Chapter 2: Deformation of Solids
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
the amount of stress a material can resist before fracture (permanently deformed)
what is strength
σ = force/instantaneous area
what is the equation for true stress
σ = force/original area
what is the equation for engineering stress
ε = change in length/original length
what is the equation for engineering strain
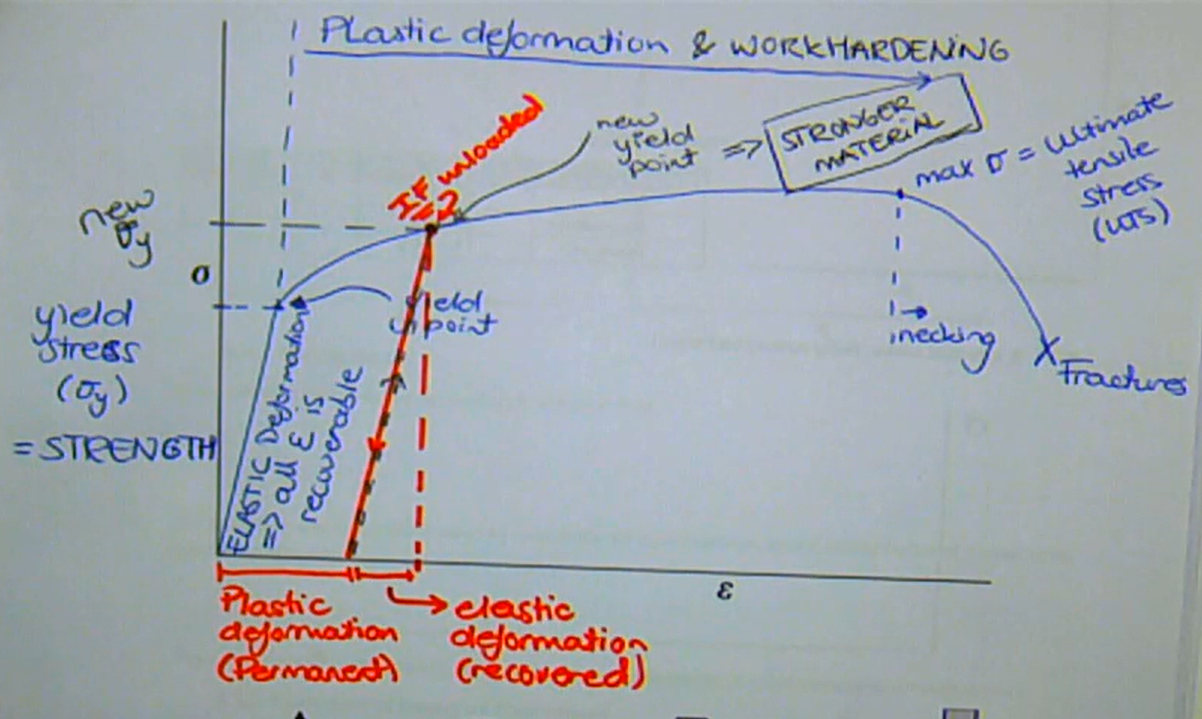
draw a stress-strain curve
recoverable
elastic deformation is what type of strain
straight line
what part of the stress-strain curve represents elastic deformation
permanent
what type of strain is plastic deformation
the maximum point
what point on the stress-strain curve represents the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
the local reduction in area of a material which occurs when stress is greater than the UTS
what is the process of necking
E = stress/strain
what is the equation for Young’s Modulus
ratio of how thin a material needs to be when stretched by a certain amount
what is Poisson’s ratio
v = - εx/εz
what is the equation for Poisson’s ratio
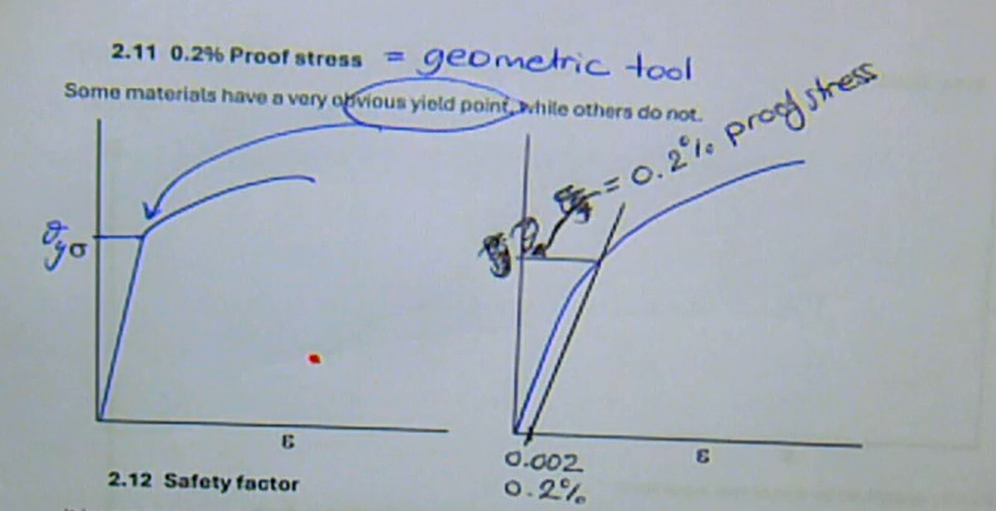
geometric tool used to find the yield point when its not very obvious
→ measure 0.2% of the total strain and draw a straight line going upwards
what is the 0.2% proof stress tool
pretend that:
material is weaker than it actually is
applied force is bigger than it actually is
what are the safety factors used by engineers when designing materials
elastic region where σ < σy
in what region of the stress-strain curve do engineers operate in
how much plastic deformation a material can withstand before fracture
what is ductility
% elongation: % EL = ∆L/∆L0 × 100%
% reduction in area: % RA = ∆A/∆A0 × 100%
what are the two equations that describe ductility
the energy required to fracture a material
what is toughness
area under the stress-strain curve
how is toughness calculated

draw the stress strain-curve for ceramics and glass, steel (Fe-C alloys), metals and ductile materials, and polymers