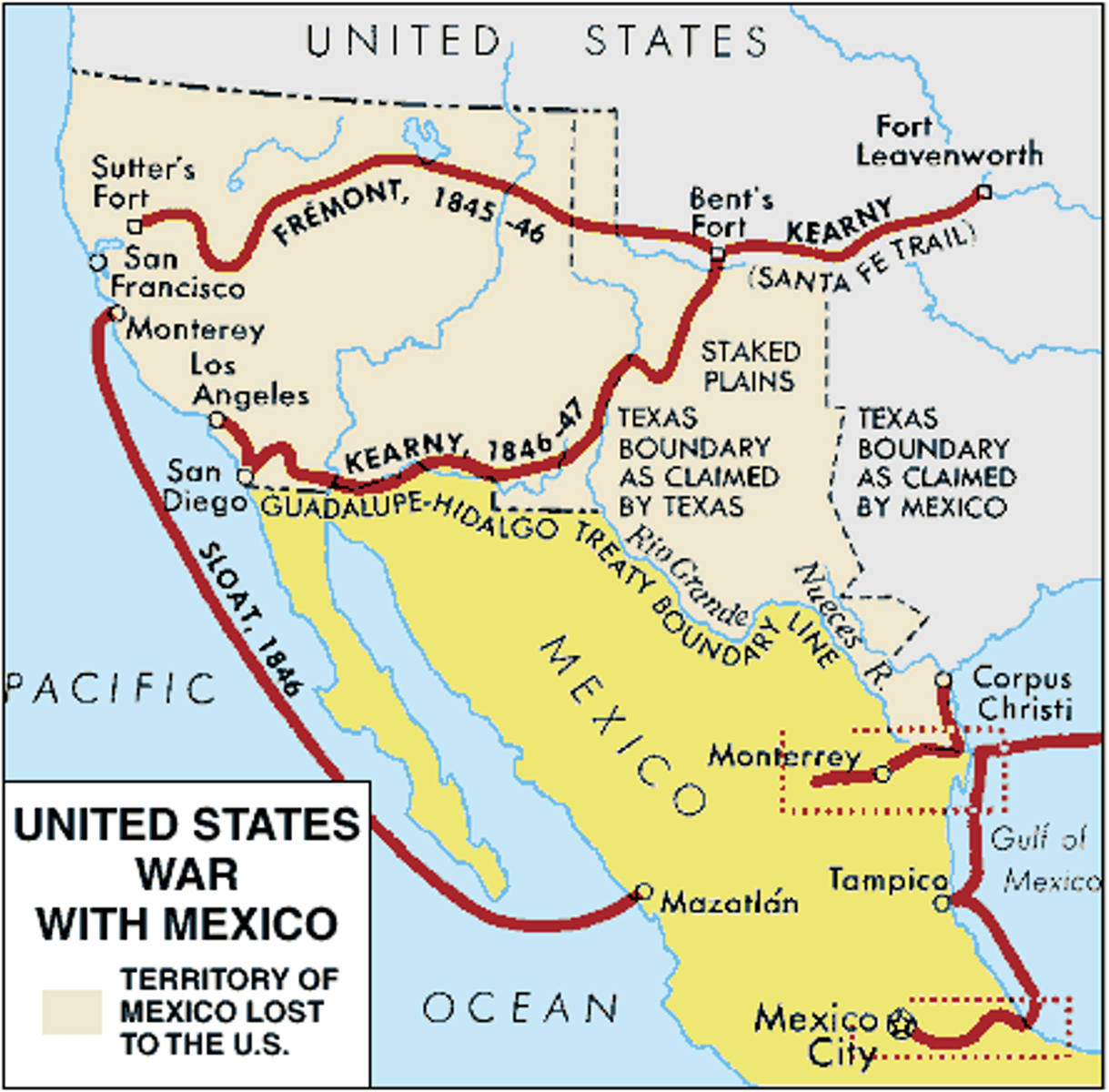
U.S.-Mexican War
Explain the causes and effects of the U.S.-Mexican War and their impact on the United States.
Tariff policies before the Civil War
Analyze the impact of tariff policies on sections of the United States before the Civil War.
Political, economic, and social factors on slaves and free blacks
Compare the effects of political, economic, and social factors on slaves and free blacks.

1850 - Fugitive Slave Act
Analyze the impact of the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 on slavery, free Blacks, and abolitionists.

Impact of slavery on different sections of the United States
Analyze the impact of slavery on different sections of the United States.
Congressional conflicts and compromises prior to the Civil War
Identify the provisions and compare the effects of congressional conflicts and compromises prior to the Civil War, including the role of John Quincy Adams.
Significant individuals during the Civil War
Explain the roles played by significant individuals during the Civil War, including Jefferson Davis, Ulysses S. Grant, Robert E. Lee, and Abraham Lincoln, and heroes such as congressional Medal of Honor recipients William Carney and Philip Bazaar.
Expansion of slavery
Explain the central role of the expansion of slavery in causing sectionalism, disagreement over states' rights, and the Civil War.
Significant events of the Civil War
Explain significant events of the Civil War, including the firing on Fort Sumter; the battles of Antietam, Gettysburg, and Vicksburg; the Emancipation Proclamation; Lee's surrender at Appomattox Court House; and the assassination of Abraham Lincoln.
Abraham Lincoln's ideas
Analyze Abraham Lincoln's ideas about liberty, equality, union, and government as contained in his first and second inaugural addresses and the Gettysburg Address and contrast them with the ideas contained in Jefferson Davis's inaugural address.

