10.C BIO, HN Darwin Presents His Case (PART C)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Inherited variation
Members of each species vary from one another in important ways. Darwin argued these small differences among individuals within a species mattered.
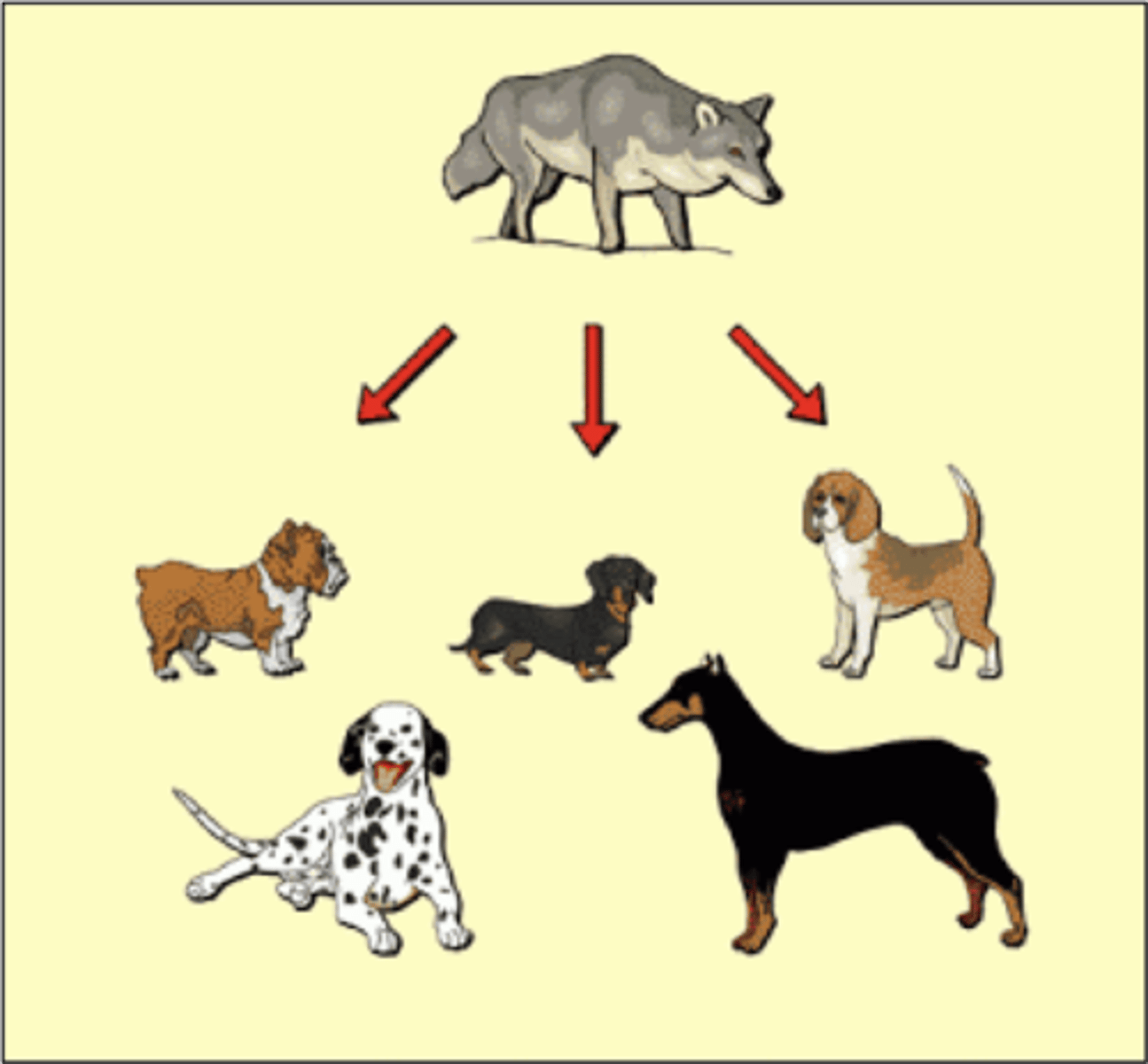
Artificial selection
Selection by humans for breeding of useful traits from the natural variation among different organisms
Natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Struggle for existence
Competition among members of a species for food, living space, and the other necessities of life
Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment
Survival of the fittest
Process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully; also called natural selection
Adaptation
