Vertebrates Exam 2
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
Salamander Families
Cryptobranchidae
Proteidae
Amphiumidae
Salamandridae
Plethodontidae
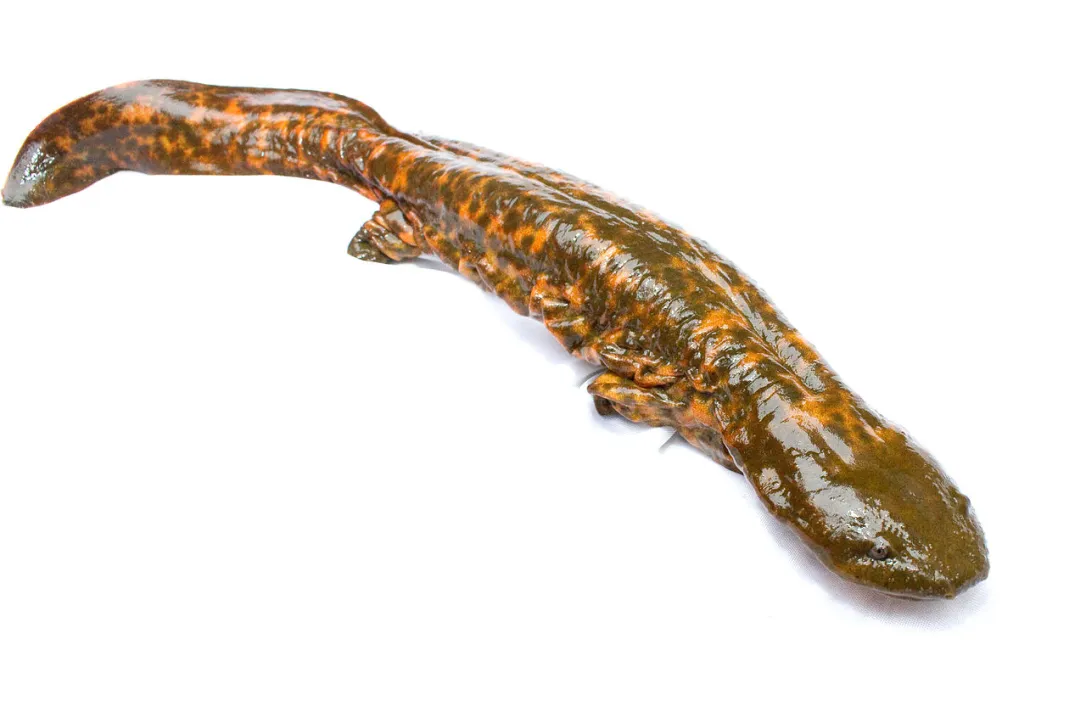

Cryptobranchidae
Aquatic but do not retain external gills as adults
Most respiration done through skin
Lungs function for buoyancy

Proteidae
Mudpuppies/waterdogs (Necturus)
Fully aquatic that retain external gills
Amphiumidae
Well developed lungs
Fully aquatic - can aestivate in mud for 2+ years
Salamandridae
Diverse family (55 species)
Bright coloration (aposematic warning of toxicity)
All produce toxic skin secretions
Textrodotoxins
Neurotoxin found in Salamandridae
100x more poisonous than potassium cyanide
Prevents action potentials from starting by blocking Na+ channels
Toxicity varies
What do male Red-Spotted Newts develop during breeding season?
Horny nuptial pads on their hind legs to help grasp the female
Plethodontidae
Lungless salamanders
380 species
Feeding specializations (tongue projection mechanism, no elongate ribs, hyobranchial apparatus)
Why is the tongue projection mechanism only possible in Plethodontidae
No lungs
Hyobranchial apparatus
Facilitates buccal pumping and could become co-opted for tongue projection
What allows tongue projection to be temperature independent?
The elastic recoil of collagen fibers within the muscle which store energy during excitation
How long before the tongue leaves the mouth are the tongue projector muscles activated?
80-180 milliseconds
What indicates a dissociation between muscle electrical activity and tongue action?