Effects of Reconstruction
Understand the effects of Reconstruction on the political, economic, and social life of the nation.

Radical Reconstruction
Evaluate legislative reform programs of the Radical Reconstruction Congress and reconstructed state governments.

Hiram Rhodes Revels
Explain the impact of the election of African Americans from the South such as Hiram Rhodes Revels.

Reconstruction Problems
Explain the economic, political, and social problems during Reconstruction and evaluate their impact on different groups.

Geographic Influences
Demonstrate an understanding of geographic and cultural influences on historical issues and events.
Major Eras and Turning Points
Locate places and regions directly related to major eras and turning points in the United States during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries.

Physical and Human Characteristics
Compare places and regions of the United States in terms of physical and human characteristics.
Geographic Factors
Analyze the effects of physical and human geographic factors such as weather, landforms, waterways, transportation, and communication on major historical events in the United States.

Population Distribution
Analyze how physical characteristics of the environment influenced population distribution, settlement patterns, and economic activities in the United States.
Human Modification
Describe the positive and negative consequences of human modification of the physical environment of the United States.
Racial, Ethnic, and Religious Groups
Identify racial, ethnic, and religious groups that settled in the United States and explain their reasons for immigration.

Urbanization Conflicts
Explain how urbanization contributed to conflicts resulting from differences in religion, social class, and political beliefs.
Conflict Resolution
Identify ways conflicts between people from various racial, ethnic, and religious groups were addressed.

Contributions to National Identity
Analyze the contributions of people of various racial, ethnic, and religious groups to our national identity.
Women's Contributions
Identify the political, social, and economic contributions of women to American society.
Abolition Movement
Describe and evaluate the historical development of the abolition movement, including activities that focused attention on the moral ills of slavery.

Impact of Reform Movements
Evaluate the impact of reform movements, including educational reform, temperance, the women's rights movement, prison reform, the labor reform movement, and care of the disabled.

Religious Freedom Development
Trace the development of religious freedom in the United States.

Religious Influences
Describe religious influences on social movements, including the impact of the first and second Great Awakenings.

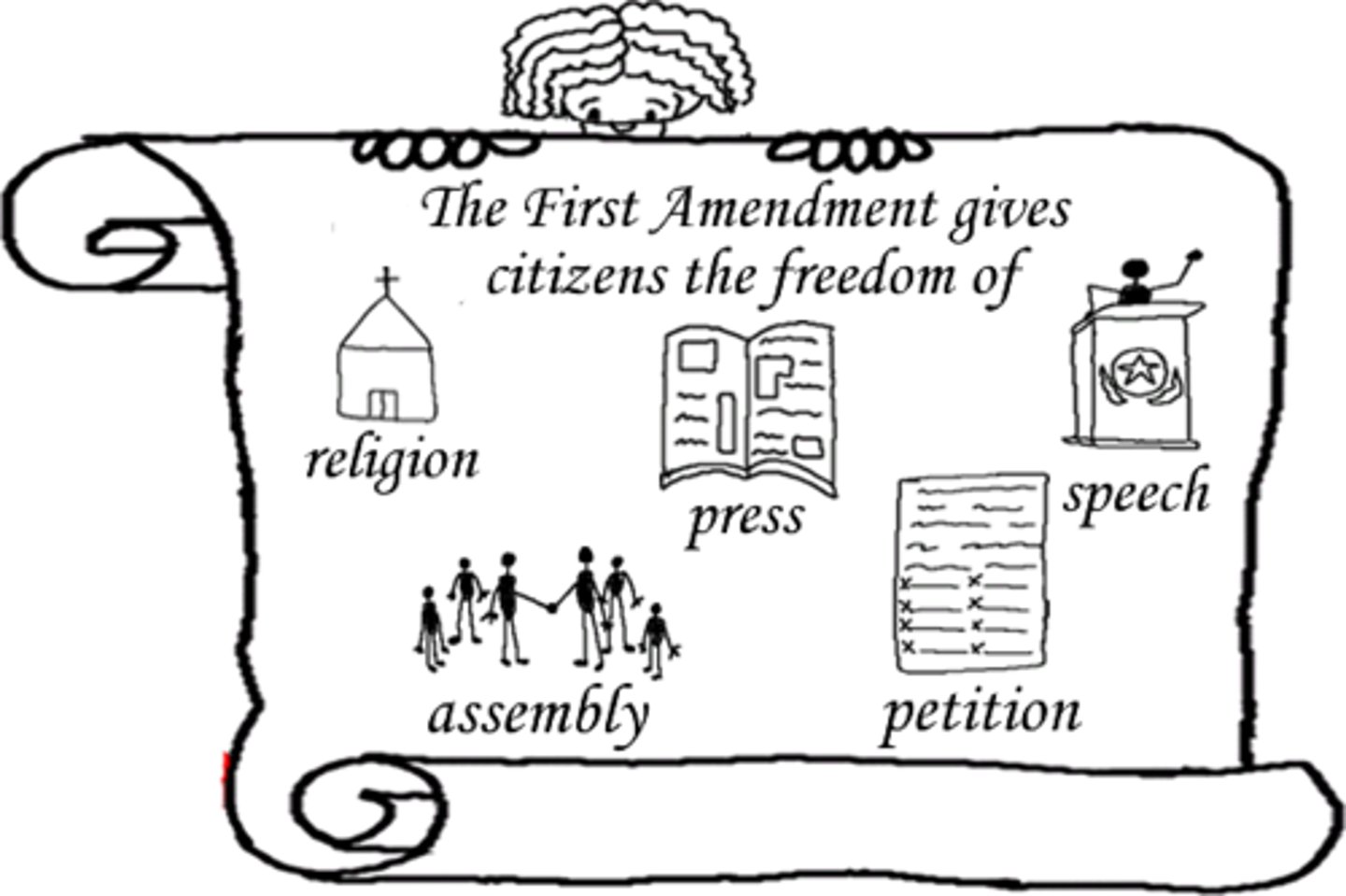
First Amendment Impact
Analyze the impact of the First Amendment guarantees of religious freedom on the American way of life.
Arts and Times Relationship
Understand the relationship between the arts and the times during which they were created.
Hudson River School artists
Examples of American art that reflect society in different eras.