Inherited characteristic that increases an organism's chance of survival that can be structural, physiological or behavioral
Structural adaptation
A physical structure possessed by organism gives it an advantage to survive. For example, large teeth/claws on a lion, spines on a cactus
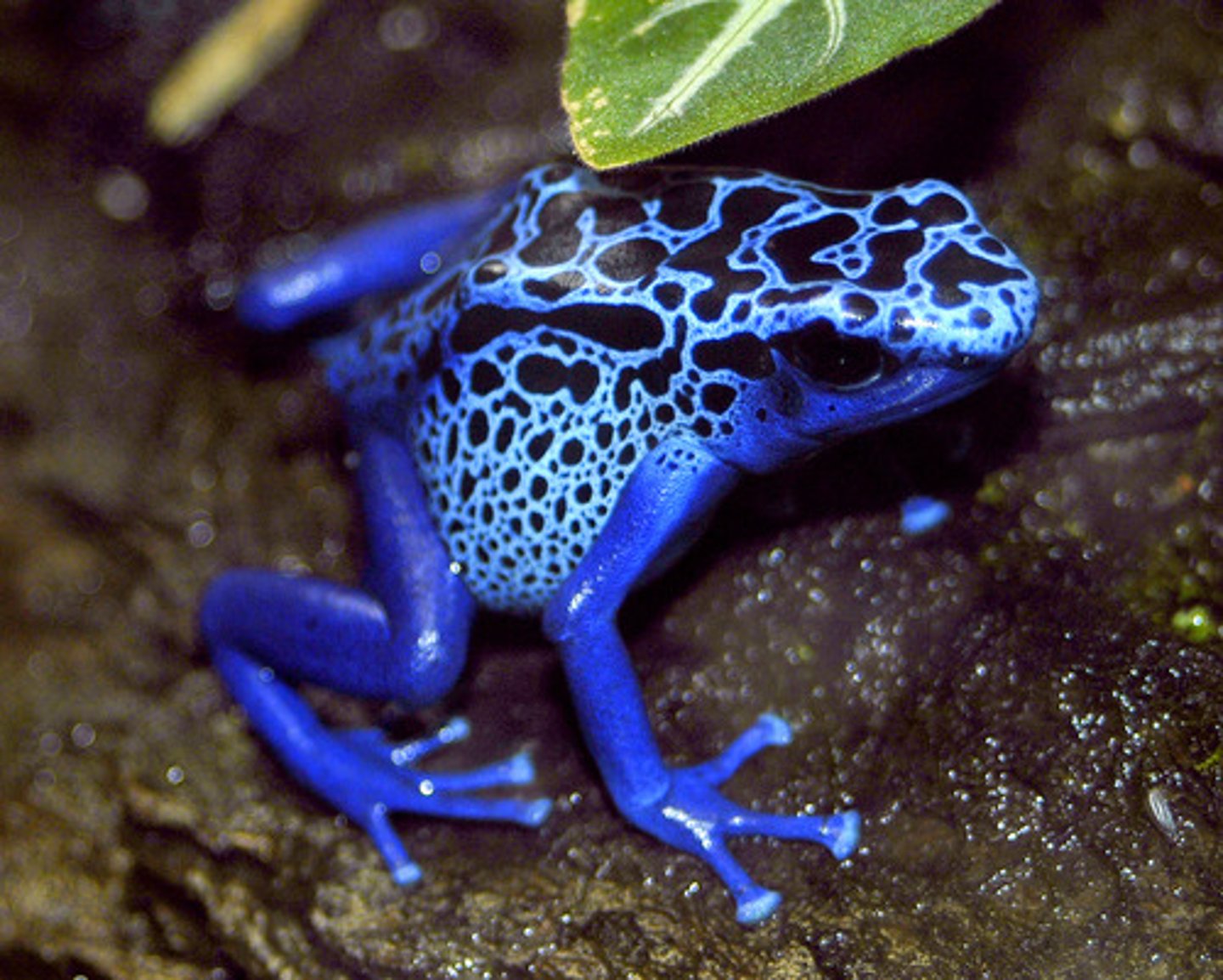
Physiological adaptation
A chemical advantage possessed by the organism that gives it an advantage. For example, penicillin and sickle cell anemia resistance.

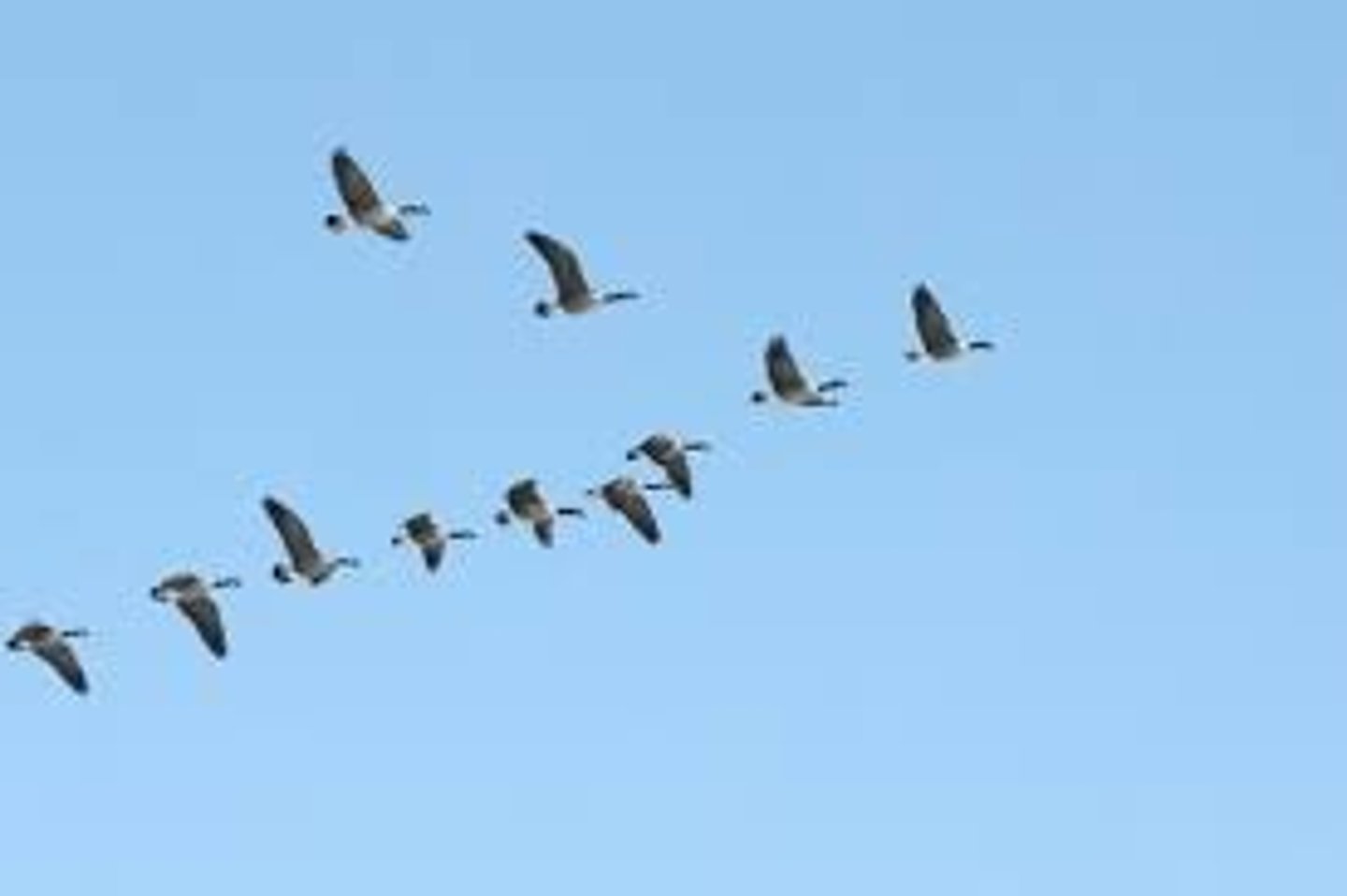
Behavioral adaptation
A behavior exhibited by the organism gives it a competitive advantage. For example, migration of birds to warmer climate, hibernation of bears, storing of nuts by squirrels in the winter

Darwin's Theory of Evolution
Modification by Natural Selection
States that evolution occurs via a process called natural selection.