Collagen fibers within the muscle are stretched during excitation, storing energy before release
What mechanism propels the tongue out of the mouth?
The stored elastic energy in collagen fibers recoiling, rather than direct muscle contraction
Evolution of tongue projection in Plethodontinae
First ceratobranchial used in larval suction feeding
Second ceratobranchial elongated after metamorphosis
Tongue projection less extensive
Evolution of tongue projection in Hemidactyliinae
No aquatic larval stage
Second ceratobranchial elongated during embryonic development
Nasolabial grooves
Fluid drawn up into groove via capillary action
Drawn into nose via ciliary movement within nasal cavity
Chemicals pass over chemoreceptors in vomeronasal organ
Most salamanders have internal fertilization except…?
Cryptobranchidae
Sirenidae
Describe internal fertilization via spermatophore
Spermatophore = sperm cap on gelatinous base
Euproctus male deposits spermatophore on female then uses his feet to grasp spermatophore and insert into female
In most species female picks up sperm cap after courtship behavior between sexes
What are the different ways female salamanders obtain sperm from spermatophores?
Aquatic
Terrestrial
Courtship
How do female salamanders obtain sperm from spermatophores aquatically?
Male releases water-borne pheromones to coax female to pick up his spermatophore
How do female salamanders obtain sperm from spermatophores terrestrially?
Male undulates tale under female to ensure spermatophore transfer
How does courtship work for salamanders?
Pheromones delivered by males via mental gland under his chin
May be slapped on female which volatilizes molecules
Sometimes delivered directly into female’s blood system (facilitated by enlarged teeth)
Spotted Salamander Egg Masses
Eggs larger in size
Stay intact when pulled out of water
Have symbiotic relationship with green algae
What does the presence of green algae with Spotted Salamander eggs result in?
Embryos hatch earlier
Decreased embryonic mortality
Synchronous hatching
Later development stage at hatching
What are the benefits from the symbiotic relationship between Spotted Salamander eggs and green algae?
Algae use nitrogenous wastes from embryos
Embryos use increased oxygen produced by algae
Jefferson Salamander egg masses
Eggs smaller in size (laid in cylindrical tubes)
Loose or drippy when pulled out of water
General features of Anura
Globose body form
Males vocalize to attract females
Toads
Frogs
Locomotion via saltation (to leap)
General features of Toads
Stout bodied
Blunt head
Short legs
Make short hops
Terrestrial
General features of Frogs
Slightly more slender than toads
Long legs
Make long leaps
Can be terrestrial, arboreal, or aquatic
Urostyle
Fusion of posterior vertebrae and elongated ilium
What locomotion mechanisms allow Anurans to leap?
Urostyle
Fusion of tibia and fibula
Stiffened vertebral column
Strong forelimbs
Flexible pectoral girdle (to absorb impact of landing)
Eyes positioned anteriorly on head to enable binocular vision
What do Anurans use to stick to smooth surfaces?
Wet adhesion
How does wet adhesion work in Anurans?
Peg-like projections within epidermal layer trap mucous secretion
Intercalary cartilage increases range of motion while allowing toe pad to remain against surface
What is phragmosis and what type of frog uses it?
Blocking entrance of burrow with part of body
Casque-headed tree frog
Toxic skin secretions from what gland in anurans?
Parotid gland
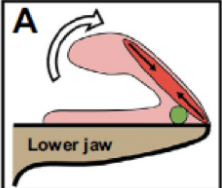
What type of tongue projection?
Mechanical pulling (basal anurans)
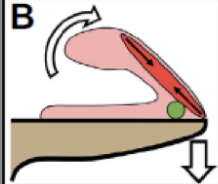
What type of tongue projection?
Inertial elongator (derived anuran)
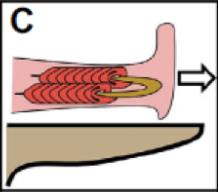
What type of tongue projection?
