Fetal pig dissection quiz
Teeth
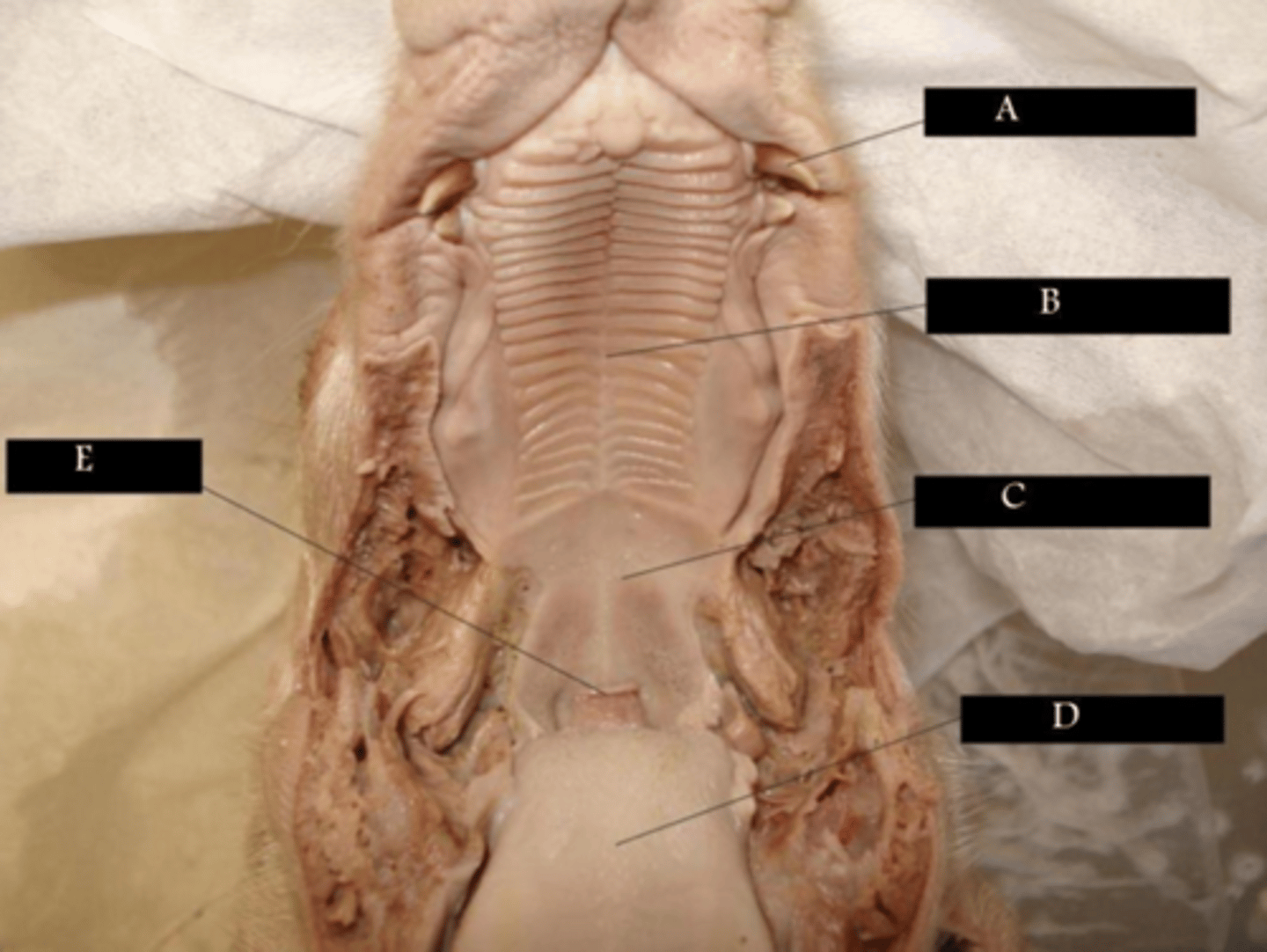
A
Break down food into smaller pieces
Tongue
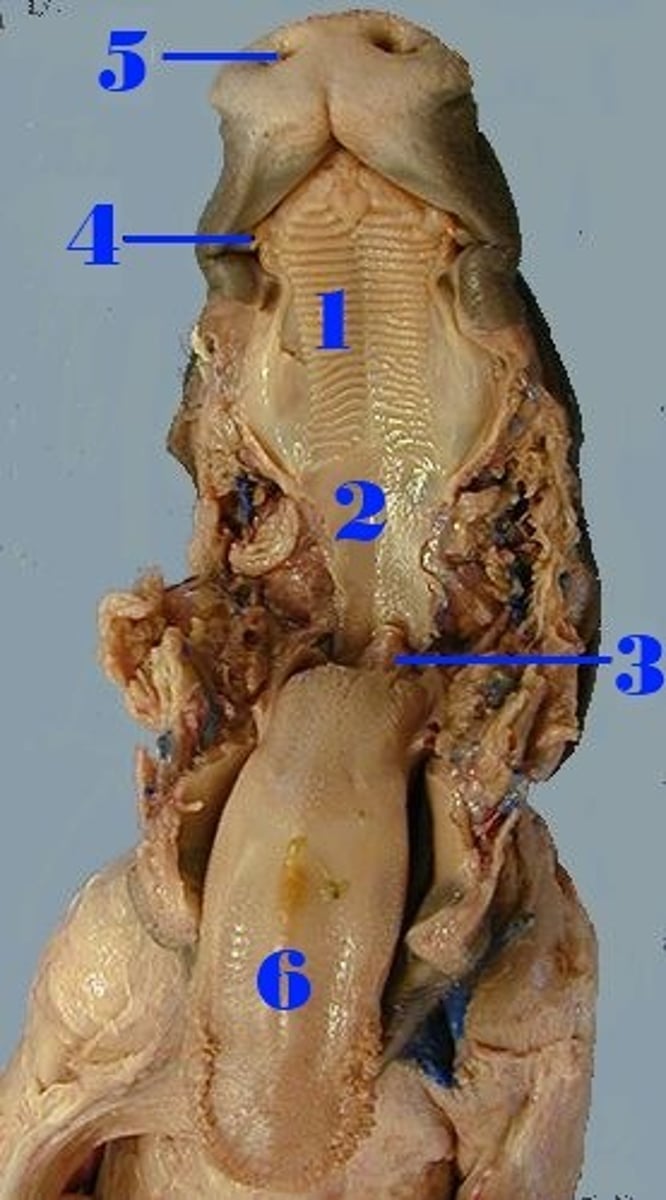
#6
Mixes food with saliva to form bolus and initiates swallowing
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Teeth
A
Break down food into smaller pieces

Tongue
#6
Mixes food with saliva to form bolus and initiates swallowing

Soft palate
#2
Softer section below hard palate that seals the nasal cavity during swallowing
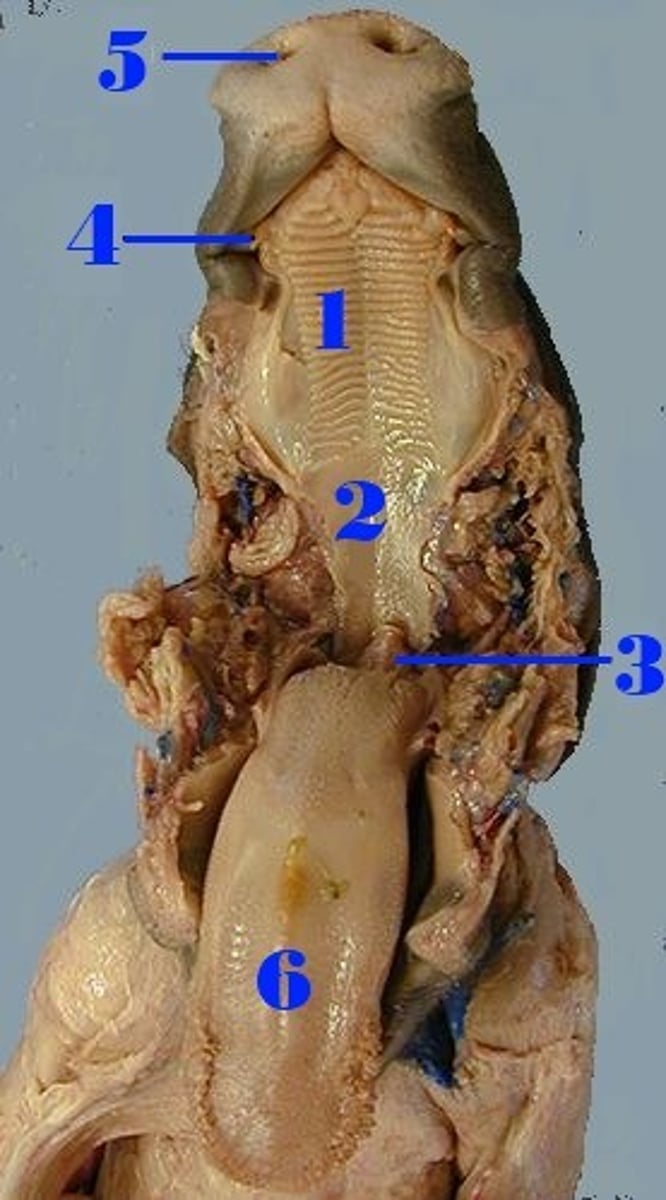
Hard palate
#1
has ridges, separates oral cavity from nasal cavities
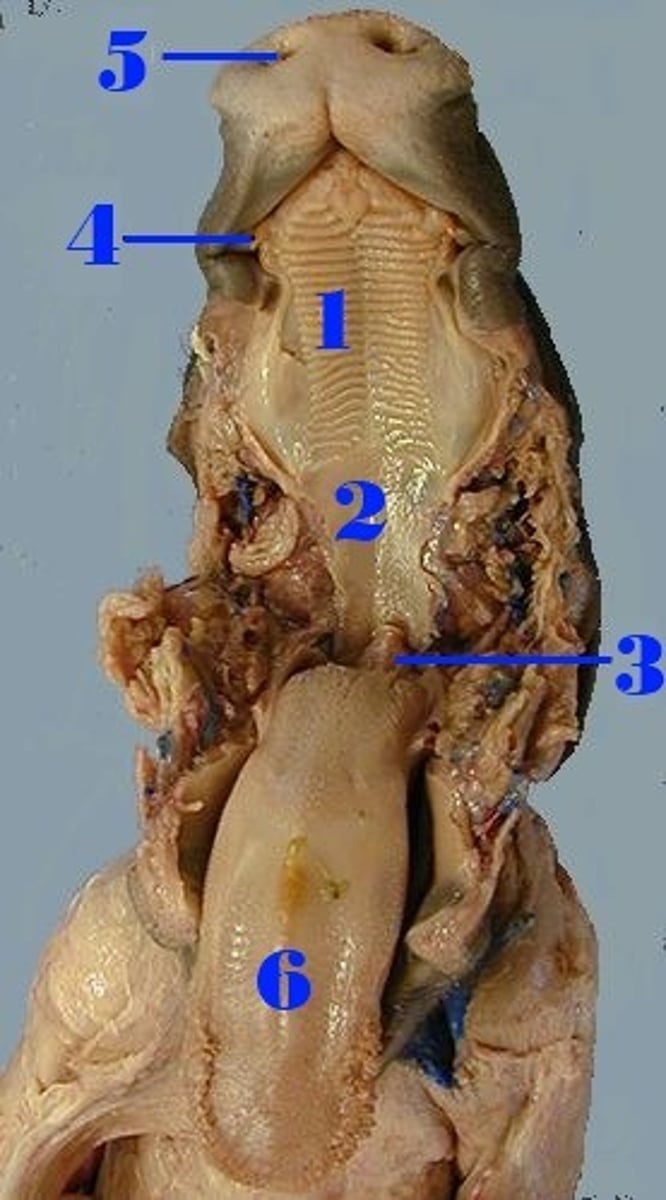
Nasopharynx
Air passageway; contains pharyngeal tonsil
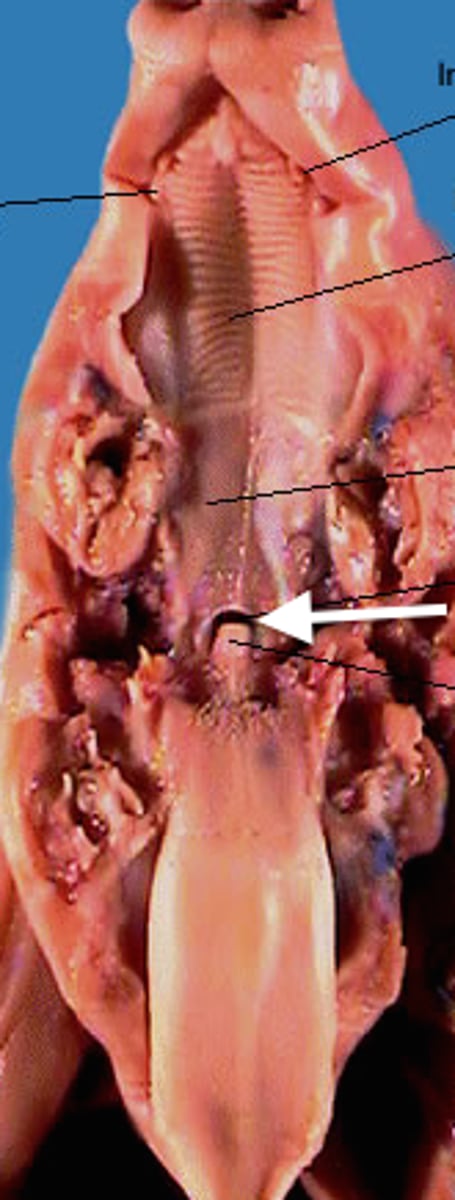
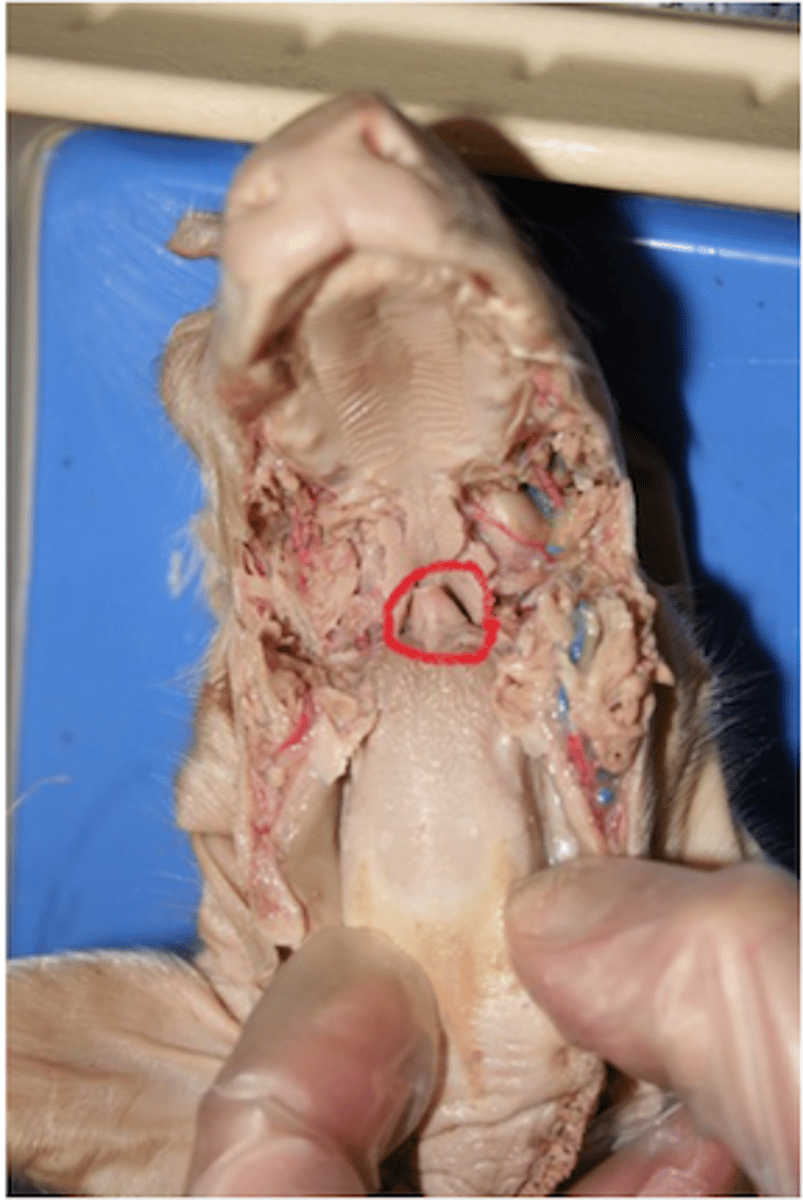
Glottis
The opening between the vocal cords and the upper larynx. The epiglottis covers this.
Epiglottis
Prevents food from entering lower respiratory system by covering glottis when swallowing; directs food to esophagus
Esophagus
Muscular tube connected from the pharynx to the cardiac sphincter of the stomach, propelling food to the stomach. To find this organ, look for the box like larynx, then follow it down to the trachea, and look for a thinner tube hidden behind the trachea.