Battle Hymn of the Republic
An example of American music that reflects society in different eras.

Transcendental literature
An example of American literature that reflects society in different eras.

American beliefs and principles
Reflected in the Declaration of Independence, the U.S. Constitution, and other important historic documents.
Magna Carta
An historic document that influenced the U.S. system of government.

English Bill of Rights
An historic document that influenced the U.S. system of government.

Federalist Papers
An historic document that influenced the U.S. system of government.

Articles of Confederation
A document whose strengths and weaknesses are summarized by students.

Colonial grievances
Listed in the Declaration of Independence and addressed in the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights.

U.S. Constitution
Reflects the principles of limited government, republicanism, checks and balances, federalism, separation of powers, popular sovereignty, and individual rights.

Thomas Hooker
A significant individual in the development of self-government in colonial America.

Charles de Montesquieu
A significant individual in the development of self-government in colonial America.

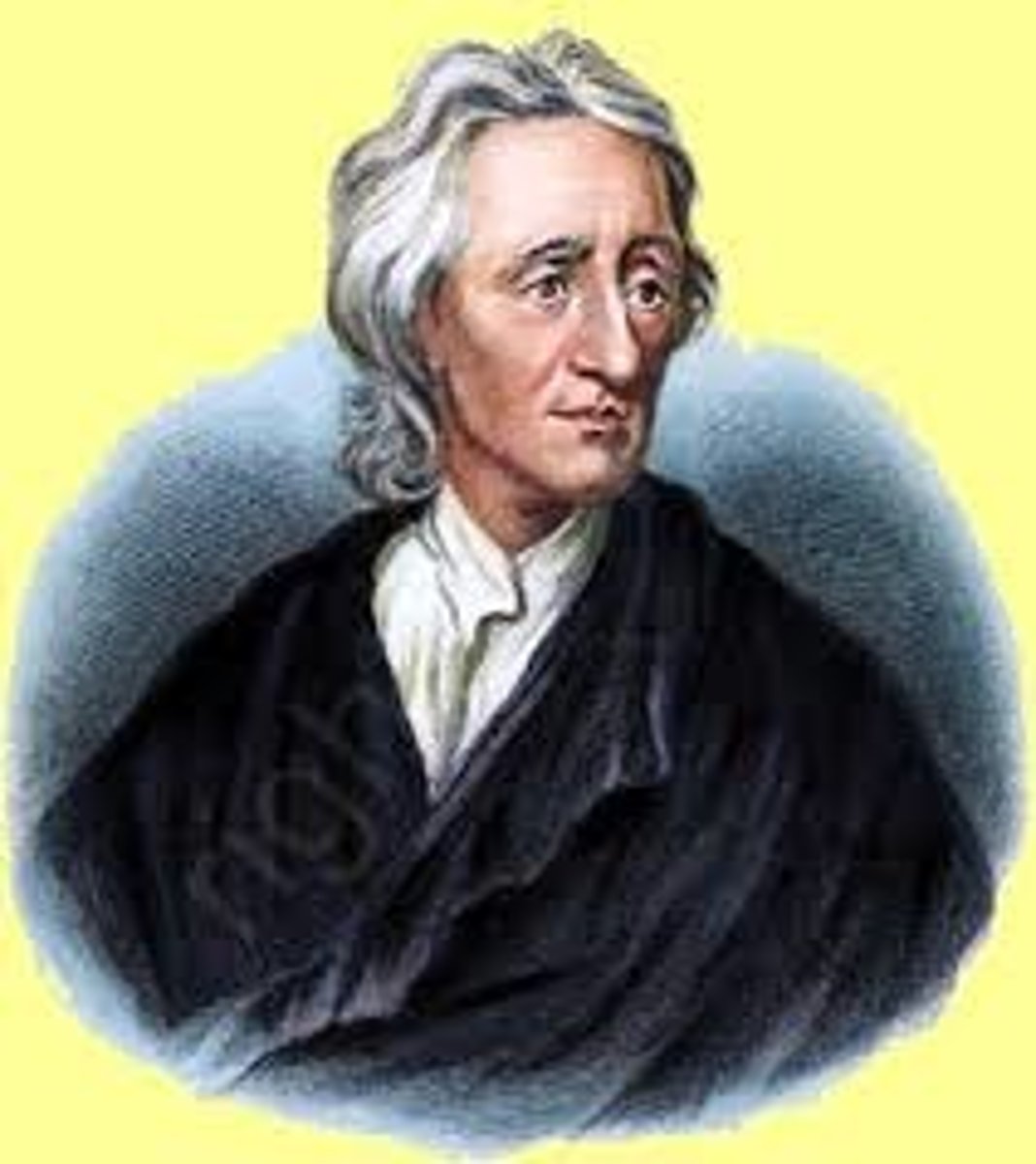
John Locke
A significant individual in the development of self-government in colonial America.