Ballistic projection (plethodontid salamander)
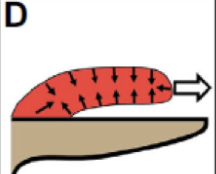
What type of tongue projection?
Hydrostatic elongator (some anurans)
Types of reproduction in Anura
Explosive breeding
Prolonged breeding
Characteristics of explosive breeding
Lasts only a few days
Breed in ephemeral aquatic habitats (ex. vernal ponds)
Males and females arrive simultaneously and in large numbers
Sex ratio close to 1:1
Mating success similar from one male to the next
Time is the main constraint on mating success
Characteristics of prolonged breeding
Breeding season may last several months
Males arrive first
Males often establish territories
Males always outnumber females who visit on one night
Male success is highly variable
Males compete for female via vocalizations
Females use multiple characters to decide suitor
What characters do female anurans use to evaluate a suitor’s call?
Pitch
Length
Repetition
Why is calling energetically costly for male anurans?
It depletes energy stores with long calls being the most costly
What percentage of glycogen stores can be depleted in a single night of calling?
Up to 50% in 2-4 hours of calling
What type of energetic investment do anurans use for calling?
Capital investment (stored energy)
How does the Borneo tree hole frog adjust its call?
It matches the frequency of its call to the resonant frequency of the tree hole
How do Agalychnis callidryas tadpoles avoid predation?
They hatch prematurely when predators vibrate the leaves/branches they are on
Modes of reproduction in Anurans that counteract egg predation
Skin brooding
Vocal sac brooding in males
Gastric brooding
Foam nest building
Describe gastric brooding (platypus frogs)
Female ingested fertilized eggs and swallowed them into her stomach
Stomach is normally functioning when eggs swallowed
Jelly substance surrounding eggs contained prostaglandin E2 (inhibited HCl production in stomach)
Once hatched tadpoles also released prostaglandin E2 from gills
What are the stages of foam nest building (tungara frogs)?
Bubble raft construction (no egg deposition)
Building foam with egg deposition (mixing is constant)
Building more foam but mixing events are intermittent with intervals increasing exponentially
Synapomorphies of Amniotes
Amniotic egg
Skin elaborations from keratin (skin, hair, feathers)
Costal rib ventilation of lungs (strong suction enables evolution of longer necks)
Complex innervation of forelimbs
What does complex innervation of forelimbs allow for in amniotes?
Complex control of limb manipulation
What are the three extraembryonic membranes of the amniotic egg and what do they do?
Chorion (surrounds entire contents of egg)
Amnion (inner membrane that surrounds just the embryo)
Allantois (storage for nitrogenous wastes)
Skull fenestration
Openings in the skull that made room for muscle bulging
Accommodates for increased muscle mass
How might skull fenestration have evolved?
No longer needed buccal pumping with costal ventilation providing large suction
Skull did not need to be as large
Muscles could diversify
What are the types of mammal-like reptiles (extinct)?
Pleycosaurs
Therapsids
Moschops
Cynodonts
Describe Pleycosaurs
Sailbacks of late Palezoic
Most were generalized carnivores
Some herbivores
Describe Therapsids
More derived than pleycosaurs
Increased metabolic rate (possibly homeothermic)
Heavy-bodied, large headed, stumpy-legged
Large temporal fenestra (suggests larger adductor muscles)
Heterodont dentition (incisors, canines, and molars)
Describe Cynodonts
Reduced body size
Multicusped cheek teeth
Probably laid eggs
Enlarged infraorbital foramen (space for snout nerves)
Nasal turbinates (scroll like bones in nasal passages that help to minimize water and heat loss)
Define synapsida
Mammals and their extinct relatives
List evolutionary trends in Synapsids
First amniotes to diversify in terrestrial habitats
Most were medium to large sized animals
Most lineages went extinct at end of Triassic period (those surviving were rat sized or smaller)
List the advanced therapsid apomorphies
Skull
Limbs
Short feet and toes
Loss of lumbar ribs
Shorter tail
Describe the skull apomorphy of therapsids
Size of temporal fenestra increased
Zygomatic arch bowed outward
Coronoid process of dentary is extended
Heterodont dentition (differentiation of function and roles in eating)
Bony secondary palate (allows for simultaneous eating and breathing)
Changes in skull structure allowed for increased jaw musculature
Many jaw bones that were either fused with dentary or shifted to the ear to help with hearing
Describe the limbs apomorphy of therapsids
Limbs placed more medially (resolves conflict between locomotion and breathing)
Limbs free to move anteriorly-posteriorly without bending of trunk
Gait not as much side to side movement
Supporting girdles more lightly built - weight of body supported more by limbs
Describe the short feet and toes apomorphy of therapsids
Gait not sprawling
Movement now more rapid
Describe the loss of lumbar ribs apomorphy of therapsids
Increased dorsoventral flexion
Describe the shorter tail apomorphy of therapsids
Indicates locomotion is now accomplished by limb propulsion rather than axial bending
What type of dentition do mammals have?