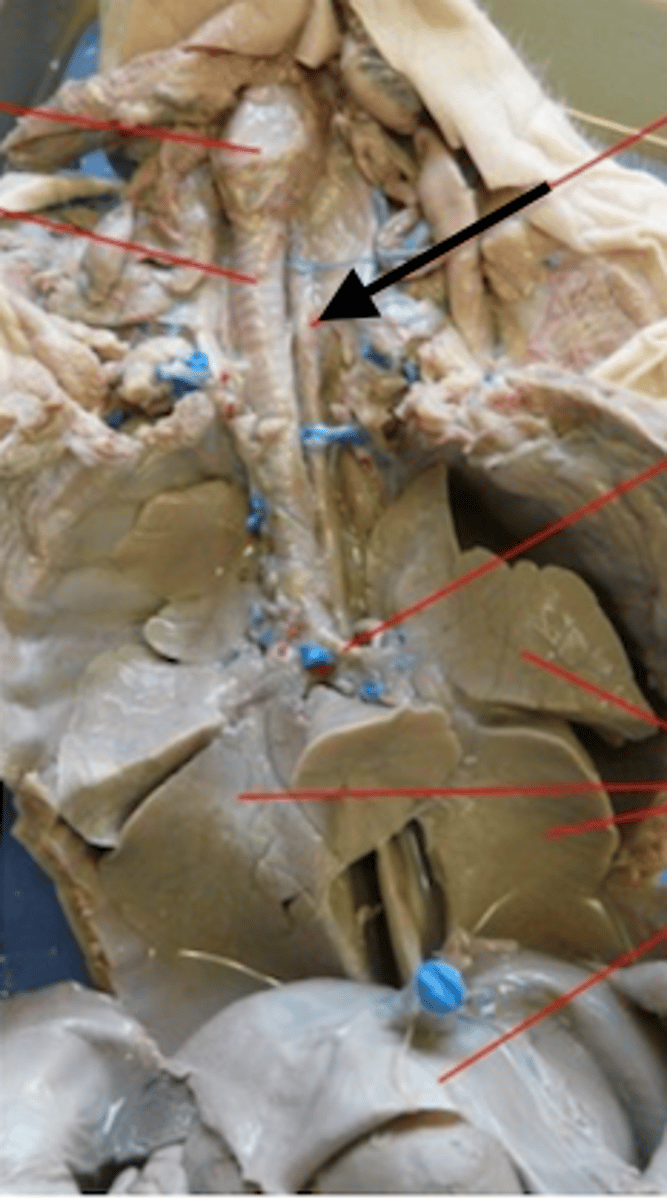
Larynx
Provides open airway, acts as switching mechanism to route air/food into proper channels, & produces voice/sounds
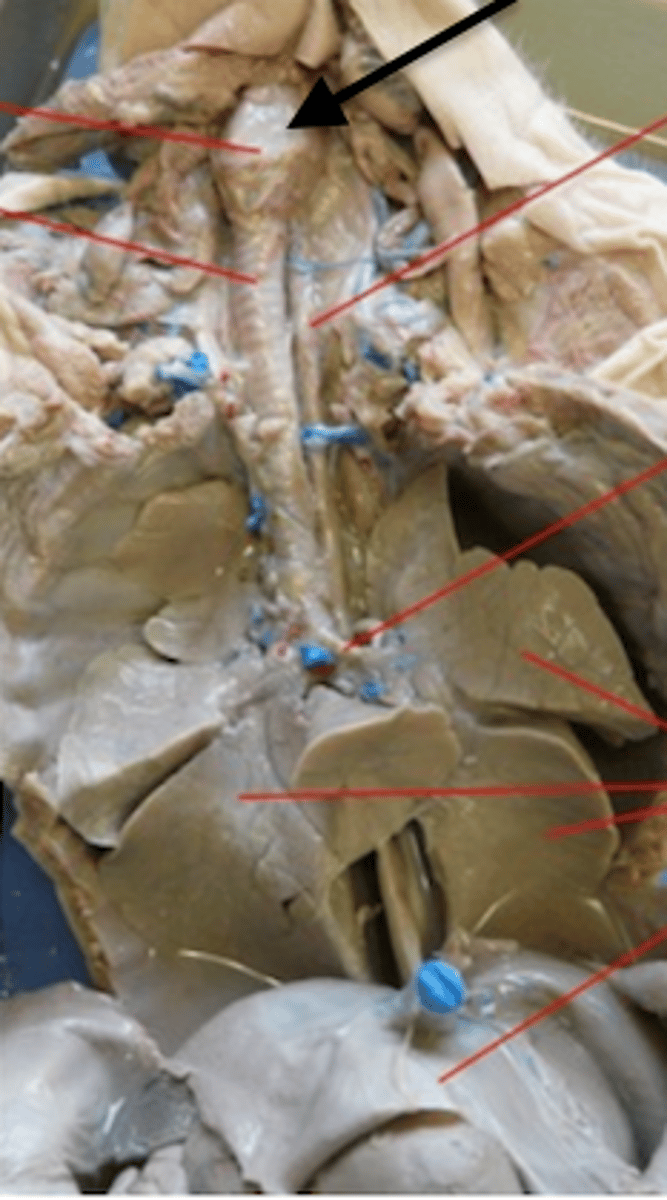
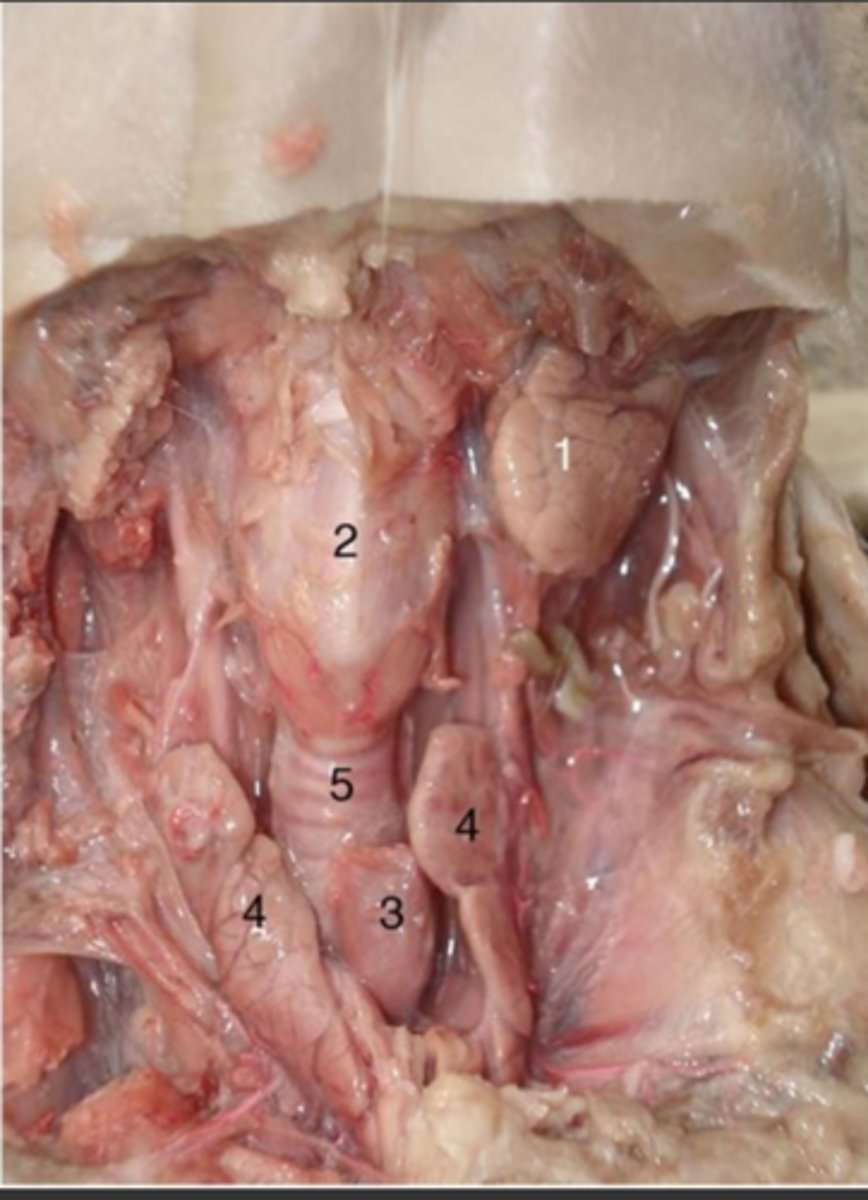
Thymus gland
#3
Lymphoid organ situated in the neck of vertebrates that produces T cells for the immune system.
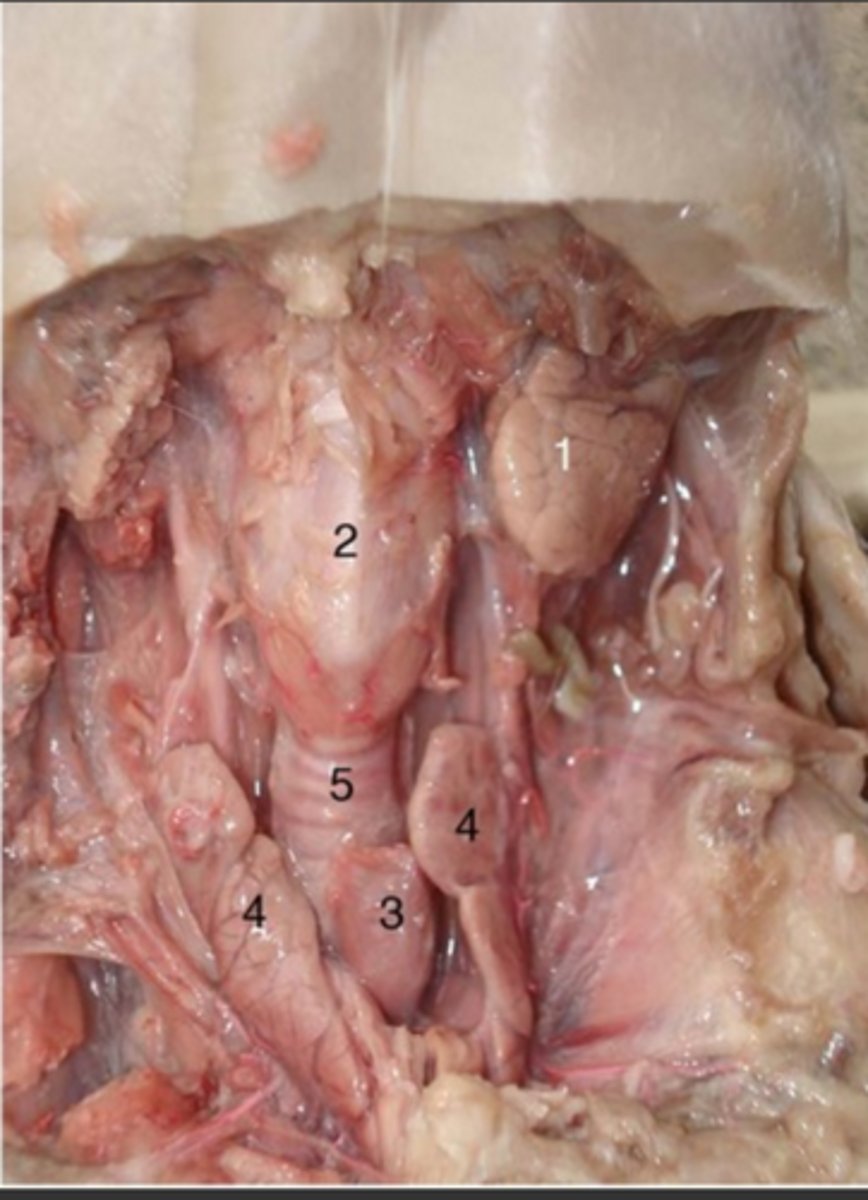
Thyroid gland
#4
large ductless gland in the neck that secretes hormones regulating growth and development through the rate of metabolism.
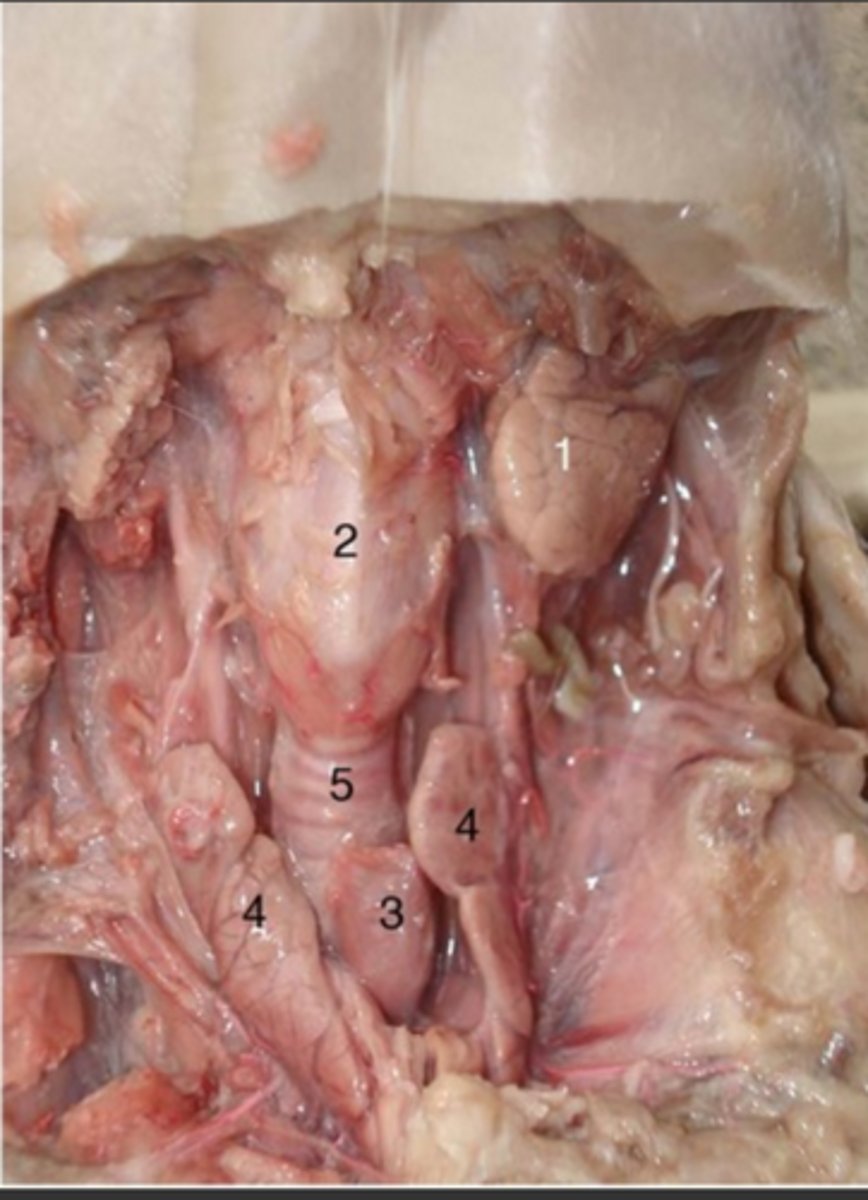
Trachea
#5
Wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx (or voice box) to the bronchi of the lungs. It is an integral part of the body's airway and has the vital function of providing air flow to and from the lungs for respiration
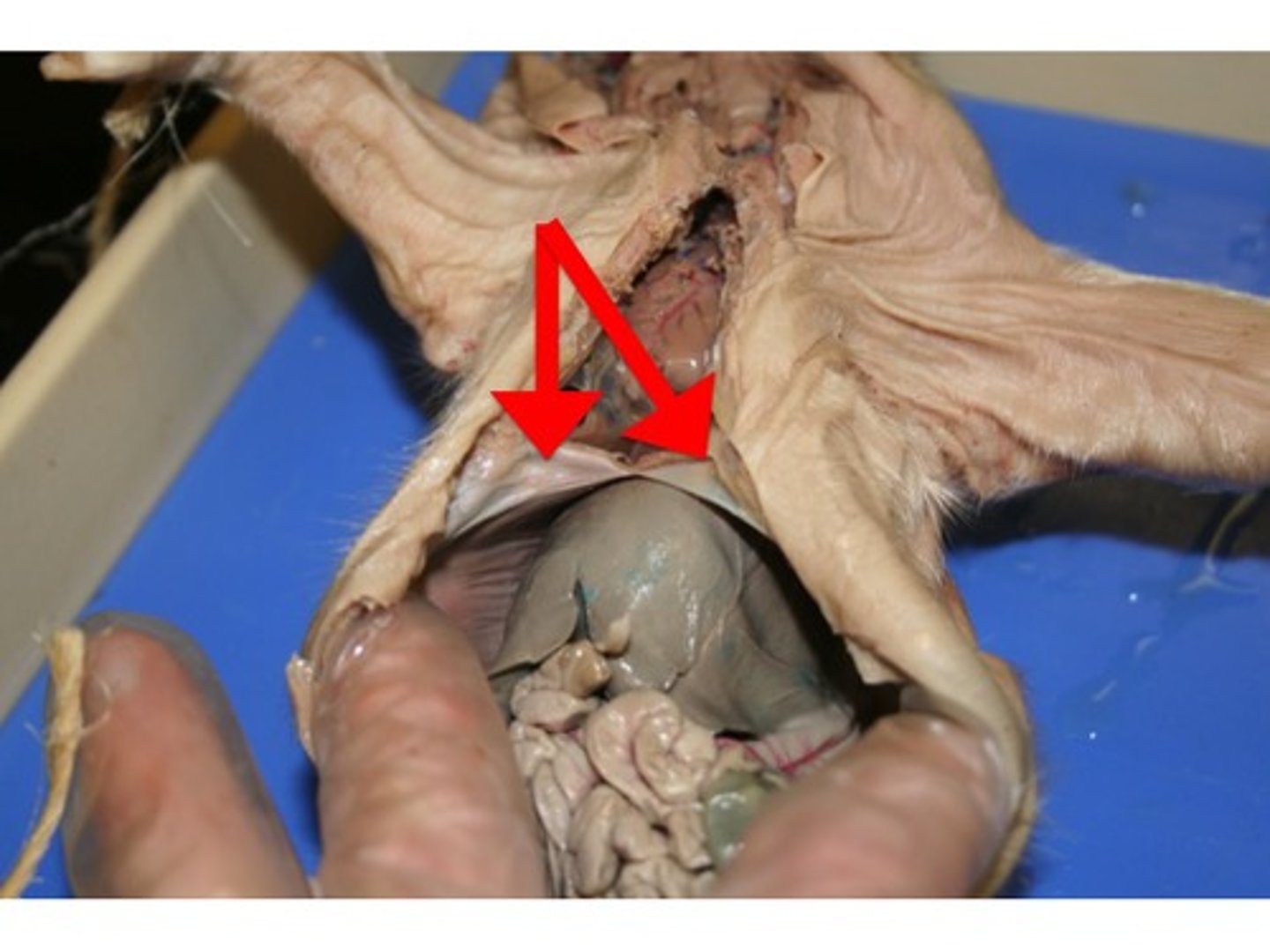
Diaphragm
Movement of air into and out of lungs; divides thoratic and abdominal cavities, Responsible for 75% of our breating
Lungs
#7
Allows oxygen in the air to be taken into the body, while also enabling the body to get rid of carbon dioxide in the air breathed out