Descent with Modification
States that newer forms appearing in the fossil record are the modified descendants of older species.
Common descent
Principle that all living things were derived from common ancestors
Common ancestor
An ancestral species from which later species evolved
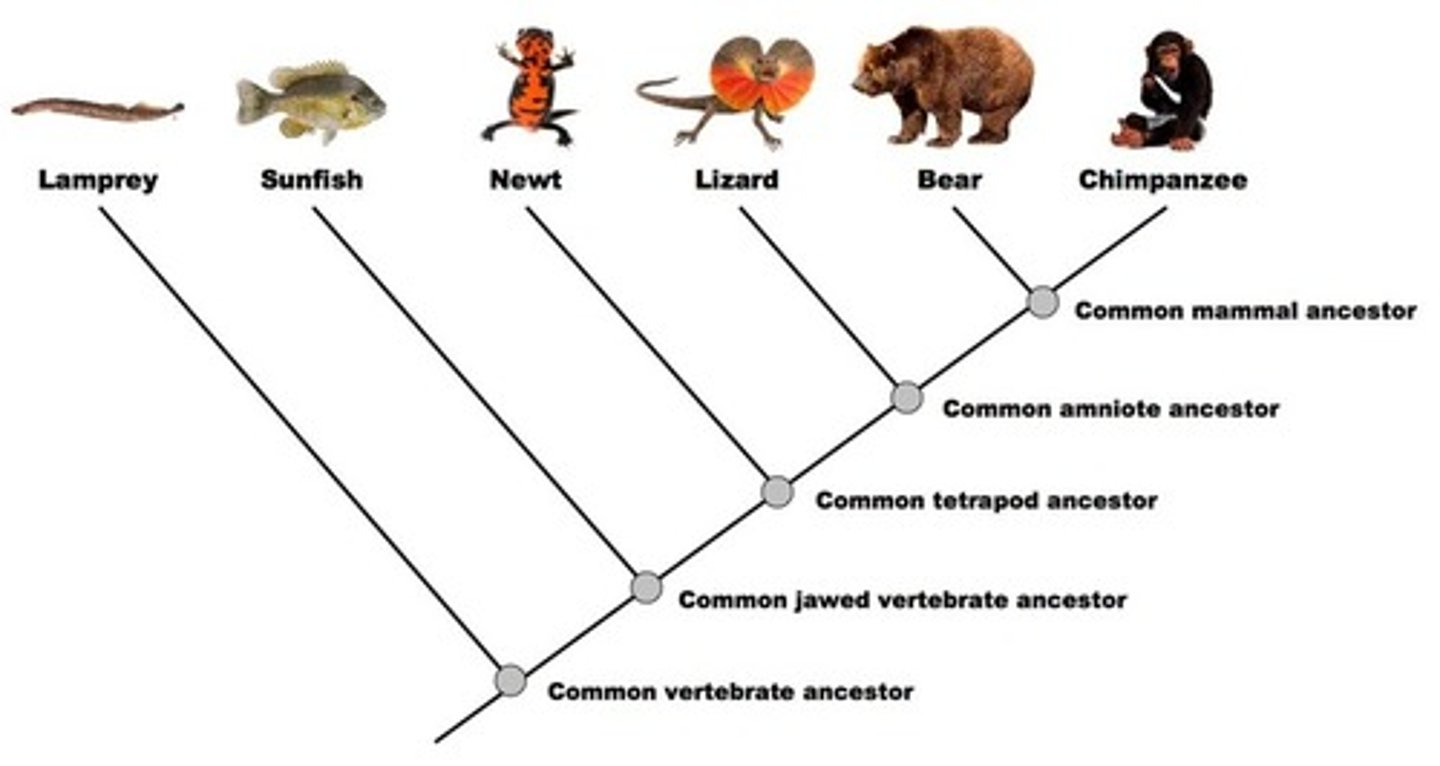