Purposes for amending the U.S. Constitution
Summarized by students.

13th Amendment
The amendment to the U.S. Constitution that bans slavery in the United States, ratified in December 1865.

14th Amendment
The amendment to the U.S. Constitution that makes anyone born in the United States a citizen and grants them equal protection of the law, ratified in July 1868.

15th Amendment
The amendment to the U.S. Constitution guaranteeing the right to vote regardless of race, ratified in February 1870.

Federalists
supporters of the U.S. Constitution.

Anti-Federalists
opponents of the U.S. Constitution.

Judicial review
The power of the U.S., Supreme Court to declare any act of Congress unconstitutional .

Marbury v. Madison
Supreme Court case establishing judicial review.

1818 - McCulloch v. Maryland
The state of Maryland passed legislation to impose taxes on the Second Bank of the United States. James W. McCulloch, the cashier of the Baltimore branch of the bank, refused to pay the tax. The 1818 state appeals court held that the Second Bank was unconstitutional because the Constitution did not provide a textual commitment for the federal government to charter a bank.

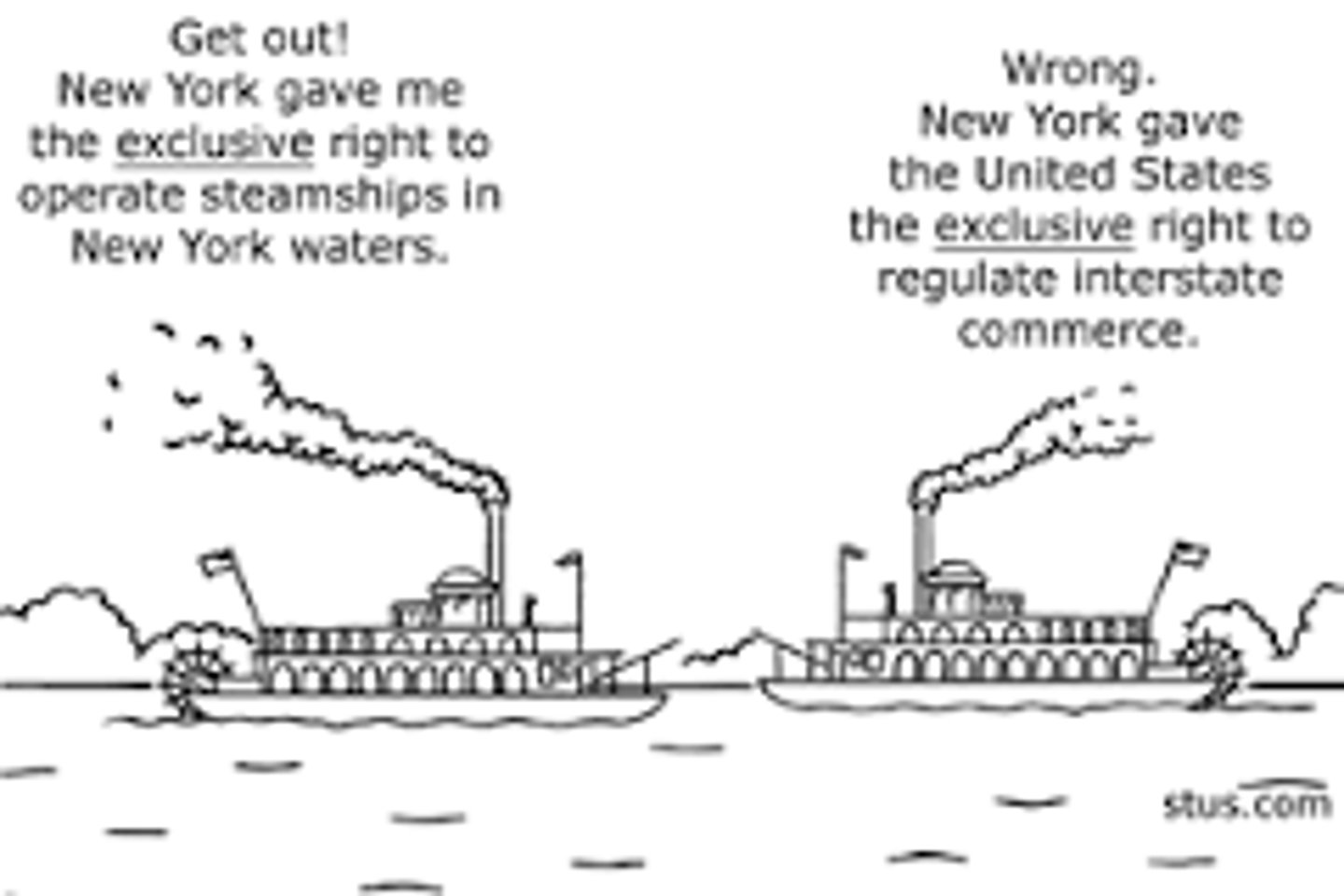
1824 - Gibbons v. Ogden
Supreme Court case establishing that only the federal government had the power to regulate commerce between states.
1857 - Dred Scott v. Sandford
Supreme Court decision stating that Congress had no power to ban slavery in federal territories.