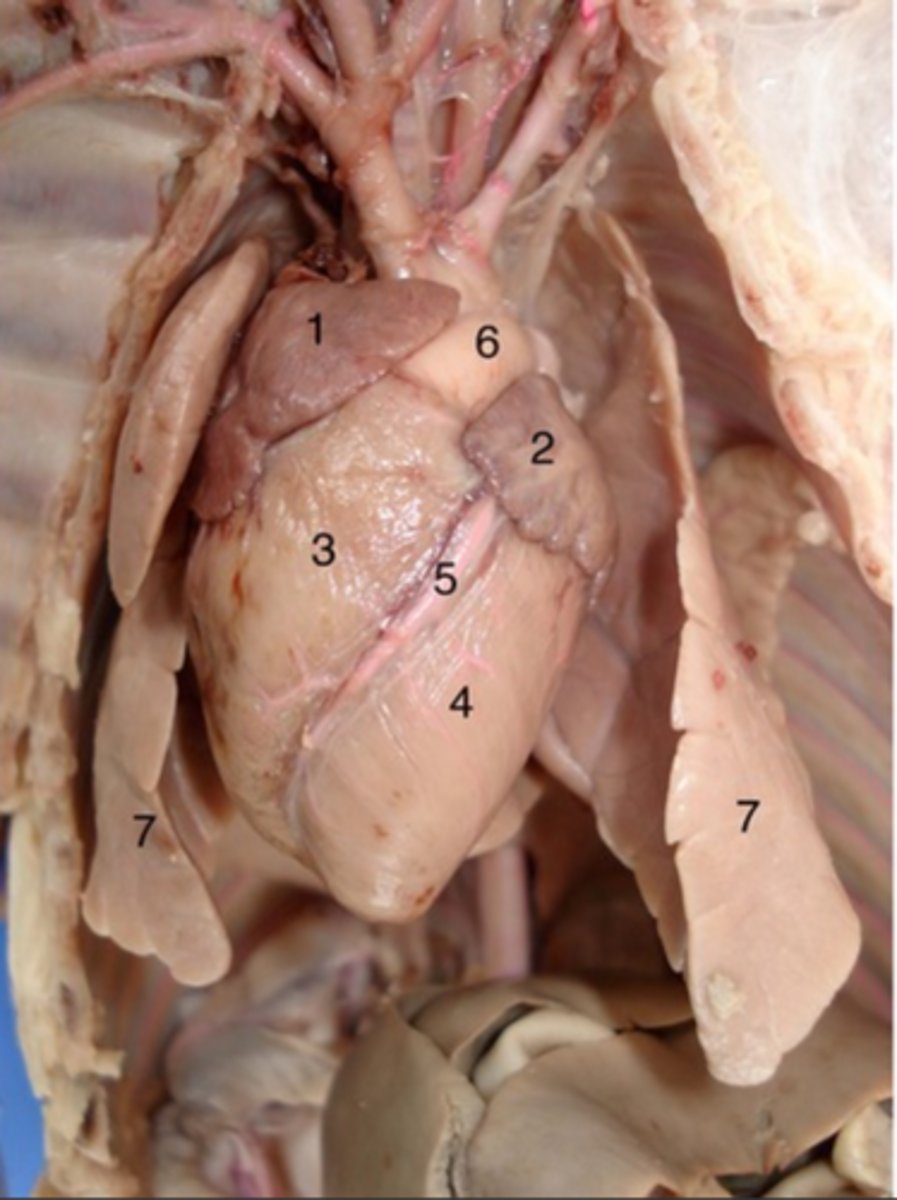
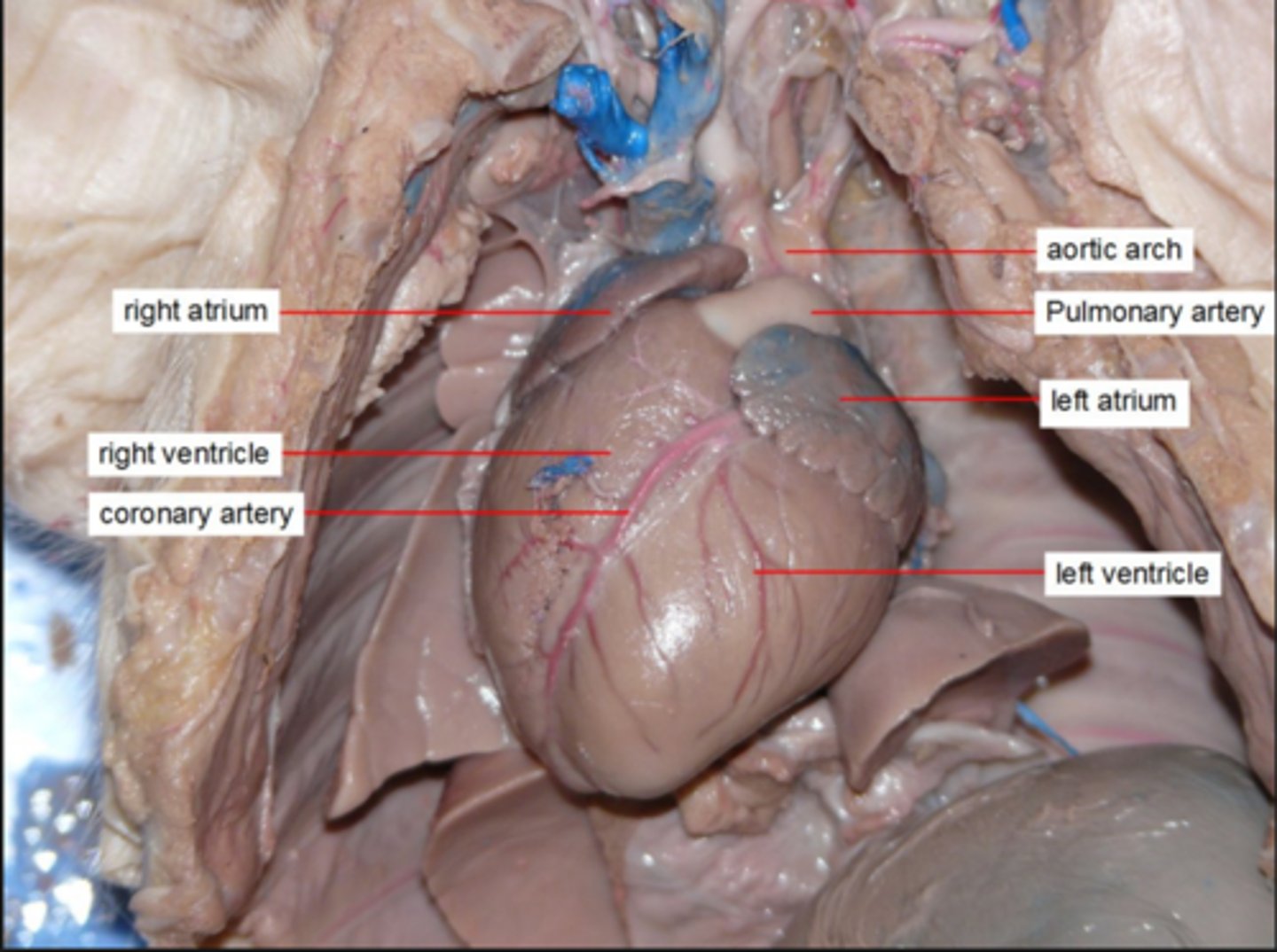
Heart
Hollow, muscular organ, which functions as a pump for the movement of blood through the body.
Mesenteries
Dual-layers of peritoneum that extend from the abdominal wall and attach the small intestines and other abdominal organs posteriorly to the wall. They are stringy connective tissue, and can be easily probed or cut away to isolate the intestines.
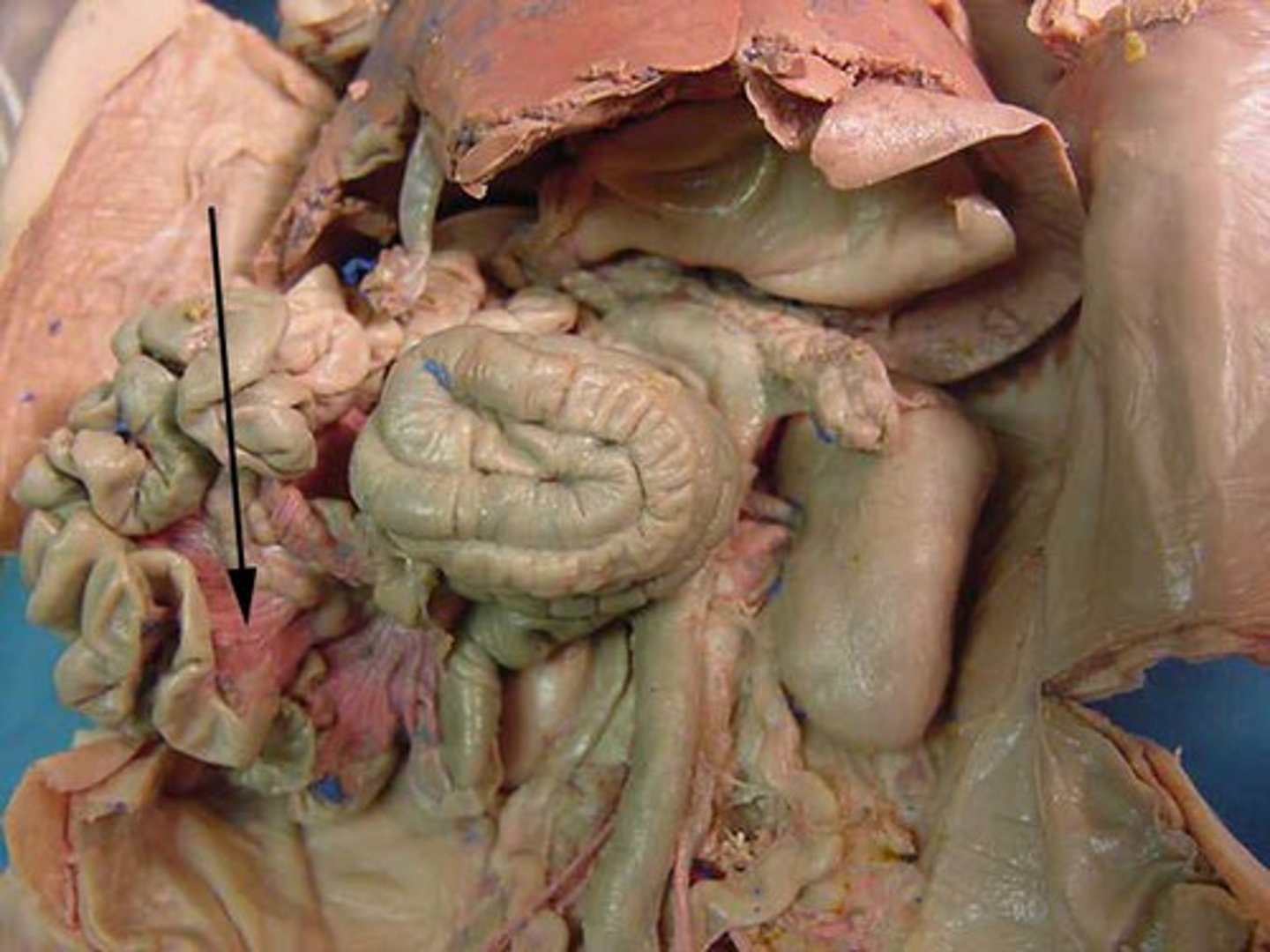
Stomach
#3
Temporary food storage organ where chemical breakdown of proteins begins & food is converted to chime. pH 1.5-3.5
Usually completely empties within 4 hrs after meal. It has small folds called rugae, the folded nature of it allows it to expand when necessary. (breaks down food and mixes it with water, mucous, HCl, and protein-digesting enzymes)
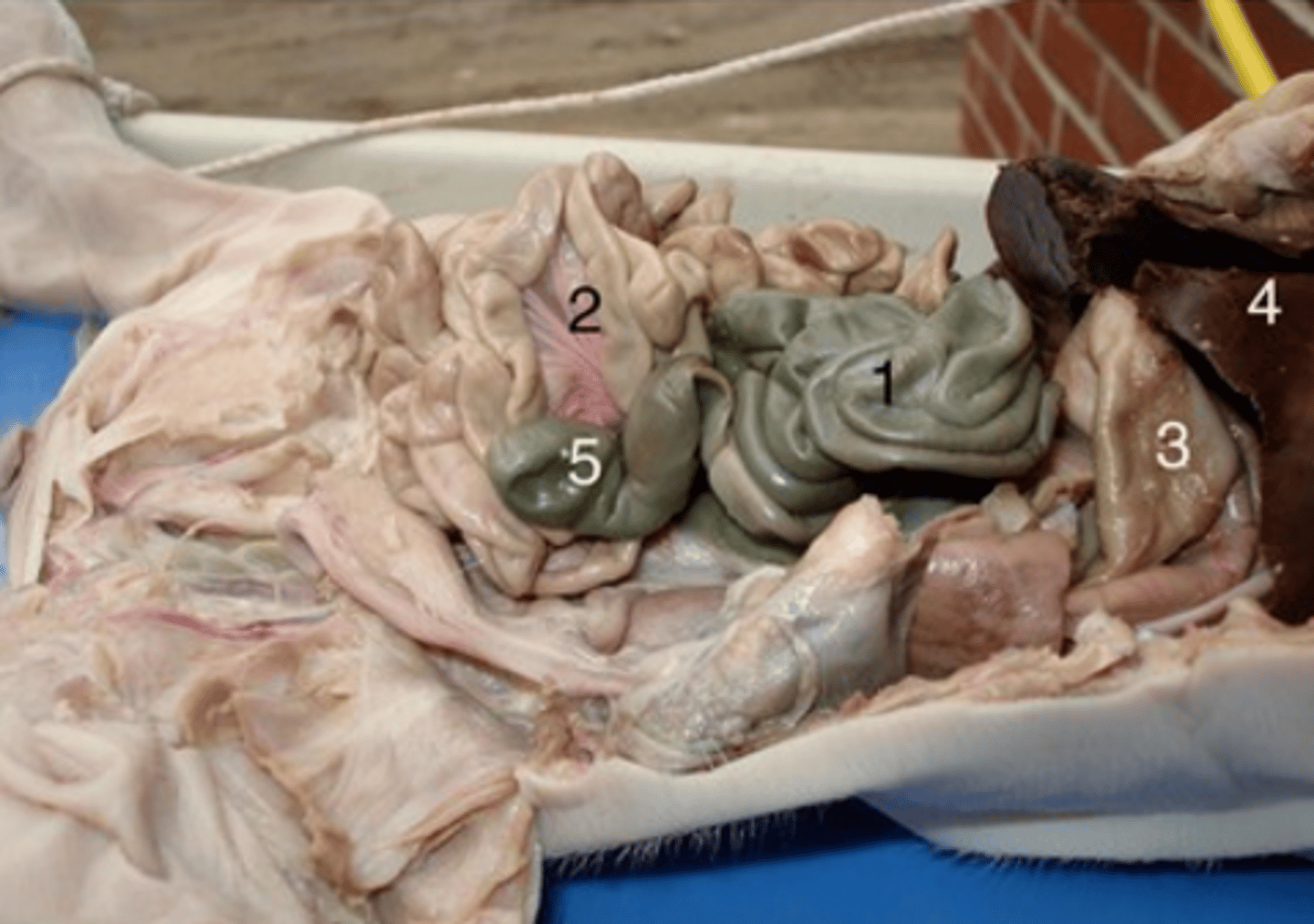
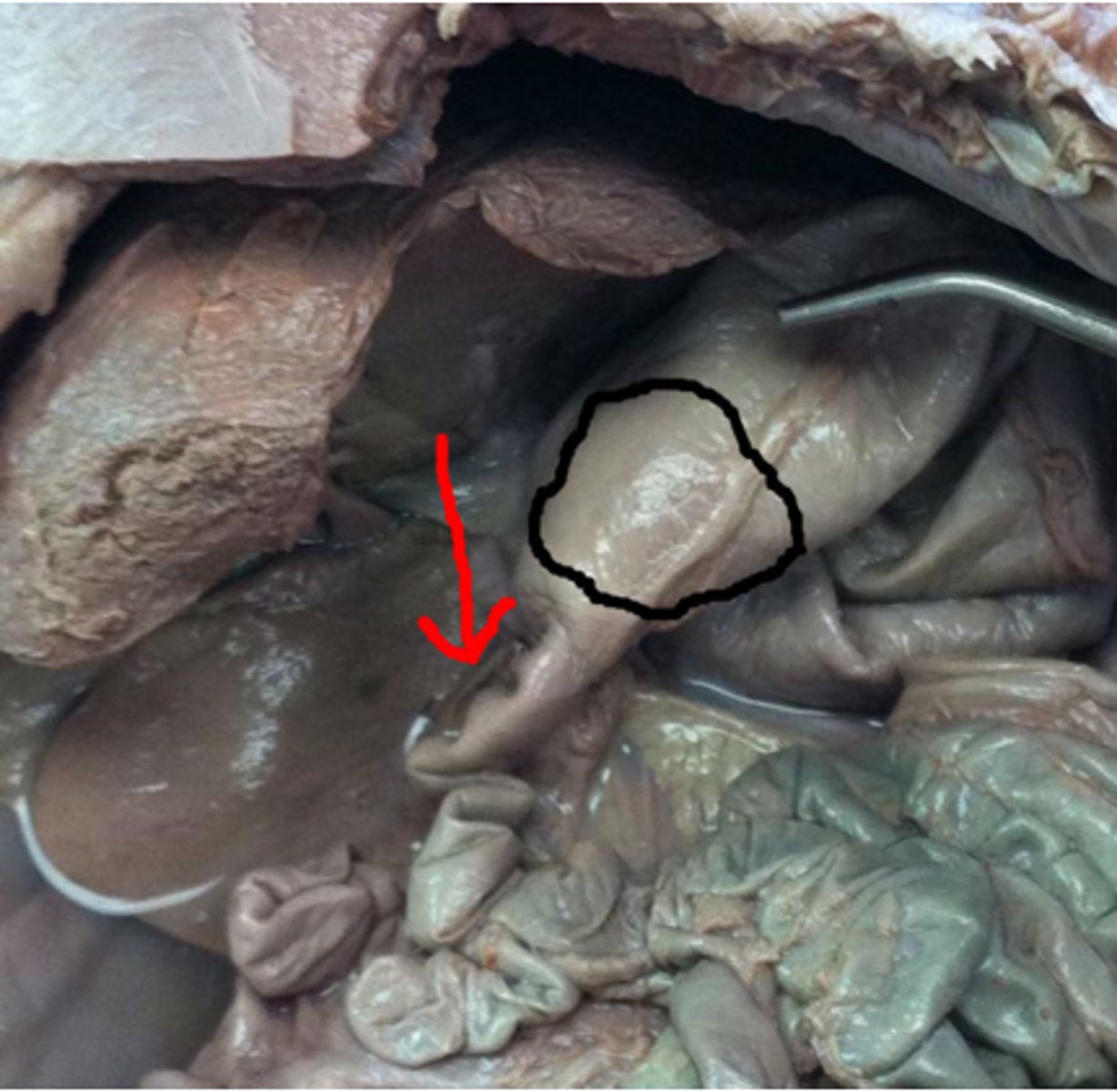
Pyloric sphincter
Black circle is the pyloric section, the red arrow is ____
It connects the stomach and small intestine, prevents flowback of food from stomach.
