Human Perception Exam 3
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Space and Time Receptive Field
motion can be defined as different positions of an object at different times.
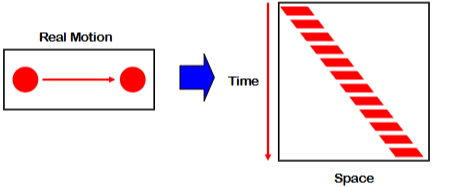
Reichardt Detector and Space-Time
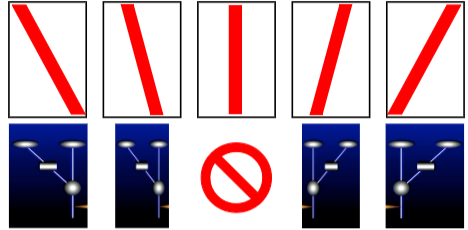
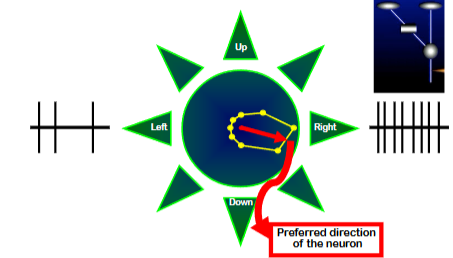
Direction Tuning Curve
Multistage Model of Motion Processing
retina —> LGN —> V1 —> MT —> MST
Local Motion Processing in V1
Optic Flow
continuous change in optic array due to movement of the observer.
What motion tells us about the visual world?
judging the speed and direction in which objects are moving.
judging impending collision.
judging our heading as we move through the environment.
Gradient of Flow
the difference in optic flow that occurs as a function of distance from the moving observer.
Focus of Expansion
the center of the observer’s destination and therefore provides information where the observer is heading.
Optic flow can be used for…
reaching destination (navigation).
maintain balance.
anticipating collision.
Affordance
the information specified by a stimuli pattern that indicates how to stimulus can be used.
Isac Newton’s Prism Experiment
colored light could be recombined to create white light (process was reversible); a basic color is one that cannot further be decomposed upon passing through a prism —> basic colors can be recombined to create new colors.
Metamers
an evidence showing that color is not in the light.
Light reflection
pigment composition of a surface determines the percentage of incident light absorbed by that surface and the percentage of light reflected from the surface.
Subtractive Color Mixture
mixing paints with different pigments; additional pigments reflect fewer and absorb more wavelengths.
Trichtomatic Theory
color vision depends on the activity of three different receptors.
Receptor Mechanisms
three different types of cones.
Dichromatism
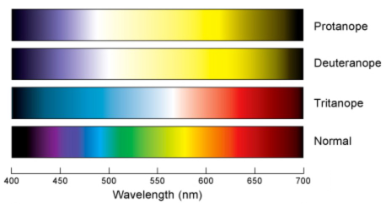
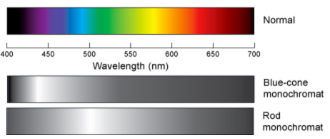
Monochromatism
Ewald Hering
is there a color appearing bluish yellow or yellowish blue? reddish green or greenish red?
Opponent Receptive Field
electrophysiological recordings from color and spatially opponent midget ganglion cell in the monkey retina (Green On/Red Off).
Hue
the experience of a chromatic color such as red, green, yellow, or blue or combinations of these colors.
Saturation
the relative amount of whiteness in a chromatic color.
Brightness
perceived light level.
What determines color appearance?
spectral content of ambient illumination.
pigmentation of surfaces of objects.
number of photoreceptor types in the eye.
adaptation state of the visual system.
Color Constancy
perception of colors as relatively constant in spite of changing light sources; works best when an object is surrounded by many colors.
Chromatic Adaption
prolonged exposure to chromatic color leads to receptors.
Color Contrast
color appearance shifts AWAY from the color of the surrounding context.
Color Assimilation
color appearance shifts TOWARDS the color of the surrounding context.
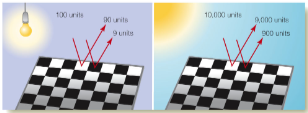
Surface Reflectance
two areas that reflect different amounts of light look the same under different illumination conditions if the ratios of their intensities are the same.
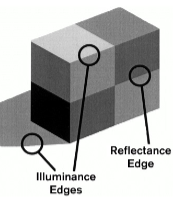
Reflectance edge
edges where the amount of light reflected changes between two surfaces.
Illumination edge
edges where lighting of two surfaces changes.