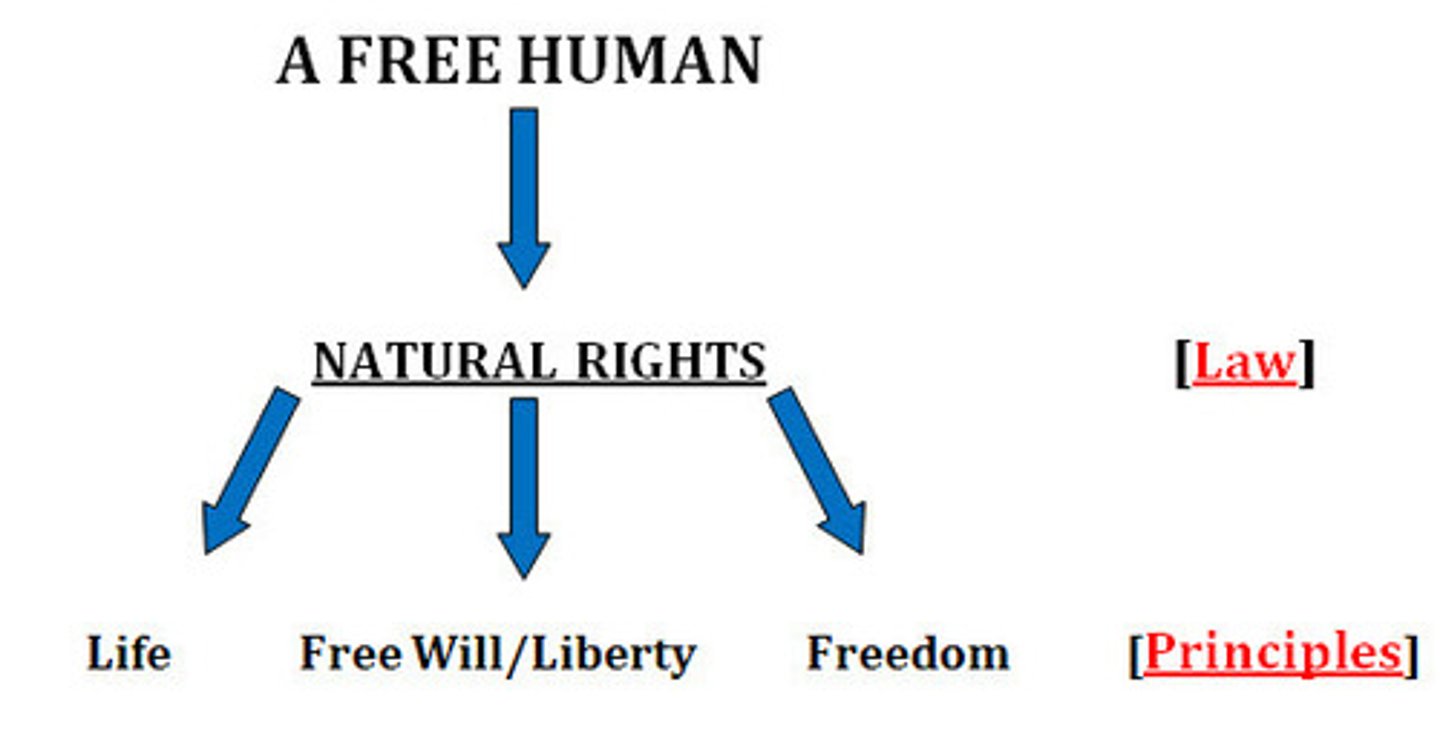
Unalienable rights
fundamental rights guaranteed to people naturally, as a result of being human, such as "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness".
Responsible citizenship
Examples include obeying rules and laws, staying informed on public issues, voting, and serving on juries.

Founding Fathers
Evaluated as models of civic virtue.
Civil disobedience
Analyzed for reasons and impact, including examples like the Boston Tea Party and Henry David Thoreau's refusal to pay a tax.
Free speech and press
Described for their importance in a constitutional republic.