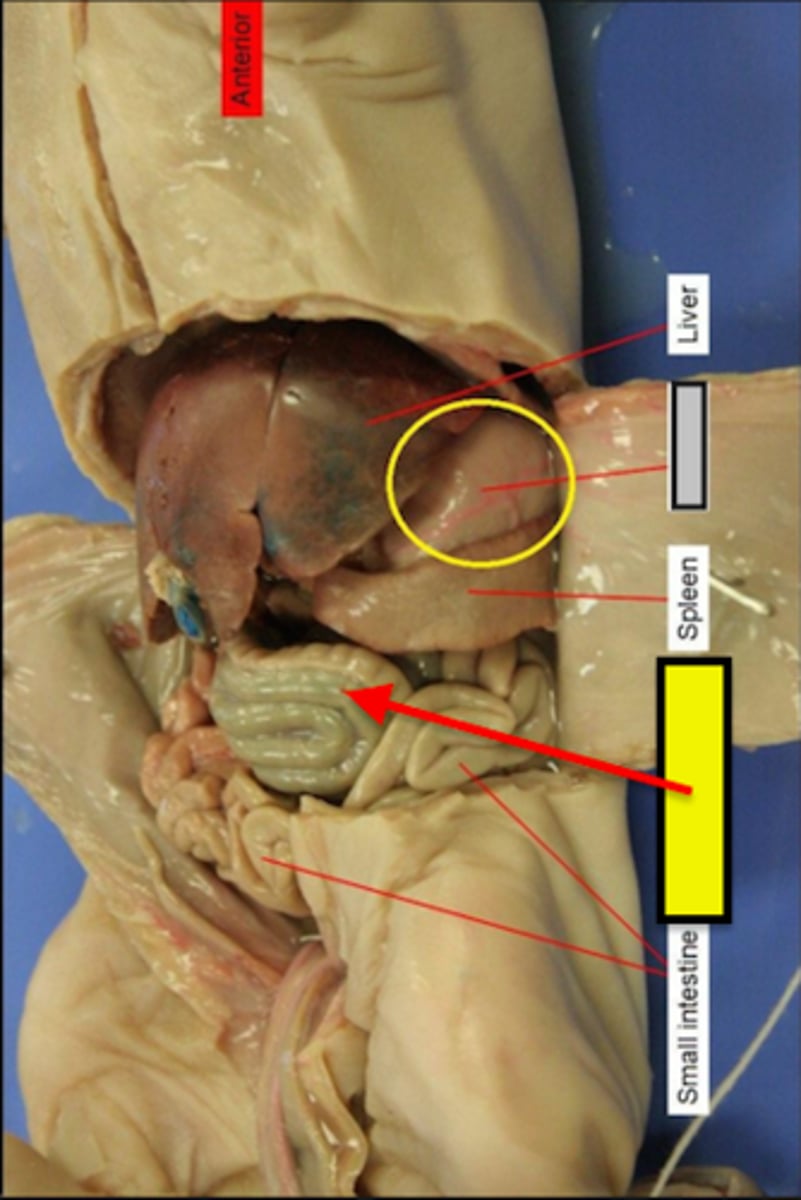
Spleen
It acts as a filter for blood as part of the immune system. Old red blood cells are recycled and platelets and white blood cells are stored there.
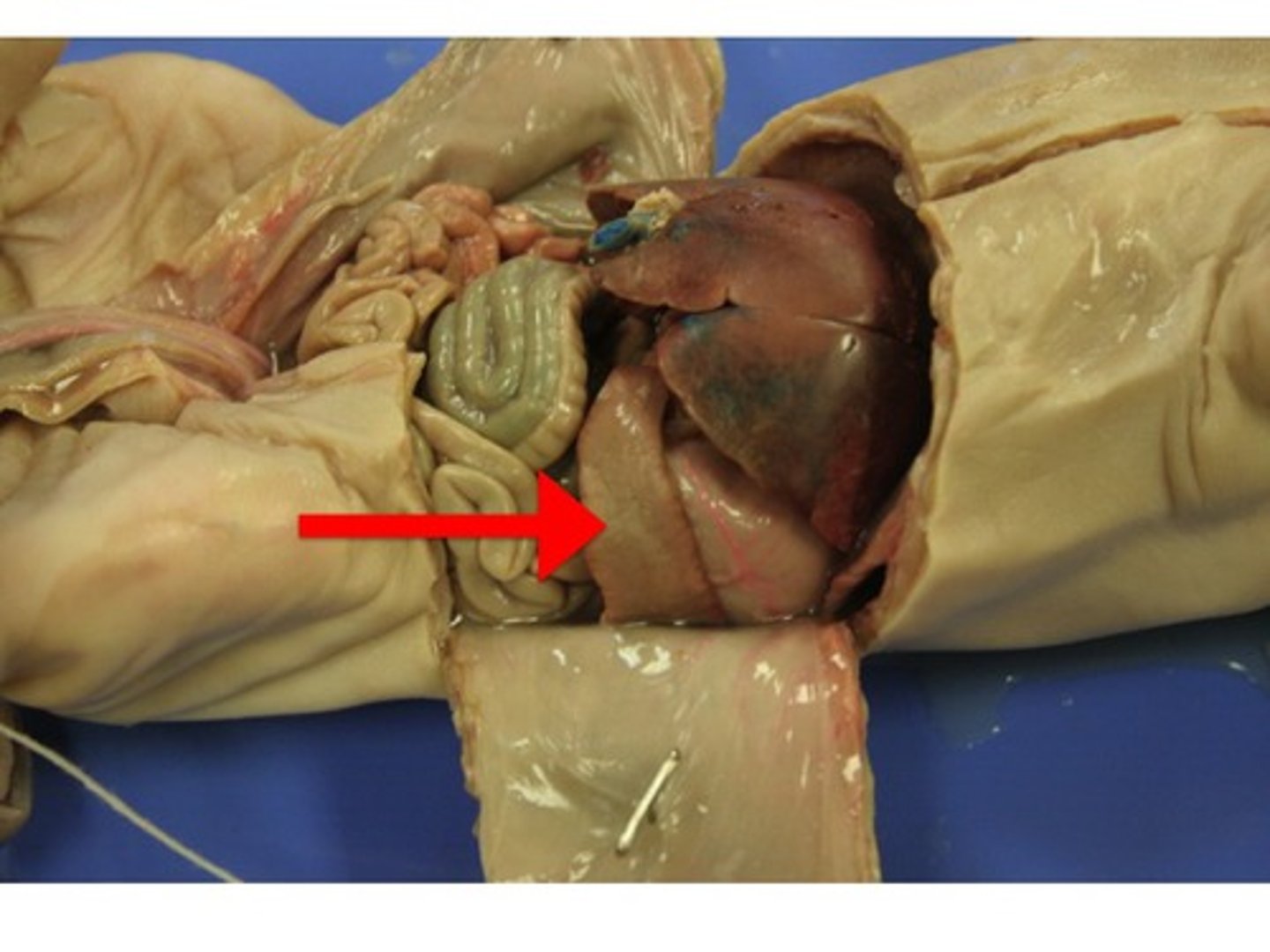
Liver
#4
Makes bile so that it can break big fat particles into smaller ones
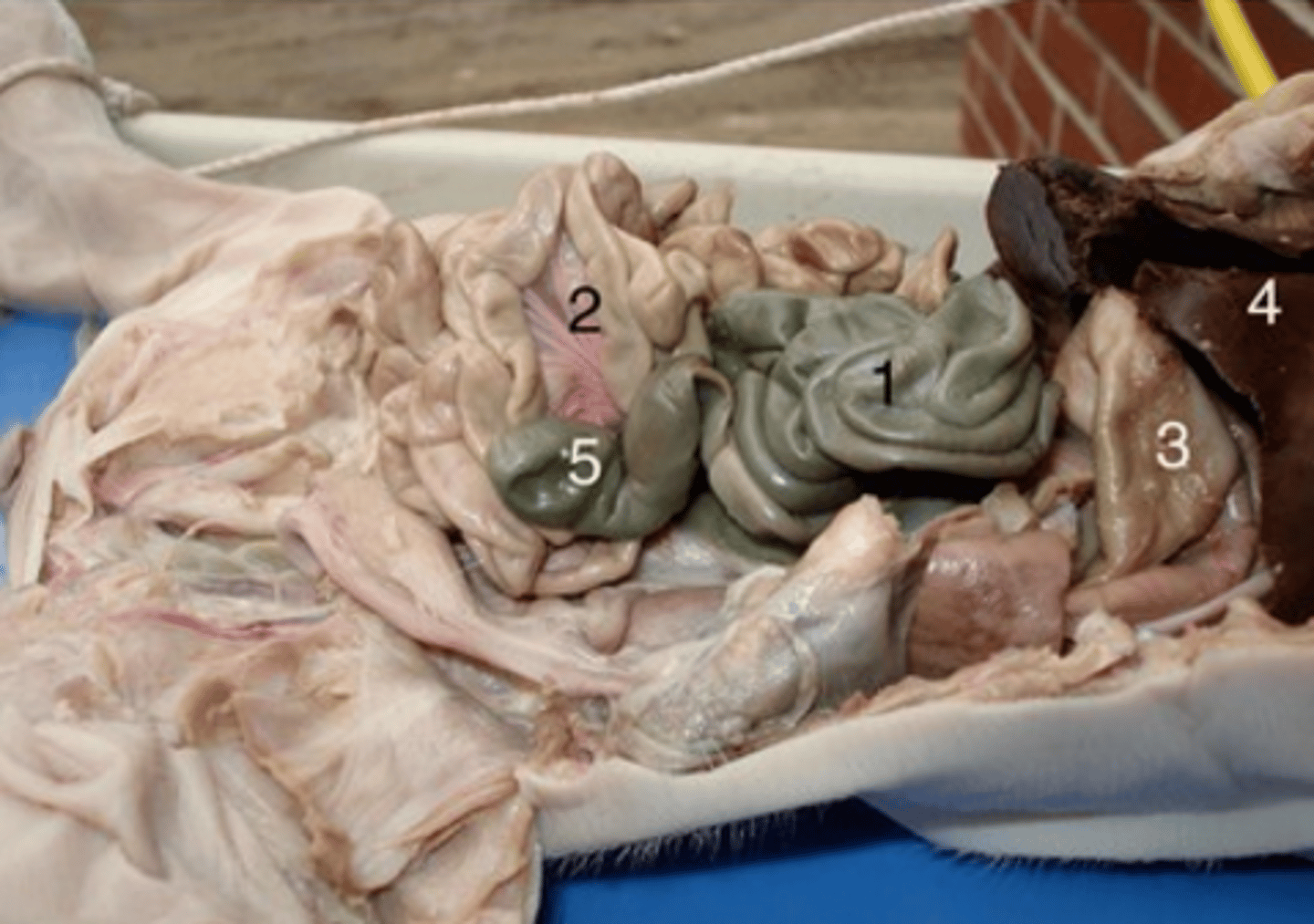
Gallbladder
- Stores and concentrates bile until ready for digestion,
- Expels bile into cystic duct; bile then flows into bile duct
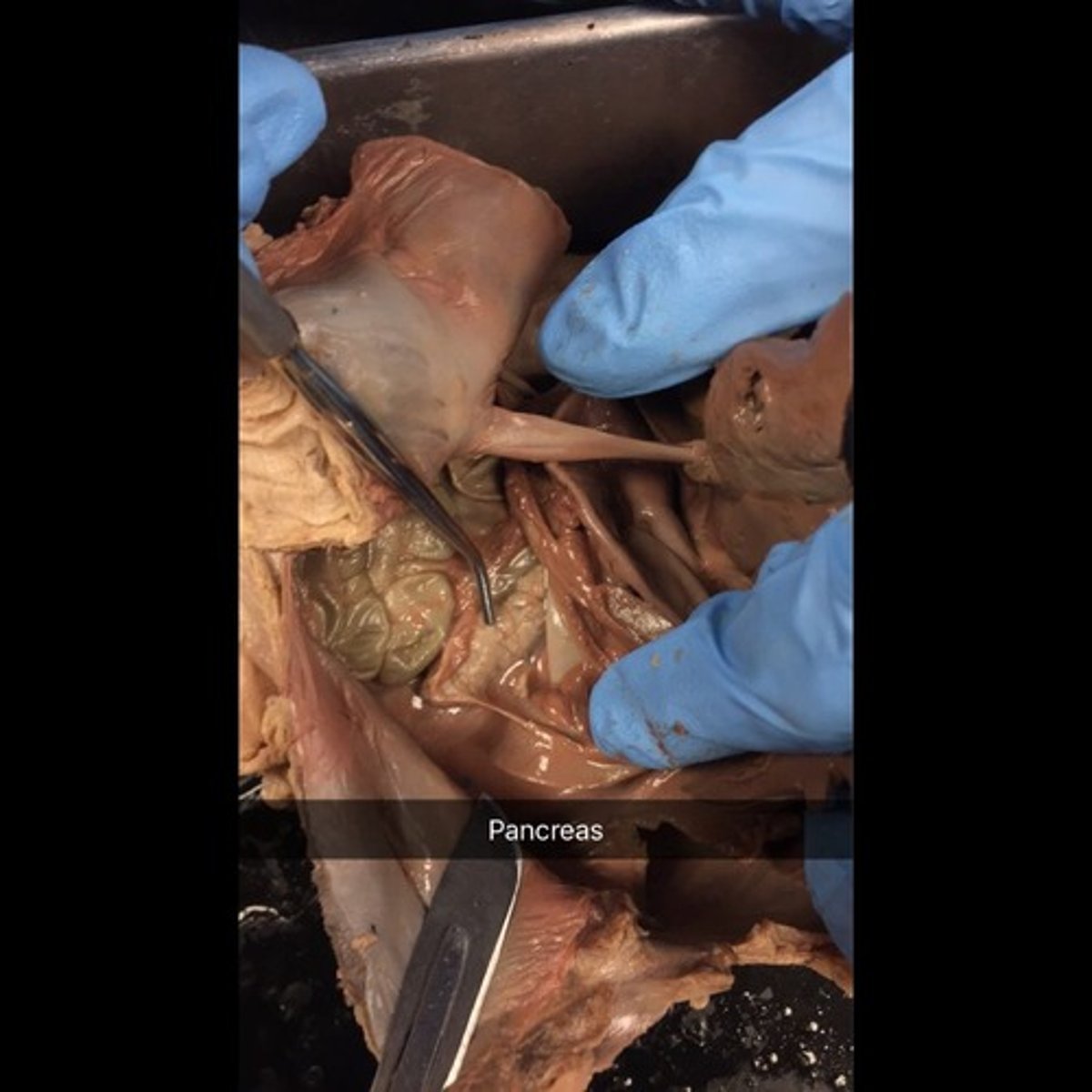
Pancreas
It is located attached to the posterior wall of the cavity. 99% exocrine function, acini produces pancreatic juice, secretes zymogen granules= inactive enzymes that get activated in the small intestine, produces enzymes that break down ALL categories of food
1% endocrine function to secrete insulin and glucagon produced by pancreatic islets. Provides bicarbonate ions for proper pH
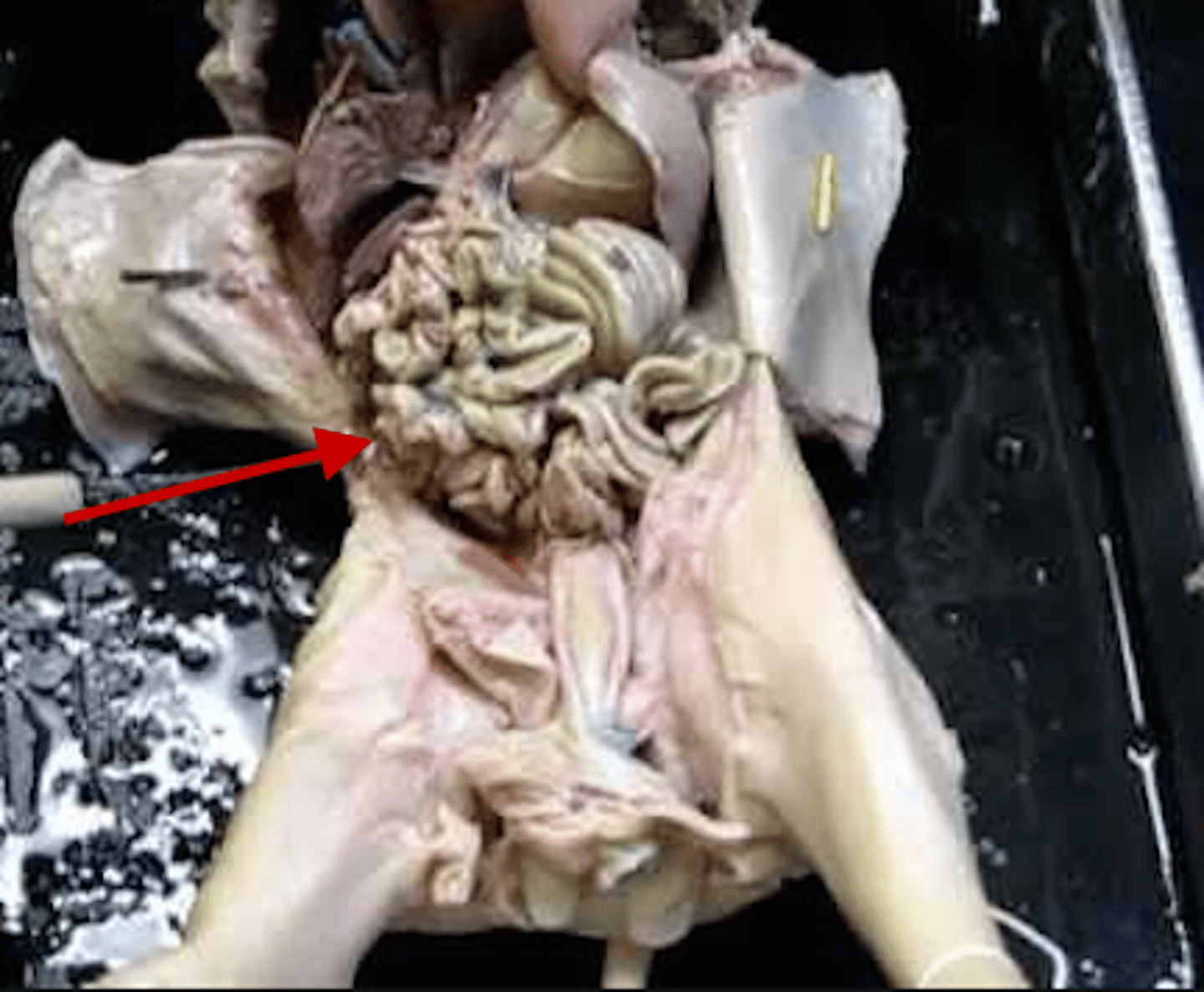
Small intestine
It has three sections, in descending order: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. The duodenum is the only section that is not attached to the abdominal wall via mesenteries. Surface area for absorbing nutrients is increased by organ's length, circular folds, villi, & microvilli.