Perception of Lightness
reflectance and illumination edges.
Oculomotor Cues
cues based on our ability to sense the position of our eyes and the tension of our eye muscles.
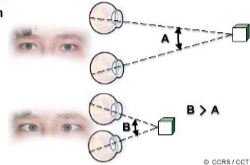
Convergence
the inward movement of the eyes that occurs when we look at nearby objects.
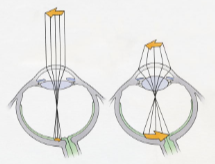
Accommodation
change in the shape of the lens that occurs when we focus on objects at various distance.
Stereopsis
3D vision resulting from slight differences in left and right eye images, arising because the two eyes view the world from slightly different perspectives.
Disparity
slight difference in positions of “features” in left and right eye views.
Corresponding Points
the places on each retina that would overlap if one retina could be slid on top of the other.
Disparity
slight difference in positions of “features” in left and right eye views.
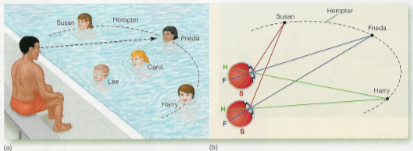
Horopter
an imaginary circle that passes through the point of fixation and indicates the location of objects that fall on corresponding points on the two retinas.
Angle of Disparity
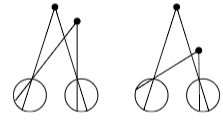
Stereogram (anaglyphs)

Size-Distance Scaling
S = K(R ́ D)
S - object’s perceived size.
K - constant.
R - size of retinal image.
D - perceived distance of the object.
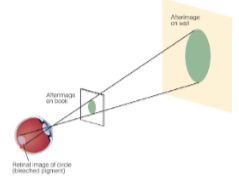
Emmert’s Law
the farther away an afterimage appears, the larger it will seem.
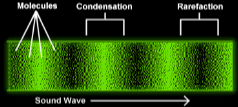
Pure Tones
changes in air pressure occur in a pattern described by a mathematical function call a ‘sine wave’.
Amplitude
the difference in pressure between the high and low peaks of the sound wave (determines loudness).
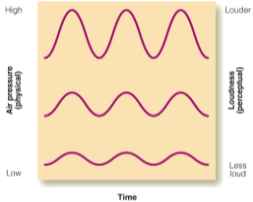
Frequency
the number of cycles per second (determines pitch).
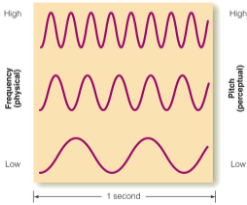
Tone Height
the perceptual experience of increasing pitch that accompanies increases in a tone’s frequency.T
Tone Chroma
sounds with the same chroma have fundamental frequencies that are whole-number multiples of one another.
Octave
doubling the frequency.
Timbre
all other perceptual aspects of a sound besides loudness, pitch, and duration; closely related to the harmonics, attack and decay of a tone.
The Outer Ear
funnel sounds the tympanic membrane.
Pinna
sound localization.
Auditory Canal
protect, amplification (resonance).
Ossicles (ossicular bridge)
three small bones.
Impedance Matching
vibration in different matters may lead to problems.

Area advantage
concentrating the vibration of the large tympanic membrane onto the much smaller stapes, which increases the pressure by a factor of about 20.
Lever advantage
being hinged to create a lever action.
The Cochlea
fluid-filled snail-like structure (35 mm long) set into vibration by the stapes; organ of corti.
Transduction
vibration to electric signal.
Basilar Membrane
location of peak vibration depends on frequency.
Phase Locking
nerve fibers fire in bursts; firing bursts happen at or near the peak of the sine-wave stimulus (locked in phase).
Binaural Cues
location cues based on the comparison of the signals received the left and right ears.In
Interaural Time Difference (ITD)
difference between the times sounds reach the two ears.
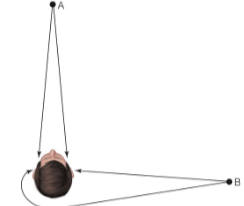
Monaural Cue
a cue that depend on information from only one ear.
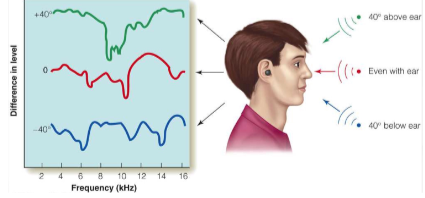
Head-Related Transfer Function (Spectral Cue)