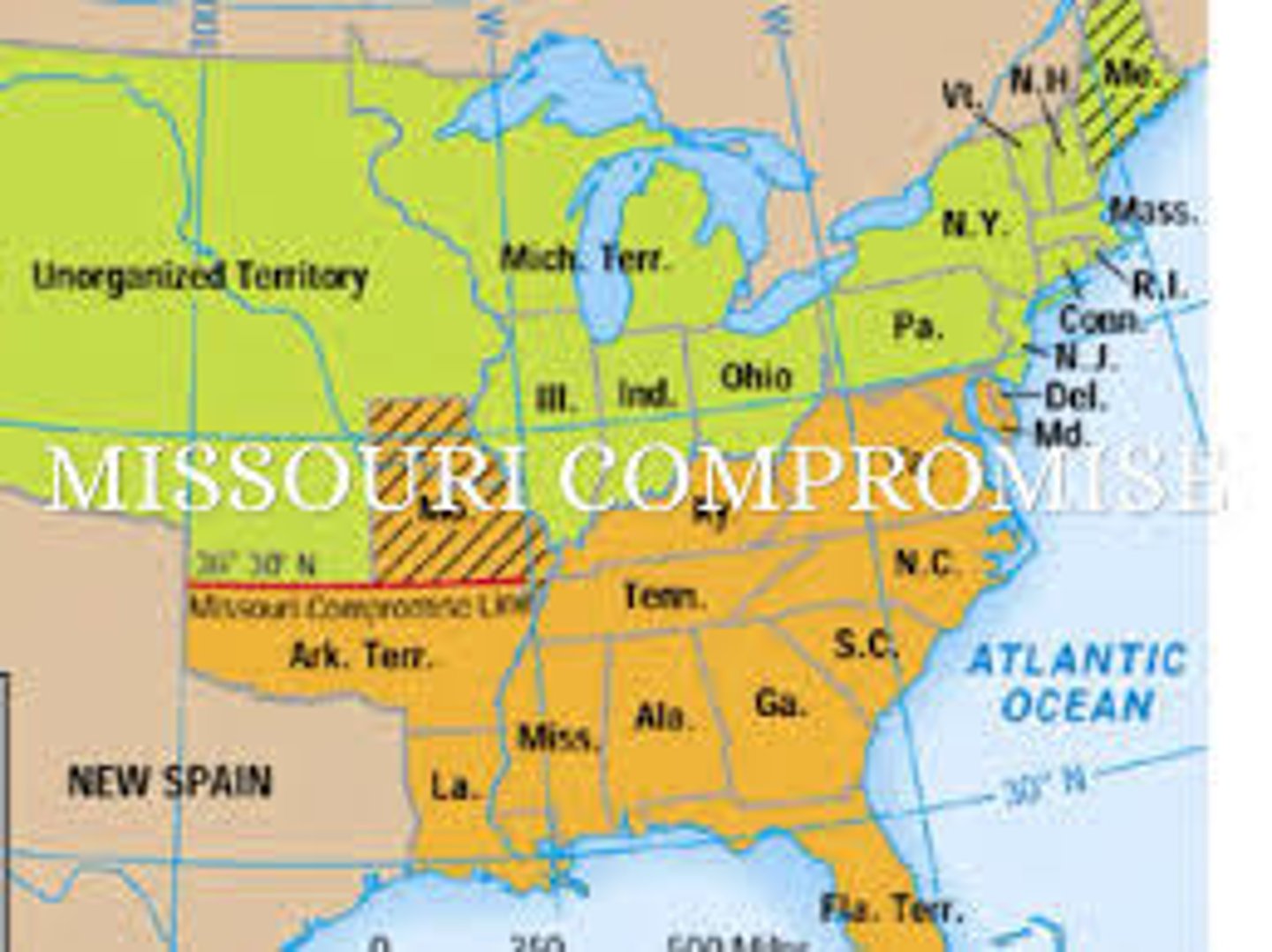
Compromise
Summarized in historical events such as the 1820 Missouri Compromise, the Compromise of 1850, and the Kansas-Nebraska Act.
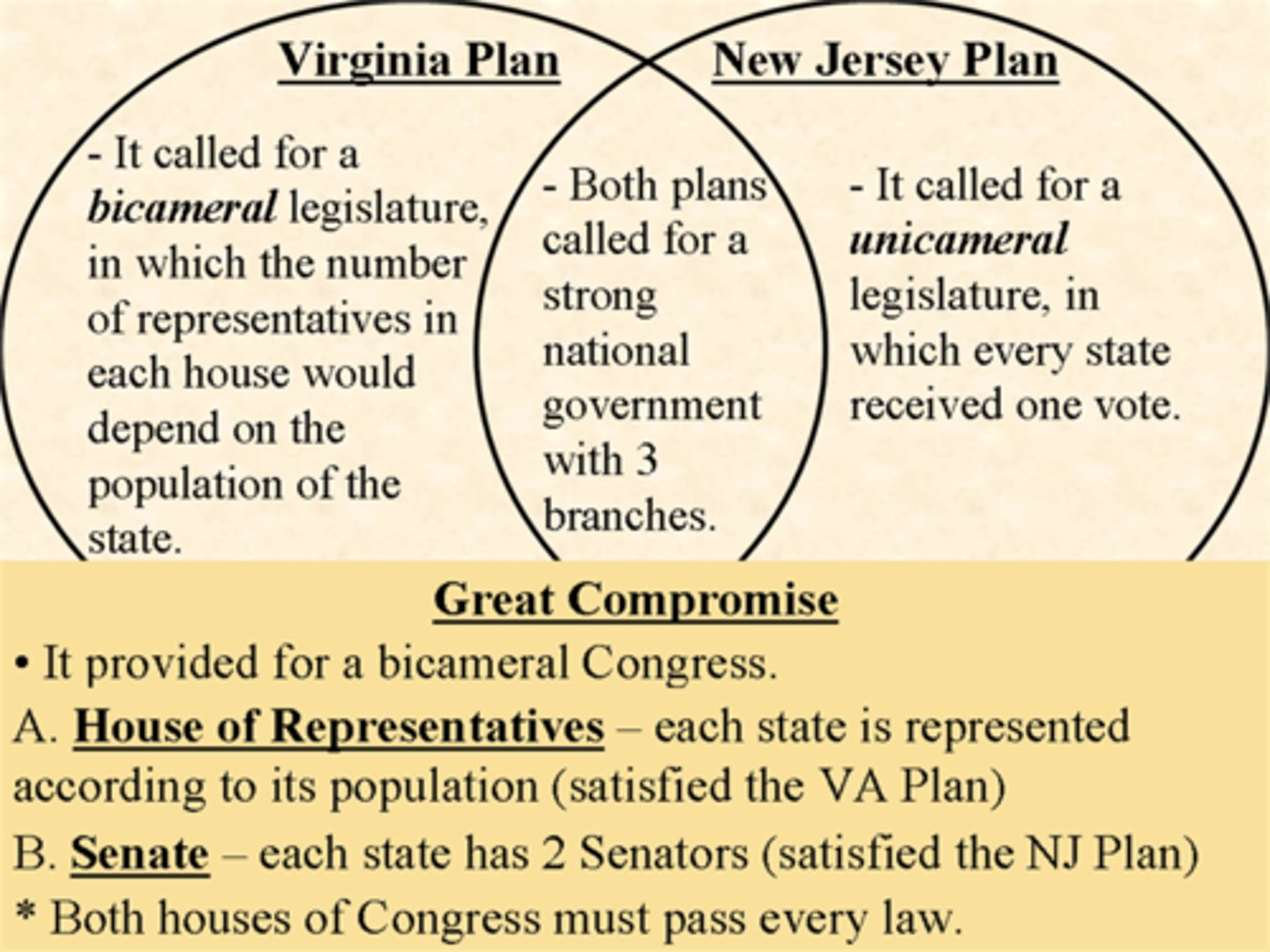