Large intestine
Water absorption and feces elimination are the primary physiological functions, it also provides a transport route and a surface for healthful bacteria. (cecum, spiral colon, ileocecal valve, tranverse, descending, and sigmoid colon)
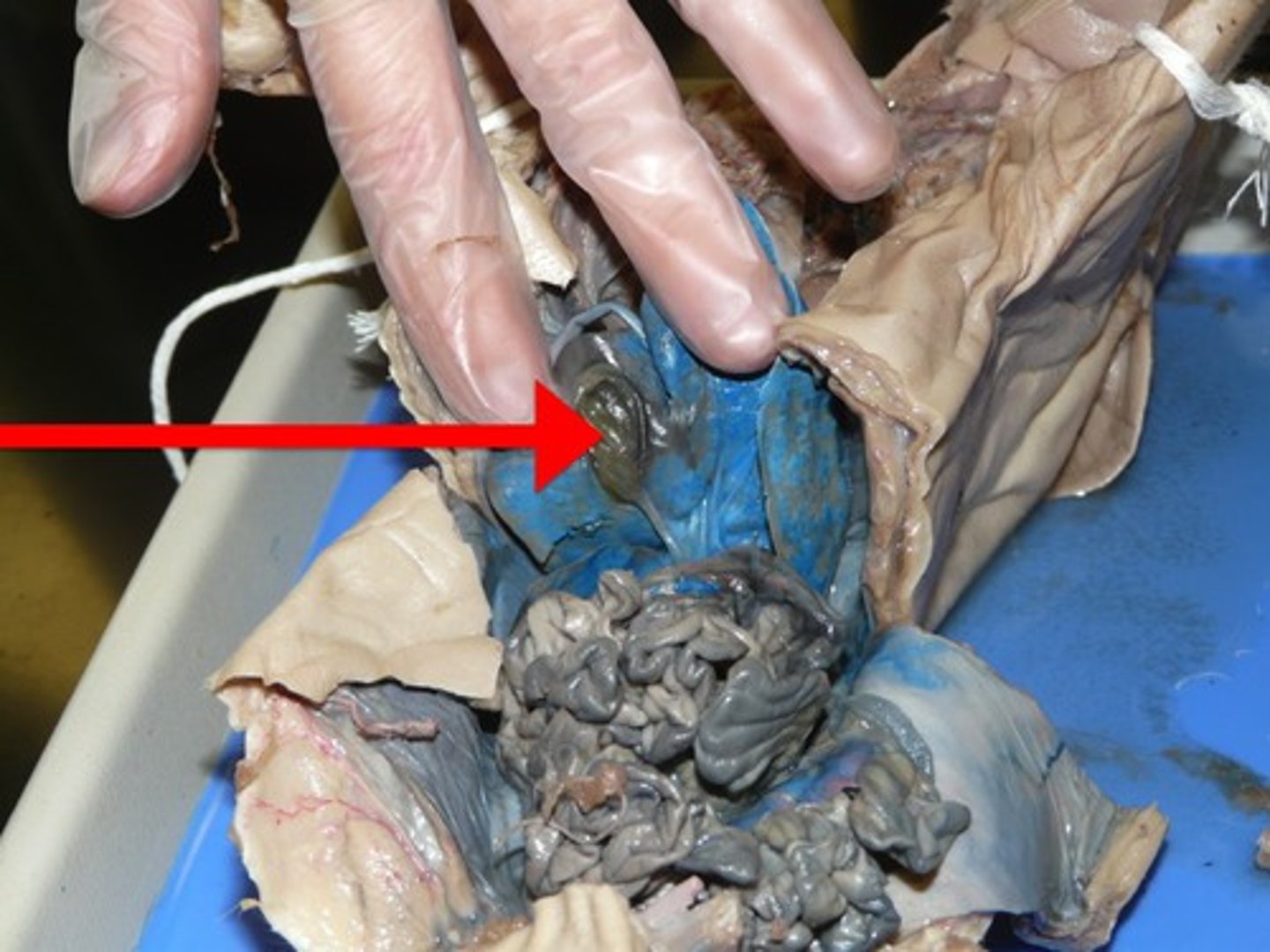
Cecum
#5
Pouch connected to the junction of the small and large intestines. The internal wall is composed of a thick mucous membrane, through which water and salts are absorbed
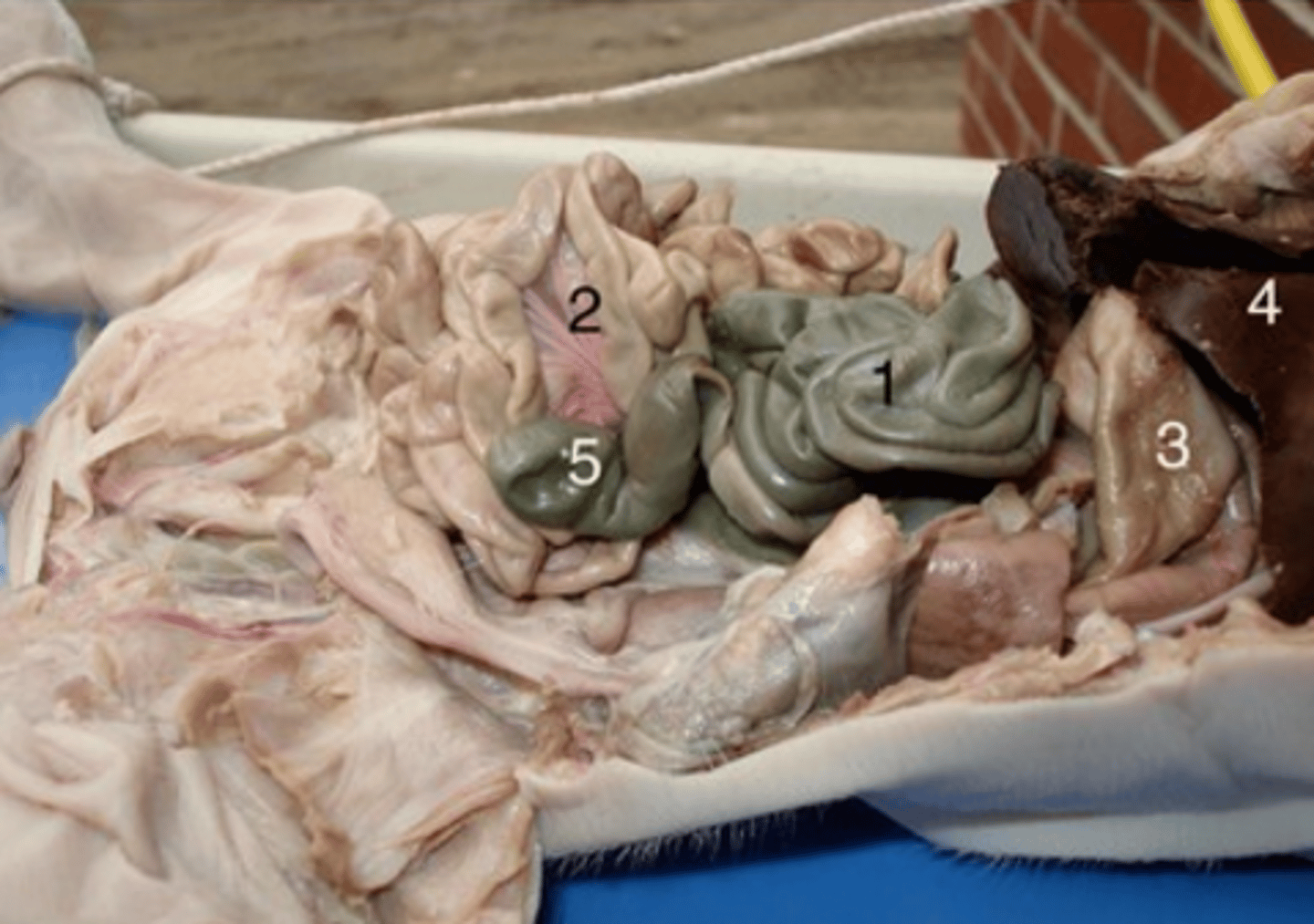
Rectum
#7
Temporary storage for feces before being expelled out of body.
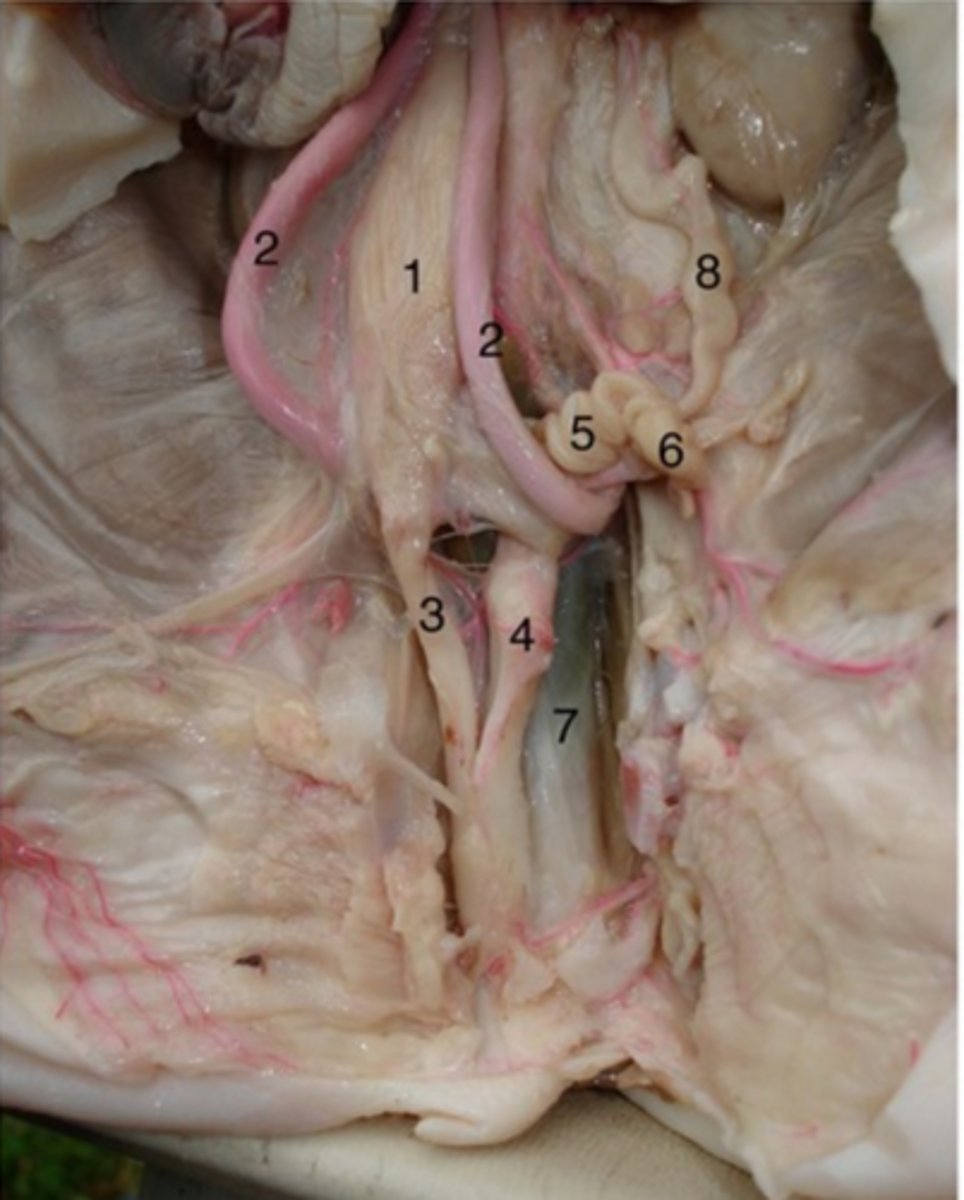
Kidneys
Major excretory organ, filter nearly 200 liters of fluid from our bloodstream
- It is anterior to the ribs, behind the peritoneum
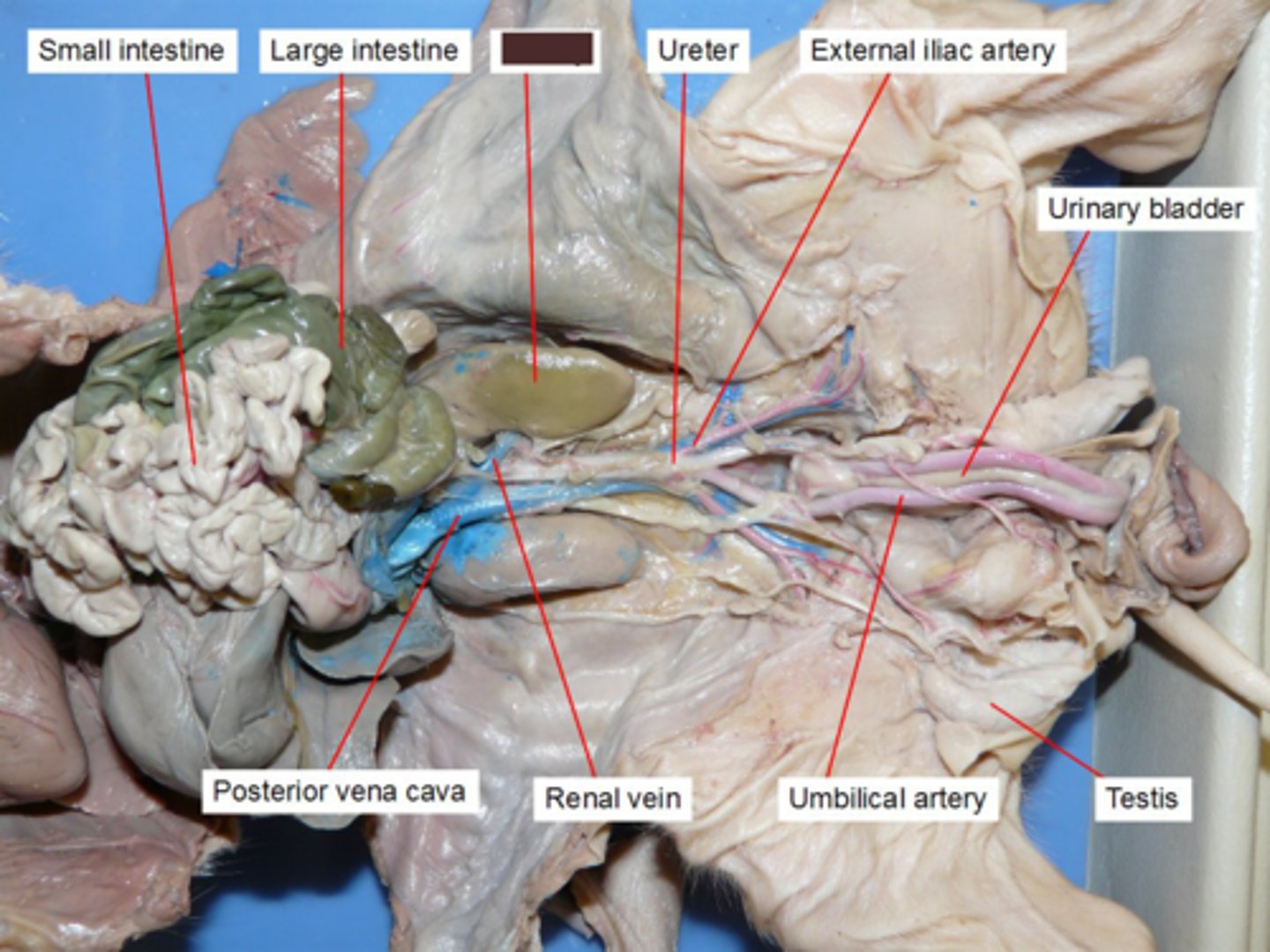
Penis
#3
Both a reproductive organ and an excretory organ