Descent with Modification
Principle that each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time
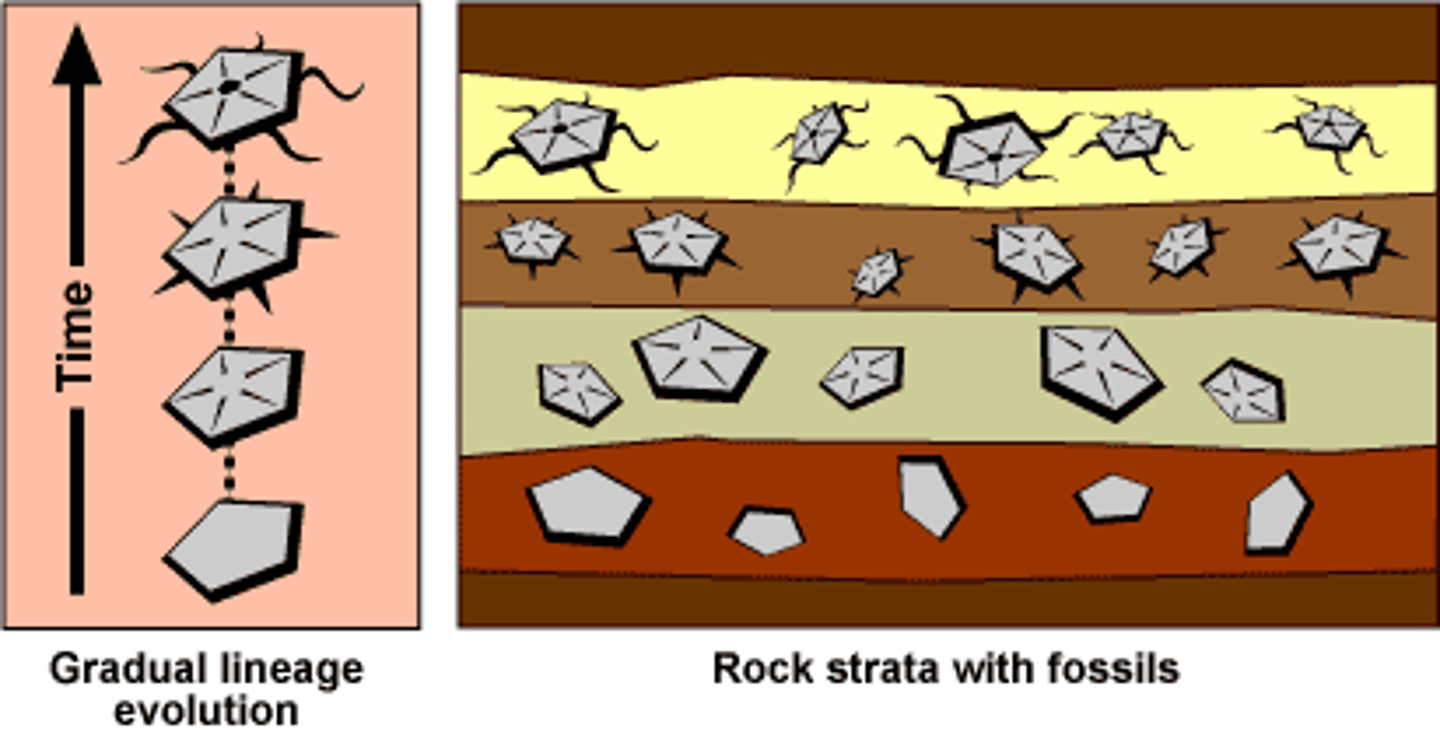
Fossil
Preserved remains or evidence of an ancient organisms
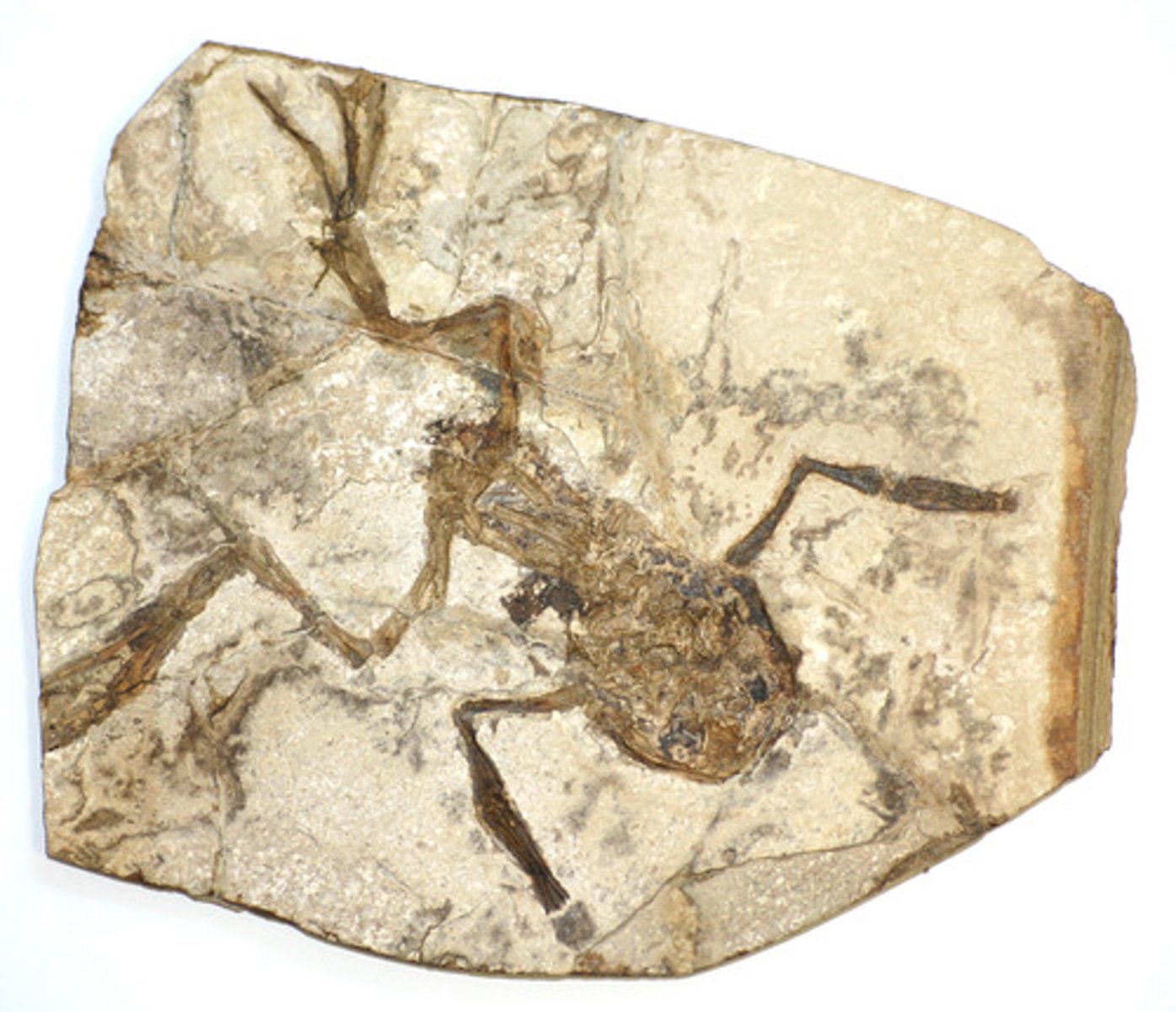

Fossil record
Information about past life, including the structure of organisms, what they