Leadership qualities
skill demonstrated by elected and appointed leaders of the United States, such as George Washington, John Marshall, and Abraham Lincoln.
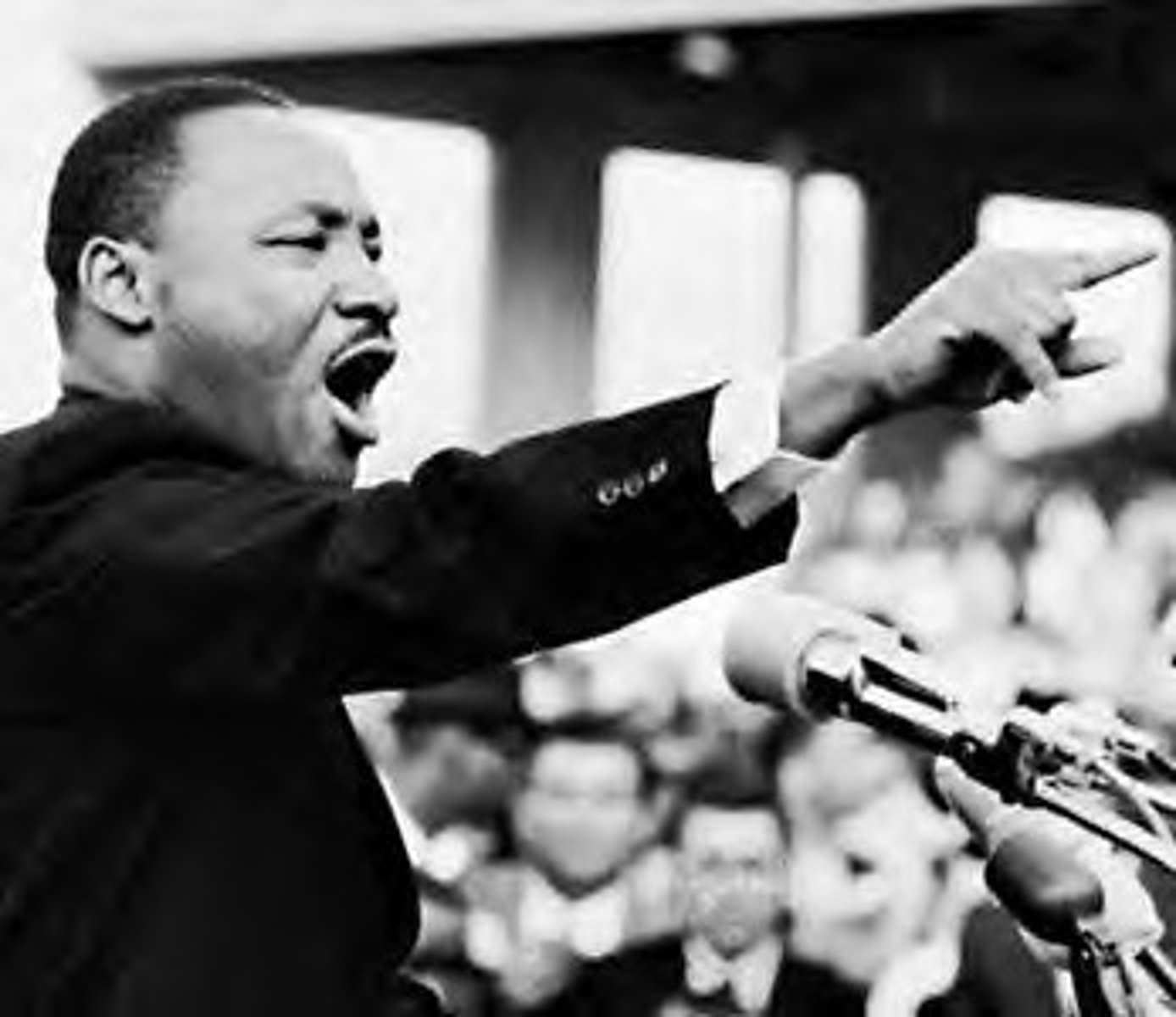