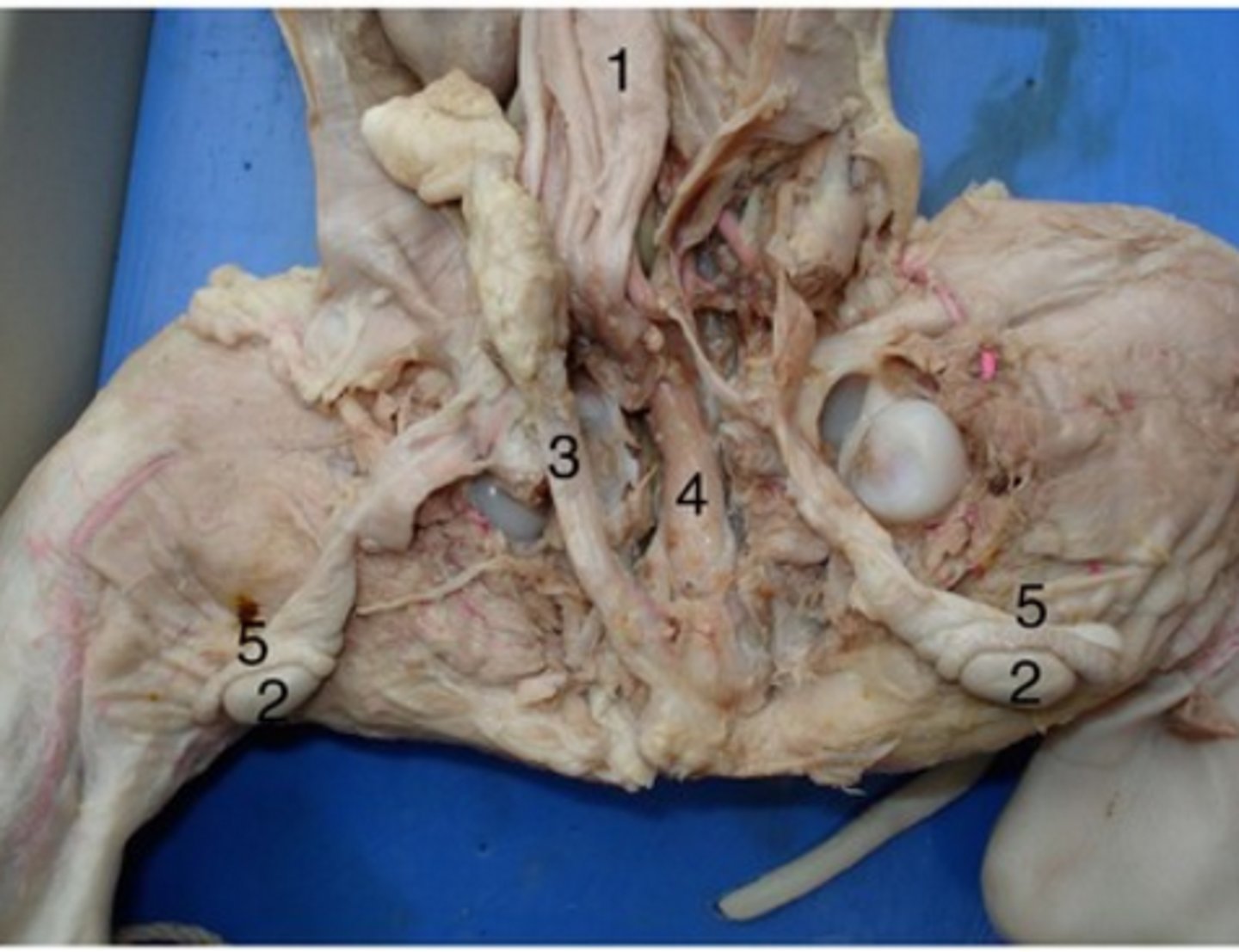
Testis
#2
Two functions - to produce sperm and to produce hormones, particularly testosterone
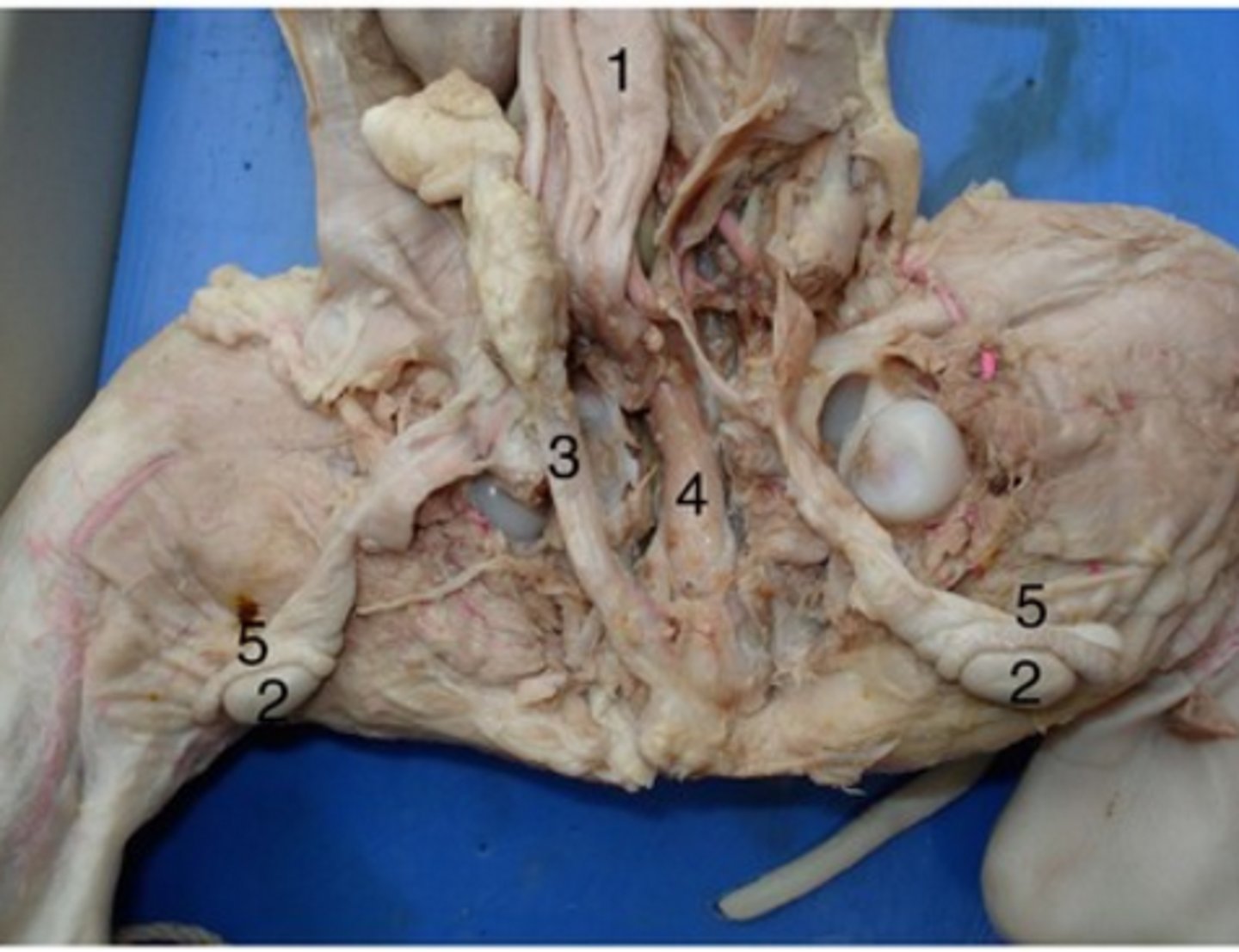
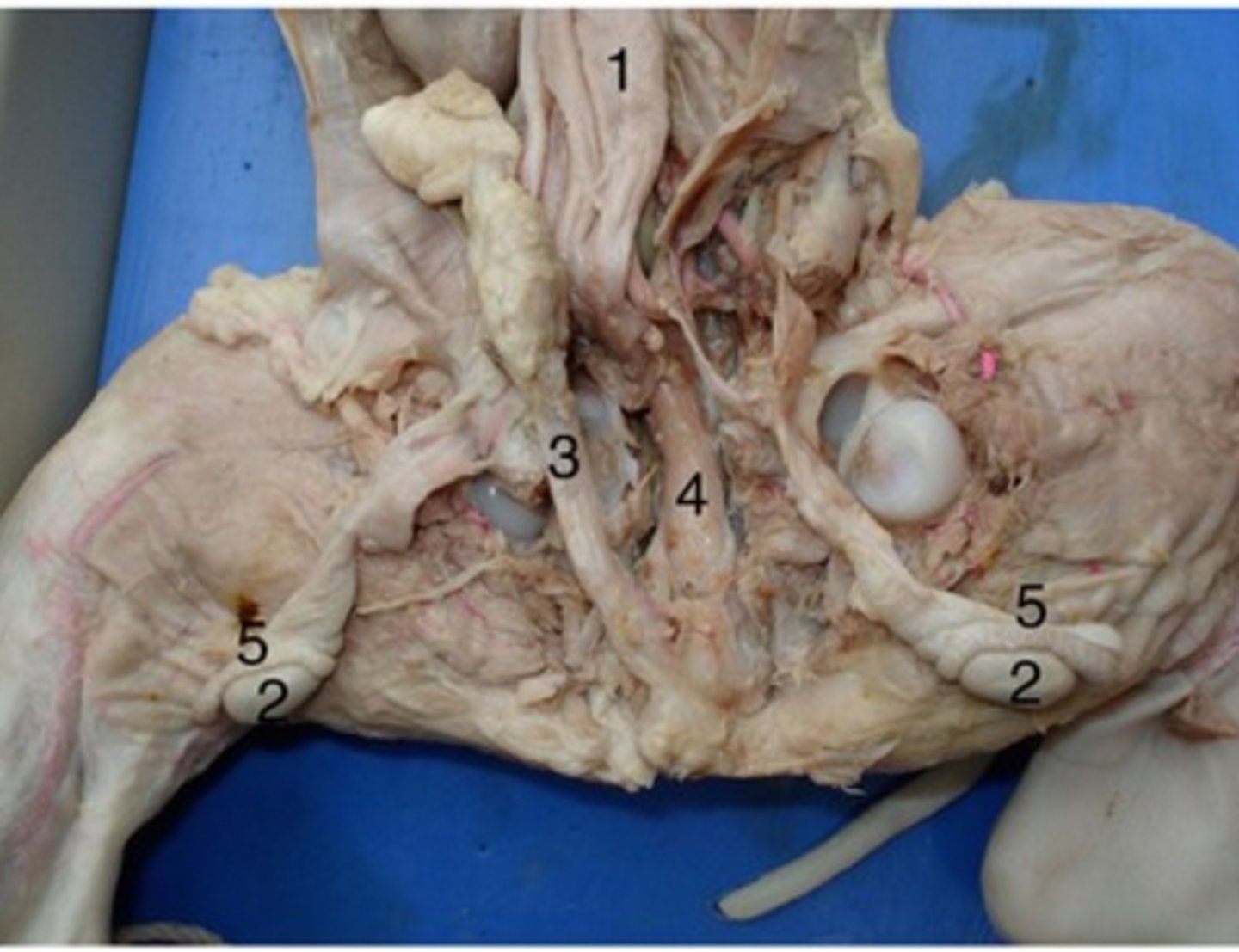
Epididymis
#5
Long, coiled tube that stores sperm and transports it from the testes
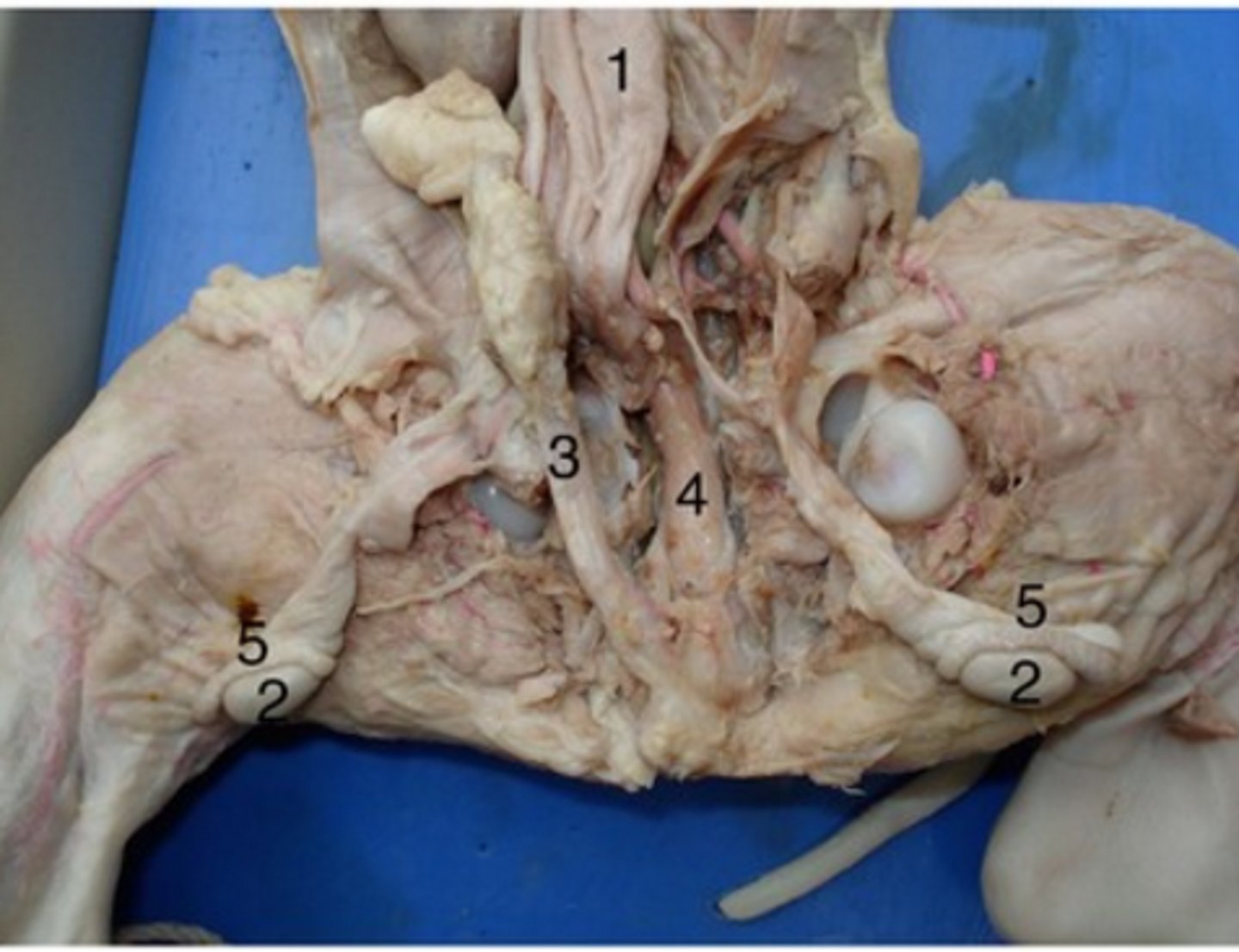
Urethra (male)
#4
Drains urine from bladder & conveys it out of body- internal urethral sphincter (smooth muscle at bladder-urethra junction) is involuntary & keeps urethra closed when urine is not being passed & prevents leaking between voiding
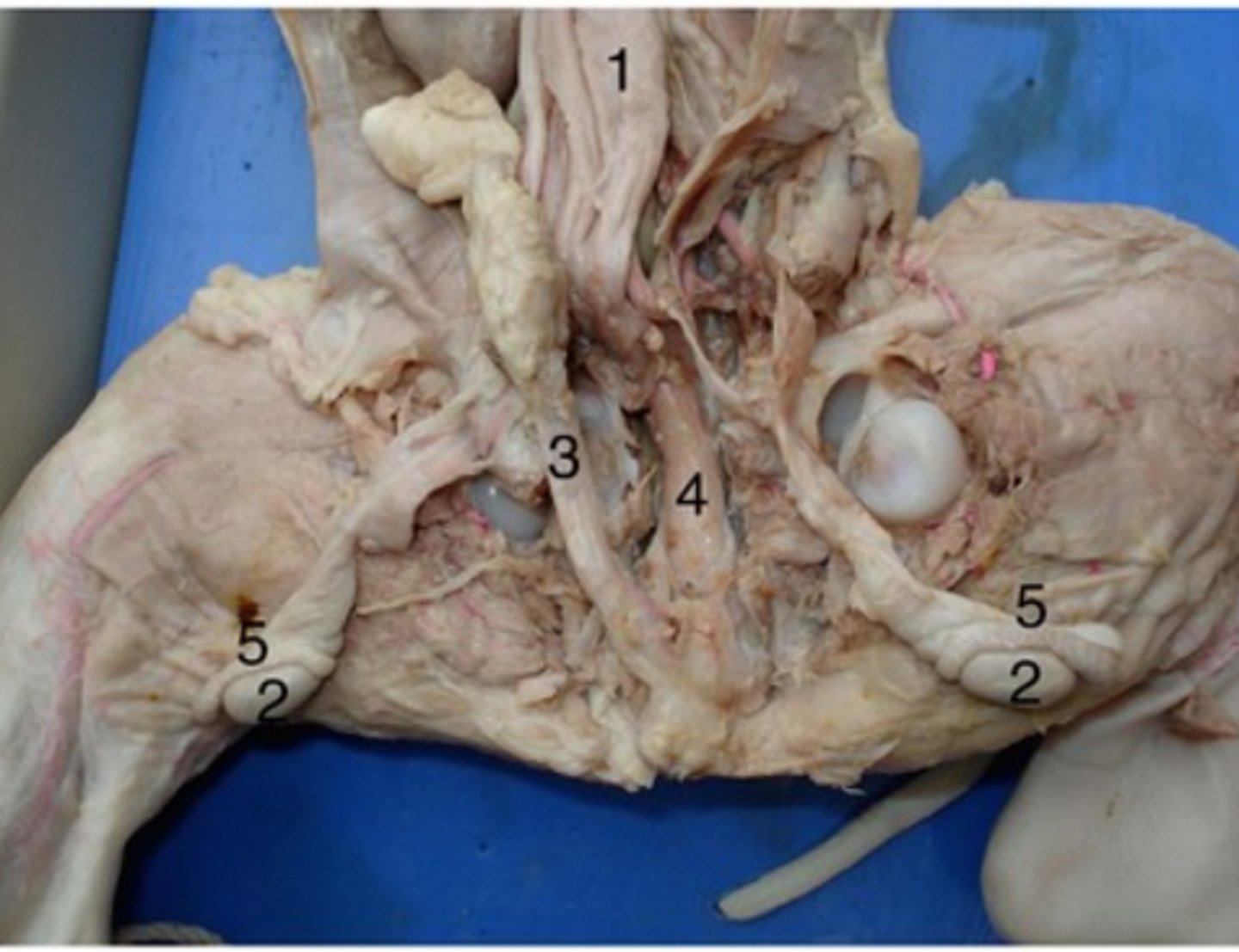
Urinary bladder (male)
#1
Stores urine
Uterine tubes
#5
primary function is to transport sperm toward the egg, which is released by the ovary, and to then allow passage of the fertilized egg back to the uterus for implantation.