ate, what ate them, in what environment they lived, and the order in which they lived
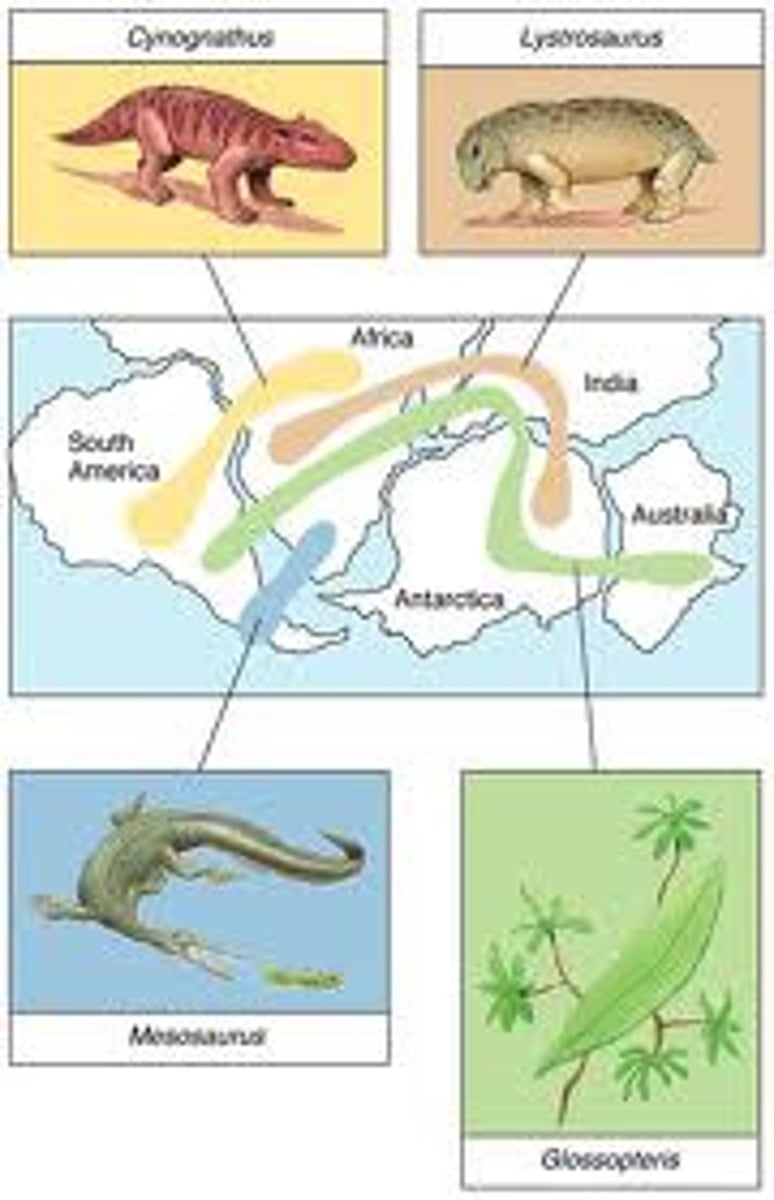
Biogeography
The study of the geographical distribution of fossils and living organisms
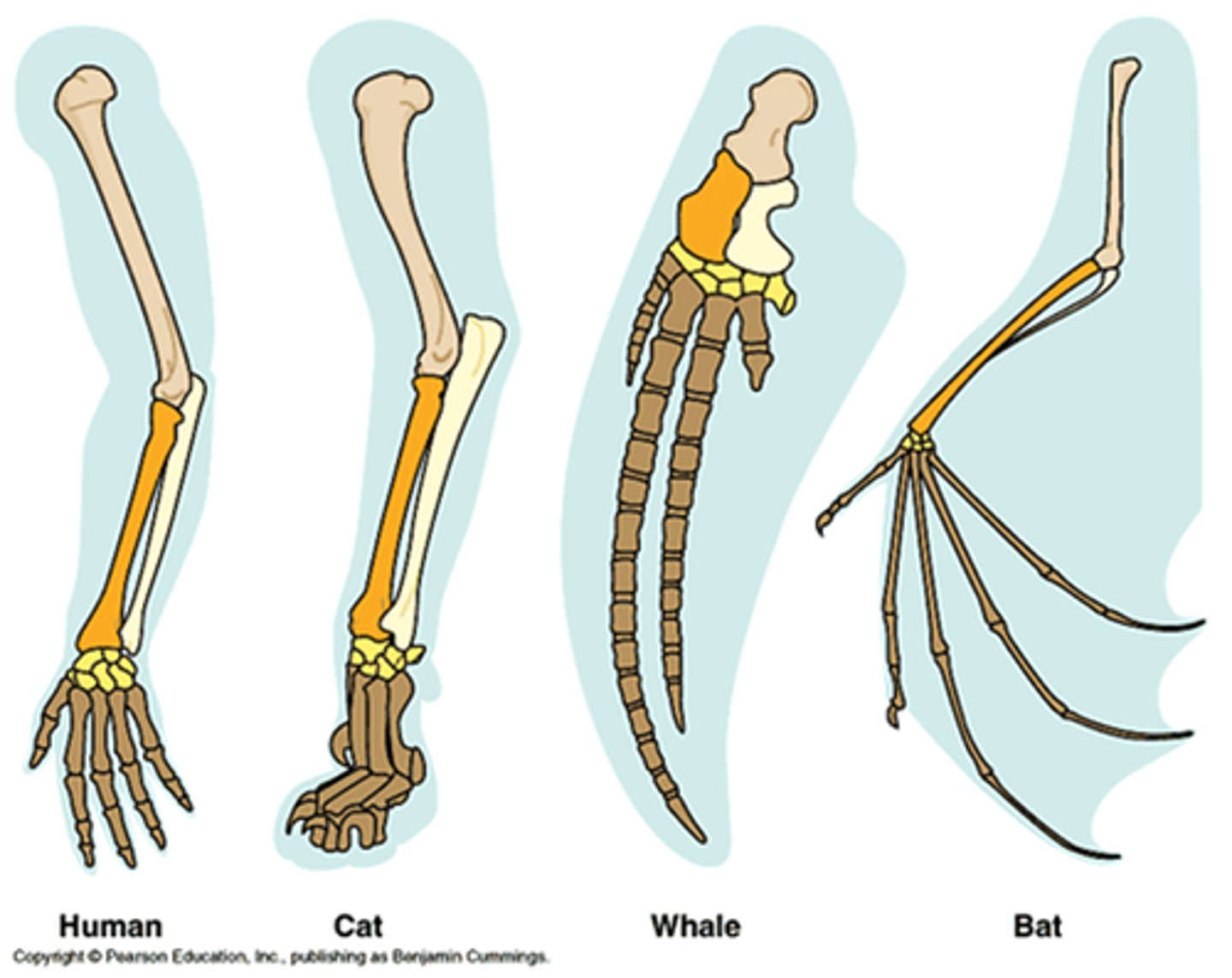
Homologous structure
Structures in different species that have different