Unit 4-Biochem(Introduction to Metabolism)
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions in living organisms
Catabolism
breaking down molecules to produce cellular energy
Anabolism
building biomolecules using cellular energ
catabolic
Glycolysis is __________ pathway
anabolic
Gluconeogenesis is __________ pathway
Phototrophs
use CO₂ (or organic matter) and light to produce cellular energy
Heterotrophs (aka chemotrophs):
use CO₂ (or organic matter) and REDOX active molecules to produce cellular energy
CO₂, organic carbon
Autotrophs use ____ and Heterotrophs use _______
Glucose, O2, H2O, CO2
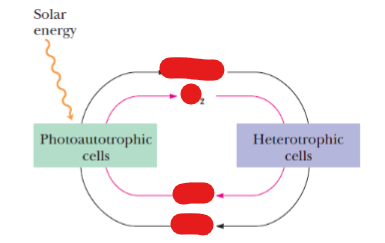
regulated independently
Parallel pathways of catabolism and anabolism must differ in at least one metabolic step so that they can be
_______________________
ATP
The energy currency of the cell
NADH and FADH2
Electron carriers involved in redox reactions
FADH2
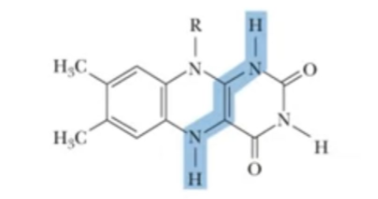
NADH
endergonic reactions
Reaction coupling of ATP drives _______________
photosynthesis, catabolism
ATP is formed via ______________ in phototrophic cells or by _____________ in heterotrophic cells
ATP hydrolysis
Energy-requiring cellular activities are powered by __________, liberating ADP and Pi
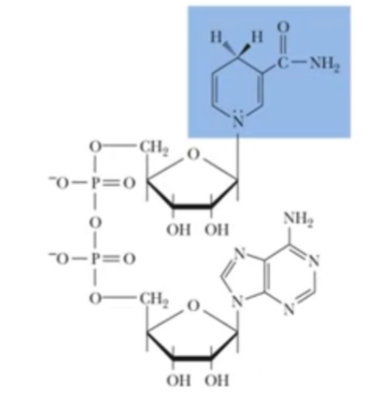
NADH and FADH₂
___________ transfer electrons to the electron transport chain
hydride ions (H:-)
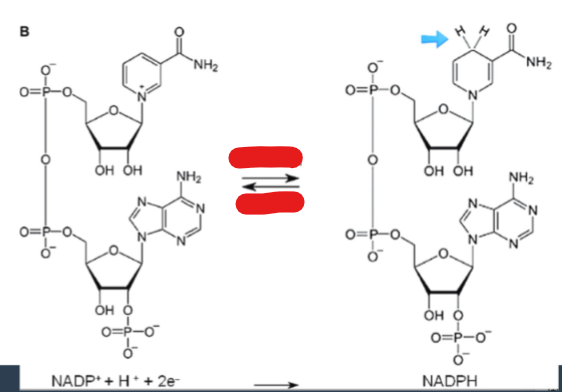
Hydrogen and electrons released in catabolism are transferred as ____________ to the pyridine nucleotide, NAD+, to form NADH + H+ in dehydrogenase reactions (reduction of NAD+ to NADH)
O2
The ultimate oxidizing agent, ___ , is the final acceptor of electrons, becoming reduced to H2 O
oxidative, reductive
Catabolism is ___________, anabolism is __________
NADPH
________ can be viewed as the carrier of electrons from catabolic reactions to anabolic reactions
NADP+
In photosynthesis, light energy is used to pull electrons from water and transfer them to _______
Reduction(top),Oxidation(bottom)
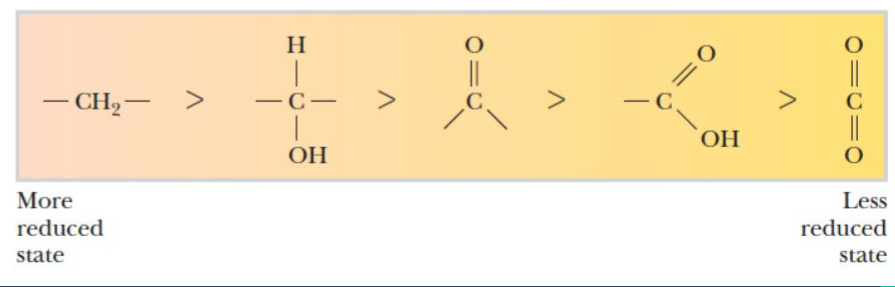
Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids
_____________________ are good sources of chemical energy because their carbon is reduced
–CH₂–
Chains of _______ groups are the most energy-rich form of reduced carbon
oxidized form
Carbon dioxide is the final product of catabolism and the most ____________ of carbon
less
The more C-O bonds the _____ reduced the molecule become
organic micronutrients
Vitamins are _______________, which are required in small daily amounts (micro to mg)
water-soluble and fat-soluble
Two major classes of vitamins
Most vitamins essential nutrients (humans _________ the basic form of the vitamin)
disease
the absence (and sometimes the excess) of certain vitamins cause _______
coenzymes
The active form of many water-soluble vitamins are also known as _________
Thiamine
B1 Vitamin
Riboflavin
B2 Vitamin
Niacin
B3 Vitamin
Pantothenic Acid
B5 Vitamin
Pyrixodine
B6 Vitamin
Biotin
B7 Vitamin
Folate
B9 Vitamin
Cobalamin
B12 Vitamin
Ascordic Acid
C Vitamin
thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP)
The active coenzyme for of thiamin is ____________________
Thiamine Pyrophosphate
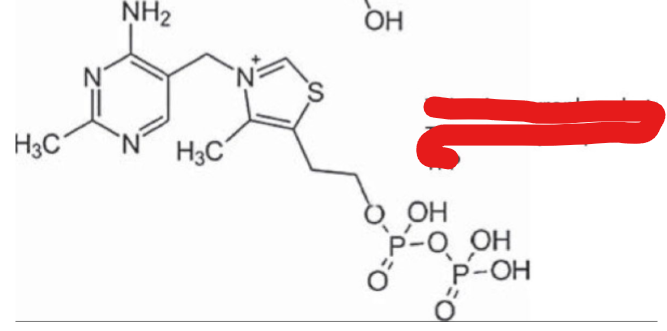
thiamine pyrophosphate transferase
thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP) is formed by the addition of 2 phosphate groups by the enzyme____________________
decarboxylation, transketolation
Thiamin Pyrophosphate(TPP) is a coenzyme for enzymes that perform _________________ (removal of a carboxyl group) and
____________ (transfer of two-carbon units)