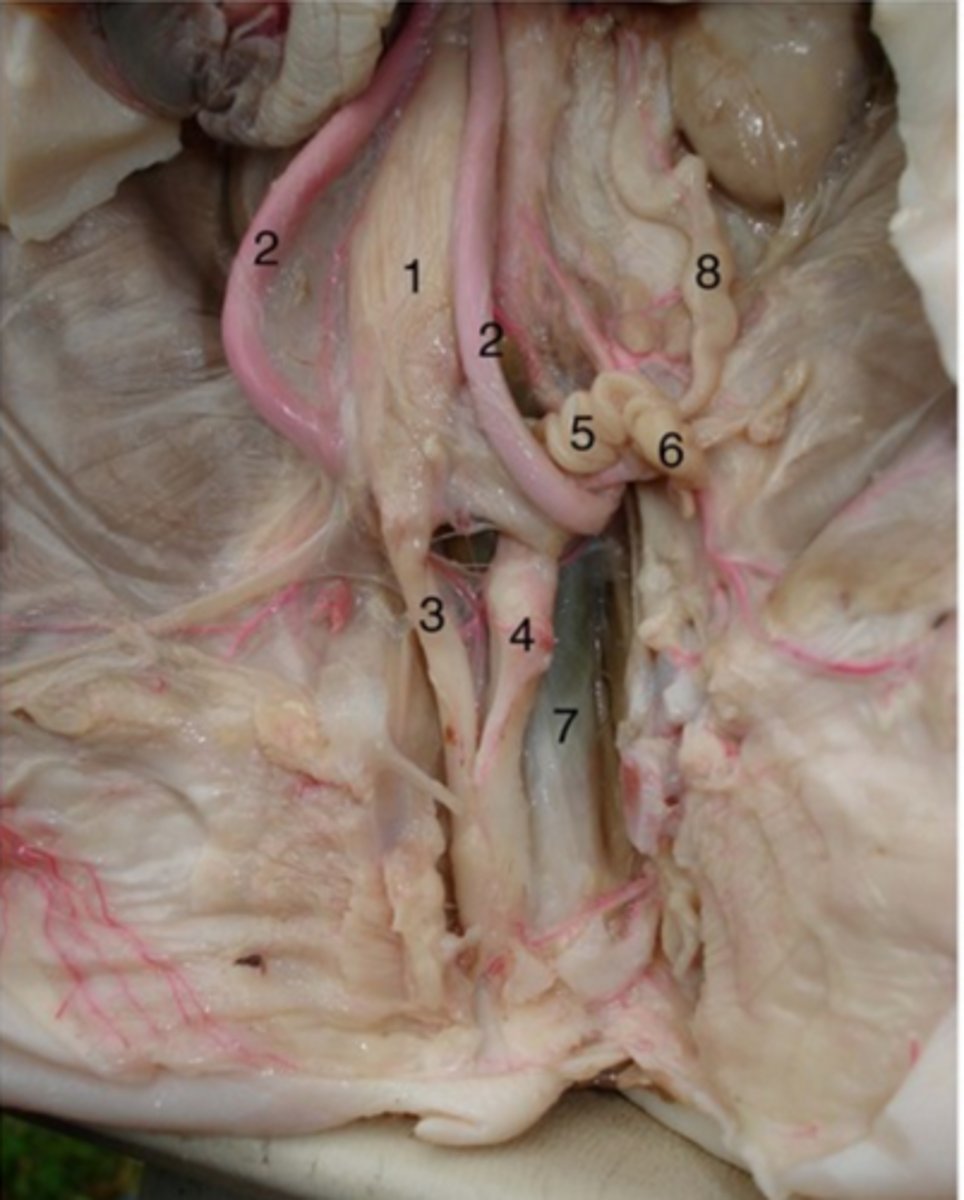
Ovaries
#6
Produce oocytes (eggs) for fertilization and they produce the reproductive hormones, oestrogen and progesterone
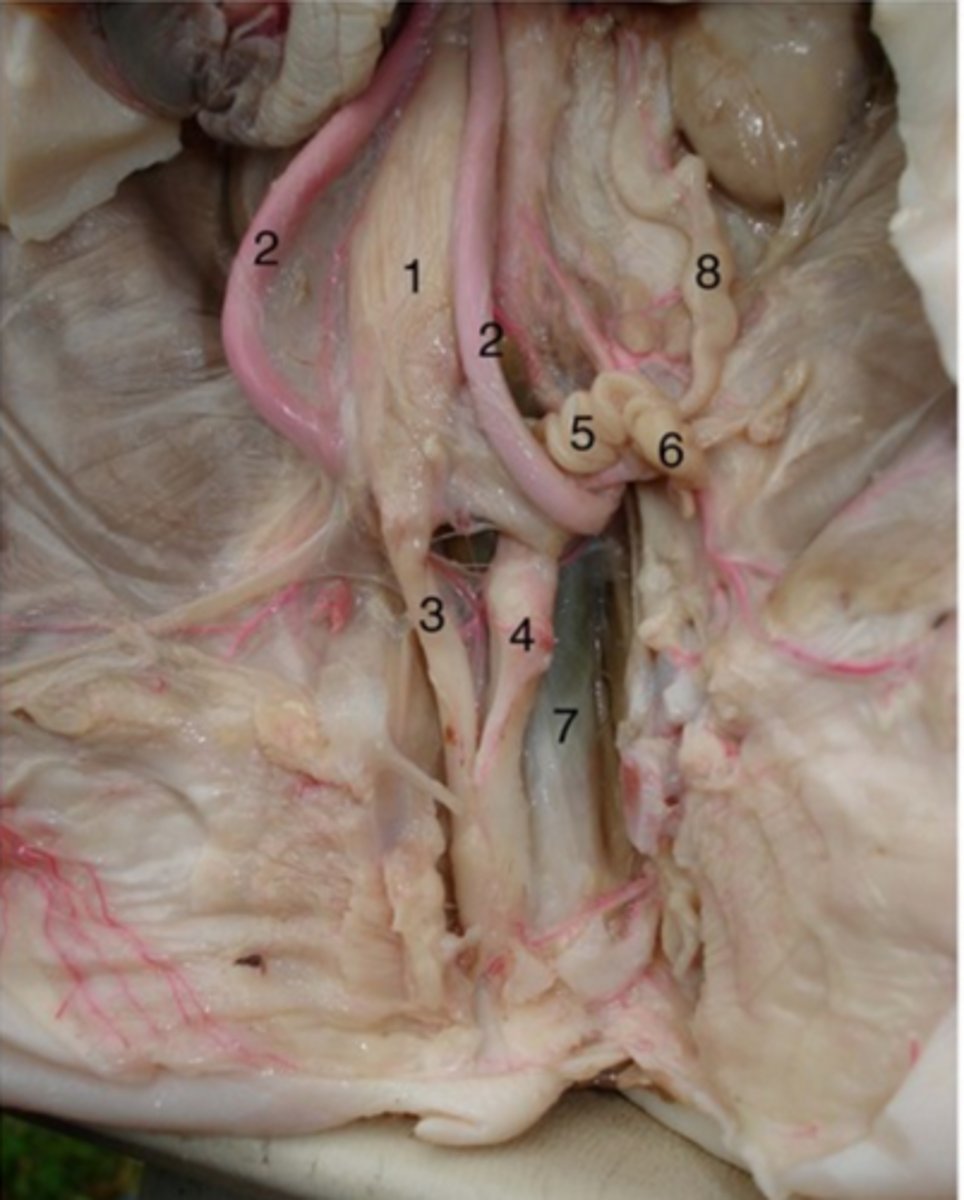
Vagina
#4
It receives the penis during sexual intercourse, provides the passageway for menstrual blood during menstruation, and serves as the birth canal for fetal offspring.
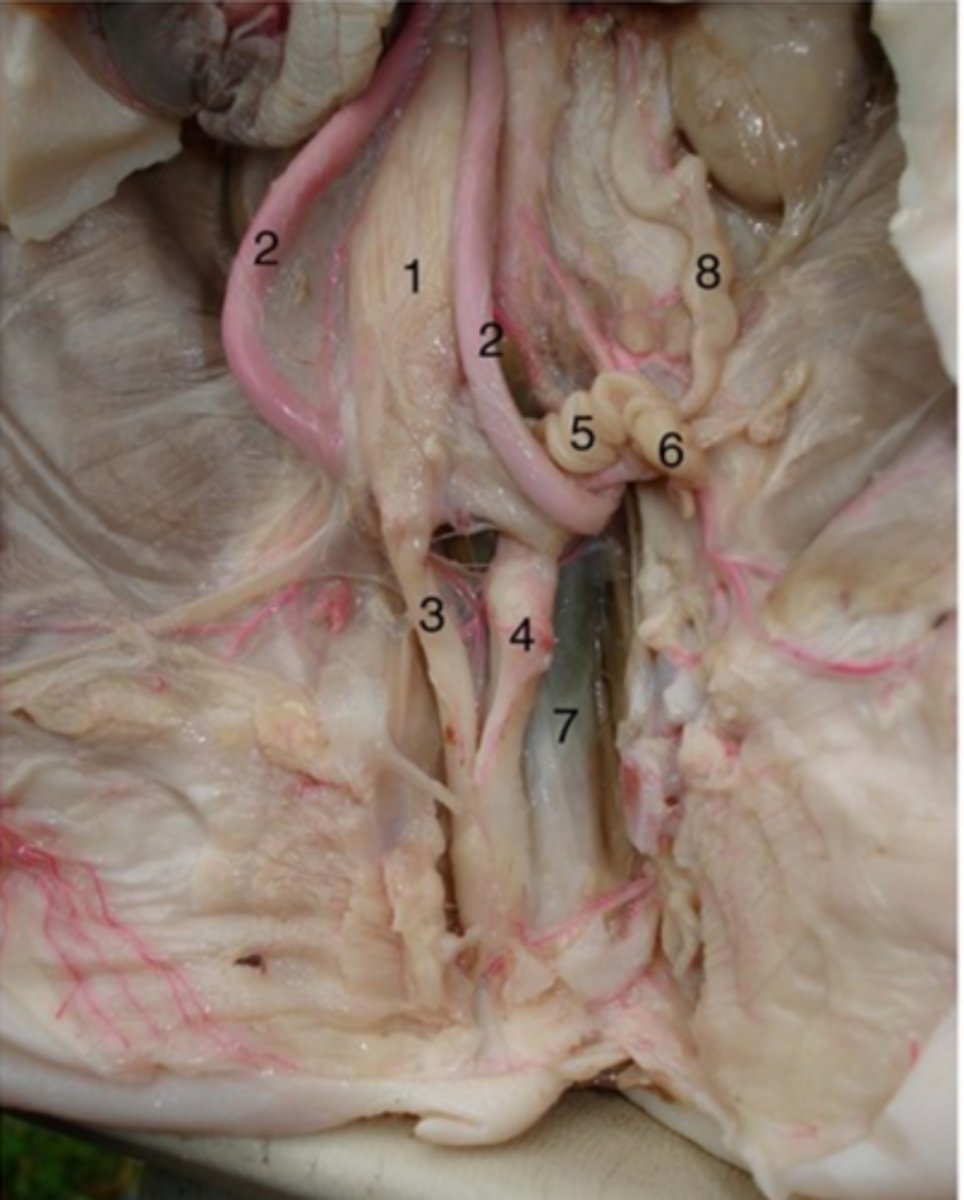
Urethra (female)
#3
Drains urine from bladder & conveys it out of body- internal urethral sphincter (smooth muscle at bladder-urethra junction) is involuntary & keeps urethra closed when urine is not being passed & prevents leaking between voiding