mature forms but develop from common embryonic structures, share a common ancestry, and result from divergent evolution.
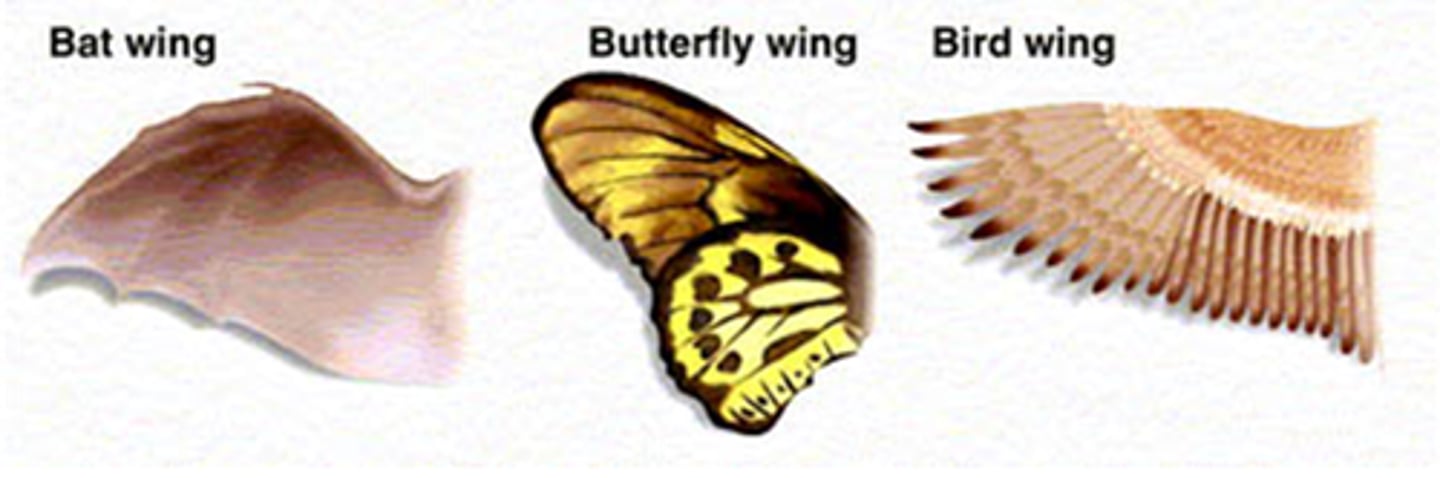
Analogous structure
Structures that have the same function but different structures that result from convergent evolution
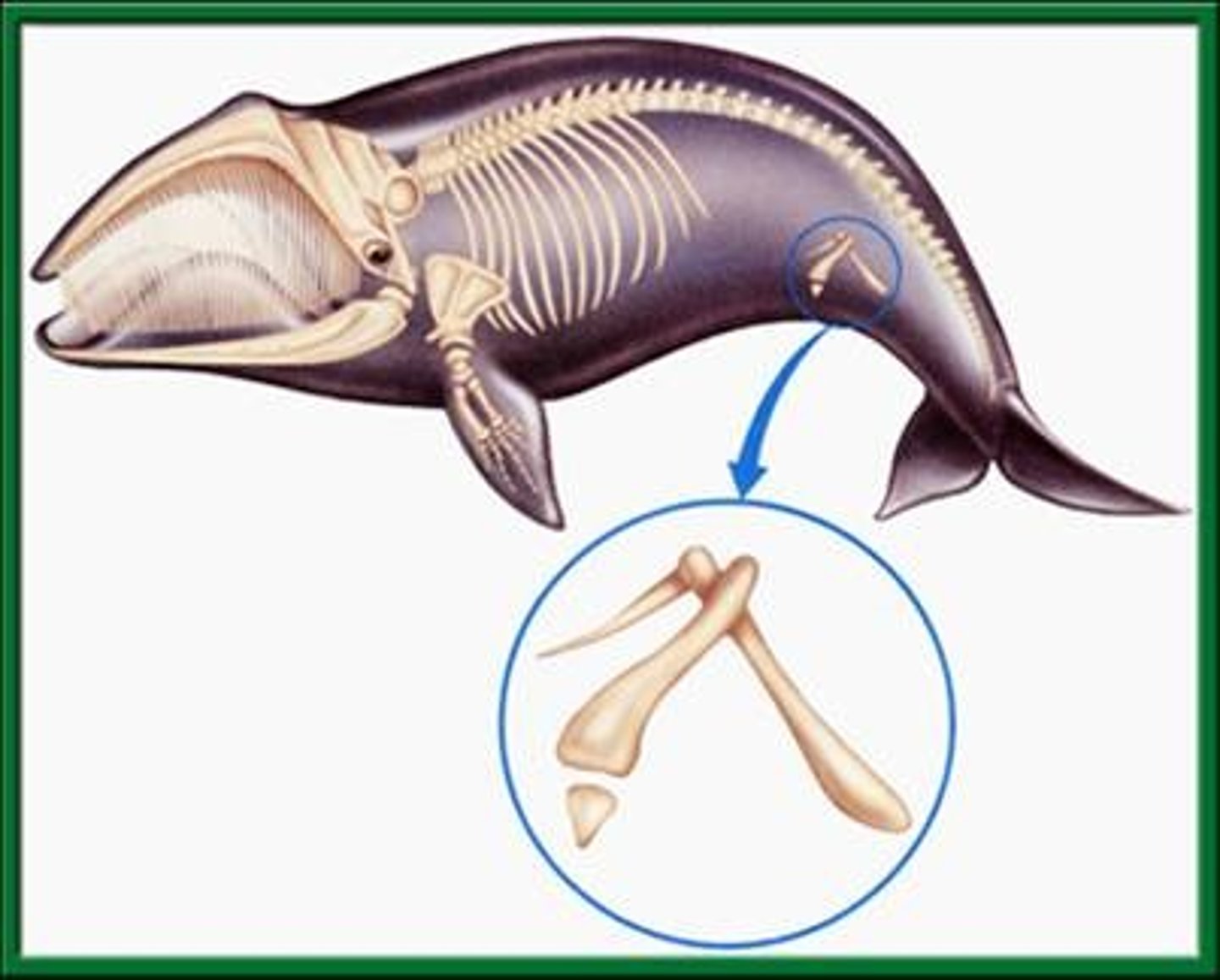