Significant political, social, and military leaders of the Sectional Crisis prior to the Civil War.
Who are Frederick Douglass, John Paul Jones, Susan B. Anthony, and Elizabeth Cady Stanton?
abolition
a complete end to slavery.

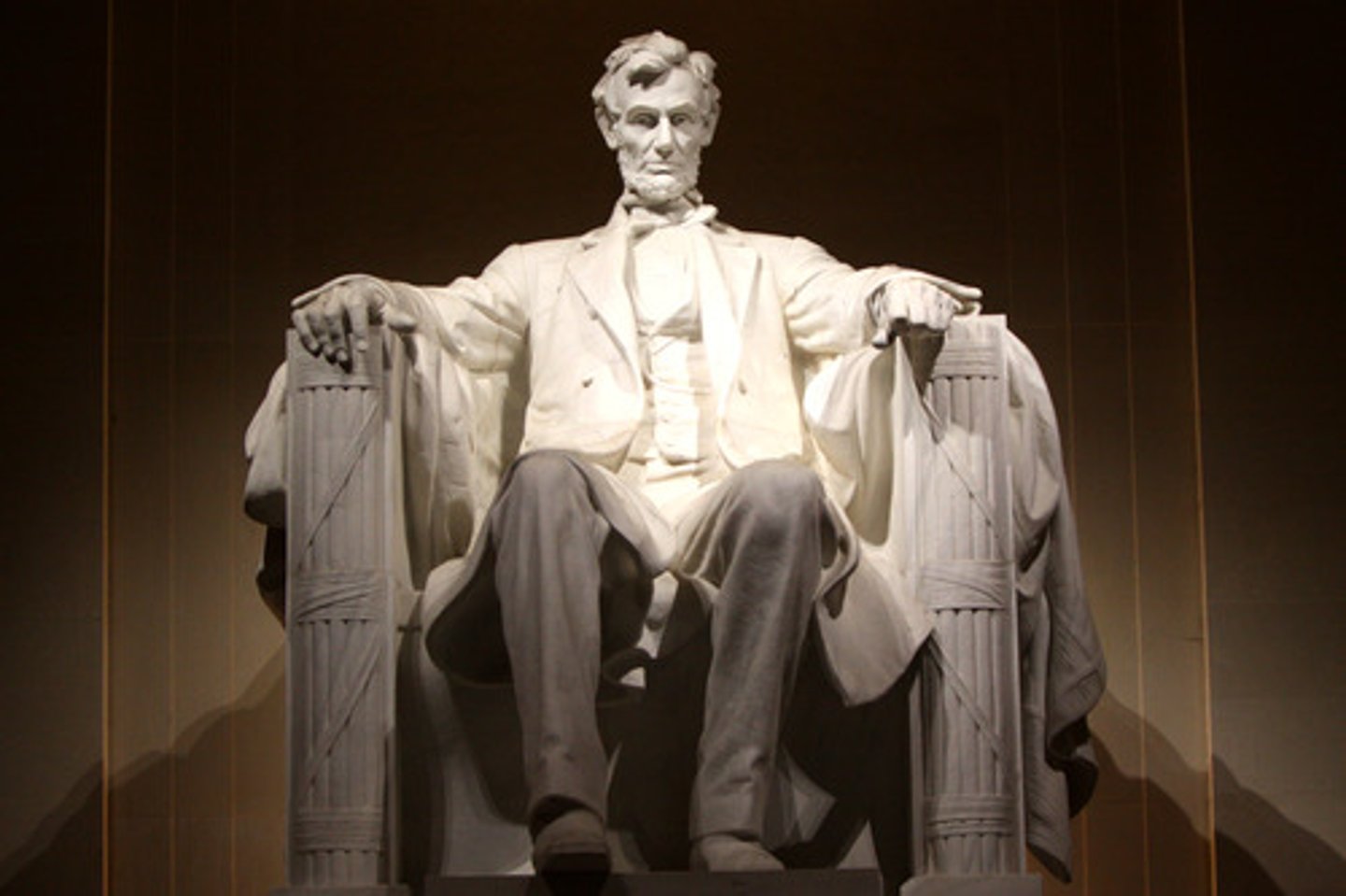
(1809-1865) Abraham Lincoln
Illinois Republican elected president in 1860 who led the Union through the Civil War.

(1755-1865) Alexander Hamilton
supporter of the U.S., Constitution and one author of the Federalist Papers.
amending
changing