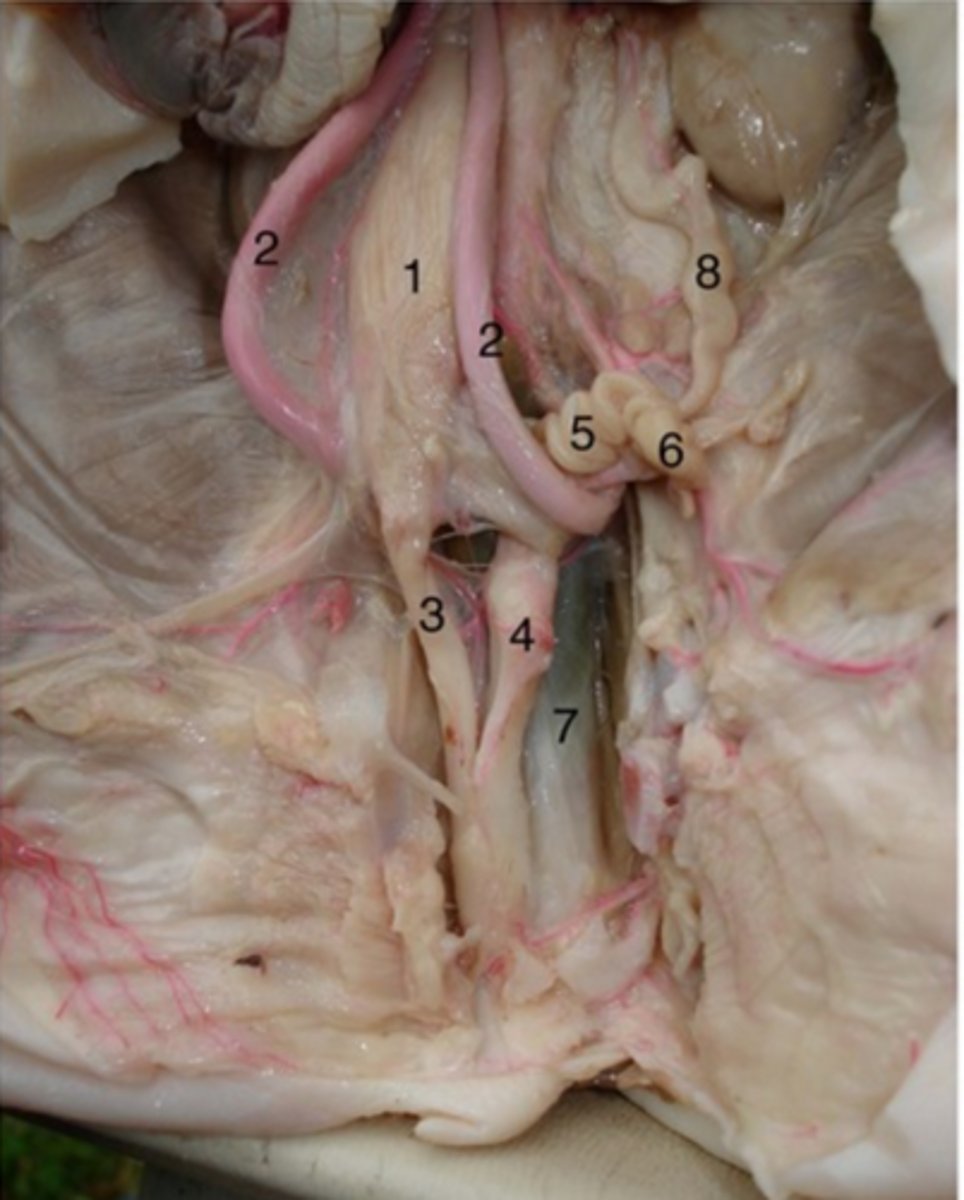
Ureter
#8
- transport urine from kidneys to bladder
- backflow prevented because increase in bladder pressure compresses & closes distal ends of ureters
- 3 layers: mucosa, muscularis, adventitia
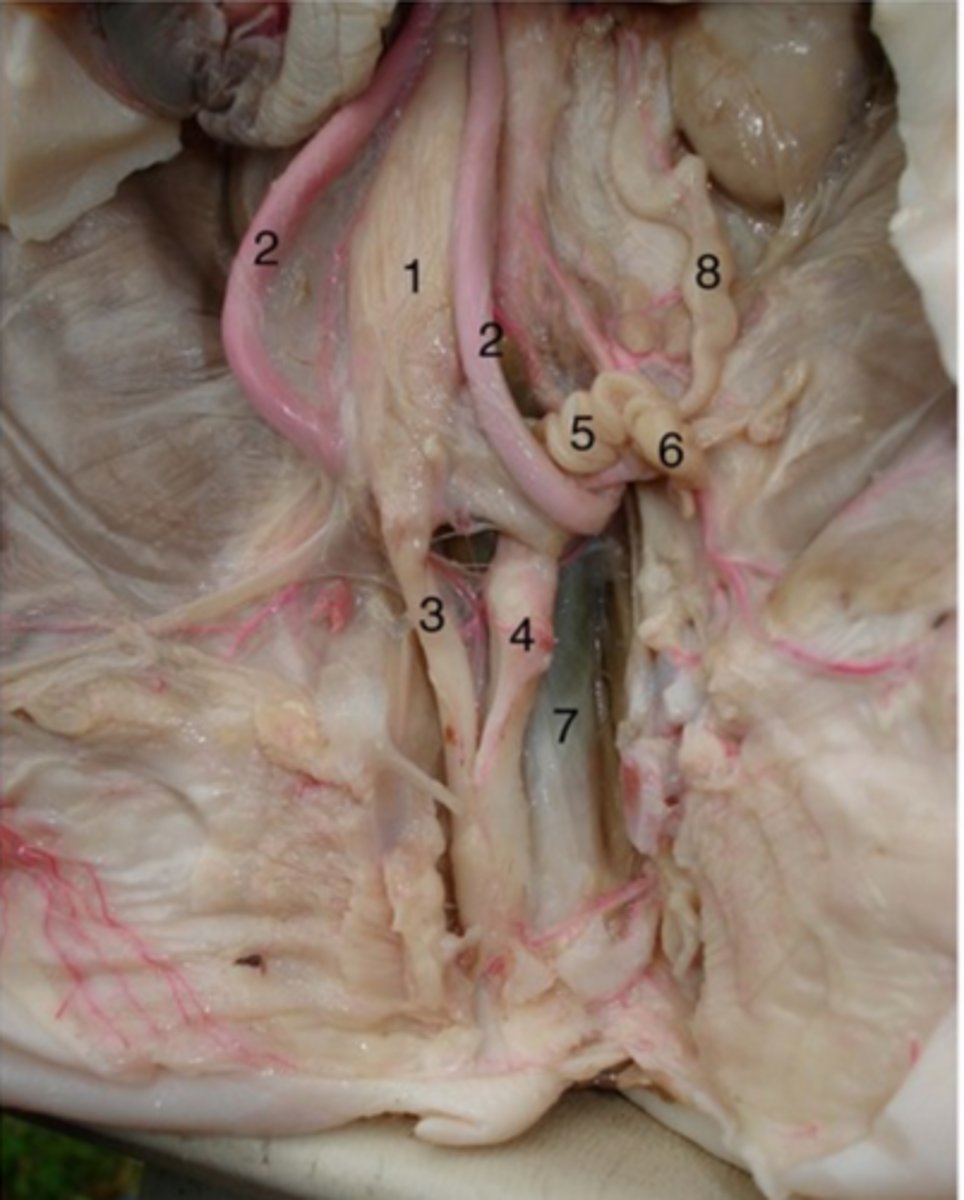
Urinary bladder (female)
#1
(#2 is umbilical arteries)
Stores urine
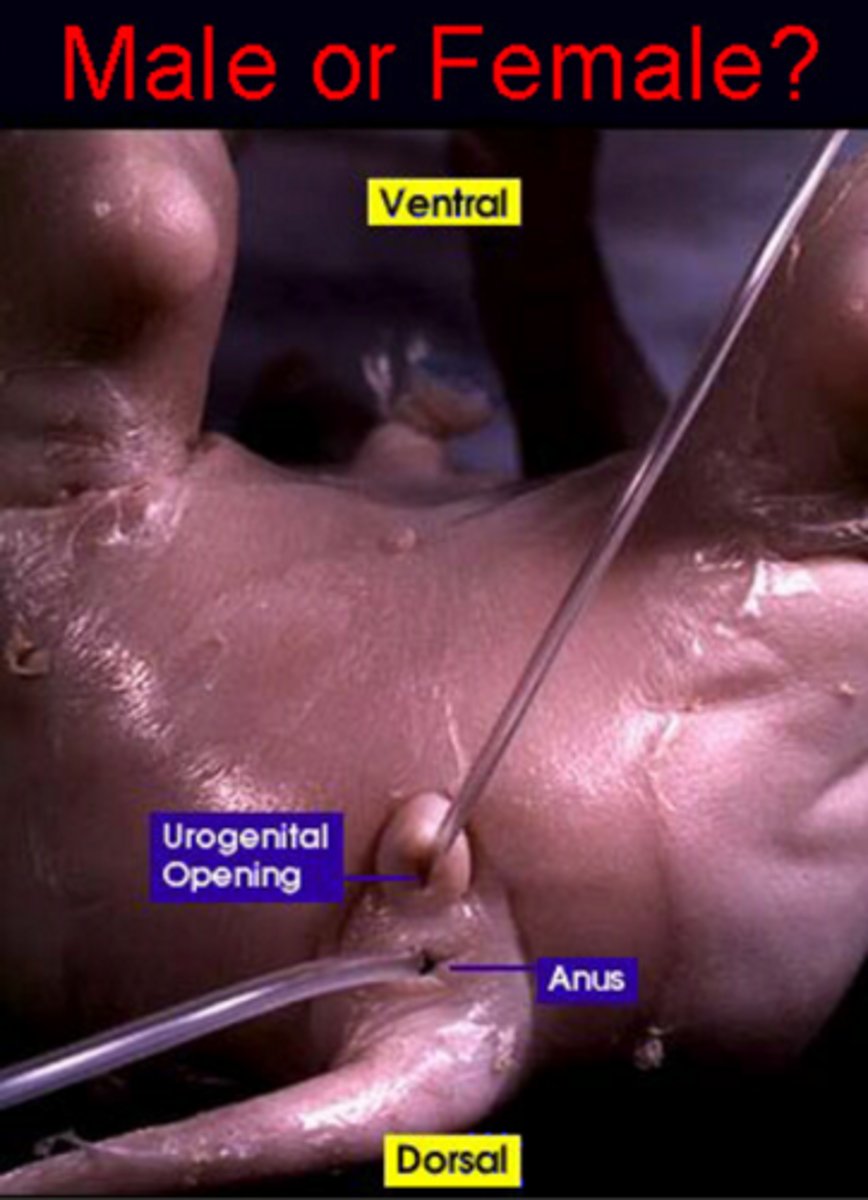
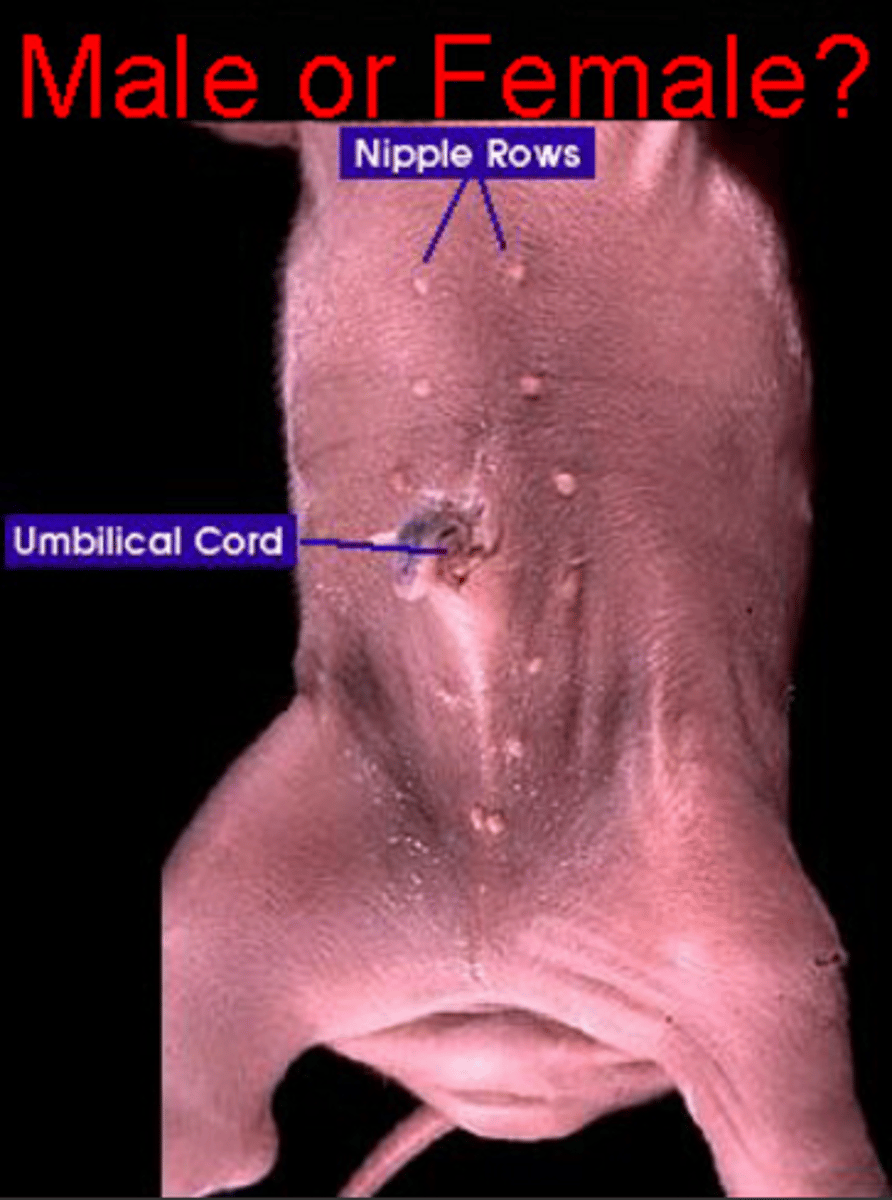
Male
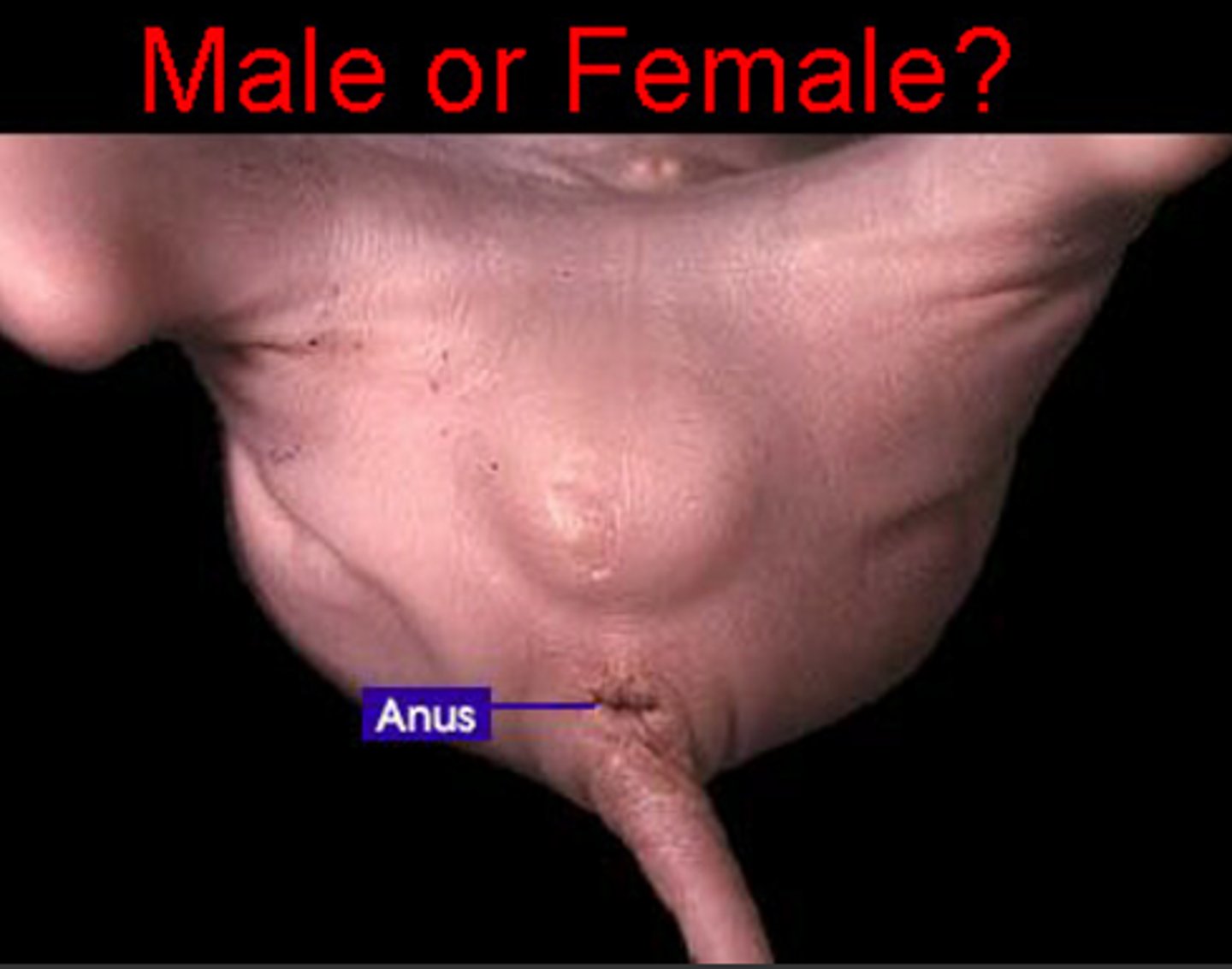
Male
Female
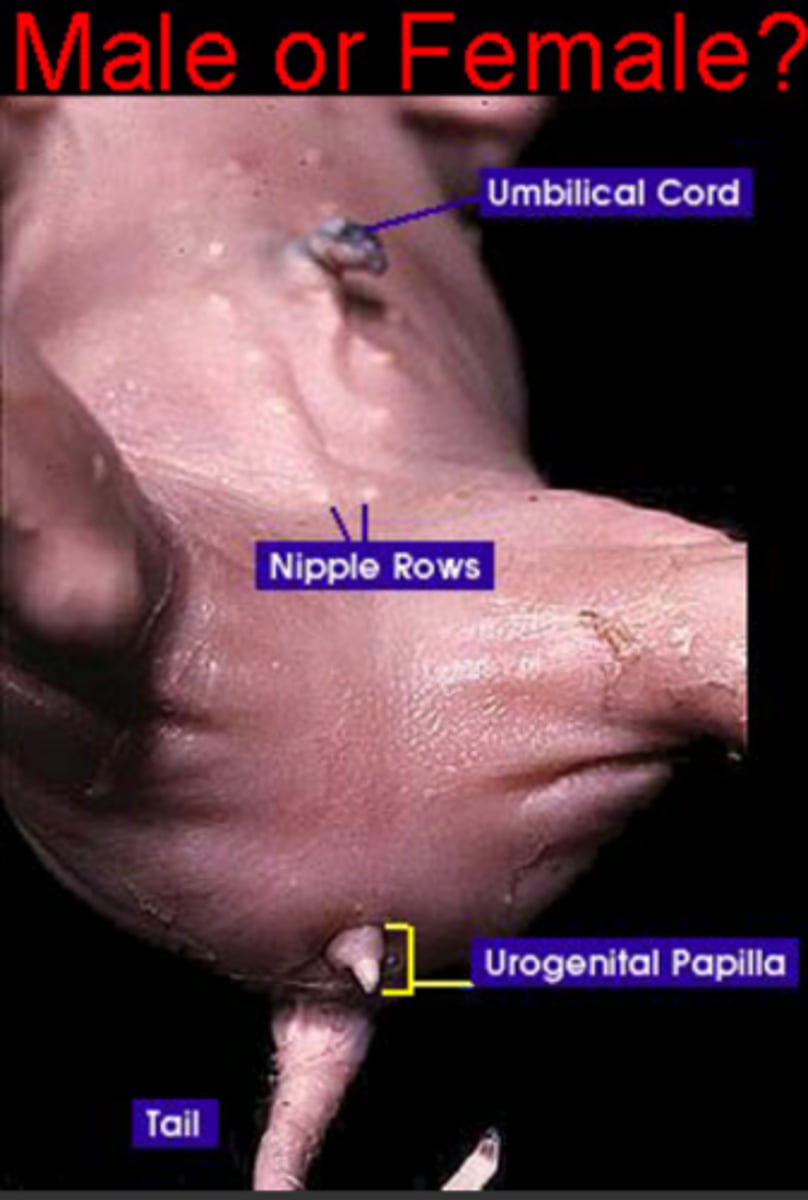
Female