Vestigial structure
Remnant of a structure that may have had an important function in a species' ancestors, but has no clear function in the modern species.
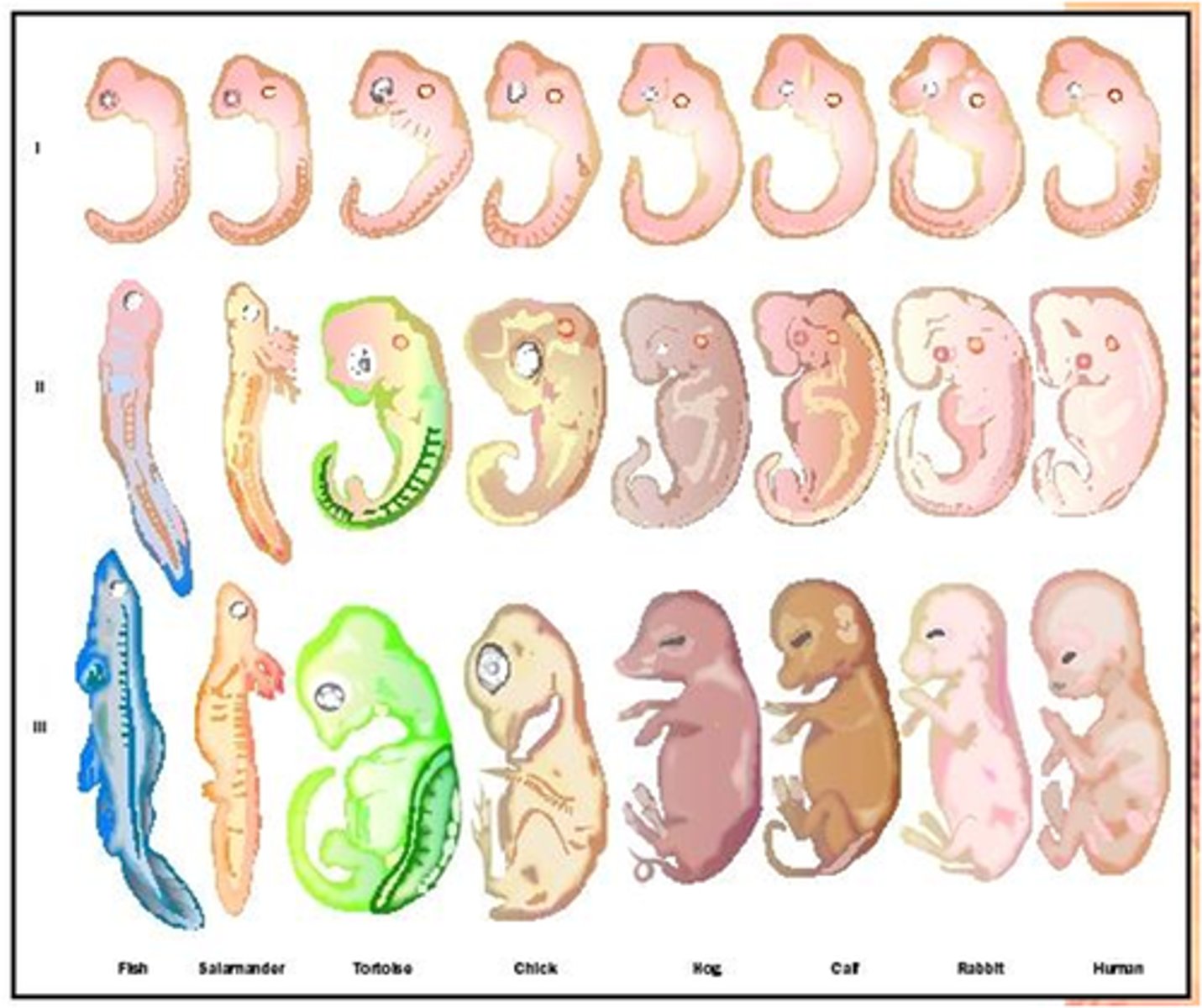
Embryology
Among different species, there are similarities in embryo appearance and anatomy. This concept supports the theory of evolution.