Mammals have diphyodont dentition, meaning they only replace their teeth once
How does diphyodont dentition differ from polyphyodont dentition?
Diphyodonts have only two sets of teeth, while polyphyodonts (most other vertebrates) continuously replace their teeth.
Which mammals are exceptions to diphyodont dentition?
Elephants and manatees continuously replace their molars from the back of the jaw
What allows mammals to efficiently chew a variety of foods?
Precise occlusion, where teeth align perfectly for efficient mastication with different diets
Why is precise occlusion difficult with only two sets of teeth?
Jaw growth could misalign teeth preventing proper occlusion
How do mammals maintain precise occlusion despite jaw growth?
Milk teeth develop when feeding on a liquid diet (where occlusion isn’t crucial) and the second set erupts when the jaw reaches full size
What glands are mammary glands similar to?
Mammary glands are similar to sebaceous glands because they secrete small amounts of organic materials
What was the likely composition of the first proto-milk?
It was produced in small quantities and contained antibacterial proteins
What was the likely function of the first proto-milk?
It helped protect thin-shelled eggs from drying out and from microorganisms
How did milk secretion evolve over time?
It became more copious and nutritive supporting the growth of young
What is a unique mammalian feature related to feeding?
Suckling
How is suckling made possible in mammals?
A fleshy seal is formed against the hard palate using the tongue and epiglottis
What is the function of the fleshy seal during suckling?
It isolates breathing and swallowing allowing both to occur simultaneously
Synapomorphies of mammals
Mammary glands
Integument (has unique features)
Skeletal System
In which male mammals are mammary glands present?
Monotremes and eutherians, but they are absent in marsupials
Which male mammal has been recently described as producing milk?
Fruit bat
In which female mammals are mammary glands present?
All species of mammals
Which mammals have nipples?
Only therian mammals (marsupials and eutherians) monotremes lack nipples
What are the unique features of mammalian integument?
Hair and glands
What are the functions of hair in mammals?
Camouflage
Communication
Sensation
Insulation
What muscle is attached midway along the hair shaft?
The arrector pili muscle
What happens when the arrector pili muscle contracts?
It raises the hair which can signal fear, anger, or cold temperature
How does hair help with insulation in cold temperatures?
The arrector pili muscle contracts making the fur stand up and trapping more air for insulation
What is the function of eccrine glands in mammals?
They produce a watery secretion that promotes adhesion
In primates they function as sweat glands for cooling
Where are eccrine glands located in most mammals?
On foot pads and prehensile tails
What is the function of sebaceous glands?
They secrete a viscous substance down the hair follicle to lubricate and maintain hair condition
What is the Harderian gland and its function?
It is a sebaceous gland associated with the eye
It secretes an oily substance that travels down the nasolacrimal duct to aid in fur preening and waterproofing
What is the function of apocrine glands?
They produce volatile secretions (mostly down the hair follicle) used in chemical communication
Where are apocrine glands found in humans?
In the armpits and pubic regions
How do ungulates use apocrine glands?
To cool their body
What type of gland are mammary glands modified from?
Apocrine glands