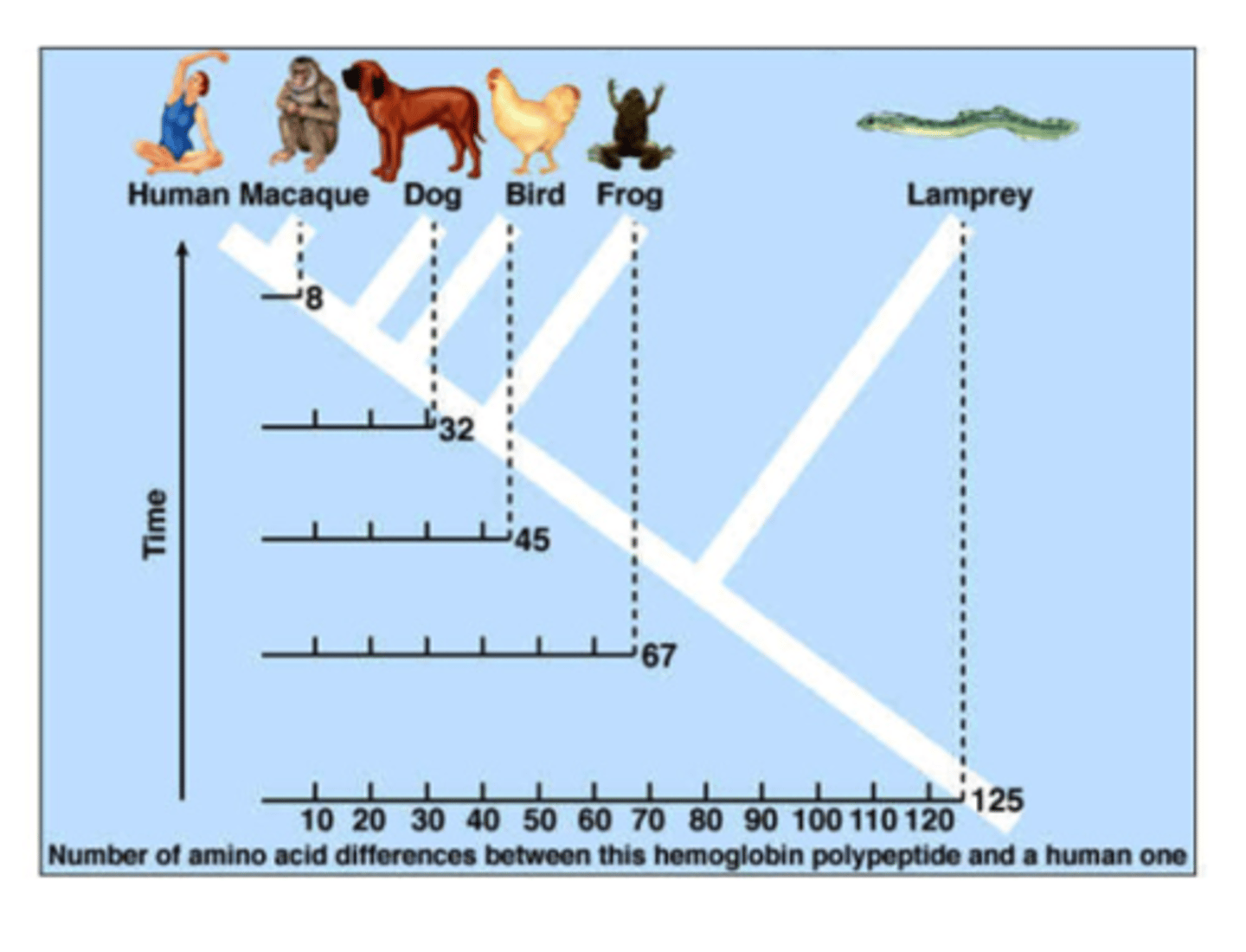
Molecular Genetics
DNA, RNA and amino acid comparisons are made between organisms; the MORE alike the organisms are the CLOSER the relationship; the LESS alike the organisms are the more DISTANT the relationship